EnterLib Print Preview
DOCNUM = PCALEM
DATETIME = 04/02/98 13:15:06
BLDVERS = 1.3.0
TITLE = GPC: Guide to IBM Global Professional Careers
AUTHOR = IBM Global Learning
Title: GPC: Guide to IBM Global Professional Careers
Authors: IBM Global Learning
Document Number: PCALEM
Build Date: 04/02/98 13:15:06 Build Version: 1.3.0
Book Path: /else/holdings/internal/not_classified/pcalem.boo
TITLE Title Page
GPC: Guide to IBM Global Professional Careers
Document Number PCALEM
April 2, 1998
IBM Global Learning
EDITION Edition Notice
First Edition, Revision four, March 24, 1998
This document is a guide to IBM Global Professional Careers for use by
all IBM organizations throughout the world. It replaces and
supersedes all previous guides to IBM Expert Careers, Specialized
Roles or IBM Worldwide Sales and Services Professions published in any
geography or country or other organization.
© Copyright IBM Corporation 1998
CONTENTS Table of Contents
[Summarize]
TITLE Title Page
EDITION Edition Notice
CONTENTS Table of Contents
FIGURES Figures
PREFACE About This Guide
1.0 Overview
1.1 Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1.1 Overview
1.1.2 Definition of a Global Professional Career
1.1.3 IBM Global Professional Careers
1.2 Chapter 2. Skills Framework and Templates
1.2.1 Introduction
1.2.2 Skill Categories
1.2.3 Skill Proficiency Levels
1.2.4 Profession Positions and Template Linkage
1.2.5 Skill Development Activities
1.2.6 Summary
1.3 Chapter 3. Certification Principles and Standards
1.3.1 Introduction
1.3.2 Criteria
1.3.3 Nomination Package
1.3.4 Certification Review Process
1.3.5 Individual Profession Requirements
2.0 Marketing Professional Career
2.1 Chapter 4. Marketing Professional Career
2.1.1 Marketing Professional Career Overview
2.1.2 Professional Career Structure
2.1.3 Marketing and Sales
2.1.4 Characteristics of the Profession
2.1.5 Potential Candidates
2.1.6 Title Structure
2.1.7 Career Growth
2.1.8 Certification
2.1.9 Performance Elements
2.1.10 Marketing Professional Career Skills Profile
2.1.11 Professional Development
2.1.12 Marketing Professional Career Position Descriptions
2.1.13 Marketing Professional Career Role Descriptions
2.2 Chapter 5. Marketing Management Profession Discipline
2.2.1 Marketing Management Profession Discipline Overview
2.2.2 Profession Discipline Structure
2.2.3 Characteristics of the Profession Discipline
2.2.4 Potential Candidates
2.2.5 Career Growth
2.2.6 Performance Elements
2.2.7 Marketing Management Profession Discipline Skills Profile
2.2.8 Professional Development
2.2.9 Marketing Management Position Descriptions
2.3 Chapter 6. Market Intelligence Profession Discipline
2.3.1 Market Intelligence Profession Discipline Overview
2.3.2 Profession Discipline Structure
2.3.3 Characteristics of the Profession Discipline
2.3.4 Potential Candidates
2.3.5 Career Growth
2.3.6 Performance Elements
2.3.7 Market Intelligence Profession Discipline Skills Profile
2.3.8 Professional Development
2.3.9 Market Intelligence Position Descriptions
2.3.10 Market Intelligence Specialty Descriptions
2.4 Chapter 7. Distribution Channels Marketing Profession Discipline
2.4.1 Distribution Channels Marketing Profession Discipline Overview
2.4.2 Profession Discipline Structure
2.4.3 Characteristics of the Profession Discipline
2.4.4 Potential Candidates
2.4.5 Career Growth
2.4.6 Performance Elements
2.4.7 Distribution Channels Marketing Profession Discipline Skills Profile
2.4.8 Professional Development
2.4.9 Distribution Channels Marketing Position Descriptions
2.4.10 Distribution Channels Marketing Specialty Descriptions
2.5 Chapter 8. Technical Support Marketing Profession Discipline
2.5.1 Technical Support Marketing Profession Discipline Overview
2.5.2 Profession Discipline Structure
2.5.3 Characteristics of the Profession Discipline
2.5.4 Potential Candidates
2.5.5 Career Growth
2.5.6 Performance Elements
2.5.7 Technical Support Marketing Profession Discipline Skills Profile
2.5.8 Professional Development
2.5.9 Technical Support Marketing Position Descriptions
2.5.10 Technical Support Marketing Specialty Descriptions
2.6 Chapter 9. Marketing Communications Profession Discipline
2.6.1 Marketing Communications Profession Discipline Overview
2.6.2 Profession Discipline Structure
2.6.3 Characteristics of the Profession Discipline
2.6.4 Potential Candidates
2.6.5 Career Growth
2.6.6 Performance Elements
2.6.7 Marketing Communications Profession Discipline Skills Profile
2.6.8 Professional Development
2.6.9 Marketing Communications Position Descriptions
2.6.10 Marketing Communications Specialty Descriptions
2.7 Chapter 10. Direct Marketing Profession Discipline
2.7.1 Direct Marketing Profession Discipline Overview
2.7.2 Profession Discipline Structure
2.7.3 Characteristics of the Profession Discipline
2.7.4 Potential Candidates
2.7.5 Career Growth
2.7.6 Certification Nomination Guide
2.7.7 Performance Elements
2.7.8 Direct Marketing Profession Discipline Skills Profile
2.7.9 Professional Development
2.7.10 Direct Marketing Position Descriptions
2.8 Chapter 11. Database Marketing Profession Discipline
2.8.1 Database Marketing Profession Discipline Overview
2.8.2 Profession Discipline Structure
2.8.3 Characteristics of the Profession Discipline
2.8.4 Potential Candidates
2.8.5 Career Growth
2.8.6 Certification Nomination Guide
2.8.7 Performance Elements
2.8.8 Database Marketing Profession Discipline Skills Profile
2.8.9 Professional Development
2.8.10 Database Marketing Position Descriptions
3.0 Sales Professions
3.1 Chapter 12. Client Relationship Profession
3.1.1 Client Relationship Profession Overview
3.1.2 Profession Structure
3.1.3 Characteristics of the Profession
3.1.4 Potential Candidates
3.1.5 Career Growth
3.1.6 Certification Nomination Guide
3.1.7 Performance Elements
3.1.8 Client Relationship Profession Skills Profile
3.1.9 Professional Development
3.1.10 Client Relationship Position Descriptions
3.2 Chapter 13. General Business Relationship Profession
3.2.1 General Business Relationship Profession Overview
3.2.2 Profession Structure
3.2.3 Characteristics of the Profession
3.2.4 Potential Candidates
3.2.5 Career Growth
3.2.6 Certification Nomination Guide
3.2.7 General Business Relationship Profession Skills Profile
3.2.8 Professional Development
3.2.9 General Business Relationship Position Descriptions
3.3 Chapter 14. Sales Specialist Profession
3.3.1 Sales Specialist Profession Overview
3.3.2 Profession Structure
3.3.3 Characteristics of the Profession
3.3.4 Potential Candidates
3.3.5 Career Growth
3.3.6 Certification Nomination Guide
3.3.7 Performance Elements
3.3.8 Sales Specialist Profession Skills Profile
3.3.9 Professional Development
3.3.10 Additional Information
3.3.11 Sales Specialist Position Descriptions
4.0 Services Professions
4.1 Chapter 15. Consultant Profession
4.1.1 Consultant Profession Overview
4.1.2 Profession Structure
4.1.3 Characteristics of the Profession
4.1.4 Potential Candidates
4.1.5 Career Growth
4.1.6 Certification Requirements
4.1.7 Certification Nomination Guide
4.1.8 Performance Elements
4.1.9 Consultant Profession Skills Profile
4.1.10 Consulting Templates
4.1.11 Professional Development
4.1.12 Consultant Position Descriptions
4.2 Chapter 16. Education Profession
4.2.1 Education Profession Overview
4.2.2 Profession Structure
4.2.3 Characteristics of the Profession
4.2.4 Potential Candidates
4.2.5 Career Growth
4.2.6 Certification Nomination Guide
4.2.7 Performance Elements
4.2.8 Education Profession Skills Profiles
4.2.9 Professional Development
4.2.10 Education Position Descriptions
4.3 Chapter 17. IT Architect Profession
4.3.1 IT Architect Profession Overview
4.3.2 Profession Structure
4.3.3 Characteristics of the Profession
4.3.4 Potential Candidates
4.3.5 Career Growth
4.3.6 Certification Nomination Guide
4.3.7 Performance Elements
4.3.8 IT Architect Profession Skills Profile
4.3.9 Skills Templates
4.3.10 Professional Development
4.3.11 IT Architect Position Descriptions
4.4 Chapter 18. I/T Availability Profession
4.4.1 I/T Availability Profession Overview
4.4.2 Profession Structure
4.4.3 Characteristics of the Profession
4.4.4 Potential Candidates
4.4.5 Career Growth
4.4.6 Certification Nomination Guide
4.4.7 Performance Elements
4.4.8 I/T Availability Profession Skills Profile
4.4.9 Professional Development
4.4.10 I/TAP Profession Position Descriptions
4.4.11 I/TAP Discipline Position Descriptions
4.5 Chapter 19. I/T Specialist Profession
4.5.1 I/T Specialist Profession Overview
4.5.2 Profession Structure
4.5.3 Characteristics of the Profession
4.5.4 Potential Candidates
4.5.5 Career Growth
4.5.6 Certification Nomination Guide
4.5.7 Performance Elements
4.5.8 I/T Specialist Profession Skills Profile
4.5.9 Professional Development
4.5.10 I/T Specialist Position Descriptions
4.6 Chapter 20. Project Management Profession
4.6.1 Project Management Profession Overview
4.6.2 Profession Structure
4.6.3 Characteristics of the Project Management Profession
4.6.4 Potential Candidates
4.6.5 Career Growth
4.6.6 Certification Nomination Guide
4.6.7 Performance Elements
4.6.8 Project Management Profession Skills Profile
4.6.9 Professional Development
4.6.10 Project Management Position Descriptions
FIGURES Figures
- 1-1. IBM Global Professional Careers - Title Structure 1.1.3
- 2-1. IBM Global Professional Careers - Template Names & Numbers 1.2.4
- 4-1. Marketing Profession Career Possibilities 2.1.5
- 5-1. Marketing Management Profession Discipline Career
- Possibilities 2.2.4
- 6-1. Market Intelligence Profession Discipline Career
- Possibilities 2.3.4
- 7-1. Distribution Channels Marketing Profession Discipline Career
- Possibilities 2.4.4
- 8-1. Technical Support Marketing Profession Discipline Career
- Possibilities 2.5.4
- 9-1. Marketing Communications Profession Discipline Career
- Possibilities 2.6.4
- 10-1. Direct Marketing Profession Discipline Roadmap - #1 2.7.2
- 10-2. Direct Marketing Profession Discipline Roadmap - #2 2.7.2
- 10-3. Direct Marketing Profession Discipline Roadmap - #3 2.7.2
- 10-4. Direct Marketing Profession Discipline: Career
- Possibilities 2.7.3
- 11-1. Database Marketing Profession Discipline Roadmap - #1 2.8.3
- 11-2. Database Marketing Profession Discipline Roadmap - #2 2.8.3
- 11-3. Database Marketing Profession Discipline Roadmap - #3 2.8.3
- 11-4. Database Marketing Profession Discipline: Career
- Possibilities 2.8.4
- 12-1. Client Relationship Profession Roadmap 3.1.2
- 12-2. Client Relationship Profession Roadmap 3.1.2
- 12-3. Client Relationship Profession Roadmap 3.1.2
- 12-4. Client Relationship Profession Career Possibilities 3.1.4
- 13-1. General Business Relationship Profession Roadmap - #1 3.2.2
- 13-2. General Business Relationship Profession Roadmap - #2 3.2.2
- 13-3. General Business Relationship Profession Roadmap - #3 3.2.2
- 13-4. General Business Relationship Profession Career
- Possibilities 3.2.4
- 14-1. Sales Specialist Profession Roadmap - #1 3.3.3
- 14-2. Sales Specialist Profession Roadmap - #2 3.3.3
- 14-3. Sales Specialist Profession Career Possibilities 3.3.4
- 15-1. Consultant Profession Roadmap - #1 4.1.2
- 15-2. Consultant Profession Roadmap - #2 4.1.2
- 15-3. Consultant Profession Career Possibilities 4.1.4
- 15-4. Dual Consulting Career Path 4.1.5
- 16-1. Education Specialist Profession Roadmap - #1 4.2.3
- 16-2. Education Specialist Profession Roadmap - #2 4.2.3
- 16-3. Education Profession Career Possibilities 4.2.5
- 17-1. IT Architect Profession Roadmap 4.3.2.1
- 17-2. IT Architect Profession Career Possibilities 4.3.4
- 18-1. I/T Availability Profession Roadmap: Associate I/TAP 4.4.2.1
- 18-2. I/T Availability Profession Roadmap: Advisory I/TAP 4.4.2.1
- 18-3. I/T Availability Profession Roadmap: Senior I/TAP 4.4.2.1
- 18-4. I/T Availability Profession Roadmap: Consulting I/TAP 4.4.2.1
- 18-5. I/T Availability Profession Roadmap: Senior Consulting
- I/TAP 4.4.2.1
- 18-6. I/T Availability Profession Career Possibilities 4.4.4
- 19-1. I/T Specialist Profession Roadmap - #1 4.5.3
- 19-2. I/T Specialist Profession Roadmap - #2 4.5.3
- 19-3. I/T Specialist Profession Career Possibilities 4.5.4
- 20-1. Project Management Profession Roadmap - #1 4.6.2
- 20-2. Project Management Profession Roadmap - #2 4.6.2
- 20-3. Project Management Profession Career Possibilities 4.6.4
PREFACE About This Guide
This is the First edition of the "Guide to IBM Global Professional
Careers." It establishes common definitions of professions to be
consistently implemented for employees throughout IBM. It incorporates the
former IBM Worldwide Sales and Services Professions, and a newly defined
Marketing Professional Career. The former S&S professions of Database
Marketing and Direct Marketing become disciplines of the new Marketing
Professional Career. The former S&S Segment Management profession is
absorbed into the Marketing Management discipline of the Marketing
Professional Career. All other S&S professions remain as IBM Global
Professional Careers to be utilized across IBM, without regard to
organizational boundaries.
This document is incomplete and a work in progress. Overtime it will
include all global professional careers in IBM, those already existing and
those to be defined. It will also bring these professional careers
together in a cohesive career framework of consistent terminology,
processes and principles that promotes a common understanding of IBM
career opportunities.
This document supersedes the "Guide to IBM Worldwide Sales & Services
Professions," first published June 26, 1995, and last updated January 6,
1997.
Subtopics:
PREFACE.1 Change History
____________________ ___________________________________________________
| Date | Change |
|____________________|___________________________________________________|
| April 15, 1997 | First Release |
|____________________|___________________________________________________|
| May 9, 1997 | Consulting Client Relationship Representative |
| | position defined. Clarification of SSR positions |
| | in I/T Availability Profession. |
|____________________|___________________________________________________|
| July 7, 1997 | Addition of Associate position descriptions for |
| | all Marketing Professional Disciplines. |
| | Profession roadmap graphics enlarged for |
| | readability. |
|____________________|___________________________________________________|
| July 23, 1997 | Deleted skills in Sales Specialist Profession |
| | Skills Profile summary to match templates in |
| | SKILLS tool, and updated contacts for additional |
| | information. |
|____________________|___________________________________________________|
1.0 Overview
Subtopics:
1.1 Chapter 1. Introduction
Subtopics:
1.1.1 Overview
IBM is constantly changing to meet new customer and market requirements.
One of the changes is the transition to a global corporation.
International businesses serving global clients have been created, and the
organization will continue to change in response to their needs.
IBM Professionals need to develop appropriate skills, knowledge,
experience and establish a track record of contribution within this
changing environment to continue to provide services that Clients and the
Corporation require. The Global Professional Careers provide a framework
for this. They are organizationally independent, and focus on the
critical major professional groups demanded by IBM Clients or that IBM
requires to support its business. The Global Professional Careers are
deployed consistently, ensuring a standard of quality throughout the
world, through definition of skills required at all positions, and
professional review that is independent of line management at critical
career stages.
Global businesses require consistency of operations. The Global
Professional Careers, linked to job classification, compensation and
skilled resource management, provide a vital foundation for consistent
operations. Because they are organization independent, they also provide
a stable career framework for employees within a changing business
environment. They affect many thousands of IBM professionals and support
IBM's initiatives by creating a career framework that develops
professionals in support of strategic business objectives.
1.1.2 Definition of a Global Professional Career
To truly be a global business, skilled resources must be readily teamed,
use common processes and methodologies, and be shared across geographic
and organizational boundaries. To meet the competitive needs of global
markets, IBM has established Global Professional Careers to identify,
define and build client valued skills that are consistently implemented.
The characteristics and objectives of the IBM Global Professional Careers
are:
- To address a business need for employees to have commonly defined
skills that are consistently implemented worldwide
- Professionals are accountable for or contribute to:
- Customer satisfaction
- IBM revenue and/or
- IBM profit
- To address the need for skilled employees within most countries
- Applicable to a critical mass of several hundred employees
worldwide
- Able to span a career from entry up to executive level positions.
- A certification of skills, experience, leadership, customer
satisfaction, contribution to the business and business need may be
required for advancement to top ranks of a profession.
In their design, the Global Professional Careers:
- May contain several disciplines, which may in turn be made up of a
number of specialties.
- Are intended to be both organizationally and geographically
independent
- Are expected to provide a measure of career planning stability to
employees while being responsive to the needs of the business.
- Have a Worldwide Executive Leader to sponsor & champion the
profession, facilitated by a support team of profession leaders from
each geography, and an appointed worldwide leader of the profession
support team.
1.1.3 IBM Global Professional Careers
IBM management has identified professions key to achievement of business
results that require common definition of professional standards and
skills for consistent worldwide implementation. The professions span 3-5
professional positions, affording employees professional growth over the
course of their careers from the entry levels of the profession to the top
levels of the profession.
The structure of the profession positions is:
____________________________________ ___________________________________
| All but some Marketing Profession | All Marketing Profession |
| Disciplines | Disciplines Except Direct |
| | Marketing & Database Marketing. |
|____________________________________|___________________________________|
| {Professional} | Associate {Professional} |
| Advisory {Professional} | Associate {Professional} |
| Senior {Professional} | {Professional} |
| Consulting {Professional} | {Professional} |
| Senior Consulting {Professional} | Senior {Professional} |
|____________________________________|___________________________________|
The Consulting and Senior Consulting positions are certified positions for
all professions, except for the Consulting Profession, where certification
is required starting at the Senior position.
The titles used by each profession are shown in Figure 1-1
The IBM Global Professional Careers are:
- Client Relationship
Understanding our customers' values and needs and properly attending
to their requirements, locally as well as globally, is extremely
critical to our success. The Client Relationship Professional is
responsible for understanding their business requirements and
influencing the inner circle of top management.
The Client Relationship Professional is responsible for the overall
Customer/IBM relationship and the execution of associated business
strategies. He/She monitors key IBM activities within the client
environment. He/She identifies and qualifies IBM opportunities, shares
information with appropriate members of the extended team supporting
the customer, gains customer commitment to solutions and ensures
overall customer satisfaction.
- Consultant
Consultants provide advice and counsel to clients for a fee. They use
their skills, experience, intellectual capital and an integrated set
of methodologies to solve client business problems, translating their
findings into written, actionable recommendations. Consultants work
in an unstructured environment creating, sharing, and reusing
intellectual capital to solve diverse, business and technology
problems
Consultants are part of the IBM Consulting Group. They belong to a
Practice, recognized by the IBM Consulting Group, usually within an
Industry Solutions Unit or in SI. They are trained in IBM's generic
issue-based consulting methodology, and they specialize in a Service
Line (such as Business Transformation, IT Strategy, Application
Development Effectiveness or Information and Technology Management).
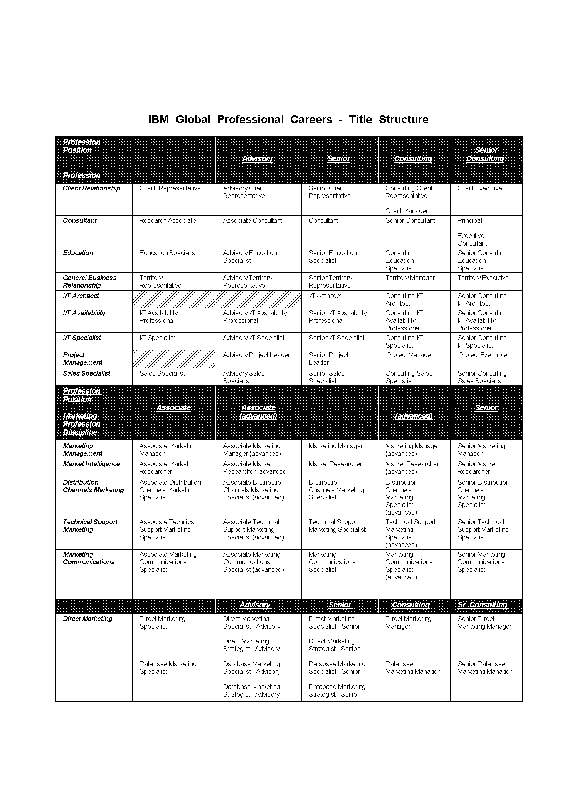
Figure 1-1. IBM Global Professional Careers - Title Structure
- Education
An Education Specialist will work in one or several areas of the
Education services business, and will normally have a high level of
skills in possibly an IT discipline, and apply that expertise in the
areas below -
There are four areas of Education Specialization:
- INSTRUCTION encompasses instructor facilitated training.
- DEVELOPMENT covers all tasks involved in preparing a training
intervention.
- PERFORMANCE CONSULTANCY involves working with clients to evaluate
and define job performance needs and to lead the activities to
achieve improvement.
- CURRICULUM SPECIALIZATION includes defining market/customer
requirements, determining training, and managing a business
portfolio.
In short, working within the Education profession covers a wide range
of services activities, connected with skills improvement, and
management of that for customers.
- General Business Relationship
The GB Relationship professional is responsible for developing client
relationships and executing an industry-aligned territory coverage
plan, ensuring overall customer satisfaction. He/she must evaluate
various distribution methods to market, develop and direct an
effective strategy based on customer requirements within the segment.
The GB Professional must have extensive industry and solution skills
to work effectively with the client, plus an excellent knowledge of
our channel strategy. He/she works closely with Marketing Management
professionals to execute the segment go-to-market plan.
- I/T Architect
The IT Architect creates information technology solutions to clients'
business problems. These IT solutions may include systems,
applications or processes, and may involve the application and
integration of a wide variety of products, technologies and services.
The IT Architect must have extensive knowledge of systems,
architectures, systems management, networking and application design
techniques, and must be able to identify, evaluate and select the
elements of the solution which best meet the client's business needs.
- I/T Availability
The I/T Availability Professional is a key contributor in maintaining
IBM as the availability services provider of choice. Their primary
responsibility is to ensure the client's I/T goals are met. The I/T
Availability Profession is structured to recognize professionals
responsible for supporting hardware, software, and I/T services. The
disciplines of the I/T Availability Profession focus on client
services relationships and satisfaction, hardware and software
maintenance support, and availability services and support.
- I/T Specialist
The I/T Specialists must have in-depth understanding of products,
offerings and services within their specialty in order to deliver high
quality solutions to clients in response to varying business
requirements. The I/T Specialist supports solution construction,
implementation, and systems integration in a Technology, Industry or
Business specialty. Specific specialities fall within the following
major discipline areas:
- Application Development and Maintenance,
- Client/Server,
- Customized Operational Services,
- Industry/Cross Industry Solutions,
- Networking, and
- Systems.
Depending on their organization or role, the I/T Specialist either
performs services for fee or provides technical support for product
sales. Currently, I/T Specialists are deployed in sales, services,
industry, manufacturing and development, and internal I/T
organizations.
- Marketing
The Marketing Profession plays an important role in IBM's ongoing
transformation into a market-driven company. Marketing professionals
support a system that manages the activities associated with bringing
offerings and solutions to the market with value recognized by the
customer. The Marketing Profession incorporates the steps necessary
to balance customer and market needs and IBM's internal capabilities
to produce global brand unit and/or business unit strategies, plans
and programs to increase both IBM's market participation and
profitability.
Marketing professionals are skilled in coordinating internal and
external resources, developing strategies and plans, utilizing market
intelligence data, understanding market and competitive trends, and
applying responsive creative thinking.
There are six profession disciplines within the Marketing Profession
as follows:
- Marketing Management
- Market Intelligence
- Distribution Channels Marketing
- Technical Support Marketing
- Marketing Communications
- Direct Marketing
- Direct Marketing
- Database Marketing
Both Direct Marketing and Database Marketing were announced as
professions in October, 1994, and the certification process remains
applicable to them within the Marketing Profession.
- Project Management
Project Management is the management of work in the information
technology environment. This includes the project plan for completing
the work, the schedule for completion and delivery of all project
deliverables, the staffing and management of the project team, the
financial plan, the tracking of the plan to actual in all areas of the
project, containment of the project scope as defined in the Statement
of Work, resolution of issues, responsibility for customer
satisfaction, and project communications - verbal and written - of
status to all parties involved. Project Management is accomplished by
the application of proven methodologies and techniques with the goal
of ensuring the consistent delivery of high quality services and/or
solutions which meet client requirements and expectations and fulfill
IBM's obligations.
- Sales Specialist
Sales specialist professionals are responsible for selling IBM
offerings (hardware, software, services and industry solutions)
directly to customers. A sales specialist specializes in a set of
related offerings, called a "discipline".
Sales specialist professionals are assigned to specific opportunities
where they possess the sales and technical expertise required to
conduct all phases of the sales cycle. They are responsible for
winning the business and the customer's satisfaction with the
engagement and the offering.
Each profession is led by a senior executive who takes responsibility for
tailoring the range and depth of skills to customer requirements and works
with the business managers to promote the spread of IBM Global
Professional Careers within the company.
Each profession has a worldwide standard in the form of a skills template,
which defines both the skills and the skill level required. Meeting this
standard demonstrates skills excellence worldwide. It is also essential
for the global management of IBM Skills.
The target is to create a global core of highly accomplished professionals
with a common level of world class skills which can be deployed rapidly,
in innovative combinations, to help Customers increase their business
success.
Individuals will also be assessing themselves against additional standards
of Skills Excellence as required by Industry, Product, Services, or
Geographic IBM Businesses.
The IBM Global Professional Careers enable IBMers to measure themselves
against worldwide standards. For professionals, these building blocks of
world class skills with high customer value, provide the raw material with
which they build their careers within the IBM global business. But it's
the flexibility with which we can combine these skills from engagement to
engagement which is key. IBM employees benefit from the increased control
of their own professional destiny, through the effective application of
their skills, in an IBM environment that recognizes their value.
1.2 Chapter 2. Skills Framework and Templates
Subtopics:
1.2.1 Introduction
As an employee your skills are critical to the IBM corporation as well as
your personal success. Your clients - whether internal or external -
value skills and experience. Now more than ever, their satisfaction
depends on your ability to apply the skills you have; and to keep pace by
developing more and deeper skills each day.
But - which skills should you develop? The SKILLS tool has thousands of
skills in its data base. Which are the ones that are valued by your
clients? The answers to those questions are provided by skills profiles
for professional careers, which are organized into templates, as windows
into the SKILLS data base.
1.2.2 Skill Categories
IBM professionals are expected to demonstrate skill proficiencies in
several major skill categories. Those categories are:
____________________________________ ___________________________________
| All but some disciplines of the | All disciplines of the Marketing |
| Marketing Professional Career | Professional Career except Direct |
| | Marketing & Database Marketing. |
|____________________________________|___________________________________|
| ° Business Acumen | ° General Marketing Skills |
| ° IBM Environment | ° IBM Internal Skills |
| ° Project Management | |
| ° Products/Technology/Services | |
| ° Personal | |
| | |
| Professionals dealing with | |
| external customers and clients are | |
| also expected to maintain skills | |
| in two additional categories. | |
| | |
| ° Client Environment | |
| ° Industry | |
|____________________________________|___________________________________|
At a minimum, each global professional career template contains skills in
these categories. The specific skills vary depending on the requirements
of the individual professions. In addition, most professions expand the
list to include specific skills that are relevant to that profession.
Thus, the client relationship professional template will include within
its expanded list additional skills specifically related to the client
environment category. Similarly, one will find additional project
management skills within the project management professional template.
The specific list of skills in each professional template can be found in
the chapter describing the profession in this guide.
1.2.3 Skill Proficiency Levels
Each skill contained within a professions template has a proficiency level
defined with it that reflects the target level of proficiency at which a
professional is expected to perform. That proficiency level has been
established according to the worldwide standard in the following table.
___________ ____________________________________ _______________________
| LEVEL | Proficiency Definition | Experience |
| | | |
|___________|____________________________________|_______________________|
| 0 | No skill | None |
| | | |
|___________|____________________________________|_______________________|
| 1 | Limited knowledge | None |
| | | |
|___________|____________________________________|_______________________|
| 2 | Limited ability to perform. Has | Very limited |
| | general conceptual knowledge only. | |
|___________|____________________________________|_______________________|
| 3 | Can perform with assistance. Has | Has performed with |
| | applied knowledge. | assistance on |
| | | multiple occasions. |
| | | Has performed in |
| | | routine situations |
| | | independently. |
|___________|____________________________________|_______________________|
| 4 | Can perform without assistance, | Repeated, successful |
| | Has in-depth knowledge. Can lead | |
| | or direct others in performing. | |
|___________|____________________________________|_______________________|
| 5 | Can give expert advice and lead | Extensive, |
| | others to perform. Is sought by | comprehensive |
| | others for consultation and | |
| | leadership. Has comprehensive | |
| | knowledge with ability to make | |
| | sound judgements. | |
|___________|____________________________________|_______________________|
When an individual assesses himself/herself against these target levels of
proficiency the same definitions should be used. This will facilitate a
consistent worldwide skill assessment.
These skill proficiency levels also differentiate the professions. For
example, a product sales specialist would be expected to have a higher
level of proficiency in product skills than a client relationship
representative. Typically, this would show up as a proficiency level of 4
or 5 in the "Understand IBM platforms skill" for a sales specialist but
only a proficiency level 3 for a client relationship representative.
1.2.4 Profession Positions and Template Linkage
As discussed in "IBM Global Professional Careers" in topic 1.1.3, each
global professional career has a position structure that potentially has
five positions. As an example, within the Sales Specialist Profession,
the generic positions are:
- Sales Specialist
- Advisory Sales Specialist
- Senior Sales Specialist
- Consulting Sales Specialist
- Senior Consulting Sales Specialist
The specific implementation of a professional career structure varies by
profession due to considerations of tradition, marketplace usage,
competition, etc., as illustrated in Figure 1-1 in topic 1.1.3. Within
any specific geography, the business title an individual uses should match
the title scheme, but may vary based on the specific needs of the
geographic unit. If individuals have or may not specifically match the
title scheme. If individuals have difficulty associating these positions
with their actual position or title, they should seek guidance from their
geography skills manager or profession leader.
Several factors are taken into account when an individual is assigned a
position within a professional career. Among them are skills and
experience; complexity of environment; impact on the business; business
need; etc. This guide focuses primarily on the skills and experience
piece and does not address the other factors which can vary significantly
by geography.
One of the prime objectives of the IBM Global Professional Careers is to
ensure all individuals performing in the same position worldwide have
equivalent skills. Accordingly, each professional position has a unique
template assigned to it. Those templates are identified by the same
titles used by the professions, following the standard of profession name
- position within the profession. Figure 2-1 contains the template name
and number of each professional template associated with the IBM Global
Professional Careers.
As might be expected, the more advanced positions within professions
typically require more in depth skills and experience. Thus, an entry
level position will typically have a preponderance of skills with a 2
proficiency level while a consulting position will have a substantial
number at a 4 and 5 proficiency level.
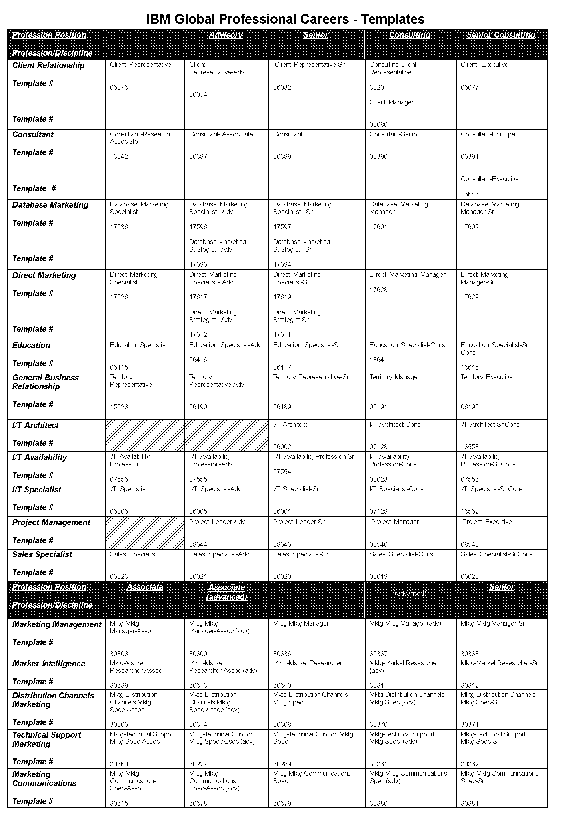
Figure 2-1. IBM Global Professional Careers - Template Names & Numbers
1.2.5 Skill Development Activities
Growing your skills requires a combination of experience, education,
training, coaching and mentoring. These elements are called Skill
Development Activities. Education and training can be separated into
several forms ranging from self study, distance learning, classroom and
seminars. The integration of these delivery methods can be an efficient
and cost effective way to build your skills. Refer to the Education
Roadmap page of the IEC Course Catalog at
http://w3.lahulpe.ibm.com/roadmaps/index.html for an overview of the
Worldwide Professions and links to the Common Skills Categories and
Professions Roadmaps.
Included in the profession chapters that follow are separate sections
titled "Skill Development Activities" that provide directions for
obtaining profession specific information.
1.2.6 Summary
As discussed, effective management of IBM skilled professionals on a
worldwide basis is required. The ability to tightly link the profession
positions with specific skill templates is critical to this management
system. This will ensure that all individuals worldwide in the same
profession position will assess themselves against the same skills and at
the same level of proficiency - a most significant step toward achieving
worldwide consistent skills.
1.3 Chapter 3. Certification Principles and Standards
Subtopics:
1.3.1 Introduction
As a professional develops knowledge and experience on the job, they are
progressing towards the ability to handle additional/more job
responsibility on a higher level. IBM views the validation of skills and
capability prior to assignment at the next profession position a critical
step in ensuring the person is truly qualified and ready for a job at this
level. In most instances, this determination is made by local management.
For some professional careers, a determination beyond local management is
required through formal examination or certification. While not required
at all levels in a profession, worldwide standards for IBM certification
have been established for defined profession positions for a number of the
professional careers, as shown below.
____________________________________ ___________________________________
| Professional Careers with IBM | Professional Careers without IBM |
| Certification | Certification |
|____________________________________|___________________________________|
| ° Client Relationship | ° I/T Availability - Systems |
| ° Consultant | Services Representative and |
| ° Education | Systems Software Specialist |
| ° General Business Relationship | ° Marketing Profession - |
| ° I/T Architect | Distribution Channels |
| ° I/T Availability - | Marketing |
| Availability Manager and | ° Marketing Profession - Market |
| Customer Services Manager | Intelligence |
| ° I/T Specialist | ° Marketing Profession - |
| ° Marketing Profession - | Marketing Communications |
| Database Marketing | ° Marketing Profession - |
| ° Marketing Profession - Direct | Marketing Management |
| Marketing | ° Marketing Profession - |
| ° Project Management | Technical Support Marketing |
| ° Sales Specialist | |
|____________________________________|___________________________________|
The standards, prerequisites, nomination and processes for IBM
certification are described in this chapter. It is intended to provide
the reader with an understanding of the common certification concepts that
these professional careers share. For detailed information on a
particular profession or information on how to become certified, review
the appropriate professions chapter in this guide.
Subtopics:
1.3.1.1 Objectives
The objective of certification is to establish an environment within IBM
to encourage, acknowledge, and recognize professional growth and
excellence. Certification is intended as a recognition for individuals
who have met at least the minimum requirements in terms of business
contribution, customer-valued skills, experience, client/segment
satisfaction, and professional contribution. It is a demonstration by the
individual of long-standing achievement within the profession, some of
which may have been achieved prior to joining IBM.
Certification ensures the skills, experience, contribution and business
need necessary for the certified individual to advance to positions and
compensation levels equivalent to management while still pursuing a career
as a professional.
1.3.1.2 Overview
The IBM Global Professional Careers have a common process for IBM
certification that is implemented worldwide. This process recognizes
those IBM professionals "who have been and currently are" working in a
specific profession "at or above" defined standards of excellence, rather
than certifying capability to begin working in a profession. That is, the
candidate's primary current responsibility must be in one of the defined
professional careers and he/she must have been practicing within that
profession for a minimum period of time.
The certification process inspects and validates a candidate against a set
of standard criteria. First and foremost, there must be a business need
for a certified position for the process to begin. The defined certified
positions within a profession equate to management positions and the
candidate's line management must concur with the business need for this
position.
The candidate prepares a nomination package that will be the vehicle for
communicating the candidate's qualifications. Management concurs with
both the business need for the certified position and the candidate's
qualifications for the certified position by signing and submitting the
nomination package.
The nomination by line management is the first of three approval
checkpoints in the certification process. The package is also reviewed by
profession and/or discipline representatives as the second checkpoint in
the process. Lastly, the candidate is reviewed by the certification
board. The board then makes a recommendation to the profession executive
who is the final authority for certifying or declining the candidate.
Individuals who have been declined for certification can resubmit their
packages once their certification requirements are met. There is no
predetermined waiting period that must expire before resubmission can take
place. Recertification is required every three years.
1.3.2 Criteria
There are five categories of criteria against which candidates for
certification will be evaluated. These categories are common to all
professional careers and are:
- Business Contribution
- Skills
- Experience
- Client/Segment Satisfaction
- Professional Contribution
The actual criteria within each category can vary by profession. For
example, an I/T specialist would be expected to have higher technical
skills than a client relationship representative, or a sales specialist's
business contribution would be expected to have an emphasis on product
revenue and profit while a consultant's would likely be measured by
personal billing and utilization. Thus, while each profession may choose
different criteria against which to measure their candidates, they will
all have at least one measure in each category.
Subtopics:
1.3.2.1 Business Contribution Criteria
While the criteria within the business contribution category will vary
across professional careers, within any particular profession the criteria
will be common worldwide. However, the quantification of that criteria
can vary either by discipline/speciality, geography/country, or
industry/segment. Some of the criteria in the business contribution
category may not be quantifiable, but may be expressed in terms of other
business results.
Again, as an example, all sales specialists worldwide are measured on
revenue. However, the quantification of that revenue can vary by
discipline. Large systems sales specialists have a different revenue
criteria in the business contribution category than sales specialist in
the networking discipline. Business contribution expressed in monetary
terms may vary by geography due to varying currencies. In the services
arena, the going market rate for services billing will affect the personal
revenue contribution that an individual can be expected to produce.
Profitability may be sacrificed in some investment market segments in
order to drive revenue share in emerging industries. The business
contribution measure needs to be flexible enough to accommodate these
requirements while still being fair and comparable across the variations.
It is up to the individual profession executives to determine what is a
comparable quantification of the business contribution criteria for their
profession.
Some examples of possible business contribution measures are revenue,
profit, market share, product volumes, utilization, competitive winbacks,
and growth. They might be measured across individual clients, sales
engagements, projects, personal billings, or market segments. The goal is
to establish comparable measures of the business contribution individuals
make while reflecting the dynamics of the marketplaces in which we are
operating.
1.3.2.2 Skills Criteria
Candidates must meet skill level proficiency requirements for their
profession and discipline. There is a common set of skills that all IBM
Certified Professionals must have. They are summarized earlier in this
guide in the Skills Categories portion of Chapter 2, "Skills Framework and
Templates" in topic 1.2. Detailed skills by profession and discipline are
defined by templates in the SKILLS tool. The required proficiency levels
for certification are also defined in the templates.
1.3.2.3 Experience Criteria
The appropriate experience is defined as the repeated application of
skills in a business environment. Sustained performance within the
profession and discipline is expected. Candidates are required to
document multiple occurrences that are evidence of successful engagements
that provide experiential support of the skill proficiencies claimed in
the Skills Section of the nomination package. SKILLS tool reports are the
preferred method of providing this experiential support.
1.3.2.4 Client/Segment Satisfaction Criteria
Candidates are expected to provide multiple evidence of a high level of
client/segment satisfaction that is a direct result of a candidate's
contribution. Typical examples are referencable engagements, client
endorsements, letters of recommendation from fellow professionals,
customer satisfaction surveys, etc.
1.3.2.5 Professional Contributions Criteria
The professional contributions criteria is meant to assess a candidate's
contributions to his/her personal and professional community. This is a
vehicle for him/her to be able to give back to others. The process looks
for involvement and professional recognition beyond an immediate sphere of
influence, situations where the candidate demonstrates thought leadership
and commitment to the profession.
There are many varied examples of how a candidate might provide evidence
of professional contribution. They include things like: mentoring,
teaching, staff assignments, authored publications, professional society
membership and accreditation, industry associations, speaking engagements,
or public service. They are included to ensure candidates for
certification are well rounded individuals ready to take a leadership role
within the professional community. This category gets additional focus
when individuals apply for recertification.
1.3.3 Nomination Package
The nomination package is the primary vehicle that candidates use to
substantiate their evidence in support of an application to be certified.
It is a collection of documentation supporting the five certification
categories discussed previously (i.e., business contribution, skills,
experiences, client satisfaction, and profession contribution). Other
items may be required as determined by the individual profession. Your
geography profession leader should be contacted if you have any questions
on how to prepare your package. Refer to the Global Professional Careers
Worldwide Contact List for the geography profession leaders for all
professional careers.
The package is individually prepared and signed by the candidate. His/her
line management is expected to review and endorse the package. Executive
sponsorship of the package is also required. Line management and
executive sign-offs on the package are in place to verify that there is a
business need for a certified professional.
1.3.4 Certification Review Process
Once local line and executive approvals are obtained, the packages are
forwarded to either the geography profession leader or discipline leader
for a package review. These reviews are conducted several weeks before
the actual certification boards are scheduled. Packages are reviewed by
profession/discipline leaders along with other certified professionals.
The objective of this review is to ensure that only candidates that have a
real chance to certify are invited to the board interviews. The package
review team either accepts, declines, or suggests modifications to the
package. Once the packages are accepted by the review team, the
individual certification board interviews are scheduled.
The certification boards are conducted on a regularly scheduled basis,
usually two to four times a year, as determined by the geography's
profession leader. In order to give individuals adequate time to prepare
their certification packages the schedule dates for the boards are
published well in advance.
The board itself consists of a minimum of three members. The majority of
the board members must be certified practitioners of the profession.
Other individuals who may be asked to participate on boards are specific
subject matter experts, former profession practitioners now in staff
positions, appropriate executives, etc.
Interviews are individually scheduled with the board members. They are
conducted on a one-on-one basis. Under most circumstances, the interviews
will be face-to-face (note: the consultant profession varies for
principals and consultants with worldwide responsibility. See the guide:
"Practice and Professional Certification - Principal Confirmation - IBM
Consulting Group").
Following the interviews, the Board members convene to discuss the
candidates. For each candidate, the Board must come to a consensus
recommendation to either accept or decline. Only board members who have
actually conducted an interview with the candidate are to participate in
the consensus voting process. Once the board comes to a consensus they
make a recommendation to the profession executive. The profession
executive makes the final decision on the candidate.
The profession or discipline leader will notify all candidates of the
decision approximately one week after the board interviews are conducted.
Subtopics:
1.3.4.1 Declined Candidates
In the case where certification board members make a recommendation not to
certify, they must have supportive evidence from either the candidate's
nomination package or from the interviews themselves. Based on that
evidence, the board will provide constructive direction to the candidate
that he/she can use to enhance their credentials. Once the candidate
meets the criteria he/she can reapply for certification. There is no
predefined period that a candidate must wait before reapplying.
1.3.4.2 Accepted Candidates
General announcement of the candidate's acceptance as an IBM Certified
Professional will be conducted by the candidate's geography. Typically,
this will take place in an INEWS announcement. Accepted candidates will
also receive an IBM Certified Professional certificate.
1.3.4.3 Recertification
Once certified, an individual is expected to remain active in the
profession. Evidence of continued activity in their profession and
discipline will be required when recertification is due.
IBM's period of certification is three years. Prior to the end of the
third year, practicing certified individuals will be required to submit
evidence that they have met the recertification criteria, which include:
- Meeting the basic certification criteria in effect at the time of
application for recertification.
- Demonstrated growth within the profession/discipline since
certification.
- Currently an active practitioner of the profession/discipline.
It is the individual's responsibility to track when it is time to apply
for recertification. The candidate should plan to apply for
recertification for the certification review board closest to the third
anniversary of their certification date.
Candidates for recertification should contact their geography's profession
leader to request the recertification package format.
1.3.5 Individual Profession Requirements
Each of the IBM Global Professional Careers utilizing IBM certification
have followed these guidelines in establishing their profession
certification process. Each has unique requirements that are documented
in their individual certification guides.
2.0 Marketing Professional Career
Subtopics:
2.1 Chapter 4. Marketing Professional Career
Subtopics:
2.1.1 Marketing Professional Career Overview
In recent years, the IBM Company has made significant strides in becoming
more market-driven. Moving toward a global brand unit and customer-set
orientation has resulted in changes to IBM's financial systems worldwide
and the creation of a new integrated planning process combining strategic
planning, operating plans and financial planning. In addition, to support
these changes, the CRM Market Management and Integrated Product
Development Portfolio Management processes have been converged and
improved.
This transformation underscores the need for clearly-defined and
expertly-staffed marketing organizations in IBM that support these changes
to our business and lead IBM into the next century. The establishment of
a Marketing Professional Career in IBM addresses these requirements by
clearly defining marketing jobs, required skills and skill levels, and
career paths.
The Marketing Professional Career has its roots in IBM's Brand Business
Management Initiative established in 1994. The initiative was created to
improve marketing, create a Global Brand Business Management System in IBM
and develop quality global business plans that lead to improved business
results. Brand management is a system that manages the activities
associated with bringing an offering or solution (i.e., hardware,
software, services) to market that has value to the customer. Its purpose
is to strengthen the meaning, integrity, and power of the IBM brand. It
incorporates the steps necessary to balance customer and market needs and
IBM's internal capabilities, to produce global strategies and plans, and
to fulfill key customer and market requirements. The Brand Business
Management System is team-based and cross-functional in design and
incorporates the inter-relationship of marketing, development, sales,
fulfillment teams, and our customers.
The change from a functionally-managed system to a business system based
on brand management principles has required significant cultural and
operational changes. With this change comes the need to shift from
geography-based to a worldwide customer and market-oriented paradigm. The
challenge is to shift from a development and technology paradigm to a
marketing paradigm that balances technology and customer-driven offerings
and solutions.
The primary goal of the IBM Brand Business Management Initiative is to
establish an environment that enables the IBM Company to increase its
market participation and profitability. The projected results are an
improvement in marketing strategies, plans and programs, development of,
and improvement to the global brand management/general management system,
and the creation and implementation of global business strategies and
plans.
Global business strategies and plans set the direction for meeting brand
unit and/or business unit objectives. The brand unit and/or business unit
strategy, plans and supporting activities create and sustain the brand
"promise of value" and/or the business unit value proposition. They are
defined by the marketing mix of elements --- strategy, offering, terms,
distribution, support/skills, fulfillment, and image and are characterized
by the following activities:
- Strategy -- customer/market segmentation, competitive assessment,
internal capabilities assessment, brand unit and/or business unit
strategy, market segmentation prioritization and selection, annual
focus items, etc.
- Offering -- offering plan, offering specifications, licensing,
strategies, campaigns, offering/solution schedules, go-to-market
strategies, announcement process management, etc.
- Terms -- Terms plans including pricing, T's & C's, warranties, special
bid strategies, customer financing plans, promotion plans/mix,
schedule of promotions, etc.
- Distribution -- Distribution plans, channel wants and needs, channel
campaigns, distribution support systems, OEM strategy, channel cost
and expense targets, etc.
- Support -- Customer/market/business partner requirements, global
strategies, plans and programs, expense and financial targets, channel
readiness, development of new technical support/services offerings/
solutions, customer satisfaction/loyalty objectives, etc.
- Fulfillment -- Fulfillment plans, manufacturing requirements,
logistics requirements, order entry requirements, fulfillment
processes/ standard, supply/demand strategy, cost targets, sourcing
requirement, target industry levels, etc.
- Image -- Image plans, message content, offering/solution names,
advertising development, media priorities and placement plans, press
kits, collateral requirements, internal communications plans,
cost/funding by geography, etc.
The marketing mix elements, the activities associated with them, and the
skills required to accomplish them, can be grouped and are expressed as
jobs within the Marketing Professional Career. Covering a broad spectrum
of tasks and responsibilities, they currently include both existing and
newly-defined positions essential to the management and performance of the
marketing mix.
The Marketing Professional Career establishes a consistent worldwide
framework for jobs, roles, and skills in support of the IBM Brand Business
Management Initiative and provides the vehicle for its effective
implementation independent of organization structure or mission.
Individuals working in the Marketing Professional Career may reside in any
IBM organization where marketing activities are performed.
Consistent with the other IBM Worldwide Professional Careers, the
Marketing Professional Career offers individuals a dual-ladder career path
from comparable positions -- entry through executive -- in both management
and non-management jobs. Each is based on a clearly-defined position
description and a set of specific skills and required skill proficiency
levels. Career movement is based on individual expertise, achievement of
required skills proficiency, experience, customer satisfaction and loyalty
contributions to the business, and business need.
2.1.2 Professional Career Structure
The Marketing Professional Career consists of profession disciplines,
specialties within disciplines, and roles which map to the activities,
tasks and responsibilities associated with the execution of the marketing
mix of elements, and which are defined as follows:
- Profession Disciplines - allow individuals to perform as functional
specialists in marketing management, market intelligence, distribution
channels marketing, technical support marketing, marketing
communications, direct marketing and database marketing. Career
opportunities exist vertically within each profession discipline and
horizontally across profession disciplines. Position descriptions
associated with each profession discipline represent either jobs to
which individuals are currently assigned or long-term growth
opportunities for others. Each position description has a
complementary skill list.
- Specialties - within disciplines allow individuals to perform more
finite tasks required by the local geography, the brand unit and/or
business unit size, scope and objectives, or in areas of critical
importance to IBM's long-term growth and vitality. Specialties allow
individuals skilled in specific marketing activities such as customer
satisfaction research, OEM marketing, advertising, and demand
generation to use their skills to meet business objectives. Career
growth may be characterized by one's ability to work in one or more
specialties. For each specialty within the disciplines of the
Marketing Professional Career there is a detailed description and a
complementary skill list.
- Roles - set of tasks which an individual may be asked to perform in
addition to his/her job is considered a role, such as a project
leader, strategist, planner, or skills planner. This assignment would
typically last for a short time -- 3 to 9 months -- or may become a
full-time job depending on business need. For each role there is a
detailed description and a complementary skill list.
The Marketing Professional Career has been designed to be implemented in
an environment that ranges from simple to complex. The factors that
govern the environment are based on business need and relate to its scope
in terms of revenue potential, number of skilled professionals needed
and/or available, business area focus, and other factors. Flexibility in
implementation is exemplified by the ability to combine profession
disciplines and/or specialties in making individual assignments that
reflect actual business needs. In one situation, for example, the
business may need full-time specialists, on staff, within specific and
distinct disciplines. On the other hand, an assessment of lesser business
needs could result in the combination of specialities, profession
disciplines, and even roles for individual assignments. These would be
reflected in the skills assigned to that person in his/her profile.
It is assumed that a position description typically cannot completely
define the responsibilities for any individual in every assignment. There
is a need to make position descriptions and their related skill lists as
flexible and modular as possible to facilitate customization to reflect
what an individual really does.
The Marketing profession disciplines are summarized as follows:
- Marketing Management
Marketing Management is the pivotal component within the Marketing
Professional Career which integrates planning and execution for the
offerings and solutions that make up the brand unit promise of value
and/or the business unit value proposition. Marketing Managers focus
on the planning and execution of the marketing mix of elements and the
integration of the functional activities (e.g., marketing,
development, sales, fulfillment, etc.) related to the creation of
offerings and solutions that meet customers needs and market dynamics.
Marketing Managers analyze market opportunities, research, select and
de-select target markets, develop marketing strategies, plan marketing
programs and define offerings/solutions that are responsive to the
needs of our priority customer segments and the market. They make
decisions on target markets, market position, offering/solution
development, terms, distribution, support/skills, fulfillment and
image. They define and implement channel strategies for
offerings/solutions that reflect customer buying patterns, provide
wide coverage plans to targeted customers segments, and support the
brand unit promise of value and/or business unit value proposition.
Marketing Managers define, develop and direct the execution of market
research and customer analysis and use the results to effectively
drive the execution of brand unit and/or business unit strategies and
plans.
Marketing Managers set objectives and track performance against them
for market participation, financial results, customer positioning,
customer satisfaction and loyalty, and other customer and market-based
measurements.
- Market Intelligence
Market Intelligence is aimed at the collection, analysis, and
interpretation of information about markets, customers, prospects,
competitors, and IBM's own offerings and capabilities. These
activities serve as the basis for reducing uncertainty, gaining a
strong view of customer wants and needs, and meeting the primary
responsibility of Market Intelligence -- the reduction of risk in
decision-making.
Specialty areas in this profession discipline are customer
satisfaction and loyalty research, marketing communications research,
new offering/solution research, competitive analysis research, and
industry/market analysis research.
- Distribution Channels Marketing
Distribution Channels Marketing is responsible for identifying and
selecting the appropriate distribution channels for IBM offerings and
solutions. They use Routes to Market tools in the creation and
implementation of go-to-market strategies and plans, distribution
channels marketing strategies and plans, and marketing programs and in
the gathering of distribution channels marketing offerings/solutions
requirements. Specializing in one channel or combinations of
channels, they understand the components, and articulate the
requirements of channel support.
These professionals also work with other functions in IBM, such as
legal, business practices, and offerings/solutions development to
ensure channels business is conducted in accordance with established
standards. Understanding competitors' distribution practices, they
are effective in creating strategies to increase IBM's channel
presence and participation.
Specialty areas in this profession discipline are face-to-face
marketing, business partner, tele marketing, electronic marketing, OEM
marketing, hybrid marketing, and fulfillment strategy.
- Technical Support Marketing
Technical Support Marketing professionals are responsible for creating
and executing global technical support and services strategies, plans,
and programs for brand unit and/or business unit offerings/solutions.
Technical Support Marketing Specialists team with sales, services and
development organizations, as well as with other elements of the
marketing mix, to gather requirements and take actions to enhance the
quality of, and customer satisfaction with IBM offerings and
solutions. They also recommend, and may oversee, the development of
new technical support and services offerings and solutions.
Specialty areas in this profession discipline are Technical Sales
Support, HW/SW Service(s), and Product Enabling Services.
- Marketing Communications
Marketing Communications is an integral part of the successful
implementation of the marketing mix of elements. Marketing
Communications focuses its efforts on developing strategies, plans and
programs for advertising, collateral/sales promotion, business shows,
corporate sponsorships, sports marketing, and/or media strategy,
planning and buying, in support of corporate, category, brand unit
and/or business unit objectives.
Marketing Communications professionals are responsible for developing
integrated marketing communications strategies and programs which are
designed to communicate with IBM's current and potential customers,
business partners, suppliers, constituents, and the general public in
order to create a positive image for IBM, thereby increasing demand
and loyalty for IBM offerings and solutions.
- Direct Marketing
Direct Marketing is a structured approach to cultivating and
maintaining lifetime customer relationships. Integrated and
consistent messages focused on retaining or reactivating customers and
acquiring new customers are developed and delivered over an extended
period of time.
The Direct Marketing profession discipline includes the existing
Direct Marketing and Database Marketing professions.
Professionals who specialize in Direct Marketing demand generation
assist brand units and/or customer set business units in translating
marketing strategies into effective direct marketing campaigns,
programs and tactics that are designed to create demand, i.e.,
measurable responses and opportunities for sales channels. Direct
Marketing professionals create demand by orchestrating the delivery of
effective messages and offers to the market through the use of
cost-effective media alternatives, which include, but are not limited
to, direct response advertising, mail, catalogs, telemarketing,
telecoverage, and interactive.
Professionals who specialize in database marketing develop and
maintain operational and analytical market information databases that
support creative and innovative direct marketing programs, as well as
provide a competitive advantage for brand and/or customer set business
units. Database Marketing is designed to develop empirically-based
and analytically-derived conclusions about the market and customers.
Direct Marketing and Database Marketing have been IBM professions
since 1994. As part of the Marketing Professional Career, individual
professionals will continue to have the same career path, including
certification for those meeting the published criteria.
2.1.3 Marketing and Sales
With the announcement of this professional career, the term "marketing"
will henceforth be used only in conjunction with marketing activities and
jobs. In 1995, the Brand Management Initiative differentiated the
responsibilities of marketing and sales. The Marketing Professional
Career provides position descriptions, dual-ladder careers, skills and
skill requirements for all Marketing professionals.
Skill enhancement development roadmaps will be provided for all profession
disciplines in Marketing summarizing the skill, contributions, leadership,
and impact requirements of the discipline. They will also address the
professional development activities that are recommended for progression
within each profession discipline. Some of these roadmaps are currently
accessible in the guide while others will be available at a later date.
2.1.4 Characteristics of the Profession
The following characteristics are viewed as common to all Marketing
professionals:
- Effectiveness in coordinating internal and external resources
- Skill in developing strategies and a plan of action to achieve the
goals of the professional career and/or profession discipline
- Use of marketing intelligence data to create plans to support
execution of strategies
- Development of targeted programs that promote strategies and achieve
business goals
- Knowledge of the IBM Brand Business Management System and the ability
to effectively apply it to marketing activities
- Ability to explain IBM short- and long-term business strategies
- Understanding of competitive trends and ability to respond effectively
- Understanding of IBM global operations
- Ability to work in cross-functional teams
- Use of creative thinking
- Application of appropriate financial management concepts to everyday
business activities
- Understanding of the CRM process
- Knowledgeable about the IBM Market Management Process
- Able to apply basic project management techniques
- Self-motivated in maintaining currency in a selected profession
discipline
2.1.5 Potential Candidates
Marketing Professional Career candidates may be sourced from current IBM
employees who represent a broad array of backgrounds and experience, i.e.,
marketing, sales, technical support, management, or other positions
related to marketing. Other candidates may be sourced from professional
hires with relevant skills and experience or from recent college
graduates.
Figure 4-1 illustrates the possibilities for movement to and from the
Marketing Professional Career. Additional information is available in
career planning guides for the profession disciplines. Where applicable,
these are specified in the profession discipline sections of this guide.
Similar "Career Possibilities" charts for each discipline appear in their
respective sections of this guide.

Figure 4-1. Marketing Profession Career Possibilities
2.1.6 Title Structure
The Marketing Professional Career uses three titles for the five
professional positions. The prefix "Associate" is used for the lowest of
these positions. No prefix is used for the middle two positions and the
prefix "Senior" is used for the highest position.
The following example illustrates the use of titles with positions:
- Associate Marketing Communications Specialist
- Associate Marketing Communications Specialist (advanced)
- Marketing Communications Specialist
- Marketing Communications Specialist (advanced)
- Senior Marketing Communications Specialist
2.1.7 Career Growth
Consistent with the characteristics and objectives common to all of the
IBM Worldwide Professional Careers, the Marketing Professional Career
provides its participants with a dual-ladder career path. This ensures
that an individual may follow either a management or non-management career
with comparable opportunity for position levels, recognition, and
compensation. Both paths enable and encourage professional growth and are
supported by formal processes, documentation, position descriptions,
skills templates, and education roadmaps. There is also a certification
process in place for Direct Marketing and Database Marketing
professionals.
The differentiating factors between one position level and another and, in
turn, the prerequisites for career growth within the Marketing
Professional Career, are skills, capabilities, experience and
responsibility.
Details regarding career growth within each profession discipline are
available in their respective sections of this guide.
2.1.8 Certification
At this time, with the exception of the Direct Marketing profession
discipline, the Marketing Professional Career will not participate in the
currently defined IBM Certification Process.
The Worldwide Direct Marketing Certification Nomination Guide and
Worldwide Database Marketing Certification Nomination Guide contain the
criteria, required documentation, and process for certification.
2.1.9 Performance Elements
Performance elements vary amongst the profession disciplines and are
addressed in their respective sections. These may include contribution to
market participation, generation of business opportunities, development of
business partner relationships, achievement of leadership objectives, and
many others. Common to Marketing professionals are, among others, market
segment satisfaction, brand unit and/or business unit satisfaction and
customer satisfaction.
2.1.10 Marketing Professional Career Skills Profile
The skills required of a Marketing professional include:
- General Marketing skills required of all individuals in the Marketing
Professional Career.
- IBM Internal skills required of all individuals in the Marketing
Professional Career.
- Specialty skills relating to areas of specialization within the
profession disciplines (one group of skills for each specialty).
- Marketing role skills (one group of skills for each role).
General Marketing skills and IBM Internal skills are listed in the chart
that follows. Proficiency level requirements are not included since they
vary by profession discipline. These are stipulated in each profession
discipline section of the guide, along with the discipline and specialty
skills and proficiency requirements for each position and position level.
The skills and proficiency levels required for each of the four roles
within the Marketing Professional Career follow.
___________________________________________________ ____________________
| | Proficiency Levels |
| MARKETING PROFESSION SKILLS |____________________|
| | * in Discipline |
| | Section |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| GENERAL MARKETING SKILLS |
|___________________________________________________ ____________________|
| Know & Apply Marketing Concepts & Methods | * |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Know & Apply Mkt Intelligence Concepts & Methods | * |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Understand Customer Reqmnts & Buying Behaviors | * |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Know & Apply Market Segmentation | * |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Develop Strategies | * |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Develop Plans | * |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Develop Programs | * |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| IBM INTERNAL SKILLS |
|___________________________________________________ ____________________|
| Know & Apply IBM Brand Business Management System | * |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Explain IBM Business Strategy | * |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Understand the IBM Brand Strategy | * |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Understand/Anticipate/Respond-Competitive Trends | * |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Articulate IBM Offerings/Technologies | * |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| IBM Formal and Informal Network | * |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Work in Cross-Functional Teams | * |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Understand IBM Global Operations | * |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Creativity/Breakthru Thinking | * |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Interpersonal Communication | * |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Negotiation | * |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Problem Solving & Decision Making | * |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Apply Basic Financial Concepts | * |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Apply Project Management Techniques | * |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Self-Directed Learning | * |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| MARKETING PROJECT LEADER ROLE |
|___________________________________________________ ____________________|
| Determine Customer Needs | 3 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Foster Teamwork/Enable Teams | 3 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Analyze Problems/Situations | 3 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Leadership | 3 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Negotiation | 3 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Initiate Projects | 3 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Plan Projects | 3 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Develop Project Plans | 3 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Project Track/Report/Deliver | 3 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Manage Project Revenue/Cost | 3 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Assesses Proposals & Project Risks | 3 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Manage Project Change | 3 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Manage Contracted Resources & Services | 3 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Conduct Project Reviews | 3 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| MARKETING STRATEGIST ROLE |
|___________________________________________________ ____________________|
| Understand Customer Reqmts & Buying Behavior | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Develop Strategies | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Perform Market Analysis | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Determine Customer/Market Needs | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Client Research & Analysis | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Analyze & Interpret Marketing Information/Data | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Synthesize Marketing Information/Data | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Perform Forecast Planning | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Develop Measurement Strategy | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Explain IBM Business Strategy | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Understand IBM Brand Strategy | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Understand IBM Corporate Planning Cycle | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Understand IBM Integrated Business Process | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Explain IBM Strategic Business Initiatives | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| IBM Vision/Mission/Strategy | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Develop Resource & Skill Plans | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| IBM Formal & Informal Network | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Work in Cross-Functional Teams | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Apply Basic Financial Concepts | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Perform Time Management | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| MARKETING PLANNER ROLE |
|___________________________________________________ ____________________|
| Understand Customer Reqmts & Buying Behavior | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Develop Plans | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Perform Market Analysis | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Determine Customer/Market Needs | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Analyze & Interpret Marketing Information/Data | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Perform Business Planning | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Business Modeling/Planning | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Explain IBM Business Strategy | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Understand the IBM Brand Strategy | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Understand IBM Corporate Planning Cycle | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Understand IBM Integrated Business Process | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| IBM Formal & Informal Network | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Work in Cross-Functional Teams | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Negotiation | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Plan Projects | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Develop Project Plans | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Develop Resource & Skill Plans | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Perform Budgeting/Planning | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Apply Basic Financial Concepts | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Perform Time Management | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| MARKETING SKILLS PLANNER ROLE |
|___________________________________________________ ____________________|
| Understand WW Skills Management Process | 5 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Use Skills Management System | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Develop Resource and Skill Plans | 5 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Identify Skills Training Requirements | 5 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Develop Skill Definitions | 3 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Develop Skill Templates | 3 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Understand IBM Global Operations | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| IBM Formal & Informal Network | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Work in Cross-Functional Teams | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Apply Basic Financial Concepts | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Apply Project Management Techniques | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Negotiation | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Problem Solving & Decision-Making | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Creativity/Breakthru Thinking | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Interpersonal Communication | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
| Manage Contracted Resource & Services | 4 |
|___________________________________________________|____________________|
2.1.11 Professional Development
Growing skills requires a combination of experience, education, training,
coaching, and mentoring and is best accomplished through the formulation
and implementation of a professional skills development plan. The
selection of development activities should reflect the specific needs of
an individual, the individual's career aspirations, the needs of the
business, and other relevant circumstances.
Many forms of education are available to help increase skill proficiency
levels. These include internal IBM education and training, external
education and training, professional associations and conferences,
self-education and reference readings (e.g., articles, books, WEB sites,
newsletters, etc.)
Specific information on skill development activities pertaining to the
profession disciplines is included in each discipline section of this
guide.
2.1.12 Marketing Professional Career Position Descriptions
Position descriptions for all positions within the Marketing Professional
Career are organized by profession discipline and are included in each
discipline's section of this guide.
2.1.13 Marketing Professional Career Role Descriptions
Subtopics:
2.1.13.1 Role Title: Marketing - Project Leader
Role Summary:
The Project Leader is responsible for leading a project team or a portion
of a larger project. His/her experience-acquired skills enable him/her to
accept assignments or provide direction for a number of tasks on a daily
basis. In turn, he/she assigns tasks to team members and offers his/her
assistance and coaching so that objectives are met with the highest levels
of quality, excellence and professionalism. Management staffs rely on the
Project Leader as the primary contact for all related project activities.
A Project Leader may work in a specialty within the Marketing Profession.
Responsibilities:
- Has a comprehensive understanding of the brand unit and/or business
unit strategies and objectives.
- Negotiates effectively with team members, management and other
internal/external staffs concerning all aspects of the project.
- Leads the project from the initiation stage to completion.
- Determines and secures resource requirements, selects team members,
and coordinates support functions.
- Reviews the status of commitments, plans, schedules and work scope,
identifies problems in each area and provides creative solutions by
using a team approach.
- Identifies team related issues (e.g., lack of consensus, inability to
work together as a team) and leads the team to resolution.
- Leads the development of creative solutions and/or resolutions to
issues that affect the successful completion of the project.
- As appropriate, assesses the performance of team members against
specific project requirements and communicates those results to
management.
- Assesses the project success, draws conclusions and makes
recommendations to improve processes.
2.1.13.2 Role Title: Marketing - Strategist
Role Summary:
The Strategist is responsible for determining longer-term, overall
strategic direction and develops specific strategies for the brand unit
and/or business unit. This is accomplished through the application of
accepted and sound strategic management concepts. The focus of the
Strategist is to develop specific strategies for any marketing function
which will effectively support and deliver the brand promise of value
and/or the business unit value proposition to the target market and to
potential or current customers.
The proper and adequate execution of this role by a marketing professional
will ensure that the selection of any marketing mix element for the
business is based on external data and factual market analysis (e.g.,
customer and market segments, industry environment, competitive postures
and programs, emerging trends, etc.).
Responsibilities:
- Employs appropriate strategic management techniques in developing
functional strategies.
- Adopts an orientation to planning which is customer- and market-driven
rather than product, sales, technology- or offering-driven.
- Conducts a market analysis of all external factors related to the
functional area assigned.
- Seeks assistance from Market Intelligence to provide appropriate data
for developing strategic direction.
- Develops functional strategies based on specific business requirements
and objectives.
- Ensures that the analytically-based conclusions used in developing
marketingional strategies of
elements clearly relate to established objectives and in turn will
produce winning strategies.
- Considers the necessary capital/financial or human resources needed to
implement chosen strategies.
- Recommends strategies to functional and marketing management.
- Based on approved strategies, either develops or coordinates the
marketingopment of specific
or and/or business plans to implement a chosen strategy.
2.1.13.3 Role Title: Marketing - Planner
Role Summary:
The marketing professional uses the Planner role to convert the approved
chosen strategy for a marketing element or marketing function into
tactical business plans. These more detailed action plans are used in a
shorter time frame to execute the strategies to achieve the brand unit
and/or business unit goals and objectives.
The focus of the Planner role is to create very specific functional plans
and programs which will enable the execution of strategies in a timely and
cost-effective manner. The end result of effectively practicing this role
will be a plan, a blue-print for prioritizing the necessary resources, a
written guide for communicating needs and requirements to other essential
functions, and a checklist to monitor progress of development and
execution of specific plans and/or programs.
Responsibilities:
- Ensures clear understanding of strategies for a requesting function.
- Creates and designs the program concept and elements required to
implement the functional strategies.
- Conducts adequate cost analysis and determines funding requirements to
execute specific plans.
- When appropriate to the function or plans, develops financial
projections or other measurement criteria.
- Presents the plans to appropriate functional or marketing management
for approval.
- Determines timetables and milestones to achieve coordinated target
dates for implementation.
- Communicates plan, elements and requirements to other functions who
must assist in plan execution.
2.1.13.4 Role Title: Marketing - Skills Planner
Role Summary:
The Skills Planner has the responsibility to understand skill requirements
for an offering or solution for internal and external sales and support
channels (and customers, as appropriate), analyze skill gaps for those
audiences, and to develop and execute skill development plans to address
those gaps. In addition, he/she develops and maintains skill templates
that support brand unit and/or business unit offerings and solutions.
This role may be performed in addition to an individual's regular
position, and/or as a full-time assignment.
Responsibilities:
- Gathers global skill requirements for offerings and solutions for
sales and support channels (e.g., IBM, business partner, electronic,
etc.) and for customers, as appropriate.
- Develops and maintains worldwide skill templates related to IBM
offerings and solutions which support the IBM Worldwide Skills
Management Process.
- Assesses, analyzes and understands critical skill gaps worldwide for
all sales and support channels and for customers, as appropriate.
- Develops a global skills development plan that supports IBM, brand
unit and/or business unit strategies for offerings and solutions and
addresses skills gaps. The plan includes, but is not limited to:
- deliverables (e.g., classes, manuals, guides, workshops, etc.)
- suppliers (e.g., E&T, consultants, vendors, etc.)
- resources (e.g. personnel, technology, tools, etc.)
- global coverage capability and issues
- Determines funding requirements (e.g., headcount, development costs,
travel, etc.) and negotiates approval for the skills development plan
from all affected constituencies (e.g., geographies, sales and
services, distribution channels, etc.).
- Negotiates with education suppliers for the fulfillment of training
requirements and secures their commitment to meet requirements of the
global plan (e.g. dates, costs, etc.).
- Monitors execution of the global skills development plan and measures
results against plan objectives for skill gap closures, customer
satisfaction, etc. Uses feedback to correct shortfalls in the plan
and to provide input to the brand unit and/or business unit marketing
and development teams, as appropriate.
2.2 Chapter 5. Marketing Management Profession Discipline
Subtopics:
2.2.1 Marketing Management Profession Discipline Overview
Marketing Management is one of six profession disciplines within the
Marketing Professional Career (see "Professional Career Structure" in
topic 2.1.2). It is the pivotal component within the Marketing
Professional Career which integrates planning and execution for the
offerings and solutions that make up the brand unit promise of value
and/or the business unit value proposition. Marketing Managers focus on
the planning and execution of the marketing mix of elements and the
integration of the functional activities (e.g., marketing, development,
sales, fulfillment, etc.) related to the creation of offerings and
solutions that meet customers needs and market dynamics.
Marketing Managers analyze market opportunities, research, select and
de-select target markets, develop marketing strategies, plan marketing
programs and define offerings/solutions that are responsive to the needs
of our priority customer segments and the market. They make decisions on
target markets, market position, offering/solution development, terms,
distribution, support/skills, fulfillment and image. They define and
implement channel strategies for offerings/solutions that reflect customer
buying patterns, provide wide coverage plans to targeted customers
segments, and support the brand unit promise of value and/or business unit
value proposition. Marketing Managers define, develop and direct the
execution of market research and customer analysis and use the results to
effectively drive the execution of brand unit and/or business unit
strategies and plans. They perform all these activities through effective
management of resources and programs in marketing management and in the
other marketing profession disciplines such as market intelligence,
distribution channels marketing, technical support marketing, marketing
communications and direct marketing/database marketing.
Marketing Managers set objectives and track performance against them for
market participation, financial results, customer positioning, customer
satisfaction and loyalty, and other customer and market-based
measurements. They set overall brand unit and/or business unit direction,
develop marketing programs to support the worldwide brand promise of value
and/or business unit value proposition, coordinate strategies and plans
with customer set units, provide leadership in planning and drive the
integration of marketing and development to solve customers' business
problems.
2.2.2 Profession Discipline Structure
The Marketing Professional Career uses three titles for the five
professional positions. The prefix "Associate" is used for the lowest of
these positions. No prefix is used for the middle two positions and the
prefix "Senior" is used for the highest position.
The following positions are defined within the Marketing Management
profession discipline:
- Associate Marketing Manager
- Associate Marketing Manager (advanced)
- Marketing Manager
- Marketing Manager (advanced)
- Senior Marketing Manager
Marketing Managers are skilled in all six marketing profession
disciplines. They have a complete understanding of the IBM Brand Business
Management System, the IBM Market Management Process and associated
business processes, and are viewed by management as experts in marketing.
Depending on the size and nature of their brand unit and/or business
unit's scope they may have professionals reporting to them in virtual or
direct teams from any or all marketing profession disciplines.
The Marketing Management team is generally led by a Vice President of
Marketing who provides leadership and direction to a global team of
marketing management executives and professionals.
2.2.3 Characteristics of the Profession Discipline
Marketing management professionals have the following characteristics:
- Skilled in the management of brand unit and/or business unit marketing
activities, including day-to-day coordination of other marketing
functions and implementing operationally-detailed marketing plans that
best support business objectives.
- Knowledgeable about terms, distribution, support, fulfillment and
image strategies, plans and programs.
- Skilled in market research and the management, use and analysis of
qualitative and quantitative market research results.
- Skilled in the management of activities relating to terms strategy and
planning such as pricing, Ts & Cs, warranties, special bids,
incentives, etc. Ensures inclusion of these elements in planning and
in the total solution.
- Effective in integrating the activities related to going to market
through multiple channels of distribution in the brand unit and/or
business unit plan.
- Knowledgeable about IBM's sales organizations.
- Effective in ensuring the activities relating to fulfillment are an
integral part of the offering/solution.
- Effective in integrating the communications activities of a brand unit
and/or a business unit into its plan. Knowledgeable about marketing
communications plans, copy strategies, media plans, business shows,
direct marketing/database marketing, collateral/sales promotion, etc.
- Knowledgeable about the management of and the activities associated
with creating new offerings/solutions.
- Self-directed in maintaining currency and expertise in all aspects of
marketing.
- Skilled in project management methods and tools.
- Strong leadership and teamwork skills.
2.2.4 Potential Candidates
Marketing Managers may be sourced from current IBM employees with the
requisite skills in marketing management. Marketing Managers may also be
sourced from professional hires who have expertise in marketing management
or in another Marketing profession discipline.
Figure 5-1 illustrates the the possibilities for movement to and from the
Marketing management profession Discipline.
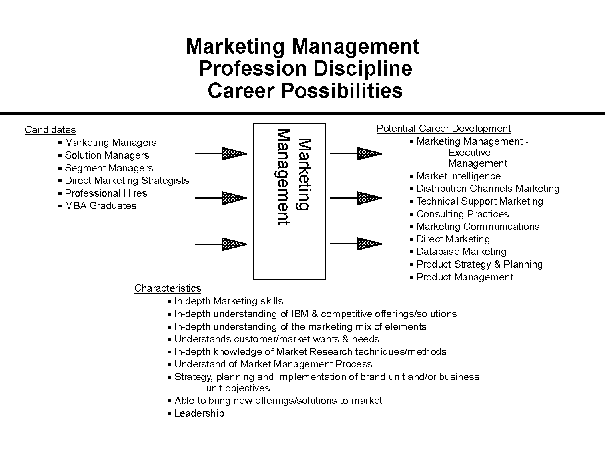
Figure 5-1. Marketing Management Profession Discipline Career
Possibilities
2.2.5 Career Growth
Marketing Managers can occupy positions from Associate Marketing Manager
to Senior Marketing Manager. The difference between the ascending
positions is a function of increasing skill, capability, experience, and
responsibility, and is reflected in the extent of a marketing manager's
demonstrated leadership, and the size and scope of his/her contributions
and impact on the business.
Growth in this discipline can be achieved through the acquisition of
skills and experiences that enable an individual to work in multiple
disciplines and/or specialty areas. Professionals can also rise to levels
comparable to executive management and career path movement can occur in
accordance with planned steps into and through other professions.
2.2.6 Performance Elements
The Marketing Management professional is an individual who generates
demand for IBM offerings/solutions and contributes to resulting revenue. A
Marketing Management professional is expected to deliver a high level of
satisfaction to both the brand unit and/or business unit, customers,
business partners, and the market.
2.2.7 Marketing Management Profession Discipline Skills Profile
The skills required of a Marketing Management professional are as follows:
- General Marketing Skills - required of all individuals in this
Marketing profession discipline
- IBM Internal Skills - required of all individuals in this Marketing
profession discipline
- Marketing Role Skills - for individuals assigned to one of the
Marketing roles (see "Marketing Professional Career Skills Profile" in
topic 2.1.10 for role skills)
_______________________________ ________________________________________
| | Profession Discipline Positions, with |
| | Associated Skill Levels |
| |________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| MARKETING MANAGEMENT SKILLS | Assoc | Assoc | | Mktg | Sr |
| | Mktg | Mktg | Mktg | Mgr | Mktg |
| | Mgr | Mgr | Mgr | (adv) | Mgr |
| | | (adv) | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| GENERAL MARKETING SKILLS |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Know & Apply Marketing | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Concepts & Methods | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know & Apply Mkt Intelligence | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Concepts & Methods | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand Customer Reqmts & | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Buying Behaviors | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know & Apply Market | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Segmentation | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Strategies | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Plans | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Programs | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Manage Marketing Mix Elements | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Strategies/Plans | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Distribution/End-User | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| Coverage Strategy | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Terms Strategy | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Perform Market Analysis | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Use Marketing Tools & Models | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Perform Marketplace Financial | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| Assessment | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Perform Marketplace Situation | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| Analysis | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Determine Customer/Market | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Needs | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Customer Satisfaction | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| & Loyalty Strategy | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Perform Market & Customer | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| Segmentation | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Market Segment | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Strategy | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Market Segment | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Business Plan | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Offerings/Solutions | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Strategy | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Offrgs/Solns | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| w/Competitive Advantage | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand Offering & | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Interface Design Issues | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand Offering/Solution | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| Profitability | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| IBM INTERNAL SKILLS |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Know & Apply IBM Brand | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Business Management System | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Explain IBM Business Strategy | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand the IBM Brand | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Strategy | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand/Anticipate/Respond | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| - Competitive Trends | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Articulate IBM | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Offerings/Technology | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| IBM Formal & Informal Network | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Work in Cross-Functional | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Teams | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand IBM Global | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Operations | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Creativity/Breakthru Thinking | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Interpersonal Communication | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Negotiation | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Problem Solving & Decision | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Making | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Apply Basic Financial | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Concepts | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Apply Project Management | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Techniques | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Self-Directed Learning | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Explain IBM & I/T Industry | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Trends/Directions | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know & Apply IBM Market | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Management Process | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know & Apply Integrated | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Product Development Proc | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know & Apply IBM Brand Naming | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Strategies | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Initiate Projects | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Manage Contracted Resource & | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Services | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Resource & Skill | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| Plans | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Leadership | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Foster Teamwork/Enable Teams | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Risk Awareness/Taking | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
2.2.8 Professional Development
Education roadmaps will be provided at a later date.
2.2.9 Marketing Management Position Descriptions
The following position descriptions describe the basic work of each of the
positions within the Marketing Professional Career. Formal descriptions
which may contain legally mandated language necessary for classifying
employees in a geography should be obtained through the approved on-line
job library, if available in the geography, or by contacting the
appropriate H.R. personnel within the geography.
Subtopics:
2.2.9.1 Position Title: Associate Marketing Manager
Position Summary and Responsibilities:
Assists with the planning and execution for a limited number of the
marketing mix elements (e.g., offering, terms, distribution,
support/skills, etc.) for non-complex assignments associated with meeting
brand unit and/or business unit objectives. Assigned to a brand unit
and/or business unit and works on plans and activities which are typically
defined by higher-level professionals and management in the department.
These activities are executed by understanding and applying
analytically-derived conclusions about the market, customers and/or
competitive postures, which were provided through research studies defined
by higher-level professionals and management in the marketing
organization. Assists with the execution of plans by understanding brand
unit and/or business unit policies and practices. May make
recommendations to more senior professionals and management in the
department on assigned activities. Understands the vision and mission of
the marketing management discipline. Interfaces on a limited basis with
the other marketing profession disciplines relative to assigned
activities.
Skills
- Environment:
Applies basic professional knowledge to some of marketing mix elements
that support daily business planning activities as well as specific
activities that support the brand unit and/or business unit mission
and objectives.
Demonstrates the skill proficiencies for this position.
- Communications/Negotiation:
Works with higher-level professionals, learning from them and
assisting them in carrying out assigned marketing activities.
Assists in the development of business plans as they apply to
assignments and negotiates with other marketing departments to obtain
informantion and data needed for the assignment or project.
- Problem Solving:
Recognizes problems, relative to assignments, when they arise and
resolves them in line with guidance from management or with existing
guidelines and procedures.
Uses professional skills to prepare alternatives to achieve marketing
goals and objectives for assigned projects.
Assists with the development and analysis of proposals for marketing
research for usability and resonableness.
Contributes to the development and implementation of new marketing
techniques and improvements to departmental processes.
Contribution and Leadership
- Works at a professional level and is reviewed as required for
developmental purposes.
- Sets priorities for own assignments and seeks advise from other
professionals from other Marketing Profession disciplines as needed.
- Understands the mission and vision of the marketing management
discipline.
- Is proficient in some of the marketing mix elements and may provide
some technical direction and assistance to less knowledgeable
department or team members.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Is held accountable for the quality, and timeliness of assignments.
- Provides input, related to assigned projects, for the brand unit
and/or business unit marketing plan.
- Advises management of all developments that affect assigned projects
and makes recommendations for resolving those issues.
- Assists in the the development of customer satisfaction and loyalty
plans that identify dissatisfiers and satisfiers and develops plans to
address those issues.
- Assists in the development, implementation and administration of all
financial activities related to assigned projects.
2.2.9.2 Position Title: Associate Marketing Manager (advanced)
Position Summary and Responsibilities:
Plans and executes a limited number of the marketing mix elements (e.g.,
offering, terms, distribution, support/skills, etc.) for non-complex
assignments associated with meeting brand unit and/or business unit
objectives. Assigned to a brand unit and/or business unit and works on
plans and activities which are typically defined by senior professionals
and management in the department. These plans and activities are executed
by understanding and applying analytically-derived conclusions about the
market, customers and/or competitive postures, which were provided through
research studies defined by senior professionals and management in the
marketing organization. Executes these plans by understanding brand unit
and/or business unit policies and practices and recognizes the need for
new policies and practices. Makes recommendations to more senior
professionals and management in the department on assigned activities and
related work as they affect the marketing management profession
discipline. Understands the vision and mission of the marketing management
discipline and other marketing profession disciplines. Interfaces on a
limited basis with the other marketing profession disciplines relative to
assigned activities.
Skills
- Environment:
Applies a professional knowledge to some of marketing mix elements
that support daily business planning activities as well as specific
activities that support the brand unit and/or business unit mission
and objectives.
Demonstrates the skill proficiencies for this position.
- Communications/Negotiation:
Works as a marketing management professional interfacing with other
members of the department during the performance of assignments.
Articulates the objectives of an assigned program or project as they
apply to the attainment of brand unit and/or business unit
objectives.
Participates in the development of business plans as they apply to
assignments and negotiates plan objectives by explaining the merits of
each recommendation.
- Problem Solving:
Analyzes the cause of issues and concerns for assigned projects and
formulates solutions by using non-traditional approaches.
Recognizes the need to develop new or revised marketing management
methods that support the objectives of the department.
Develops or analyzes proposals for marketing management research for
usability and reasonableness.
Reviews marketing management practices with the intention of improving
and/or simplifying them.
Contribution and Leadership
- Works on special assignments that relate to the successful planning
and execution of some of the marketing mix elements associated with
brand unit and/or business unit objectives.
- Sets own priorities when managing assignments and involves other
professionals from other Marketing Profession disciplines as needed.
- Understands the mission and vision of the marketing management
discipline and other related functions and incorporates them into
assigned projects.
- Is proficient in some of the marketing mix elements and is able to
provide advice and counsel to other professionals within the
department.
- May discharge the basic management responsibilities common to all IBM
managers.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Is held accountable for the quality, and timeliness of assignments.
- Participates in setting the direction of the brand unit and/or
business unit marketing plan.
- Advises management of all developments that affect assigned projects
and resolves the issues that have an effect on the marketing mix
elements being implemented.
- Develops customer satisfaction and loyalty plans that identify
dissatisfiers and satisfiers and develops plans to address those
issues.
- Participates in the development, implementation and administration of
all financial activities related to assigned projects. Ensures all
financial objectives are met.
2.2.9.3 Position Title: Marketing Manager
Position Summary and Responsibilities:
Plans and executes all the marketing mix elements (i.e., strategy,
offering, terms, distribution, support/skills, fulfillment and image) for
several moderately complex projects/assignments associated with meeting
brand unit and/or business unit objectives. Assigned to a brand unit
and/or business unit and ensures strategies, plans and activities are in
place for all assignments. These strategies, plans and activities are
developed and executed by taking analytically-derived conclusions about
the market, customers and/or competitive postures, which were obtained
through senior professionals and management in the marketing organization,
and applying them to assigned activities. Develops and executes these
plans by understanding and interpreting brand unit and/or business unit
policies and practices. Makes recommendations to more senior
professionals and management in the department on assigned activities and
related work as they affect the entire marketing organization.
Understands the vision and mission of all of the Marketing Profession
disciplines and their related specialty areas. Interfaces with all
functions within the brand unit and/or business unit relative to assigned
activities.
Skills
- Environment:
Applies advanced professional knowledge to all of the marketing mix
elements to ensure there is consistency in their usage in advanced
business planning. These plans support the growth and profitability
of the brand unit and/or business unit.
Demonstrates the skill proficiencies for this position.
- Communications/Negotiation:
Advises other professionals within the market management discipline on
day-to-day activities that affect the implementation of the brand unit
and/or business unit strategies.
Assigned to a number of projects and negotiates all aspects of the
projects with management and members of other marketing disciplines
and functions.
- Problem Solving:
Analyzes the objectives of complex business and marketing problems,
programs and issues which are related to all of the marketing mix
elements. Uses sound judgment in recommending solutions.
Identifies issues as they relate to the market management discipline
and recommends new procedures or practices as they are related to
those issues.
Contribution and Leadership
- Leads implementation teams with little direction and reports the
results to the senior management team in the brand unit and/or
business unit.
- Works with all of the marketing mix elements, defines their objectives
and includes them in the overall business plan for the brand unit
and/or business unit.
- Provides technical or operational advice and counsel to other
less-experienced professionals in the department. Contributes to the
overall mission of the department or function.
- May discharge the basic management responsibilities common to all IBM
managers.
Impact of Business/Scope
- Accountable for the results of a number of marketing projects,
analyzes them with the intention of improving their performance.
- Participates in marketing management planning sessions.
- The results of the assigned programs are subject to customer
satisfaction and loyalty measurements and, based on those
measurements, develops programs to address those issues.
- Ensures that the development, implementation and administration of all
financial activities related to assigned programs are met.
2.2.9.4 Position Title: Marketing Manager (advanced)
Position Summary and Responsibilities:
Directs, plans and executes all of the marketing mix elements (i.e.,
strategy offerings, terms, distribution, support, fulfillment and image)
for multiple complex projects/assignments associated with meeting a
geography or major brand unit and/or business unit objectives. Assigned
to a major geography or brand unit and/or business unit and ensures
strategies are based on analytically-derived conclusions about the market,
customers and/or competitive postures. Develops requirements for market
research projects and manages internal and external resources in the
execution, analysis and proper use of research results. Ensures
strategies are clearly-defined and properly executed and meet business
objectives for the geography or major brand unit and/or business unit.
Develops recommendations for policies and practices for a geography or
major brand unit and/or business unit used as guidance to sales, services
and channel units management teams regarding assigned activities.
Provides advice and counsel to management and lower-level professionals
within the geography or brand unit and/or business unit. Understands the
mission/vision of the geography or major brand unit and/or business unit.
Interfaces with/provides direction to all functions in the geography or
major brand unit and and/or business unit.
Skills
- Environment:
Applies professional knowledge and expertise to all of the marketing
mix elements to ensure there is consistency in their usage in advanced
integrated business and marketing plans. Understands organizational
resources, priorities, needs and plans. Can speak with authority on
all elements.
Demonstrates the skill proficiency levels for this position.
- Communications/Negotiations:
Gives guidance to other professionals on designing and developing
marketing-related activities that will implement a geography or major
brand unit and/or business unit strategy.
Negotiates at the executive level to obtain agreement concerning the
delivery of all of the marketing mix elements as well as for resource
requirements.
- Problem Solving:
Analyzes the requirements of a geography or major brand unit and/or
business unit business strategy that are new and complex in nature,
and anticipates any potential exposures or trends.
Assesses opportunities as they apply to all of the marketing mix
elements and determines their impact on assigned marketing programs.
Contribution/Leadership
- Analyzes the external and internal competitive situations for their
impact on the marketing elements and recommends to executive and
senior management strategies, plans that support the geography or
major brand unit and/or business unit objectives.
- Has considerable latitude to define and decide which courses of action
should be taken when delivering all of the marketing mix elements.
- Understands the long-term vision and mission of the geography or major
brand unit and/or business unit and how they fit into their long-term
business objectives.
- Influences executive management when dealing with complex issues
concerning business plans.
- Acknowledged as an expert in all aspects of marketing management by
all professionals within the assigned geography or major brand unit
and/or business unit.
- Has the responsibility for leading multi-functional teams within a
geography or major brand unit and/or business unit in order to address
business plan concerns.
- May discharge the basic management responsibilities common to all IBM
managers.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Is held accountable for the results of projects or programs that
impact the marketing mix elements in a geography or major brand unit
and/or business unit and ensures the success of these elements.
- All assigned projects and programs are subject to established business
measurements and use quality principles in the development of all
assignments.
- Purchases outside services and materials to meet the requirements and
specifications of the project. Has budgetary responsibility.
- Influences marketing management planning sessions.
2.2.9.5 Position Title: Senior Marketing Manager
Position Summary and Responsibilities:
Lead professional position for the Marketing Management function, directs
and plans the execution of all marketing mix elements (i.e., strategy,
offerings, terms, distribution, support, fulfillment and image) for
multiple, very complex and strategically important projects/assignments
associated with meeting corporate, geography or major brand unit and/or
business unit objectives. Is relied on as the expert within the marketing
management profession discipline regarding all aspects of marketing.
Assigned to an international or corporate marketing function or to a
geography or major brand unit and/or business unit. Articulates the
long-term vision of the marketing mix elements and aligns them with IBM's
long-term strategies and strategic initiatives and leads strategy
development. Develops new concepts for market research studies. Creates
strategies based on analytically-derived conclusions about the market,
customers and/or competitive postures. Ensures strategies are
clearly-defined and meet overall business objectives on a international,
corporate, geography, brand unit and/or business unit level. Exhibits
worldwide marketing leadership by working with executive management in the
development of corporate policies and practices. Provides advice and
counsel to management on the intent and strategic direction of corporate
policies and practices. Assists executive management in the development of
the worldwide mission and vision for the marketing profession. Interfaces
with all levels of management in the function worldwide on all
marketing-related issues.
Skills
- Environment:
Applies professional knowledge and in-depth expertise of all of the
marketing mix elements to ensure there is consistency in their usage
in unique and innovative integrated business strategies and plans. Has
an in-depth awareness and understanding of organizational resources,
priorities and needs. On a worldwide basis, guides these plans toward
leading-edge solutions.
Demonstrates the skill proficiency levels for this position.
- Communications/Negotiation:
Takes a leadership role by using the experience of senior
professionals in order to design and develop marketing-related
activities that will implement the geography or major brand unit
and/or business unit strategies on a world-wide basis.
Leverages all marketing management resources to deliver all the
marketing mix elements. Participates in complex negotiations with
executive management to obtain worldwide agreement for the overall
implementation of marketing programs.
- Problem Solving:
Anticipates the requirements of the marketing management discipline
and designs marketing strategies that are innovative and contributes
to the formulation of marketing policies.
With executive review, acts as the leading interface responsible for
the delivery of all marketing mix elements and marketing-related
activities.
Contribution and Leadership
- Understands all of the marketing mix elements and can articulate the
worldwide vision of these elements and how they fit into the long-term
strategies of IBM's business strategies and plans.
- Acknowledged as an expert in all aspects of marketing management by
all professionals within this discipline on a worldwide basis.
- Has the responsibility for taking the lead professional role for the
marketing management function and leads international, corporate,
geography or major brand unit and/or business unit teams.
- May discharge the basic management responsibilities common to all IBM
managers.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Develops plans and programs for specific complex to very complex
offerings/solutions and executes chosen strategies for corporate,
geography or major brand unit and/or business unit on a world-wide
basis.
- With executive review, develops and implements strategies for new or
improved complex to very complex offerings/solutions with the
intention of expanding sales, gaining market share and increasing
IBM's competitive advantage.
- Integrates the marketing mix elements into cohesive business plans
which can be taken to market to win, while appropriately using
resources and budgets.
- Participates in corporate-wide policy and program planning sessions.
- Commits financial resources and coordinates human resources which
significantly impact budgets and other activities.
- Develops plans based on customer satisfaction and loyalty survey
results and sets measurement objectives to address all concerns.
2.3 Chapter 6. Market Intelligence Profession Discipline
Subtopics:
2.3.1 Market Intelligence Profession Discipline Overview
Market Intelligence is one of six profession disciplines within the
Marketing Professional Career (see "Professional Career Structure" in
topic 2.1.2) and is responsible for critical components of the marketing
mix of elements.
Market Intelligence is concerned with providing relevant market
information, derived from research, for the professional marketing team
specifically, but also to all corporate managers involved in both short-
and long-term planning. Essential elements in this information are the
particular types of data critical to the planning process. These include
elements about customers/clients, markets, competitors and the business
environment.
The primary responsibility of Market Intelligence is to minimize risk in
the making of business decisions. This is accomplished through thorough
analysis of relevant data and the formulation of comprehensive meaningful
action scenarios. Market Intelligence is an organized way of finding
objective answers to questions every business must answer to succeed.
They include:
- Who are the customers or potential customers?
- What kind of people are they?
- Can and will they buy?
- Are the kinds of goods and services they want being offered by my
business?
- Are my prices consistent with what buyers view as the products' value?
- Are promotional programs working?
- What do customers think of my business?
- How does my business compare with that of my competitors?
Market Intelligence learns about markets by gathering facts in an orderly
and objective manner and by determining what customers want to buy, not
just what a business wants to sell them. This research focuses and
organizes marketing information. It ensures that such information is
timely and provides what is needed to:
- Reduce business risks.
- Identify trends in the current market.
- Identify and confirm sales opportunities.
- Gather facts about selected markets to ensure better decision-making.
- Assist in setting up action plans.
Investment in Market Intelligence is increasing because it will accomplish
the following:
- Reducing chance in decision making by providing data needed to
evaluate all options.
- Enabling managers to forecast trends more quickly and accurately.
- Identifying and validating business opportunities.
- Revealing weaknesses in the competition.
- Justifying assumptions upon which marketing strategies are formulated.
- Aiding in formulating the elements of the marketing mix, such as
product, price, promotion, channel, etc.
Skilled researchers can apply principles of sample size, sample design,
and other disciplines to their tasks. These professionals may be
specialized by skill, by industry, or by type of project.
Common activities in this profession discipline are:
- Determination of market characteristics
- Measurements of market potentials
- Market participation vs market-share analysis
- Sales analysis
- Studies of business trends
- Competitive product studies
- Short-range forecasting
- Long-range forecasting (one year or more)
- Pricing studies
- Product acceptance and potential
Three important functions of Market Intelligence are to evaluate and
recommend market opportunities; examine the offerings and identify the
best target markets; decide on the best competitive position for the
organization within the target as well as the best mode of entry and
timing.
2.3.2 Profession Discipline Structure
The Marketing Professional Career uses three titles for the five
professional positions. The prefix "Associate" is used for the lowest of
these positions. No prefix is used for the middle two positions and the
prefix "Senior" is used for the highest position.
The following positions are defined within the Market Intelligence
profession discipline:
- Associate Market Researcher
- Associate Market Researcher (advanced)
- Market Researcher
- Market Researcher (advanced)
- Senior Market Researcher
The Market Intelligence profession discipline is comprised of five
specialties as follows:
- Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty Research -- This specialty is
concerned with the acquisition, codification, analysis, and
presentation of marketplace information relative to IBM's and
competitors' relationships to customers and business partners. This
research helps drive decisions about IBM's offerings to the
marketplace, relative to its key internal and external competitors.
- Marketing Communications Research -- These individuals are concerned
with marketplace information relating to IBM's communications about
the Company and its offerings and solutions. They consult with
others, including management, in advertising, collateral/sales
promotion, business shows, and related activities on the development
and assessment of marketing communications directed to both internal
and external audiences. They also design and implement various
research studies.
- New Offerings/Solutions Research -- The New Offerings/Solutions
Researcher validates customer requirements from various market
segments for all of IBM's offerings/solutions. Their research focuses
on both current and future offerings to the marketplace. They
determine issues to be researched, establish requisite methodologies
for study, assess how customers get work done with both IBM and
competitive offerings, and provide market intelligence before an
offering is included in the business plan. Keys to success in this
specialty include competencies ranging from consulting and problem
identification through research planning and design, sampling, data
collection and analysis, to overall management of the research
process.
- Competitive Analysis Research -- These professionals are concerned
with current and future IBM and competitors' offerings and solutions
in the marketplace. They work closely with brand unit and/or business
unit management in assessing offerings to be made in a competitive
environment. They are responsible for gaining acceptance of new
technologies by marketplace targets, and assessments of how customers
do and get work done with IBM and competitive offerings/solutions.
- Industry/Marketing Analysis Research -- The focus of activity in this
specialty is on marketplace information relative to IBM and
competitive offerings within each of IBM's key market segments. These
individuals forecast the potential for IBM growth within the segments
and they profile competitors and their capabilities. They determine
the problems and issues to be researched, and provide secondary
research of either internal databases or external sources.
Market Intelligence professionals are expected to demonstrate expertise in
at least one specialty depending on the size and scope of the
organization, and on assigned responsibilities. In addition, individuals
assigned to one of the Marketing roles will add to their skills profile
the skills template for that role (see "Marketing Professional Career
Skills Profile" in topic 2.1.10, for role skills)
2.3.3 Characteristics of the Profession Discipline
Market Intelligence professionals have the following characteristics:
- Able to gather information and provide analysis to all levels of
management that identifies business opportunities and anticipates
business trends.
- Provide assistance to minimize risk in decisions about IBM's offerings
to the best target marketplace.
- Help determine the optimum timing and entry into a target market and
the best competitive position within that market.
- Consult with marketing and product management on the position,
features, and functions of IBM and competitive offerings.
- Design or identify appropriate primary or secondary research
activities which address tactical or strategic business problems.
- Develop research protocols for use in qualitative or quantitative
research; conduct univariate and multivariate analysis planning
activities and disseminate the research findings.
- Have strong oral and written communication skills.
- Can manage contracted resources and services.
2.3.4 Potential Candidates
Market Intelligence professionals may be sourced from current IBM
employees who have the basic skills and qualifications. They are
concerned with incisive, relevant marketplace information captured through
planned short- and long-term processes that support the management
systems. Employees in the Market Intelligence profession discipline may
also be interested in pursuing careers as consultants and strategists and
in market segment management, database marketing, and related fields.
Market Intelligence professionals may also be sourced from professional
hires who have the combination of training in research and planning.
Figure 6-1 illustrates the the possibilities for movement to and from the
Market Intelligence Profession Discipline.
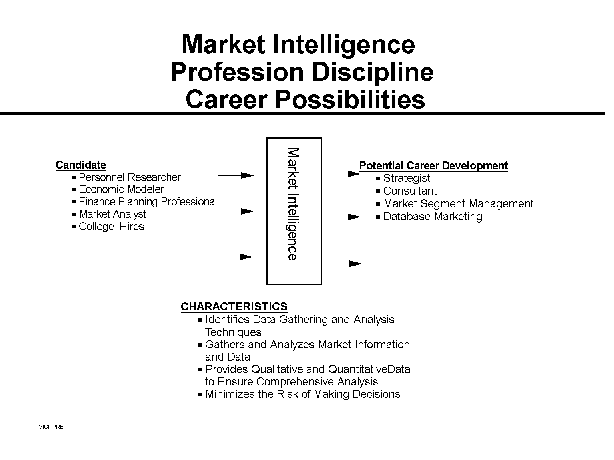
Figure 6-1. Market Intelligence Profession Discipline Career
Possibilities
2.3.5 Career Growth
Market Intelligence professionals may be assigned positions from Associate
Market Researcher through Senior Market Researcher in any of the five
specialties. The difference between the ascending levels is a function of
increasing skill, capability, experience, and responsibility and are
reflected in the extent of an individual's leadership, contributions, and
impact on the business.
Growth in this discipline can be achieved through the acquisition of
skills and experiences that enable an individual to work in multiple
specialty areas. Professionals can also rise to levels comparable to
executive management and career path movement can occur in accordance with
planned steps into and through other professions.
2.3.6 Performance Elements
Market Intelligence professionals are measured on the the execution of
projects within established time and budget parameters. They are also
responsible for providing market intelligence information to management to
enable them to develop business solutions and make offering decisions. A
primary performance element is the reduction of the uncertainty in the
decision-making process. Market Intelligence professionals are key
members of the Marketing Professional Career and provide a strong
influence on the short- and long-term business direction of the brand unit
and/or business unit.
2.3.7 Market Intelligence Profession Discipline Skills Profile
The skills required of a Market Intelligence professional are as follows:
- General Marketing Skills - required of all individuals in this
Marketing profession discipline
- IBM Internal Skills - required of all individuals in this Marketing
profession discipline
- Market Intelligence Discipline Skills
- Market Intelligence Discipline Specialty Skills
- Marketing Role Skills - for individuals assigned to one of the
Marketing roles (see "Marketing Professional Career Skills Profile" in
topic 2.1.10, for role skills)
_______________________________ ________________________________________
| | Profession Discipline Positions, with |
| | Associated Skill Levels |
| |________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| MARKET INTELLIGENCE SKILLS | Assoc | Assoc | | Mkt | Senior|
| | Mkt | Mkt | Mkt | Resrch| Mkt |
| | Resrch | Resrch| Resrch| (adv) | Resrch|
| | | (adv) | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| GENERAL MARKETING SKILLS |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Know & Apply Marketing | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Concepts & Methods | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know & Apply Mkt Intelligence | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| Concepts & Method | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand Customer Reqmts & | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| Buying Behaviors | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know & Apply Market | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Segmentation | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Strategies | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Plans | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Programs | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Use Market Intelligence | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| Consulting Techniques | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Select Market Intelligence | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Research Methods | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Perform Primary Research | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Perform Secondary Research | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Communicate Market | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Intelligence Findings | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Use Market Intelligence Data | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| IBM INTERNAL SKILLS |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Know & Apply IBM Brand | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Business Management System | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Explain IBM Business Strategy | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand the IBM Brand | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Strategy | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand/Anticipate/Respond | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| - Competitive Trends | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Articulate IBM | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Offerings/Technologies | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| IBM Formal & Informal Network | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Work in Cross-Functional | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Teams | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand IBM Global | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| Operations | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Creativity/Breathru Thinking | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Interpersonal Communications | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Negotiation | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Problem Solving & Decision | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Making | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Apply Basic Financial | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| Concepts | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Apply Project Management | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| Techniques | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Self-Directed Learning | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Manage Contracted Resource & | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Services | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| CUSTOMER SATISFACTION AND LOYALTY RESEARCH SPECIALTY SKILLS |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Develop Customer Satisfaction | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| & Loyalty Strategy | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Evaluate Total Customer | 1 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Satisfaction | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Perform Customer Satisfaction | 1 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Analysis | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Measure MDQ/TQM Performance | 1 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| MARKETING COMMUNICATIONS RESEARCH SPECIALTY SKILLS |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Understand Creative | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| Development Concepts | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand Market Segment | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Business Plan | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know & Apply Media Planning | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| Development | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand Attitude | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Measurement & Attitude Change | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know & Apply Advertising | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Measurement Techniques | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| NEW OFFERINGS/SOLUTIONS RESEARCH SPECIALTY SKILLS |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Manage Marketing Mix Elements | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| Strategies/Plans | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Perform Market Segmentation | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Offrgs/Solns | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| w/Competitive Advantage | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Perform Marketplace Situation | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Analysis | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| COMPETITIVE ANALYSIS RESEARCH SPECIALTY SKILLS |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Know Specific Competitors | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Create Competitor Profiles | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 5 |
| from Incomplete Info | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Analyze Relevant Industry | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Legislation | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Track Emerging Technologies | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| INDUSTRY/MARKET RESEARCH SPECIALTY SKILLS |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Forecast Emerging Industry | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Trends | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Analyze Relevant Industry | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Legislation | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Track Emerging Technologies | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
2.3.8 Professional Development
Education roadmaps will be provided at a later date.
2.3.9 Market Intelligence Position Descriptions
The following position descriptions describe the basic work of each of the
positions within the Marketing Professional Career. Formal descriptions
which may contain legally mandated language necessary for classifying
employees in a geography should be obtained through the approved on-line
job library, if available in the geography, or by contacting the
appropriate H.R. personnel within the geography.
Subtopics:
2.3.9.1 Position Title: Associate Market Researcher
Position Summary and Responsibilities:
Assists higher-level professionals and management with the capture of
incisive, relevant marketplace information understanding the planned
processes that support management systems for offerings/solutions within a
brand unit and/or business unit. Participates in less complex aspects of
the design of market research studies to address tactical business
problems. With assistance, researches customer requirements, and
recommends changes that will improve the competitive position of a
specific offering or solution within the brand unit and/or business unit.
Might interact on a limited basis, with brand unit and/or business unit
professionals/management on the positioning of IBM's offerings/solutions.
Skills
- Environment:
Applies basic professional knowledge to ensure there is consistency in
the use of market research approaches as they apply to an
offer/solution.
Demonstrates the skill proficiency levels for this position.
- Communications/Negotiation:
Works with higher-level research professionals, learning from them and
assisting them in carrying out assigned research activities.
Can articulate lesscomplex design methods and instruments for studies
as they apply to the attainment of the brand unit and/or business unit
objectives.
Assists in the development of study requirements as they apply to
assignments and negotiates the objectives within a defined goal.
- Problem Solving:
Analyzes the cause of problems associated with studies and formulates
solutions.
Develops and analyzes proposals for non-complex market research
requests.
Understands and applies research guidelines and methods that support
the objectives of the department.
Contributions and Leadership
- Works on non-complex aspects of market research studies as requested
by management.
- Sets priorities for own assignments and seeks advice from other
professionals as needed, in order to produce studies that provide
value-add to the assignment.
- Understands the Market Intelligence department mission and vision and
applies them to all assigned market research studies.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Assists in the development of programs for the Market Intelligence
department's mission.
- Informs management of all developments that affect the assigned
project or proposal. With assistance, resolves all issues relative to
assignments on proposed offerings/solutions.
- Assists in the development, implementation and administration of all
financial activities related to assigned studies.
2.3.9.2 Position Title: Associate Market Researcher (advanced)
Position Summary and Responsibilities:
Captures incisive, relevant marketplace information through planned
processes that support management systems for offerings/solutions within a
brand unit and/or business unit. Participates in the design of market
research studies to address tactical business problems. Researches
customer requirements, and recommends changes that will improve the
competitive position of a specific offering/solution within the brand unit
and/or business unit. Interacts with brand unit and/or business unit
professionals/management on the positioning of IBM's offerings/solutions.
Develops consulting skills through work assignments.
Skills
- Environment:
Applies professional knowledge to ensure there is consistency in the
use of market research approaches as they apply to an offer/solution.
Demonstrates the skill proficiency levels for this position.
- Communications/Negotiation:
Works independently as a professional researcher by interfacing with
brand unit and/or business unit teams during the performance of an
assignment.
Capable of articulating the study's design, methods and instruments as
attainmentpply to the
of the brand unit and/or business unit objectives.
Participates in the development of study requirements as they apply to
assignments and negotiates the objectives within a defined goal.
- Problem Solving:
Analyzes the cause of a study's problems and formulates solutions.
Recognizes the need to develop market research methods as applicable
to research requests.
Develops and analyzes proposals for market research requests.
Reviews and challenges research guidelines with the intention of
improving them.
Contributions and Leadership
- Works on a market research study as requested by management.
- Sets own priorities in managing an assignment and ensures the
involvement of the appropriate professionals in order to produce
studies that provide value-add to the assignment.
- Understands the Market Intelligence department mission and vision and
applies them to all assigned market research studies.
- Employs project management techniques to ensure that studies are
coordinated and lead to results based of the initial objectives.
- May discharge the basic management responsibilities common to all IBM
Managers.
Impact on Business Scope
- Participates in the development of programs for the Market
Intelligence department's mission.
- Advises management of all developments that affect the assigned
project or proposal. Resolves all issues that have an effect on a
proposed offering/solution.
- Participates in the development, implementation and administration of
all financial activities related to assigned studies. Ensures
financial objectives are met.
2.3.9.3 Position Title: Market Researcher
Position Summary and Responsibilities:
Captures incisive, relevant marketplace information for a number of
offerings/solutions within a brand unit and/or business unit. Improves
the planned short and long-term processes that capture this information.
Selects and designs market research methods to address tactical business
problems. Leads the analysis of competitors, industries, markets and
customer requirements for a brand unit and/or business unit. Identifies
issues to be researched and consults with brand unit and/or business unit
management on the positioning of IBM competitive offerings/solutions.
Based on research results, makes recommendations to management to optimize
the success of offerings/solutions, including selection of market
segments.
Skills
- Environment:
Applies advanced professional knowledge to ensure there is consistency
in the use of market research approaches as they apply to a number of
offerings/solutions.
Demonstrates the skill proficiency levels for this position.
- Communications/Negotiation:
Selects or designs the appropriate market research method (primary or
secondary, quantitative or qualitative techniques) that addresses
business problems and negotiates to defined goals with a business
unit's senior management team.
Advises other professionals within the market intelligence discipline
in day to day activities that implement a business unit's strategy.
- Problem Solving:
Applies creativity in conducting research activities in support of
complex offerings/solutions.
Based on the customer's needs, develops new procedures or processes to
assist in the achievement of the offerings/solutions' business goals.
Identifies complex business problems by using advanced market research
methods aimed at improving an offerings/solutions competitive
position.
Contribution/Leadership
- Conducts a number of projects and studies of a complex nature as
requested by brand unit and/or business unit management teams.
- Advises management on all developments that affect the market research
study's short-and long-term objectives, reviews recommendations, and
resolves all issues.
- Understands the Marketing Intelligence department's mission and vision
and applies them to all research assignments.
- Influences other professionals within the brand unit and/or business
unit during the performance of research studies.
- Provides technical guidance to less-experienced market researchers who
are involved in the implementation of research assignments.
- May discharge the basic management responsibilities common to all IBM
Managers.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Is held accountable for the research results and analyzes them in
order to suggest new and/or enhanced methods of study design.
- Participates on a regular basis in the development of the direction of
the market research studies that may affect brand unit and/or business
unit.
- The results of all studies performed are subject to established
business measurements.
- Ensures that the development, implementation and administration of all
financial activities related to complex studies are met.
2.3.9.4 Position Title: Market Researcher (advanced)
Position Summary and Responsibilities:
Captures incisive, relevant marketplace information for a major business
unit or geography. Designs long-term processes that improve the capture
of relevant market information according to global market intelligence
policies. Acknowledged as an expert in market intelligence research
techniques. Oversees the analysis of competitors, industries, markets,
and customer requirements for a major business unit or geography. Selects
and designs advanced research methods to address long range tactical and
strategic business problems. Provides advice and counsel on market
intelligence to geographies, business partners, joint ventures and
subsidiaries. Identifies highly complex, emerging issues to be researched
and consults with executive management in the geographies on the
positioning of major IBM competitive offerings/solutions. Based on
research results, negotiates with executive management to optimize the
success offerings/solutions within a major business unit or geography,
including the selection of market segments.
Skills
- Environment:
Applies expert knowledge to ensure there is consistency in the use of
advanced market research approaches as they apply to
offerings/solutions for a major business unit or geography.
Demonstrates the skill proficiency levels for this position.
- Communications/Negotiations:
Establishes the priority for a number of advanced and unique research
projects and advises senior management on all developments that affect
short- and long-range business objectives for a geography or major
business unit.
Leverages available research resources and negotiates goals and
approaches to optimize IBM's competitive advantage. Negotiations
result in agreements of all functions involved.
- Problem Solving:
Anticipates future trends and potential issues associated with the
gathering and analysis of Market Intelligence, assesses their impact
and develops appropriate actions.
Identifies the unique and complex situations for major research
projects and programs and provides appropriate solutions.
Uses advanced research techniques to provide solutions to complex
design problems in order to improve IBM's competitive position.
Contribution/Leadership
- Oversees a number of special research projects and programs of a
complex or unique nature at a major business unit or geography.
- Provides guidance in market research methods and instruments and acts
as a mentor to less-experienced professionals who are involved in the
planning and implementation of research programs. Provides advice
concerning staffing and organization.
- Has considerable latitude in directing the activities of research
processes by employing effective management techniques that ensure
that appropriate design resources are deployed.
- Participates in the establishment of the mission and vision for the
Market Intelligence discipline.
- May discharge the basic management responsibilities common to all IBM
managers.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Defines major research projects by conducting research activities and
is held accountable for research results.
- Keeps abreast of changes and improvements in the areas of product
design and incorporates them into research programs and projects.
- All research projects and results are subject to established business
measurements geography or major business unit.
- Ensures that the development, implementation and administration of all
financial activities related to design programs are met. Attainment
of financial targets has a direct impact on financial results of the
Market Intelligence discipline.
2.3.9.5 Position Title: Senior Market Researcher
Position Summary and Responsibilities:
Develops market intelligence strategies at the geographic, international
or corporate level. Relied on as the expert on market research techniques
that capture incisive, and relevant marketplace information for a variety
of new and leading edge products and solutions. Develops future market
research strategies, requirements and objectives for the analysis of
competitors, industries and markets. Contributes to policy formulation
which improves the capture of market information through long-term
processes and ensures these processes are implemented through all levels
of the Market Intelligence function. Conducts complex negotiations with
executive management to ensure market research results drive decisions
about IBM's strategic offering/solutions in the marketplace. Through
significant expertise and leadership supports IBM corporate marketing by
understanding and communicating corporate objectives and by continually
improving the effectiveness of research methods and techniques.
Skills
- Environment:
Takes a lead role to ensure there is consistency in research methods
and techniques in all approaches used on a worldwide basis.
Demonstrates the skill proficiency levels for this position.
- Communications/Negotiation:
Takes a leadership role at the geography, international or corporate
level to communicate the latest research techniques to be used in
research projects.
Leverages all available resources and is involved in the most complex
negotiations that have lasting agreements and commitments that have
worldwide implications..
Advises, on a worldwide basis, executive management of all
developments that affect the Market Intelligence discipline's
long-term design strategies.
- Problem Solving:
Understands the changing and improving environment within the Market
Intelligence discipline and incorporates them into the long-term
strategies.
Assesses business opportunities as they apply to market intelligence
projects and determines their impact on future offerings.
Contribution/Leadership
- Uses professional experience in developing the overall mission and
vision of the Market Intelligence discipline. Actively participates
in functional planning.
- Recognized as the expert in the Market Intelligence field by both IBM
professionals and outside organizations.
- Directs the activities of complex research assignments by employing
effective management techniques to ensure appropriate resources are
deployed.
- Leads major research strategy sessions made up of senior professionals
that evaluate complex offerings for competitive advantages and
opportunities.
- May discharge the basic management responsibilities common to all IBM
managers.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Has high-impact on long-term Market Intelligence strategies and is
held accountable for the business performance of those strategies.
- Develops return-on-investment evaluations of offerings/solutions and
presents the recommendations for executive review at the geography,
international or corporate level.
- Takes a lead role in the formulation of research policies, practices,
and strategies.
- Commits financial resources and coordinates human resources which have
a significant impact on budgets and other activities. Responsible for
the attainment of all project costs, schedules and functional
requirements.
2.3.10 Market Intelligence Specialty Descriptions
Subtopics:
2.3.10.1 Specialty Title: Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty Research
Specialty Summary:
The customer satisfaction and loyalty research specialty is concerned with
the acquisition, codification, analysis and presentation of marketplace
information relative to IBM's and competitor's relationships with
customers and business partners. This research helps drive decisions
about IBM's offerings/solutions to the marketplace relative to its key
internal and external competitors. It is also concerned with identifying
key customer satisfaction and loyalty dimensions which optimize IBM's
position relative to competitors in the marketplace. The function tracks
the progress of IBM's efforts in increasing satisfaction and loyalty with
its customers. The research helps to prepare go-to-market strategies and
impacts future IBM revenue. Key to the success of this position is a broad
set of competencies ranging from consulting and problem identification
through research planning, research design, sampling, data collection,
measurement instrument design, data collection and analysis, communication
of results and overall management of the research process.
Responsibilities:
- Consults with brand unit and/or business unit management on the
development and assessment of customer satisfaction and loyalty
relative to both internal and external customers and business
partners.
- Determines the problems or issues that need to be researched and
establishes the requisite methodologies to be implemented for a
particular study.
- Evaluates customer research design involving secondary research of
either internal IBM databases or external sources.
- Designs and implements tracking studies to assesses impressions of IBM
and competitive offerings/solutions, analysis of customer and business
partner relationships, marketing processes and perceptions of IBM's
value-add.
2.3.10.2 Specialty Title: Marketing Communications Research
Specialty Summary:
Marketing communications research is concerned with the acquisition,
codification, analysis and presentation of marketplace information
relative to IBM's communications about the company and its
offerings/solutions. This research helps drive decisions about IBM's
marketing communications offerings/solutions to the marketplaces relative
to its key internal and external competitors. Success depends on
competencies ranging from consulting and problem identification through
research planning, research design, sampling, data collection, measurement
instrument design, data collection analysis, communication of results and
overall management of the research process.
Responsibilities:
- Consults with advertising, collateral/sales promotion, business shows,
etc., brand unit and/or business unit management on the development
and assessment of marketing communications activities directed at
internal and external audiences.
- Determines the problems or issues that need to be researched and
establishes the requisite methods to be implemented for a particular
study.
- Implements custom research designs of which many elements may involve
secondary research of either internal IBM databases or external
sources.
- Designs and implements tracking studies to assess impressions of the
company and offerings/solutions among key constituencies.
- Conducts studies that involve concept tests, collateral/advertising,
sales promotions, internal communications, Internet programs,
executive communications and public relations.
2.3.10.3 Specialty Title: New Offering/Solution Research
Specialty Summary:
New offering research identifies and validates customer requirements from
various market segments for all of IBM's offerings/solutions. In addition,
offering research is concerned with the acquisition, codification,
analysis and presentation of marketplace information relative to IBM's
current and future offerings/solutions into the marketplace. This research
helps shape and drive decisions about IBM's offerings/solutions relative
to its key internal and external competitors. Success depends on
competencies ranging from consulting and problem identification through
research planning, research design, sampling, data collection, measurement
instrument design, data collection and analysis, communication of results
and overall management of the research process.
Responsibilities:
- Consults with brand unit and/or business unit management on the
development and assessment of offerings/solutions directed to internal
and external audiences.
- Determines the problems of issues that need to be researched and
establishes the requisite methods to be implemented for a particular
study.
- Conducts studies with target audiences to determine required features
and ideal positions for new offerings/solutions.
- Analyzes the competitor's offerings.
- Provides market intelligence before an offering/solution is included
in the brand unit and/or business unit plan.
2.3.10.4 Specialty Title: Competitive Analysis Research
Specialty Summary:
Competitive analysis research is concerned with the acquisition,
codification, analysis and presentation of marketplace information
relative to IBM's and a competitor's current and future
offerings/solutions in the marketplace. This research helps shape and
drive decisions about IBM's offerings/solutions relative to its key
internal and external competitors. Success depends on competencies ranging
from consulting and problem identification through research planing,
research design, sampling, data collection, measurement instrument design,
data collection and analysis, communication of results and overall
management of the research process.
Responsibilities:
- Consults with brand unit and/or business unit management on the
development and assessment of offerings/solutions directed to internal
and external audiences.
- Determines the problems of issues that need to be researched and
establishes the requisite methods to be implemented for a particular
study.
- Conducts studies with target audiences to determine required features
and ideal positions for new offerings/solutions.
- Analyzes the competitor's offerings.
- Provides market intelligence before an offering/solution is included
in the brand unit and/or business unit plan.
2.3.10.5 Specialty Title: Industry/Market Research
Specialty Summary:
Industry/market analysis research is concerned with the data sources,
acquisition, codification, analysis and presentation of marketplace
information relative to IBM's and competitor's current and future
offerings/solutions within each of IBM's key market segments. This
function helps define customer sets, forecasts potential for segment
growth, and the identifies key internal and external customer sets and
competitors and their strategy within each segment. This research helps
shape and drive decisions about IBM's offerings/solutions and coverage
plans relative to its key internal and external competitors. Key to the
success of this position depends on competencies ranging from consulting
and problem identification, research design, sampling, data collection and
analysis, communication of results, overall management of the research
process, Market Management process, understanding segment business plans,
and solution marketing plans.
Responsibilities:
- Contributes to the segmentation of customer sets and solution areas of
an industry opportunity.
- Analyzes economic and I/T trends driving the target industry/segment.
- Uses available data to assess IBM's position in the industry (e.g.,
market share, image, etc.).
- Tracks technology that may impact the industry, customer set or brand.
- Monitors relevant regulations and legislation.
- Supports the development of segment business plans and solution
marketing plans.
- May lead the development of the M/SAR (Marketplace/Segment Analysis
Report).
- May facilitate the execution of the VOC (Voice of the Customer) study.
2.4 Chapter 7. Distribution Channels Marketing Profession Discipline
Subtopics:
2.4.1 Distribution Channels Marketing Profession Discipline Overview
Distribution Channels Marketing is one of six profession disciplines
within the Marketing Professional Career (see "Professional Career
Structure" in topic 2.1.2), and is an integral part of the marketing mix
of elements. Distribution Channels Marketing professionals are
responsible for identifying and selecting the appropriate distribution
channels or mix of channels for IBM offerings/solutions. The
responsibilities of these individuals include participation in the
creation and implementation of go-to-market plans, distribution channels
marketing strategies and plans, and marketing support programs; and for
the gathering and coordination of distribution channels marketing
offerings/solutions requirements. In addition, these marketing
professionals may specialize in specific channels or combinations of
channels, e.g., face-to-face marketing, business partner, tele marketing,
electronic marketing, or OEM marketing, or may be assigned as a hybrid
marketing or fulfillment specialist.
The Distribution Channels Marketing professional understands the
components of channel support, e.g., sales strategies, technical support,
marketing communications, education, manufacturing and logistics, etc.,
required to ensure brand unit and/or business unit channels marketing
readiness. This professional also works with a variety of functions
within IBM such as legal, business practices, offerings/solutions
development and others, to ensure channels business is conducted in a
manner consistent with corporate and brand unit and/or business unit
standards.
The Distribution Channels Marketing professional understands the
offerings/solutions, terms and conditions, and distribution practices of
IBM's competitors and is capable of successfully creating strategies to
increase IBM's channels presence and participation. This individual is a
primary resource to the Marketing Management profession discipline within
the brand unit and/or business unit management system. They create
strategies, plans and programs that support all channels including the
client relationship, general business relationship, and sales specialist
professionals.
The measures of this discipline are revenue contribution, channel
optimization, market participation, and IBM cost of distribution.
2.4.2 Profession Discipline Structure
The Marketing Professional Career uses three titles for the five
professional positions. The prefix "Associate" is used for the lowest of
these positions. No prefix is used for the middle two positions and the
prefix "Senior" is used for the highest position.
The following positions are defined within the Distribution Channels
Marketing profession discipline:
- Associate Distribution Channels Marketing Specialist
- Associate Distribution Channels Marketing Specialist (advanced)
- Distribution Channels Marketing Specialist
- Distribution Channels Marketing Specialist (advanced)
- Senior Distribution Channels Marketing Specialist
This profession discipline is comprised of seven specialties as follows:
- Face-to-Face Marketing
- Business Partner
- Tele Marketing
- Electronic Marketing
- OEM Marketing
- Hybrid Marketing
- Fulfillment
Distribution Channels Marketing professionals are expected to demonstrate
expertise in at least one specialty depending on the size and scope of the
organization and on assigned responsibilities and job position. In
addition, individuals assigned to one of the Marketing Profession roles
will add to their skills profiles the skills template for that role (see
"Marketing Professional Career Skills Profile" in topic 2.1.10, for role
skills).
2.4.3 Characteristics of the Profession Discipline
Distribution Channels Marketing professionals have the following
characteristics:
- Manage the creation and implementation of the "go-to-market" plans.
- Knowledgeable of major or primary distribution channels.
- Can articulate the overall IBM distribution channels marketing
strategy.
- Gather and coordinate related offerings/solutions requirements with
marketing management.
- Skilled in performing market analysis, assessing IBM's position in the
market, and understanding total market opportunity.
- Develop marketing support programs and deliverables.
- Able to develop channels communications programs to ensure effective
communications with business partners.
- Develop and implement distribution channels management controls and
techniques.
- Develop distribution/coverage strategy using routes-to-market tools
and analyses of existing and alternative coverage and distribution
channels.
- Understand the components of distribution channels support to ensure
channels marketing readiness to implement routes to market plans.
- Establish strong cross-discipline linkages within the Marketing
Professional Career and with other global functions to ensure program
consistency and to maximize efforts for assigned channels or
specialties.
- Work with a variety of IBM functions such as legal, business practices
and development groups to ensure channels business is conducted in a
manner consistent with corporate and brand unit and/or business unit
standards.
- Understand the elements of an offering/solution marketing plan.
- Apply expertise in customer (relationship) coverage planning.
- Skilled in determining resource and skill requirements to support
selected offerings/solutions at each step of the sales cycle and in
determining actions required to resolve resource and skill gaps.
2.4.4 Potential Candidates
Distribution Channels Marketing professionals may be sourced from IBM
employees who represent a wide array of backgrounds and experience:
client relationship, general business, sales, and tele sales
professionals. Persons with technical services and/or communications
skills, combined with strong marketing skills and expertise would also be
candidates.
There are five distribution channels marketing positions which create
opportunities for multiple entry points, assuming the individual satisfies
certain requirements, including skill proficiency.
Candidates may also be sourced from professional hires who have
distribution channels marketing experience or an advanced degree in
distribution channels marketing.
Figure 7-1 illustrates the the possibilities for movement to and from the
Distribution Channels Marketing Profession Discipline.
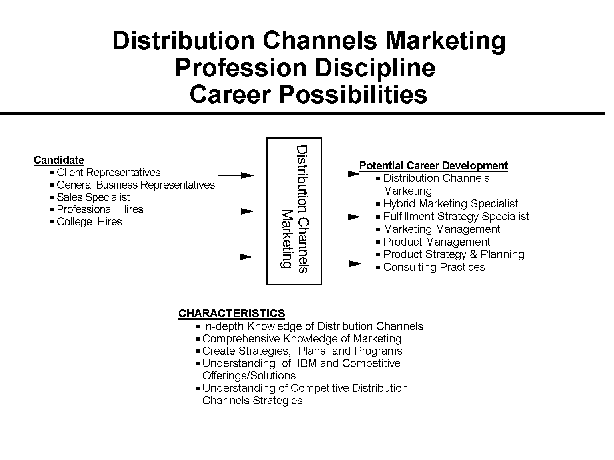
Figure 7-1. Distribution Channels Marketing Profession Discipline Career
Possibilities
2.4.5 Career Growth
Distribution Channels Marketing specialists can occupy several positions
from Associate Distribution Channels Marketing Specialist to Senior
Distribution Channels Marketing Specialist. The difference between the
ascending levels is a function of increasing skill, capability,
experience, and responsibility which are reflected in the extent of an
individual's demonstrated leadership, and the size and scope of his/her
contributions and impact on the business.
Growth in this discipline can be achieved through the acquisition of
skills and experiences that enable an individual to work in multiple
specialty areas. Professionals can also rise to levels comparable to
executive management and career path movement can occur in accordance with
planned steps into and through other business areas.
2.4.6 Performance Elements
The Distribution Channels Marketing professional is measured on the
following factors:
- Revenue, Year-to-Year Growth
- Market Participation
- Customer (Channel) Satisfaction
The Distribution Channels Marketing professional is a key member of a
brand unit and/or business unit and strongly influences the long-term
direction of the unit.
2.4.7 Distribution Channels Marketing Profession Discipline Skills Profile
The skills required of a Distribution Channels Marketing professional are
as follows:
- General Marketing Skills - required of all individuals in this
Marketing profession discipline
- IBM Internal Skills - required of all individuals in this Marketing
profession discipline
- Distribution Channels Marketing Discipline Specialty Skills
- Marketing Role Skills - for individuals assigned to one of the
Marketing Profession roles (see "Marketing Professional Career Skills
Profile" in topic 2.1.10, for role skills)
_______________________________ ________________________________________
| | Profession Discipline Positions, with |
| | Associated Skill Levels |
| DISTRIBUTION CHANNELS |________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| MARKETING SKILLS | Assoc | Assoc | | DCM | Sr |
| | DCM | DCM | DCM | Spec | DCM |
| | Spec | Spec | Spec | (adv) | Spec |
| | | (adv) | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| GENERAL MARKETING SKILLS |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Know & Apply Marketing | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Concepts & Methods | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know & Apply Mkt Intelligence | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Concepts & Methods | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand Customer Reqmts & | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Buying Behaviors | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know & Apply Market | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| Segmentation | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Strategies | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | User |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Plans | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | User |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Programs | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Distribution Channel | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | User |
| Strategies | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand | | | | | |
| Offerings/Solutions Marketing | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Plan | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Create Marketing Programs | 3 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Promotional Materials | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 3 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Distribution Channels | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Contract Reqmts | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Perform Market Analysis | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Design/Develop Channel | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Communications Programs | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Implement Partnership | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Enhancement Process | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| IBM INTERNAL SKILLS |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Know & Apply IBM Brand | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Business Management System | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Explain IBM Business Strategy | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand the IBM Brand | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Strategy | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand/Anticipate/Respond | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| - Competitive Trends | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Articulate IBM | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Offerings/Technology | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| IBM Formal & Informal Network | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Work in Cross-Functional | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| Teams | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand IBM Global | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Operations | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Creativity/Breakthru Thinking | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Interpersonal Communication | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Negotiation | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Problem Solving & | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Decision-Making | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Apply Basic Financial | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | User |
| Concepts | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Apply Project Management | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Techniques | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Self-Directed Learning | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Explain IBM Distribution | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Strategy | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know Channel Businesses | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Risk Awareness/Taking | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Manage Customer Satisfaction | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| & Loyalty | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand Global Business | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Partner | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Distribution/End-User | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | User |
| Coverage Strategy | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Client Issue ID | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Customer Relationship | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | User |
| Coverage Plan | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Resource & Skill | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Plans | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Terms Strategy | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Business Partner Conduct | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Guidelines | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| FACE-TO-FACE SPECIALTY SKILLS |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Develop Face-to-Face Channel | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Strategies & Plans | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know IBM's Face-to-Face | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Channel Customer Sets | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Communicate Segment Strategy | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know Why Customers Buy From | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Different Channels | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Determine Customer/Market | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Needs | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| BUSINESS PARTNER SPECIALTY SKILLS |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Develop Business Partner | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 4 |
| Channel Strats/Plans | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know IBM's Business Partner | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 4 |
| Customer Sets | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Client Strategy & Planning | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Communicate Segment Strategy | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Business Partner/End-User/IBM | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Business Partner | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 4 |
| Executive Communication | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand IBM Business | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 4 |
| Partner Programs | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know IBM Distrb Channels BP | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Distributor Segment | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know IBM Distrb Channels BP | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Product Agent Segment | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know IBM Distrb Channels BP | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Reseller Segment | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know IBM Distrb Channels BP | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Sales Agent Segment | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know IBM Distrb Channels BP | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Solution Provider Seg | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know IBM Distrb Channels BP | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Sys Integrator Segment | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know Independent SW Vendor | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Segment | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| TELE MARKETING SPECIALTY SKILLS |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Develop Tele Marketing | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Channel Strategies & Plans | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know IBM's Tele Marketing | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Channel Customer Sets | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Communicate Segment Strategy | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know Why Customers Buy From | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Different Channels | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| ELECTRONIC MARKETING SPECIALTY SKILLS |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Develop Electronic Channel | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Strategies & Plans | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know IBM's Electronic Channel | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 4 |
| Customer Sets | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand Internet | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand Internet/Intranet | 3 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 4 |
| Market | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand Internet/Intranet | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Targets | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know Internet Service | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 4 |
| Providers | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| OEM MARKETING SPECIALTY SKILLS |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Develop OEM Channel | 2 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 4 |
| Strategies & Plans | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know IBM's OEM Customer Set | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Support Integration of IBM | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Offrgs/Solns in OEMs | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand OEM Market Place | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand IBM OEM Contract | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know & Apply Integrated | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Product Development Proc | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| HYBRID MARKETING SPECIALTY SKILLS |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Build Distribution Plan | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand Offering | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 4 |
| Distribution Life Cycle | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Perform Marketplace Financial | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Assessment | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Determine Customer/Market | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Needes | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know Why Customers Buy From | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Different Channels | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Determine Marketing Resources | 3 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Execute Segment Study | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know & Use Routes-To-Market | 2 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| Tools/Methodologies | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| FULFILLMENT SPECIALTY SKILLS |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Develop Fulfillment | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Strategies & Plans | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know Customer Fulfillment | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand Global Fulfillment | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand Logistics | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know Order Entry Process | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand Supply Chain Flow | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand J-I-T Delivery | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand Non-traditional | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Distribution Channels | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Linkages/Partnership | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
2.4.8 Professional Development
Education roadmaps will be provided at a later date.
2.4.9 Distribution Channels Marketing Position Descriptions
The following position descriptions describe the basic work of each of the
positions within the Marketing Professional Career. Formal descriptions
which may contain legally mandated language necessary for classifying
employees in a geography should be obtained through the approved on-line
job library, if available in the geography, or by contacting the
appropriate H.R. personnel within the geography.
Subtopics:
2.4.9.1 Position Title: Associate Distribution Channels Marketing Specialist
Position Summary and Responsibilities:
Works on activities and projects that support the implementation of the
"go-to-market" plans for an assigned specialty (e.g., Face-to-Face,
Business Partner, Electronic, Tele, OEM) in a brand unit and/or business
unit. Distribution Channels strategies and plans are defined by
management or senior professionals, and generally fall within established
guidelines and procedures. Assists with the implementation of distribution
channels management controls and techniques as defined by management for
an assigned specialty. Gathers distribution channels marketing
offerings/solutions requirements from channel sales professionals as
defined by higher-level professionals and management. Works, on a limited
basis, with other professionals in the marketing function as well as other
global functions (e.g., legal, business practices, offering/solution
development, communications, etc.) to support channels business consistent
with corporate and brand unit and/or business unit standards for an
assigned specialty.
Skills
- Environment:
Applies basic professional knowledge of distribution channels and the
marketing function to the attainment of business objectives for
assigned areas.
Demonstrates the skill proficiencies for this position.
- Communications/Negotiation:
Understands and assists with the resolution of distribution channels
marketing issues.
Assists with research of distribution alternatives as part of a
Routes-to-Market (RTM) team. Is able to articulate, at a basic level,
various approaches.
Assists team members and others from functional and/or other
professional areas to negotiate channel marketing support and/or
offerings/solutions requirements.
Assists in the development of channels offerings/solutions
requirements which are communicated to offerings/solutions development
and fulfillment.
- Problem Solving:
Recognizes problems, related to assignments in the distribution
channels marketing function and recommends alternatives.
Analyzes basic processes and challenges proposed offerings/solutions
to reach optimum marketplace results.
Analyzes distribution channels marketing problems using existing
techniques and tools.
Contribution and Leadership
- Assists higher-level professionals on special projects related to
functional objectives.
- Sets own priorities for work assignments and seeks advice from other
professionals as needed.
- Understands department/function mission and applies this understanding
to assigned areas of responsibility.
- Provides basic technical advice to less knowledgeable team members for
assigned specialty.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Is held accountable for the quality and timeliness of completed
assignments.
- Participates, on a limited basis, with department program planning.
- Understands the need for activities that contribute to business
results and customer satisfaction and are subject to business
measurements for assigned specialty.
- Activities have limited effect on costs and expenses to the
organization as distribution plans are implemented.
2.4.9.2 Position Title: Associate Distribution Channels Marketing Specialist (advanced)
Position Summary and Responsibilities:
Professionals and/or managers implement the "go-to-market" plans for an
assigned specialty (e.g., Face-to-Face, Business Partner, Electronic,
Tele, OEM) in a brand unit and/or business unit. Distribution Channels
strategies and plans are typically defined by management or senior
professionals, but approaches and activities used to achieve distribution
channels marketing readiness and effectiveness for an assigned specialty
are left to the professional/manager to define and negotiate. Works on
marketing programs as assigned. Implements distribution channels
management controls and techniques as defined by management for an
assigned specialty. Gathers distribution channels marketing
offerings/solutions requirements from channel sales professionals and
submits to other discipline professionals and/or managers. Works with
other professionals in the marketing function as well as other global
functions (e.g., legal, business practices, offering/solution development,
communications, etc.) to conduct channels business consistent with
corporate and brand unit and/or business unit standards for an assigned
area.
Skills
- Environment:
Applies professional knowledge of distribution channels and the
marketing function to the attainment of business objectives for
assigned areas.
Demonstrates the skill proficiencies for this position.
- Communications/Negotiation:
Engaged independently on distribution channels marketing issues.
Identifies new approaches and negotiates resolutions with appropriate
organizations.
Occasionally researches distribution alternatives as part of a
Routes-to-Market (RTM) team. Is able to articulate various approaches.
Works with team members and others from functional and/or other
professional areas to negotiate channel marketing support and/or
offerings/solutions requirements.
Creates distribution channels awareness with discipline management to
promote a broader portfolio of IBM offerings/solutions in assigned
specialty.
Gathers and communicates channels offerings/solutions requirements to
offerings/solutions development and fulfillment.
- Problem Solving:
Recognizes problems related to the distribution channels marketing
function and proposes offerings/solutions.
Analyzes processes and challenges proposed offerings/solutions to
reach optimum marketplace results.
Applies creativity and judgment in creating distribution channels
marketing support programs and deliverables.
Contribution and Leadership
- Works on special projects related to functional objectives.
- Generally controls own work priorities within related channels
marketing projects. May lead small teams on project assignments.
- Understands department/function mission and applies this understanding
to assigned areas of responsibility.
- Provides on-going channel advice to discipline team members throughout
the offering/solution life-cycle, for assigned specialty.
- Managers will discharge the basic management responsibilities common
to all IBM managers.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Is accountable for achieving individual results on projects and for
the impact of results on multi-functional team activities.
- Participates in department program planning.
- Supports activities that contribute to business results and customer
satisfaction and are subject to business measurements for assigned
specialty.
- Activities have immediate effect on costs and expenses to the
organization as distribution plans are implemented.
2.4.9.3 Position Title: Distribution Channels Marketing Specialist
Position Summary and Responsibilities:
Professionals and/or managers develops the "go-to-market" plans with
management and senior professionals for a number of assigned specialties
(e.g., Face-to-Face, Business Partner, Electronic, Tele, OEM) in a brand
unit and/or business unit. Implements these plans by developing
distribution channels marketing support programs and deliverables and
ensuring distribution channels marketing readiness for assigned
specialties. Selects and implements appropriate channel management
controls and techniques to ensure success for assigned specialties.
Defines distribution channels marketing offering/solution requirements for
assigned specialties. Establishes linkages with a variety of functions
(e.g., legal, business practices, offering/solution development,
communications, etc.) to ensure channels business is conducted consistent
with corporate and brand unit and/or business unit standards for assigned
area.
Skills
- Environment:
Applies advanced professional knowledge of distribution channels
marketing and related marketing functions for the attainment of brand
unit and/or business unit objectives.
Demonstrates the skill proficiencies for this position.
- Commmunictions/Negotiation:
Articulates the overall distribution channels marketing strategy for
the brand unit and/or business unit.
Researches complex distribution alternatives as a part of a
Route-to-Market's (RTM) team. Is able to articulate conclusions.
Works effectively with team members, including professionals from
other functional areas to negotiate distribution channel
offering/solution requirements and/or channel marketing support.
Creates distribution channels awareness and provides advice and
counsel to management in order to promote a broader portfolio of IBM
offerings/solutions for assigned specialties.
- Problem Solving:
Recognizes and articulates complex problems related to the
distribution channels marketing function and proposed project driven
solutions being developed.
Analyzes channel issues and implements solutions involving marketing
staffs, offering/solution development, business practices, etc., for
optimum marketplace results.
Applies a high level of creativity and judgment in creating channels
marketing support programs and deliverables.
Contribution/Leadership
- Understands department/function mission and applies this understanding
to related activities.
- Directly influences other professionals in offering/solution planning,
fulfillment and development.
- Provides on-going business guidance to organization team members
throughout the offering/solution life-cycle.
- Manages and motivates team members and leads project teams.
- Manages the life cycle of an offering/solution within distribution
channels and re-evaluates the channels' strategy when the
offering/solution moves from a growth to mature state.
- Managers will discharge the basic management responsibilities common
to all IBM managers.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Is accountable for achieving results of projects involving
multi-functional teams and/or departments.
- Regularly participates in overall functional planning. Identifies,
estimates and presents cost exposures for proposed solutions.
- Applies awareness of competitive offerings/solutions and position in
market to planning and strategy development activity.
- Marketing activities directly contribute to business results, customer
satisfaction and are subject to business measurements.
- Activities impact project/function costs and expenses as
Routes-to-Market are implemented.
2.4.9.4 Position Title: Distribution Channels Marketing Specialist (advanced)
Position Summary and Responsibilities:
Professionals and/or managers manages the creation and implementation of
the "go-to-market" plans for multiple specialties (e.g., Face-to-Face,
Business Partner, Electronic, Tele, OEM) for a major brand unit and/or
business unit or geography. Recognized as an expert in distribution
marketing, leads the creation of distribution channels marketing support
programs and deliverables for multiple specialties. Oversees the
implementation of distribution plans for multiple specialties and develops
strategies to ensure distribution channels marketing readiness for a major
brand unit and/or business unit or geography. Develops and implements
distribution channels management controls and techniques to ensure success
for multiple specialties. Participates in complex negotiations with a
variety of functions, (e.g., legal, business practices, offering/solution
development teams, communications, etc.) to ensure channels business is
conducted consistent with corporate and brand unit and/or business unit
standards for multiple specialties and/or areas.
Skills
- Environment:
Applies expert knowledge of distribution channels marketing
disciplines and processes as they relate to IBM's strategic marketing
functions brand unit and/or business unit and/or geography
distribution objectives.
Understands IBM's organizational resources, priorities, needs and
policies as well as brand unit and/or business unit strategies.
Demonstrates the skill proficiencies for this position.
- Communications/Negotiation:
Compares "go-to-market" strategies and plans to competition to
identify strengths, exposures and conflicts and takes appropriate
action for improvement.
Creates distribution channels awareness with brand unit and/or
business unit management to promote a broader offering/solution
representation in multiple channels.
Negotiates offering/solution requirements with development and
manufacturing teams for assigned areas of responsibility.
Leads and negotiates the development of channel marketing support
program deliverables.
- Problem Solving:
Anticipates potential channel related problems. Utilizes problem
management tools to identify potential business risk, evaluates risk
factors and resolves the problems.
Analyzes future trends and analyzes competitive situations and
assesses these opportunities for impact and distribution channel
alternatives.
Contribution/Leadership
- Leads and guides the efforts of cross-functional teams in gaining
consensus for "go to market" plans for assigned areas of
responsibility.
- Exhibits strategic vision of functional or unit mission and applies
this vision to assignments.
- Influences people and organizations, including executive management,
when issues are complex or difficult, requiring considerable
diplomacy. Is respected and recognized as an expert in the
Distribution Channels Marketing discipline.
- Leads multi-functional teams on initiatives in new and complex areas.
- Managers will discharge the basic management responsibilities common
to all IBM managers.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Is accountable for complex projects including multi-functional,
country-wide or geographically dispersed teams and is responsible for
overall program success.
- Is responsible for major components in functional planning with
executive review.
- Activities are subject to business measurement, are directly related
to customer satisfaction and drive follow-on business through major or
primary distribution channels.
- Identifies, estimates and resolves channel cost issues and implements
management controls for multiple channels.
- Activities impact the marketing function, brand unit and/or business
unit or country costs and expense for multiple channels
2.4.9.5 Position Title: Senior Distribution Channels Marketing Specialist
Position Summary and Responsibilities:
Professionals and/or managers are responsible for the overall design,
creation and implementation of the "go-to-market" plans for the total set
of IBM's offerings/solutions within an assigned area at the geography or
international level. Relied on as the expert in distribution channels
marketing within the marketing profession and other brand unit and/or
business unit professionals. Leads the creation of distribution channel
marketing strategies for multiple, very complex and strategically
important projects/assignments associated with meeting corporate,
geography or major brand unit and/or business unit objectives.
Responsible for the overall implementation of distribution plans and
channel readiness at the geography or international level. Influences
executive management within Marketing Management and other functions
regarding requirements for new or improved offerings/solutions. Evaluates
skill base of department members by ensuring their high degree of
involvement in functional activities. Leads complex negotiations with a
variety of functions (e.g., legal, business practices, offering/solution
development, communications, etc.) to ensure channels business is
conducted consistent with corporate and brand unit and/or business unit
standards at the geographic or international level.
Skills
- Environment:
Applies professional expertise to define and lead the development of
offerings/solutions in leading edge or critical situations, on
projects of strategic importance to brand unit and/or business unit,
country or corporate objectives. Demonstrates professional mastery
of distribution channels marketing.
Demonstrates the skill proficiencies for this position.
- Communications/Negotiation:
Engages in teamwork at the highest management and professional levels
of IBM.
Plans and conducts negotiations which result in strategic agreements
and commitments among various IBM organizations (i.e.,
offering/solution development teams, brand unit and/or business unit
management, etc.).
Leads communications efforts to build awareness of distribution
channels role in expanding marketing effectiveness.
- Problem Solving:
Anticipates future customer, market and business trends. Applies this
understanding to develop a strategic vision which influences brand
units and/or business units.
With executive review, develops and implements offering/solution,
market, business or technology strategies. Applies marketing skills
to thoroughly evaluate offering/solution and viability in the market.
Contribution and Leadership
- Articulates vision of long-term IBM marketing, business and technology
directions which guides distribution channels.
- Recognized as the expert and leader by other members of the marketing
profession, related functions and multi-country organizations within
IBM.
- Leads project teams for brand units and/or business units, country or
global teams.
- Engages team members in development activity to build and establish
required skills within the marketing organization. Acts as mentor to
team members to ensure maximum performance of the marketing
profession.
- Leads, manages and guides the creation of distribution channel
marketing support programs and deliverables.
- Managers will discharge the basic management responsibilities common
to all IBM managers.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Is accountable for brand unit and/or business unit, major country or
international projects and programs.
- Develops and implements distribution channels marketing business
strategies with executive management review and concurrence.
- Responsible for committing multiple resources (internal and external)
and achieving customer satisfaction, cost, expense, revenue and all
other geographic/international/corporate business measurements.
- Responsible for achieving quality output and value add for highly
visible channel marketing activity and offering/solution flow.
2.4.10 Distribution Channels Marketing Specialty Descriptions
Subtopics:
2.4.10.1 Specialty Title: Face-to-Face Marketing
Specialty Summary:
Individuals working in this Distribution Channels Marketing specialty
direct customer programs to a successful conclusion in the ISU's and in
General Business. Initiates new marketing programs, provides financial
justifications, and develop practical implementation plans. Establishes
the business plan and forecasts for the coordination of systems technical
support/marketing efforts.
Responsibilities:
- Defines and develops face-to-face channels strategies and processes
that support the distribution channels strategy framework.
- Ensures face-to-face channels design and management activities support
brand unit and/or business unit or offering/solution strategy and
implement recommendations which facilitate complementary strategies.
- Establishes and maintains marketing programs designed to prevent
competitive losses.
- Is responsible to acquire and demonstrate basic knowledge of
offering(s)/solution(s) and industry applications.
- Understands and uses available IBM resources including complementary
and alternative marketing channels.
- Understands and negotiates terms and conditions appropriate to
channels needs and requirements.
- Develops, documents and communicates schedules, business plans, issues
and results to distribution channels and brand unit and/or business
unit management.
- Develops, designs and implements face-to-face channels requirements
and processes.
- Identifies successful programs and communicates to other brand unit
and/or business unit or channels management for implementation.
2.4.10.2 Specialty Title: Business Partner
Specialty Summary:
Individuals working in this Distribution Channels Marketing specialty
design and develop business partner programs in order to drive revenue,
profit and market share for IBM and its Business Partners. Redesigns
channels marketing programs and processes to provide added value and to
optimize the effectiveness of the Business Partner.
Responsibilities:
- Develops, designs and implements processes to gather business partner
channels requirements.
- Defines and develops business partner channels strategies and
processes that support the distribution channels strategy framework.
- Ensures business partner channels design and management activities
support brand unit and/or business unit offering/solution strategy and
implement recommendations which facilitate complementary strategies.
- Works with geographic brand unit and/or business unit and channels
teams to ensure channels design and management activities support the
field structure and implement recommendations which facilitate
complementary strategies using the Routes-To-Market process.
- Identifies successful programs and communicates to other brand unit
and/or business unit or channels management for implementation.
- Develops, documents and communicates schedules, business plans, issues
and results to channels and field management and business partners.
- Uses Market Driven Quality principles in the development and
assessment of all projects by identifying the customer and their
requirements, creating a closed loop process that shows continual
improvement and reporting results on a regular basis.
2.4.10.3 Specialty Title: Tele Marketing
Specialty Summary:
Individuals working in this Distribution Channels Marketing specialty are
responsible for developing tele marketing opportunities which are a result
of distribution plans and strategies.
Responsibilities:
- Identifies opportunities, risks, resources, and offerings/solutions
required to grow the tele marketing distribution channels marketing.
- Ensures tele marketing channels design and management activities
support brand and/or business unit or offering/solution strategy and
implement recommendations which facilitate complementary strategies.
- Develops, documents and communicates schedules, business plans, issues
and results to distribution channels and brand unit and/or business
unit management.
- Identifies unique methods to deliver offerings within tele marketing
distribution channels.
- Communicates tele marketing channels trends and directions to
distribution channels marketing and brand unit and/or business unit
management.
- Gathers and analyzes tele marketing channels and/or
offerings/solutions requirements and communicate those requirements to
distribution channels marketing and brand unit and/or business unit
management.
- Designs and executes marketing campaigns anticipating customer demand,
which creates customer preference for brand unit and/or business unit
offerings/solutions over competitive alternatives.
- Understands tele marketing technology, trends and directions and is
capable of anticipating their impact on strategies and programs.
2.4.10.4 Specialty Title: Electronic Marketing
Specialty Summary:
Individuals working in this Distribution Channels Marketing specialty
design and develop channels programs in order to drive revenue profit and
market participation for electronic distribution channels marketing.
Redesigns channels marketing programs and processes to optimize the
effectiveness of the electronic distribution channel.
Responsibilities:
- Defines and develops electronic distribution channels strategies and
processes that support the distribution channels strategy framework.
- Develops, designs and implements electronic channels requirements and
processes.
- Identifies successful programs and communicates to other brand unit
and/or business unit or channels management for implementation.
- Ensures electronic channels design and management activities support
brand unit/business unit or offering/solution strategy and implement
recommendations which facilitate complementary strategies.
- Develops, documents and communicates schedules, business plans, issues
and results to distribution channels and brand unit/business unit
management.
- Uses Market Driven Quality principles in the development and
assessment of all projects by identifying the customer and their
requirements, creating a closed loop process that shows continual
improvement and reporting results on a regular basis.
- Understands electronic technology, trends and directions and is
capable of anticipating their impact on strategies and programs.
2.4.10.5 Specialty Title: OEM Marketing
Specialty Summary:
Individuals working in this Distribution Channels Marketing specialty are
responsible for developing OEM marketing opportunities, which requires a
potential OEM channels business to be fully analyzed and understood, e.g.,
offering/solution, positioning, forecast, long/short-term strategies, and
programs. Responsible for technical depth for the OEM offering/solution,
for creating and marketing OEM offerings/solutions and for efficient and
accurate backlog management.
Responsibilities:
- Identifies opportunities, risks, resources, and solutions required to
grow the OEM distribution channels marketing.
- Ensures OEM channels design and management activities support brand
unit and/or business unit or offering/solution strategy and implement
recommendations which facilitate complementary strategies.
- Develops, documents and communicates schedules, business plans, issues
and results to distribution channels and brand unit and/or business
unit management.
- Identifies unique methods to deliver offerings/solutions within OEM
distribution channels.
- Develops appropriate strategies for communicating new developments or
announcements to OEM channels members, distribution channels marketing
and brand unit and/or business unit management.
- Communicates OEM channels trends and directions to distribution
channels marketing and brand unit and/or business unit management.
- Gathers and analyzes OEM channels and/or offerings/solutions
requirements and communicates those requirements to distribution
channels marketing and brand unit and/or business unit management.
- Designs and executes marketing campaigns anticipating customer demand,
which creates customer preference for brand unit and/or business unit
offerings/solutions over competitive alternatives.
2.4.10.6 Specialty Title: Hybrid Marketing
Specialty Summary:
Individuals working in this Distribution Channels Marketing specialty
create distribution plans. Based on an understanding of customers buying
behavior determine the optimal routes to market to optimize coverage,
profit and customer and business partner satisfaction. Routes to Market
tools/methodologies are used to develop plans that are tailored to the
individual requirements and/or opportunities of any specific brand
unit/business unit, offering/solution or customer set.
Responsibilities:
- Leads the creation of distribution plans for brand unit and/or
business unit offerings /solutions.
- Ensures marketing profession disciplines (i.e., Market Intelligence,
Technical Support, Marketing Communications and Direct Marketing)
consensus for and commitment to a distribution plan.
- Leverage channels and support resources to optimize distribution plan.
- Optimizes selling expense against marketing coverage.
- Maintains RTM tools/methodologies with regular database updates
- Responsible for planning and scheduling GTM reassessments.
2.4.10.7 Specialty Title: Fulfillment Strategy
Specialty Summary:
Individuals working in this Distribution Channels Marketing specialty must
understand and participate in the Routes To Market process; understand
fulfillment processes unique to offering/solution, channels and/or
geography; leverage the fulfillment system/process to IBM's competitive
advantage. This individual provides the fundamental linkage between
marketing management, manufacturing, and sales and services.
Responsibilities:
- Participates in distribution plan development and implementation, to
ensure the fulfillment requirements are integrated into overall
distribution plans.
- Understands the fundamentals of the fulfillment process, (e.g., terms
and conditions, order entry, logistics, lead times, delivery, accounts
receivable, etc.), to support geography requirements.
- Understands and creates channels distribution fulfillment requirements
(e.g., order entry, order turnaround, order cycle, invoicing quality,
etc.). Functions as contact point for and interface to manufacturing
and global fulfillment.
- Coordinates the supply/demand process with manufacturing and sales,
and between channels.
- Understands and works with (utilizes) the offering/solution
development and the manufacturing process, which includes the
marketing related aspects of logistics management, offering/solution
supply, and availability.
- Understands how to leverage the fulfillment system (e.g., communicate
unique channels requirements to manufacturing, just-in-time delivery,
etc.) to IBM' s competitive advantage.
- Understands the SAP system and process.
2.5 Chapter 8. Technical Support Marketing Profession Discipline
Subtopics:
2.5.1 Technical Support Marketing Profession Discipline Overview
Technical Support Marketing is one of six profession disciplines within
the Marketing Professional Career (see "Professional Career Structure" in
topic 2.1.2), and plays a key role in the marketing mix of elements.
Analysis has shown that technical support is one of the most critical and
influential factors affecting customer buying decisions - whether they buy
a company's goods and services directly from the vendor or from another
solution provider. The kind and quality of technical support provided,
before and after a purchase, and the resulting satisfaction of the
customer and/or business partner with the service and support provided is
a deciding factor in whether or not an established customer will purchase
again in the future and remain loyal.
When we refer to "technical support," we mean the pre- through post-sales
support provided to a customer or business partner, including the
offering/solution services, to ensure that the offering or solution meets
a customer's needs and solves their business problem(s). Technical
Support Marketing, as a key element of the Brand Business Management
System, should ensure that an offering/solution can be successfully
installed in a customer's environment and adopted quickly and easily by
the end-users. This includes ensuring that the offering/solution can be
easily integrated with other IBM and non-IBM offerings/solutions.
Technical Support Marketing specialists develop global technical support
strategies and plans for an offering/solution, and ensure that they are
enabled and executed. To accomplish this, they must understand IBM, brand
unit and/or business unit objectives, strategies and offerings/solutions,
and their respective technical support strategies, as well as those of
their competitors. They must also understand, from the customer's point
of view, the key requirements for technical support and services for each
market segment they are targeting. This is followed by the definition of
the technical support and services offerings and solutions necessary to
meet these requirements, deliver the brand "promise of value" and/or
business unit value proposition, and attain a competitive advantage. In
light of this, Technical Support Marketing is a critical member of the IPD
or solution planning process, from concept through delivery to sunset of
the offering/solution.
Technical Support Marketing specialists define and ensure that the right
technical sales support skilled resources, programs, and education and
training are in place; this includes assessing the readiness of the
channels to sell and support the offering/solution. They ensure
appropriate support of these technical sales resources, so that the right
offering or solution is sold to the customer. They also ensure that
quality and serviceability are built into the offering/solution, and that
the appropriate HW maintenance and/or SW defect and usage support is
easily available. In addition, they ensure that the customer or business
partner can get quick access to skilled resources to resolve any problems
that may arise during implementation and usage of the offering/solution.
To assure easy installation, they also determine that the appropriate
services offerings/solutions are available and that the necessary
resources are defined, trained and available to deliver these services.
These specialists link and team with the geographies, sales, services,
development and other marketing teams to ensure execution of the
strategies and programs. They measure the satisfaction with technical
support and take corrective actions or differentiating actions, as
required. In addition, they ensure that financial objectives are met.
Technical support has been a key differentiator for the IBM Company. With
the appropriate implementation of the Technical Support Marketing
profession discipline, technical support will provide an even stronger,
IBM, brand unit and/or business "promise of value."
2.5.2 Profession Discipline Structure
The Marketing Profession uses three titles for the five professional
positions. The prefix "Associate" is used for the lowest of these
positions. No prefix is used for the middle two positions and the prefix
"Senior" is used for the highest position. All five positions do not
occurr in all of the Marketing Profession disciplines.
The following positions are defined within the Technical Support Marketing
profession discipline:
- Associate Technical Support Marketing Specialist
- Associate Technical Support Marketing Specialist (advanced)
- Technical Support Marketing Specialist
- Technical Support Marketing Specialist (advanced)
- Senior Technical Support Marketing Specialist
This profession discipline is comprised of three specialties, as follows:
- Technical Sales Support -- An individual working in this specialty
develops strategies and ensures enablement for the technical sales and
installation support that is required for an offering or solution.
This includes, in general, the non-fee support associated with the
offering/solution related to technical sales and installation
assistance. The objective is a satisfied and loyal customer at the
conclusion of the installation activity.
- HW/SW Service(s) -- An individual working in this specialty develops
strategies for, and ensures enablement of the hardware and/or software
service(s) required to support the customer over the life cycle of an
offering or solution and to provide IBM and brand unit and/or business
unit differentiation. This profession discipline specialty typically
focuses on hardware maintenance and software service(s) related to
defect and usage.
- Product Enabling Services -- An individual working in this specialty
defines and ensures the development and availability of the skilled
resources and Product Enabling Services offerings/solutions (e.g.,
"Smooth Start," migration and assistance, etc.) needed to drive
placement of offerings and solutions. Generally, these services are
fee-based and locally delivered by channels (IBM and business
partners), and assist the customer in enabling and exploiting hardware
and/or software offerings and solutions.
Each individual in this profession discipline is expected to perform in at
least one of these specialties, depending on the size and scope of the
organization, responsibilities, and job position. Individuals in higher
positions are expected to perform in multiple specialties, or for more
than one brand unit and/or business unit, or to implement global
cross-brand unit and/or business unit strategies.
In addition, individuals assigned to one of the Marketing Profession roles
will add to their skills profile the skills template for that role (see
"Marketing Professional Career Skills Profile" in topic 2.1.10, for role
skills).
2.5.3 Characteristics of the Profession Discipline
Technical Support Marketing professionals have the following
characteristics:
- Establish and maintain strong linkages with other elements of the
marketing mix (i.e., offering, terms, distribution channels,
support/skills, fulfillment and image) as well as with other functions
(e.g., market intelligence, marketing communications, development,
sales and services, etc.), to ensure synergy and consistency of plans
worldwide and present a single IBM image.
- Develop global strategies and plans for brand unit and/or business
unit offerings/solutions which cover one or more specialties within
Technical Support Marketing (Technical Sales, HW & SW Service(s),
Product Enabling Services), align with brand unit and/or business unit
strategies, meet IBM and brand unit and/or business unit financial
targets and deliver the brand "promise of value" and/or business unit
value proposition for technical support and services. These plans
must, to the greatest extent possible, be consistent across brand
units and/or business units and present a single IBM image.
- Pro-actively ensure that global technical support and services
strategies and plans are successfully executed (e.g., technical
support and services channels are identified and in place, training
and support materials are developed and delivered, infrastructure
dependencies are satisfied, etc.)
- Aggressively monitor and measure the execution of global technical
support and services plans and programs (e.g., determines how well
they meet targets, deliver the brand "promise of value" and/or
business unit value proposition for technical support and services,
build customer and business partner loyalty, etc.), and provide
feedback to the brand unit and/or business unit team, and takes
corrective actions, as needed.
2.5.4 Potential Candidates
Professionals or managers in sales and services organizations today with
the appropriate skills and experience (e.g., technical support, marketing,
technical sales, project management, etc.) are potential candidates for
the Technical Support Marketing profession discipline. These include I/T
Specialists, I/T Architects, I/T Availability Services Specialists, Sales
Specialists, Project Managers and others, (and managers of these
professionals). Candidates may also be drawn from technical support or
planning functions within the marketing and development organizations, in
particular Engineering and Software Engineering. Program Managers from HQ
or other staff functions and professional hires may also be considered, if
they have the requisite technical and marketing skills. Since the
Technical Support Marketing profession discipline spans four positions
from Associate through Senior positions, opportunities exist for multiple
entry points into the profession discipline, assuming that the skill
proficiency levels are achieved and other requirements are satisfied.
Figure 8-1 illustrates the the possibilities for movement to and from the
Technical Support Marketing Profession Discipline.
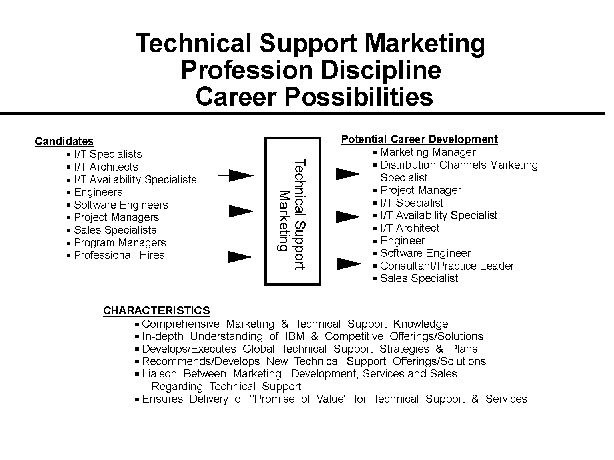
Figure 8-1. Technical Support Marketing Profession Discipline Career
Possibilities
2.5.5 Career Growth
Technical Support Marketing specialists can occupy positions from
Associate Technical Support Marketing Specialist through Senior Technical
Support Marketing Specialist in any of the three specialties. The
difference between the ascending levels is a function of increasing skill,
capability, experience and responsibility, which are reflected in the
extent of an individual's demonstrated leadership, contributions, and
impact on the business. Individuals in the higher professional positions
will be expected to support more than one specialty, or more than one
brand unit and/or business unit, or to develop global strategies that
cross brand units and/or business units.
Growth in this profession discipline can be achieved through the
acquisition of skills and experiences that enable an individual to work in
multiple specialty areas and/or span multiple brand units and/or business
units. Professionals can rise to positions comparable to executive
management, and career path movement can occur in accordance with planned
steps into, and through other professions.
2.5.6 Performance Elements
Technical Support Marketing specialists from all three specialties are
measured on a number of factors including: building customer and business
partner satisfaction and loyalty; developing strategies, plans and
programs which are comprehensive, executable/adaptable worldwide, simple
for the customer to understand, acquire and use, and easy for the support
delivery channels to implement; establishing and maintaining effective
communication linkages with field sales and services organizations,
business partners, development, vendors, etc. which result in the
development and execution of successful technical support and services
plans and programs; ensuring synergy with other elements of the marketing
mix; developing new/enhanced technical support and services approaches and
offerings/solutions; achieving brand unit and/or business unit financial
targets.
2.5.7 Technical Support Marketing Profession Discipline Skills Profile
The skills required of a Technical Support Marketing professional are as
follows:
- General Marketing Skills - required of all individuals in any
Marketing Profession discipline
- IBM Internal Skills - required of all individuals in any Marketing
Profession discipline
- Technical Support Marketing Discipline-Specific Skills - required of
all individuals in the Technical Support Marketing profession
discipline
- Technical Support Marketing Specialty Skills
- Marketing Profession Role Skills - for individuals assigned to one of
the Marketing Profession roles (see "Marketing Professional Career
Skills Profile" in topic 2.1.10, for role skills)
_______________________________ ________________________________________
| | Profession Discipline Positions, with |
| | Associated Skill Levels |
| TECHNICAL SUPPORT MARKETING |________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| PROFESSION DISCIPLINE SKILLS | Assoc | Assoc | | TSM | Sr |
| | TSM | TSM | TSM | Spec | TSM |
| | Spec | Spec | Spec | (adv) | Spec |
| | | (adv) | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| GENERAL MARKETING SKILLS |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Know & Apply Marketing | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| Concepts & Methods | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know & Apply Mkt Intelligence | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Concepts & Methods | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand Customer Reqmts & | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| Buying Behavior | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know & Apply Market | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Segmentation | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Strategies | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Plans | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Programs | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Customer Satisfaction | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| & Loyalty Strategy | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Manage Customer Satisfaction | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| & Loyalty | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| IBM INTERNAL SKILLS |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Know & Apply IBM Brand | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| Business Management System | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Explain IBM Business Strategy | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand the IBM Brand | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| Strategy | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand/Anticipate/Respond | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| - Competitive Trends | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Articulate IBM | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Offerings/Technologies | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| IBM Formal & Informal Network | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Work in Cross-Functional | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| Teams | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand IBM Global | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Operations | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Creativity/Breakthru Thinking | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Interpersonal Communication | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Negotiation | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Problem Solving & | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Decision-Making | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Apply Basic Financial | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Concepts | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Apply Project Management | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Techniques | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Self-Directed Learning | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand WW Skills | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Management Process | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Project Track/Report/Deliver | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Manage Contracted Resource & | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Services | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Risk Awareness/Taking | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Leadership | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Foster Teamwork/Enable Teams | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Eliminate Barriers/Inhibitors | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Build Shared Commitment | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| PROFESSION DISCIPLINE-SPECIFIC SKILLS |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Know IBM Global Technical | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Support & Services Orgs | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand Global Technical | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Support Issues | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know Competitive Technical | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Support Offerings/Solns | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know & Apply Integrated | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Product Development Proc | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand & Implement | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Solution Assurance Process | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Recommend New Technical | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| Support Offerings/Solns | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Apply Key Technical Support & | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| Services Reqmts | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| TECHNICAL SALES SUPPORT SPECIALTY SKILLS |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Develop Technical Sales | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Support Programs | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Installation Support | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Programs | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Demo Programs | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Utilize User Groups | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| HW/SW SERVICE(S) SPECIALTY SKILLS |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Understand & Apply IBM's HW | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Service Strategy | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand & Apply IBM's SW | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Services Strategy | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Use Root Cause Analysis | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Address Offering/Solution | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| Serviceability Reqmts | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Address Customer Sat & | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Loyalty Reqmts for Service | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand Hardware (HW) | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| Service T's&C's | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand Software (SW) | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| Services T's&C's | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| PRODUCT ENABLING SERVICES SPECIALTY SKILLS |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Define New Services | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Offerings/Solutions | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand Services Support | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Requirements | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand Services Business | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Management Process | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Services Business | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Plan | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Sample Services SOW | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| for Proposed Service | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Offerings/Solutions | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Strategy | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand Offering/Solution | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Profitability | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Distribution/End-User | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Coverage Strategy | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Terms Strategy | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
2.5.8 Professional Development
Education roadmaps will be provided at a later date.
2.5.9 Technical Support Marketing Position Descriptions
The following position descriptions describe the basic work of each of the
positions within the Marketing Professional Career. Formal descriptions
which may contain legally mandated language necessary for classifying
employees in a geography should be obtained through the approved on-line
job library, if available in the geography, or by contacting the
appropriate H.R. personnel within the geography.
Subtopics:
2.5.9.1 Position Title: Associate Technical Support Marketing Specialist
Position Summary and Responsibilities:
Working within a brand unit and/or business unit, assists with the
development of or develops technical support strategies and plans for some
non-complex offerings/solutions. Responsibility is typically limited to
one specialty within the Technical Support Marketing profession discipline
(e.g., Technical Sales Support, HW/SW Service(s), Product Enabling
Services, etc.). Interacts with some of the elements of the marketing mix
and related functions to ensure consistency of plans and programs
worldwide. Assists team in ensuring successful implementation of
technical support and services plans and programs within area of
responsibility. Monitors and measures the execution of non-complex plans
and programs, assists in the analysis of results, and makes
recommendations to the brand unit and/or business unit team for corrective
actions.
Skills
- Environment:
Applies basic professional knowledge of the technical support and
services environment to the attainment of business objectives for an
assigned area or project.
Demonstrates professional skill proficiency for this position.
- Communication/Negotiation:
Works with higher-level professionals on the selection of technical
support alternatives, services offerings/solutions and delivery
channels, as well as the identification of new approaches for
providing technical support and services for offerings and solutions.
As part of team responsibilities, assists with research and makes
recommendations for new, non-complex technical support alternatives
and related services offerings/solutions.
Negotiates to gather information from other functional and
professional areas.
On a limited basis, interacts with other professionals in
offering/solution development, brand unit and/or business unit
marketing and the technical support community on issues regarding
technical support and services.
- Problem Solving:
Recognizes problems related to assignments and recommends alternatives
for resolving them in line with existing guidelines and procedures.
Analyzes technical support marketing problems using existing
techniques and tools.
Analyzes processes and makes recommendations to change or update
current procedures with marketing/development staffs for optimum
marketplace results.
Contribution/Leadership
- Sets own work priorities for assignments within a related
marketing/technical support and services project that supports the
department's objectives, and seeks advice from other professionals
within the department.
- Understands department/function mission. Applies this understanding
to assigned areas of responsibility.
- Provides basic technical advice to less knowledgeable professionals
regarding the Technical Support Marketing profession discipline.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Is held accountable for the quality and timeliness of assignments.
- Assists in identifying for review measurement exposures for
non-complex technical support and services plans and programs.
- Contributes, on a limited basis, to business and customer and business
partner satisfaction and loyalty results, and monitors execution of
plans against brand unit and/or business unit objectives.
- Activities contribute, on a limited basis, to business results and
costs and expenses, as technical support and services programs are
implemented.
- Assists team with ensuring readiness of the technical support and
services delivery channels (e.g., skilled technical support and
services channels are identified and in place, training and support
materials are developed and delivered, infrastructure dependencies are
satisfied, etc.).
2.5.9.2 Position Title: Associate Technical Support Marketing Specialist (advanced)
Position Summary and Responsibilities:
Working within a brand unit and/or business unit, develops technical
support strategies and plans for non-complex offerings/solutions, or
participates in the development of strategies and plans for more complex
and/or global offerings/solutions. Responsibility is typically limited to
one specialty within the Technical Support Marketing profession discipline
(e.g., Technical Sales Support, HW/SW Service(s), Product Enabling
Services, etc.). Interacts with other elements of the marketing mix and
related functions to ensure consistency of plans and programs worldwide.
Participates with team in ensuring successful implementation of technical
support and services plans and programs within area of responsibility.
Monitors and measures the execution of plans and programs, assists in the
analysis of results, and provides feedback to the brand unit and/or
business unit team for corrective actions.
Skills
- Environment:
Applies professional knowledge of the technical support and services
environment to the attainment of business objectives for an assigned
area or project.
Demonstrates professional skill proficiency for this position.
- Communication/Negotiation:
Engages independently on the selection of technical support
alternatives, services offerings/solutions and delivery channels, as
well as the identification of new approaches for providing technical
support and services for offerings and solutions.
As part of team responsibilities, researches and recommends new
technical support alternatives and related services
offerings/solutions.
Negotiates with other team members (direct or virtual), and
individuals from other functional and professional areas, to define
technical support plans and programs.
Interacts with other professionals in offering/solution development,
brand unit and/or business unit marketing and the technical support
community on issues regarding technical support and services.
- Problem Solving:
Recognizes problems related to the function and to offerings/solutions
being developed to support brand unit and/or business unit objectives.
Applies creativity and judgment to defining and/or recommending
solutions to marketing and technical support and services issues.
Analyzes processes and challenges current procedures with
marketing/development staffs for optimum marketplace results.
Contriburion/Leadership
- Works on special projects on topics related to functional objectives.
- Controls own work priorities within a related marketing/technical
support and services project that supports the department's
objectives. May lead small virtual teams on project assignments.
- Understands department/function mission. Applies this understanding
to related activities.
- Provides advice to other professionals regarding the Technical Support
Marketing profession discipline or specialty issues throughout the
life cycle of an offering or solution.
- May discharge the basic management responsibilities common to all IBM
managers.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Accountable for achieving individual results for projects involving
cross-functional team activity.
- Identifies, estimates and presents for review measurement exposures
for technical support and services plans and programs.
- Contributes to business and customer and business partner satisfaction
and loyalty results, and monitors execution of plans against brand
unit and/or business unit objectives.
- Activities contribute to business results and costs and expenses, as
technical support and services programs are implemented.
- Shares responsibility with team for ensuring readiness of the
technical support and services delivery channels (e.g., skilled
technical support and services channels are identified and in place,
training and support materials are developed and delivered,
infrastructure dependencies are satisfied, etc.).
2.5.9.3 Position Title: Technical Support Marketing Specialist
Position Summary and Responsibilities:
Working within a brand unit and/or business unit, develops technical
support strategies and plans for complex offerings/solutions and/or
multiple offerings/solutions. Responsibility may cover more than one
specialty within the Technical Support Marketing profession discipline
(e.g., Technical Sales Support, HW/SW Service(s), Product Enabling
Services, etc.). Understands brand unit and/or business unit objectives
and plans and aligns plans and programs with them. Establishes and
maintains linkages with other elements of the marketing mix and related
functions to ensure that plans and programs are consistent worldwide and
present a single IBM image. Ensures successful execution of global and/or
geographic strategies and plans. Coordinates team efforts to monitor and
measure implementation of plans and programs, analyzes the results, and
provides recommendations to the brand unit and/or business unit team for
corrective actions.
Skills
- Environment:
Applies advanced professional knowledge of technical support and
services environment and related marketing activities to the
attainment of IBM and brand unit and/or business unit objectives.
Demonstrates professional skill proficiency for this position.
- Communication/Negotiation:
Advises and directs other team professionals on the selection of
technical support alternatives, related services offerings/solutions
and support delivery channels, as well as the identification of new
approaches to meet brand unit and/or business unit requirements.
Researches and recommends new technical support alternatives and
related services offerings/solutions.
Works effectively with other professionals on a direct or virtual
team. Guides, leads and selects team members (from own and other
functional and professional areas) to accomplish marketing and
technical support and services goals.
Negotiates effectively with team members and management across
functions to define goals and to develop technical support and
services offerings/solutions.
- Problem Solving:
Recognizes and articulates complex problems related to the function
and to offerings/solutions being recommended/developed to support
brand unit and/or business unit objectives.
Applies creativity and judgment in developing multiple/complex
solutions to address marketing and/or technical support issues and
objectives.
Analyzes problems and implements solutions involving
marketing/development staffs, business practices, etc. for optimum
marketplace results.
Contribution/Leadership
- Conducts projects on special topics related to functional objectives.
- Defines and controls objectives within a related marketing/technical
support and services project from a cost, schedule, technical and
quality perspective. Leads and guides the efforts of others in these
areas.
- Understands profession discipline and marketing function mission and
applies this understanding to related activities.
- Directly influences people outside of department and marketing
function by making recommendations that affect their area.
- Provides on-going business guidance to team members throughout the
life cycle of the offering/solution. Leads projects and is
responsible for results. Leads and motivates team members.
- May discharge the basic management responsibilities common to all IBM
managers.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Accountable for achieving results of projects involving
cross-functional teams.
- Regularly participates in overall functional planning. Identifies,
estimates and presents business measurement exposures for technical
support and services plans and programs.
- Activities directly contribute to business and customer and business
partner satisfaction and loyalty results. Monitors execution of plans
against brand unit and/or business unit objectives and recommends
corrective actions.
- Activities impact business plan costs and expenses, as technical
support and services plans and programs are implemented.
- Coordinates activities of team to ensure the readiness of technical
support and services delivery channels (e.g., skilled technical
support and services channels are identified and in place, training
and support materials are developed and delivered, infrastructure
dependencies are satisfied, etc.).
2.5.9.4 Position Title: Technical Support Marketing Specialist (advanced)
Position Summary and Responsibilities:
Working within a brand unit and/or business unit, directs the development
and implementation of technical support and services strategies and plans
for multiple complex offerings/solutions for a major business unit and/or
geography. Regarded as an expert in at least one specialty within the
Technical Support Marketing profession discipline (e.g., Technical Sales
Support, HW/SW Service(s), Product Enabling Services, etc.). Drives the
relationship of the Technical Support Marketing team with other elements
of the marketing mix, and related functions, and ensures synergy and
consistency of plans and programs worldwide and that they present a single
IBM image. Responsible for successful deployment of global strategies and
plans (all dependencies are satisfied, financial targets met and programs
are in place to ensure the readiness of the technical support and services
delivery channels). Assesses results of plans and programs against
objectives, and drives necessary changes to marketing/services/development
plans and programs. This is a leadership position within a geography or
major brand unit and/or business unit.
Skills
- Environment:
Applies expert knowledge of the technical support and services
environment and related marketing activities to the development of
global technical support and services strategies, plans and programs
that align with IBM and brand unit and/or business unit strategic
marketing objectives.
Demonstrates skill proficiency level for this position.
- Commuication/Negotiation:
Negotiates plan requirements with executive management in other
profession disciplines and other functions to obtain agreement on
technical support and services strategies, plans and programs, as well
as resource requirements.
Guides other professionals. Acts as a mentor to others in the
Technical Support Marketing function. Provides guidance to team
members in developing new or complex technical support alternatives
and related services offerings/solutions.
- Problem solving:
Anticipates potential major business unit/geography technical support
issues. Utilizes refined problem-solving skills to identify,
eliminate or contain potential business risks when developing and
executing technical support and services strategies and plans.
Understands future offering/solution trends. Analyzes competitive
offerings/solutions and strategies and assesses them for impact on
current/proposed technical support and services plans and programs.
Develops innovative offerings/solutions with a global perspective.
Contribution/Leadership
- Conducts special projects. Leads team in exploring leading-edge
technical support and services alternatives, and guides the efforts of
others in understanding and delivering on brand unit and/or business
unit objectives.
- Demonstrates understanding of profession discipline and marketing
function strategic vision/mission and applies this to all activities.
- Influences people and organizations, including executive management,
when issues are complex or difficult and require considerable
diplomacy. Is respected and recognized as an expert in the Technical
Support Marketing profession discipline.
- Leads cross-functional teams on strategic initiatives in complex
and/or emerging areas.
- May discharge the basic management responsibilities common to all IBM
managers.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Accountable for complex projects including cross-functional,
geographic and/or major business unit teams. Responsible for overall
program success.
- Responsible for major components in functional planning. Develops
technical support and services strategies, plans and programs, with
executive review. Identifies, estimates and resolves cost/expense
issues associated with brand unit and/or business unit financial
objectives, and with the delivery of the brand "promise of value"
and/or business unit value proposition.
- Activities are subject to business measurement, relate directly to
customer and business partner satisfaction and loyalty results and
drive follow-on business through delivery of technical support and
services for multiple, complex and/or leading-edge
offerings/solutions.
- Activities impact business measurements for the marketing function in
a major business unit or geography.
2.5.9.5 Position Title: Senior Technical Support Marketing Specialist
Position Summary and Responsibilities:
Working within a major business unit or geography, leads the development
and deployment of global technical support and services strategies and
plans for multiple and complex offerings/solutions for multiple
specialties (e.g., Technical Sales Support, HW/SW Service(s), Product
Enabling Services etc.); or, spanning multiple brand units and/or business
units, leads the development and deployment of global technical support
and services strategies and plans for multiple and complex
offerings/solutions for one or more specialties. Contributes to policy
formulation to align technical support and services offerings/solutions
with brand unit and/or business unit strategies, meet IBM and brand unit
and/or business unit financial targets and deliver the brand "promise of
value" and/or business unit value proposition for technical support and
services. Conducts complex negotiations within the Technical Support
Marketing function, with other elements of the marketing mix, and related
functions, to drive synergy and consistency of plans and programs
worldwide and present a single IBM image. Drives successful deployment of
global strategies and plans. Anticipates potential problems and drives
mid-course corrections with marketing/services/development teams.
Develops and sets measurement objectives for technical support and
services on a geographic and/or global basis and ensures their attainment.
This is a position denoting worldwide leadership within the Technical
Support Marketing profession discipline, and typically reports to
executive management within a geography or brand unit and/or business
unit.
Skills
- Environment:
Applies professional expertise to defining and leading the development
of programs and technical support and services offerings/solutions in
leading-edge or critical situations, and on projects of strategic
importance to IBM. Demonstrates professional mastery in the technical
support and services environment and related marketing activities.
Demonstrates the skill proficiency level for this position.
- Communication/Negotiation:
Leads negotiations with executives and managers from other profession
disciplines and other functions to define team goals and approaches
for attaining them. Adapts communication techniques to conclude
negotiations with various organizations which result in common
agreement on technical support strategies, plans and programs.
Ensures clear feedback to major business units and/or geographic teams
for action items.
Guides other professionals. Acts as a mentor to others in the
Technical Support Marketing function. Leads the development of new,
complex and/or leading-edge technical support alternatives and related
services offerings/solutions.
- Problem Solving:
Anticipates future customer requirements, market/channel needs and
business trends, as well as potential technical support and services
issues within a major business unit or geography. Applies this
understanding to developing a strategic vision for technical support
and services which influences business area, geography and global
objectives..
Develops and implements technical support and services, marketing,
and/or brand unit and/or business unit strategies, with executive
review.
Contribution/Leadership
- Engages in teamwork at the highest management and professional levels
of IBM.
- Articulates technical support and services vision/mission to address
long-term IBM, marketing, business and technology directions, and
guides related business area strategies. Ensures the development of
needed skills within the profession discipline and the professional
growth of all Technical Support Marketing team members.
- Recognized as the expert and leader in the Technical Support Marketing
profession discipline by other members of the marketing profession,
related functions and geographic organizations.
- Leads brand unit and/or business unit, geographic, and/or global
Technical Support Marketing teams.
- May discharge the basic management responsibilities common to all IBM
managers.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Accountable for the success of technical support and services programs
within a geography or globally.
- Develops and deploys global technical support and services strategies
for multiple offerings/solutions and/or for multiple brand units
and/or business units, with executive management review and
concurrence.
- Leads in the development of global technical support and services
policies and practices.
- Responsible for committing multiple resources, achieving customer and
business partner satisfaction, expense, revenue and all other critical
business measurements and building customer and business partner
loyalty.
- Responsible for delivering differentiated technical support and and
related services offerings/solutions, achieving quality results and
delivering customer value.
2.5.10 Technical Support Marketing Specialty Descriptions
Subtopics:
2.5.10.1 Specialty Title: Technical Sales Support Specialty
Specialty Summary:
An individual working in this Technical Support Marketing specialty
develops strategies and ensures enablement for the technical sales and
installation support that is required for an offering or solution. This
includes, in general, the non-fee support associated with the
offerings/solutions related to technical sales and installation
assistance. The objective is a satisfied and loyal customer at the
conclusion of the installation activity.
Responsibilities:
- Works closely with technical sales support organizations that perform
direct customer and business partner sales and installation support in
geographies to understand requirements for technical sales support in
all environments (e.g., face-to-face, voice, electronic, etc.).
- Defines the technical sales support coverage model, skills and
resources required to achieve business objectives (IBM and non-IBM
channels).
- Influences and provides marketing guidance to all technical sales
support delivery channels (e.g., IBM, business partners, Internet,
etc.)
- Ensures appropriate education, training and certification testing
are developed and available to enable all channels prior to
offering/solution availability and throughout the life cycle of
the offering/solution.
- Assures availability of technical sales and installation support
tools (e.g., configurators, sizing tools, demonstration support,
marketing campaign support, etc.) to all sales and technical
support channels to drive placement of IBM offerings/solutions.
- Initiates actions to meet "special" technical sales requirements
(those needing immediate attention to satisfy sales objectives or
customer satisfaction concerns), such as: "critical situations,"
"hotline" support, solution centers, information dissemination,
etc.
- Understands customer satisfaction and loyalty measurements for
technical sales support and plays a key role in defining actions to
generate "best of competition" customer satisfaction and loyalty
results.
- Understands and addresses the needs of "user groups," such as GUIDE,
COMMON, SHARE, in order to increase customer awareness of new
offerings/solutions and to transfer skills and knowledge directly to
customers.
- Ensures deployment of the Solution Assurance Process and development
of SAPR guides and tools to facilitate quality engagements resulting
in satisfied and loyal customers.
- Integrates overall technical sales support requirements into the
development process and consolidates all requirements into global
technical support strategies and plans.
2.5.10.2 Specialty Title: HW/SW Service(s) Specialty
Specialty Summary:
An individual working in this Technical Support Marketing specialty
develops strategies and ensures enablement for the hardware and/or
software service(s) required to support the customer over the life cycle
of an offering or solution and to provide IBM and brand differentiation.
This specialty typically focuses on hardware maintenance and software
service(s) related to defect and usage.
Responsibilities:
- Understands customer satisfaction and loyalty measurements for HW and
SW service(s), assists in performing root cause analysis, and plays a
key role in defining actions to generate "best of competition"
customer satisfaction and loyalty results.
- Ensures that appropriate maintenance, service(s) offerings/solutions
and skilled resources are in place to support customer installations
over the life cycle of an offering/solution.
- Establishes linkages with development, HW and SW service(s) delivery,
sales, finance, customers, etc.:
- To ensure that serviceability requirements are defined and driven
into offering/solution plans based on customer feedback mechanisms
- To ensure that quality HW and/or SW service(s) are available at
"offering/solution availability" (i.e., Early Support Programs or
General Availability)
- To play a pivotal role in establishing appropriate entitlements
and customer expectations for IBM HW and/or SW service(s) during
the development and announcement processes
- To ensure capability of brand units and/or business units,
cross-brand units and/or business units, and other Marketing
Profession strategies and plans
2.5.10.3 Specialty Title: Product Enabling Services Specialty
Specialty Summary:
An individual working in this Technical Support Marketing specialty
defines and ensures the development and availability of the skilled
resources and Product Enabling Services offerings/solutions (e.g.,
"SmoothStart," migration and assistance, etc.) needed to drive placement
of offerings and solutions. Generally, these services are fee-based and
locally delivered by channels (IBM and business partners) and assist the
customer in enabling and exploiting hardware and/or software offerings and
solutions.
Responsibilities:
- Teams with offering/solution and services development to identify
customer, business partner and market requirements, define
offering/solution composition and ensure that services are a part of
brand unit and/or business unit offerings and solutions and marketing
campaigns.
- Architects "best of competition" services which support brand unit
and/or business unit strategies and plans.
- Builds the business plan and secures funding for new services
offerings/solutions which best meet brand unit and/or business
unit financial targets.
- Identifies services delivery channels using Routes to Market
methodologies for offerings and solutions.
- Provides critical feedback to brand unit and/or business unit
marketing, offering/solution and services development and the
support channels to ensure profitability, and customer and
business partner satisfaction.
- Initiates and oversees development of Product Enabling Services
offerings/solutions.
- Provides input to the announcement process through the development
process.
- Ensures readiness of services delivery channels at "availability" (ESP
and/or GA) with the required technology, tools, packaged services,
sales support mechanisms, skills, education offerings, services
perform deliverables, etc.
2.6 Chapter 9. Marketing Communications Profession Discipline
Subtopics:
2.6.1 Marketing Communications Profession Discipline Overview
Marketing Communications is one of six profession disciplines within the
Marketing Professional Career (see "Professional Career Structure" in
topic 2.1.2) and is an integral part of the successful implementation of
the marketing mix of elements. Marketing Communications focuses its
efforts on developing strategies, plans and programs for advertising,
collateral/sales promotion, business shows, corporate sponsorships, sports
marketing, and/or media strategy, planning and buying, in support of
corporate, category, brand unit and/or business unit objectives.
Marketing Communications Specialists are responsible for developing
integrated marketing communications strategies and programs which are
designed to communicate with IBM's current and potential customers,
business partners, suppliers, constituents, and the general public in
order to create a positive image for IBM, thereby increasing demand and
loyalty for IBM offerings and solutions.
In order to successfully develop long-range strategies and plans and
execute strategic marketing communications programs, Marketing
Communications Specialists must have a comprehensive understanding of
IBM's culture, and of IBM as a business, an organization, and an industry
leader. Marketing Communications Specialists are adept at examining the
environmental factors and cultural variables that influence consumer
behavior and buyers' decision-making. They expertly use this information
to develop creative and innovative strategies, plans and programs that
provide a competitive advantage for the IBM brand and/or the brand unit
and/or business unit and positively affect customer behavior, increase
awareness and get measurable, actionable results.
Working with marketing managers and marketing communications researchers,
they define appropriate communications research methods and use market
research tools and techniques to help determine program objectives and
desired response. They are skilled at obtaining measurable results for all
programs and using results to improve future programs.
Marketing Communications Specialists commit significant financial
resources for program implementation and coordinate the efforts of direct
and/or virtual teams of internal and external resources at levels which
significantly impact budgets and other fiscal activities.
2.6.2 Profession Discipline Structure
The Marketing Profession uses three titles for the five professional
positions. The prefix "Associate" is used for the lowest of these
positions. No prefix is used for the middle two positions and the prefix
"Senior" is used for the highest position. All five positions do not
occurr in all of the Marketing Profession disciplines.
The following positions are defined within the Marketing Communications
profession discipline:
- Associate Marketing Communications Specialist
- Associate Marketing Communications Specialist (advanced)
- Marketing Communications Specialist
- Marketing Communications Specialist (advanced)
- Senior Marketing Communications Specialist
The Marketing Communications profession discipline is comprised of five
specialties as follows:
- Advertising
- Collateral/Sales Promotion
- Business Shows
- Corporate Sponsorships
- Sports Marketing
- Media Strategy, Planning & Buying
Marketing Communications Specialists are expected to demonstrate expertise
in at least one specialty depending on the size and scope of the
organization to which they report, and on assigned responsibilities and
job position. In addition, individuals assigned to the role of Project
Leader or Planner will add to their skills profile the skills template for
those role (see "Marketing Professional Career Skills Profile" in
topic 2.1.10, for role skills).
2.6.3 Characteristics of the Profession Discipline
Marketing Communications professionals have the following characteristics:
- Effective in creating and implementing operationally-detailed plans
that best support business objectives.
- Knowledgeable about business situations, customer behaviors, wants and
needs, marketplace trends and directions, competitive strategies, and
customer feedback.
- Effective in applying qualitative and quantitative communications
research techniques such as focus groups and STARCH Readership
reports.
- Knowledgeable about the IBM Market Management process and marketing
communications processes to be more customer- and market-driven within
a strategic marketing communications framework.
- Effective in selecting the best tools (e.g., advertising,
sponsorships, business shows, etc) from the communications mix that
achieve business objectives.
- Effective in developing integrated marketing communications plans
based on marketplace information and brand unit and/or business unit
objectives.
- Effective in developing marketing communications strategies and plans.
- Skilled in developing creative and innovative marketing communications
programs aimed at increasing customer acceptance of IBM offerings and
solutions.
- Skilled in project management methods and tools.
- Strong leadership and teamwork skills.
2.6.4 Potential Candidates
Marketing Communications Specialists may be sourced from current IBM
employees with the requisite skills in Marketing Communications and with
expertise in at least one of the Marketing Communications specialties.
Marketing Communications Specialists may also be sourced from professional
hires who have expertise in one or more specialty, or who have expertise
in marketing management.
Figure 9-1 illustrates the the possibilities for movement to and from the
Marketing Communications Profession Discipline.
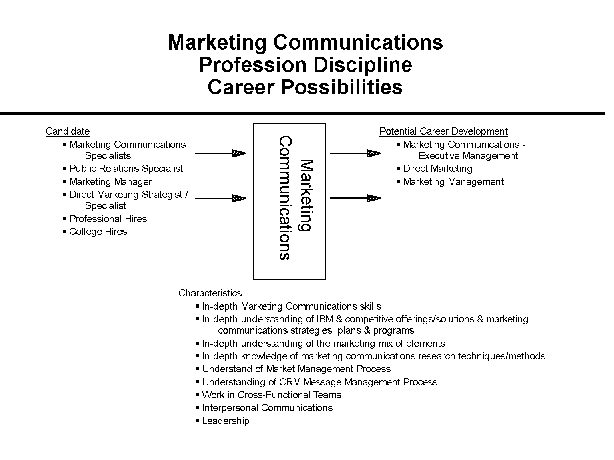
Figure 9-1. Marketing Communications Profession Discipline Career
Possibilities
2.6.5 Career Growth
Marketing Communications professionals may be assigned positions from
Associate Marketing Communications Specialist through Senior Marketing
Communications Specialist. The difference between the ascending positions
is a function of increasing skill, capability, experience, and
responsibility, and is reflected in the extent of an individual's
demonstrated leadership, the size and scope of his/her contributions and
impact on the business.
Growth in this discipline can be achieved through the acquisition of
skills and experiences that enable an individual to work in multiple
specialty areas. Professionals can also rise to levels comparable to
executive management and career path movement can occur in accordance with
planned steps into and through other professions.
2.6.6 Performance Elements
The Marketing Communications Specialist creates awareness for IBM
offerings/solutions and enhances the image of IBM, and therefore
indirectly contributes to resulting revenue. Marketing Communications
professionals help create awareness for IBM offerings/solutions, enhance
the image of IBM, the brand unit and/or business unit overall. A marketing
communication professional is expected to deliver a high level of
satisfaction to IBM, the brand unit and/or business unit, target markets,
customers, business partners, and the general public.
2.6.7 Marketing Communications Profession Discipline Skills Profile
The skills required of a Marketing Communications professional are as
follows:
- General Marketing Skills - required of all individuals in any
Marketing Profession discipline
- IBM Internal Skills - required of all individuals in any Marketing
Profession discipline
- Marketing Communications Discipline Specialty Skills
- Marketing Profession Role Skills - for individuals assigned to one of
the Marketing Profession roles (see "Marketing Professional Career
Skills Profile" in topic 2.1.10, for role skills)
_______________________________ ________________________________________
| | Profession Discipline Positions, with |
| | Associated Skill Levels |
| |________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| MARKETING COMMUNICATIONS | Assoc | Assoc | | Mktg | Senior|
| SKILLS | Mktg | Mktg | Mktg | Comm | Mktg |
| | Comm | Comm | Comm | Spec | Comm |
| | Spec | Spec | Spec | (adv) | Spec |
| | | (adv) | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| GENERAL MARKETING SKILLS |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Know & Apply Marketing | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Concepts & Methods | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know & Apply Mkt Intelligence | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| Concepts & Methods | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand Customer Reqmts & | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| Buying Behaviors | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know & Apply Market | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Segmentation | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Strategies | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Plans | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Programs | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Use Persuasive Ideas & | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| Language | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Use Copywriting Techniques | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Communicate-Appeal to Target | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Audience Values | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Key Message | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Strategies | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Select Among Media | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Alternatives-Message | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Define Research Projects | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know & Apply IBM Brand Naming | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Strategies | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| IBM INTERNAL SKILLS |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Know & Apply IBM Brand | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Business Management System | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Explain IBM Business Strategy | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand the IBM Brand | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Strategy | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand/Anticipate/Respond | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| - Competitive Trends | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Articulate IBM | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| Offerings/Technologies | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| IBM Formal & Informal Network | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Work in Cross-Functional | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Teams | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand IBM Global | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Operations | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Creativity/Breakthru Thinking | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Interpersonal Communication | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Negotiation | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Problem Solving & Decision | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Making | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Apply Basic Financial | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Concepts | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Apply Project Management | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Techniques | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Self-Directed Learning | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand WW CRM Message | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Management Process | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Intellectual Capital | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Business Intellect | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Explain IBM Communications | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Vision/Strategy | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| IBM Vision/Mission/Strategy | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Plan Projects | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Project Track/Report/Deliver | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Report on Projects | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Manage Project Risk | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Manage Contracted Resource & | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Services | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Leadership | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Foster Teamwork/Enable Teams | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Risk/Awareness Taking | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Apply Technologies & Tools | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Consulting Methods | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Perform Time Management | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| ADVERTISING SPECIALTY SKILLS |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Develop Advertising Programs | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know & Apply Advertising | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Measurement Techniques | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand | | | | | |
| Advertising/Promotion Agency | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Operations | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand Creative | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Development Concepts | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand 2-Dimensional | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Design | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know TV/Video Production | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand Market Segment | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| Business Plan | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| COLLATERAL/SALES PROMOTION SPECIALTY SKILLS |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Develop Collateral/Sales | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Promotion Programs | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know & Apply Advertising | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Measurement Techniques | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand | | | | | |
| Advertising/Promotion Agency | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Operations | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand Creative | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Development Concepts | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand 2-Dimensional | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Design | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know TV/Video Production | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand Market Segment | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| Business Plan | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| BUSINESS SHOWS SPECIALTY SKILLS |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Develop Marketing Special | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Events Programs | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know & Apply Advertising | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Measurement Techniques | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Select Trade/Business Shows | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know & Apply Exhibit Design & | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Construction | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand Creative | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Development Concepts | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand 2-Dimensional | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Design | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know TV/Video Production | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand Market Segment | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| Business Plan | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| CORPORATE SPONSORSHIPS SPECIALTY SKILLS |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Develop Corporate Sponsorship | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Programs | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Press/Media Relations | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Deliverables | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know & Apply Advertising | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Measurement Techniques | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand | | | | | |
| Advertising/Promotion Agency | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Operations | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand 2-Dimensional | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Design | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand Creative | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Development Concepts | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand TV/Video | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Production | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| SPORTS MARKETING SPECIALTY SKILLS |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Develop Sports Marketing | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Programs | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Press/Media Relations | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Deliverables | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know & Apply Advertising | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Measurement Techniques | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand | | | | | |
| Advertising/Promotion Agency | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Operations | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand 2-Dimensional | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Design | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand Creative | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Development Concepts | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand TV/Video | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Production | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| MEDIA STRATEGY, PLANNING & BUYING SPECIALTY SKILLS |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Know & Apply Media Planning | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Development | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know & Apply Media Audience & | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Distrb Meas Techs | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know & Apply Advertising | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Measurement Techniques | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Select, Evaluate & Negotiate | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Media Opportunities | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know & Apply Media Ordering & | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Billing | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Manage Media Budgets & | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Expenditures | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Know & Apply Media | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Post-Analysis | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Understand | | | | | |
| Advertising/Promotion Agency | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Operations | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
2.6.8 Professional Development
Education roadmaps will be provided at a later date.
2.6.9 Marketing Communications Position Descriptions
The following position descriptions describe the basic work of each of the
positions within the Marketing Professional Career. Formal descriptions
which may contain legally mandated language necessary for classifying
employees in a geography should be obtained through the approved on-line
job library, if available in the geography, or by contacting the
appropriate H.R. personnel within the geography.
Subtopics:
2.6.9.1 Position Title: Associate Marketing Communications Specialist
Position Summary and Responsibilities:
Works on marketing communications activities and projects that support the
department's mission or that are part of the implementation of marketing
communications programs for the brand unit and/or business unit.
Assignments are primarily limited within a single marketing communications
specialty, such as advertising, collateral/sales promotion, business
shows, etc. Marketing communications objectives and programs are defined
by management or senior professionals in the department or by work group,
and generally fall within established guidelines and procedures. Requires
basic marketing communications skills. Knowledge of IBM's business is
acquired through work assignments.
Skills
- Environment:
Applies basic professional knowledge to assigned marketing
communications activities and projects in support of the day-to-day
business operations of the brand unit and/or business unit and/or
departmental objectives.
Demonstrates the skill proficiencies for this position.
- Communications/Negotiation:
Works with higher-level professionals, learning from them and
assisting them in carrying out marketing communications activities and
programs for which they are responsible. Absorbs business knowledge
quickly to develop professional effectiveness.
Negotiates with other marketing communications functions and marketing
departments to obtain information and data needed for the assignment
or project.
- Problem Solving:
Recognizes problems when they arise and resolves them in line with
existing guidelines and procedures.
Uses professional skills to determine the best approach to achieve
marketing communications effectiveness for assigned tasks.
Contributes to the development and implementation of new marketing
communications techniques and improvements to departmental processes.
Contribution/Leadership
- Works at a professional level and is reviewed as required for
developmental purposes.
- Understands the value of the work assigned and its contribution to the
brand unit and/or business unit or department overall mission.
- May draw upon marketing communications skills and knowledge to
recommend improvements to the marketing communications deliverables.
- May provide some technical direction and assistance to less
knowledgeable department or team members.
Impact of Business/Scope
- Is accountable for the quality and timeliness of completed
assignments. Is also responsible for evaluating the services or
materials that are purchased from creative service providers. May
select vendors to perform services.
- Assignments may be part of a larger project or campaign which may
affect the acceptance of the brand unit and/or business unit
objectives, performance, profitability and customer satisfaction.
- Timeliness and quality of completed assignments affect client
satisfaction in the brand unit and/or business unit, department or
function being supported.
2.6.9.2 Position Title: Associate Marketing Communications Specialist (advanced)
Position Summary and Responsibilities:
Plans and implements marketing communications programs that are part of an
overall marketing communications program or part of the total
communications support provided to a brand unit and/or business unit.
Involvement is typically limited to one marketing communications specialty
at one time (e.g. advertising, collateral/sales promotion, business shows
etc.). Marketing Communications objectives and programs are typically
defined by management or by senior professionals, but approaches and
activities used to achieve marketing communications effectiveness are
often left to the professional to define and negotiate. Requires
knowledge of the brand/business unit and/or organization's mission,
culture, products and services.
Skills
- Environment:
Applies professional knowledge to marketing communications activities
and programs in support of the day-to-day business operations of the
brand unit and/or business unit. Understands IBM and brand unit
and/or business unit strategies and business objectives.
Demonstrates the skill proficiencies for this position.
- Communications/Negotiation:
Determines and compares alternative approaches that can be taken to
achieve marketing communications effectiveness and negotiates a
solution by articulating the merits of each approach.
Identifies those factors and/or inhibitors that may affect the success
of an assignment and develops/recommends plans for its successful
implementation.
- Problem Solving:
Uses creativity and sound business judgment in maximizing marketing
communications effectiveness by going beyond traditional
implementation approaches.
Develops and recommends new marketing communications concepts and
techniques. Also works to improve and streamline departmental
procedures and processes.
Contribution and Leadership
- Works on special marketing communications projects and programs that
may support brand unit and/or business unit and/or departmental
objectives. May manage the technical and operational activities of
assigned programs.
- Generally controls own work priorities and makes tradeoffs to ensure
brand unit and/or business unit and/or departmental marketing
communications objectives, budgets and schedules are met.
- Works to underscore and enhance the department's value to the brand
unit and/or business unit organization it supports.
- Draws upon marketing communications skills and knowledge to recommend
improvements to marketing communications deliverables in development.
- Provides technical direction and assistance to less knowledgeable
department or team members.
- May discharge the basic management responsibilities common to all IBM
managers.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Is accountable for the quality and timeliness of completed
assignments. Is also responsible to ensure that value is received for
creative services or materials that are purchased. May select
vendors to perform services.
- Assignments may range from a small independent program, project or
campaign which may affect the acceptance of the brand unit and/or
business unit objectives, performance, profitability and customer
satisfaction.
- Timeliness and quality of completed assignments affect client
satisfaction in the brand unit and/or business unit, department or
function being supported.
2.6.9.3 Position Title: Marketing Communications Specialist
Position Summary and Responsibilities:
Plans, develops and leads the implementation of key marketing
communications programs and assignments of a complex nature in support of
brand unit and/or business unit objectives. Involvement spans one or more
marketing communications specialties at one time (e.g., advertising,
collateral/sales promotion, business shows, etc.).. Works with management
and more senior professionals to define programs and objectives but
approaches and activities used to achieve marketing communications
effectiveness are the responsibility of the professional to define and
negotiate. Identifies and evaluates relevant factors and/or inhibitors
which may affect the success of these programs, and develops action plans.
Requires an understanding of the brand and/or business unit objectives and
business plans, as well as knowledge of the competitive environment and
industry trends.
Skills
- Environment:
Applies advanced professional knowledge to assigned marketing
communications programs and activities in support of brand/buisness
unit business objectives. Has an overall understanding of IBM and the
brand/business unit strategy and current status, and can articulate
Demonstrates the skill proficiencies for this position.
- Communications/Negotiation:
Works effectively in a team environment, which may include members
from other functions, vendors and external partners. Guides the team
in accomplishing its goals, and negotiates the details of program
implementation with management and team members.
- Problem Solving:
Analyzes the objectives and implications of major marketing
communications programs. Recognizes problems and uses creativity and
sound judgment to develop and recommend workable solutions.
Makes recommendations to more senior professionals and management in
the department on assigned marketing communications activities and
related work as they affect the entire marketing organization.
Develops, recommends and implements new marketing communications
concepts and techniques that enhance marketing communications
effectiveness, and works to ensure their use. Recommends improvements
to departmental procedures and processes. Communicates direction to
lower-level team members.
Contribution/Leadership
- Conducts special projects that support brand unit and/or business unit
and/or departmental objectives as requested by executive management.
- Manages the implementation of complex marketing communications
programs. Defines work objectives and assignments for less-experienced
professionals, vendors and external partners. Also advises and
directs the activities of these individuals and/or organizations.
- Contributes to the overall mission of the department or function.
- Provides technical advice to peers and lower-level professionals.
- Leads implementation teams assigned to a program or project.
- May discharge the basic management responsibilities common to all IBM
managers.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Is accountable for the effectiveness of assigned marketing
communications programs, and for their impact on brand unit and/or
business unit or departmental results. Ensures that value is received
for creative services or materials that are purchased and recommends
areas for quality, cost and schedule improvements. Selects vendors to
perform services.
- Participates in departmental planning.
- Assigned activities contribute to the overall effectiveness of
marketing communications programs which are designed to positively
affect customer behavior, increase awareness, and get measurable,
actionable results.
- Assigned activities contribute to line management's view of the
marketing communications function within the brand unit and/or
business unit.
- Has budgetary responsibility.
2.6.9.4 Position Title: Marketing Communications Specialist (advanced)
Position Summary and Responsibilities:
Develops strategies and plans for marketing communications programs and
activities in support of the brand/business unit's business objectives.
Leads program implementation. Involvement spans multiple marketing
communications specialties at one time (e.g., advertising,
collateral/sales promotion, business shows, etc.) with a mastery in at
least two. Is able to articulate the brand unit and/or business unit
strategy and current events in the external environment -- both from a
professional and business standpoint. Anticipates reaction and identifies
issues which may arise from strategic business decisions or from current
or planned programs. This is a leadership position typically found at the
geography or major brand unit and/or business unit or corporate level.
Skills
- Environment:
Applies expert professional knowledge and expertise to assigned
marketing communications programs and activities in support of
brand/business unit strategic business objectives. Possesses a
high-level of understanding of IBM, geography or major brand unit
and/or business unit strategy and current status, and can speak with
confidence on these matters.
Demonstrates the skill proficiencies for this position.
- Communications/Negotiation:
Provides advice and counsel to other marketing profession disciplines
and other functions in a brand unit and/or business unit on all
aspects of marketing communications policies and programs for a
geography or major brand unit and/or business unit. Acts as a mentor
to those with less experience. Ensures the work of lower-level
professionals, vendors and external partners meets established
standards for quality and usability.
Negotiates at the executive level to obtain agreement on marketing
communications strategies and programs, as well as for implementation
of programs and resource requirements.
- Problem Solving:
Plans and develops marketing communications programs and strategies
that support the brand unit and/or business unit objectives, including
product announcements and initiatives of a complex or sensitive
nature. Leads program implementation, anticipates public reaction and
issues which may arise.
Analyzes the internal and external environment, as well as industry
trends, for their impact on marketing communications programs and
objectives. Recommends to executive management position statements and
other marketing communications actions as needed.
Contribution/Leadership
- Manages the implementation of special marketing communications
programs and projects of a complex nature, as requested by executive
management. Defines work objectives and manages assignments for less
experienced professionals, vendors, and external partners. Advises
and directs the activities of these individuals and/or organizations.
- Is recognized for professional expertise in marketing communications.
Has expertise in two or more marketing communications specialties
(e.g., advertising, collateral/sales promotion, business shows, etc.).
- Contributes to the overall mission of the department or function.
Participates in functional planning.
- Acts as a technical advisor to the department and other marketing
functions.
- May discharge the basic management responsibilities common to all IBM
managers.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Is accountable for achieving maximum effectiveness for marketing
communications programs and activities, while ensuring schedules are
met and costs, as agreed to by management, are controlled.
- Assigned activities affect the achievement of the brand unit and/or
business unit objectives, performance, profitability and customer
satisfaction.
- Assigned activities and actions impact line management's view of the
marketing communications function within the brand unit and/or
business unit.
- Purchases creative services or materials to meet schedule requirements
and job specifications. Has budgetary responsibility.
2.6.9.5 Position Title: Senior Marketing Communications Specialist
Position Summary and Responsibilities:
Manages strategies and plans for marketing communications programs and
activities in support of the brand unit and/or business unit business
objectives. Also acts in a consulting capacity, providing marketing
communications advice and counsel to executive line management. Work
output is of the highest level, demonstrating mastery in two or more
marketing communications specialties (e.g., advertising, collateral/sales
promotion, business shows, etc.). Is recognized as the expert in all
aspects of marketing communications by line management for knowledge and
understanding of the business. This is a position denoting worldwide
leadership in the marketing communications discipline, and typically
reports to senior marketing communications management at the geography,
business unit or corporate level.
Skills
- Environment:
Applies professional knowledge and expertise on all marketing
communications programs and activities in support of brand unit and/or
business unit strategic business objectives. Possesses in-depth
awareness and understanding of IBM/brand unit and/or business unit
business strategy and current status, and speaks with authority on
these matters.
Demonstrates the skill proficiencies for this position.
- Communications/Negotiations:
Provides expert guidance and acts as a mentor to other marketing
communications professionals and to professionals in other marketing
functions, demonstrating a high-level of knowledge, expertise, and
sound judgment. Sets quality standards for the work by lower-level
professionals, vendors and external partners.
Plans and conducts complex negotiations for assigned marketing
communications strategies and programs, as well as for the overall
implementation of programs and resource requirements. Reaches
consensus and gains lasting agreements.
- Problem Solving:
Anticipates reaction and potential issues which may arise from
strategic business decisions and from current or planned programs.
Designs and develops, with executive review, corresponding marketing
communications strategies and support/response programs.
Contribution and Leadership
- Develops integrated marketing communications strategies which provide
competitive advantage for the brand unit and/or business unit.
Develops creative and innovative marketing communications programs
designed to positively affect customer behavior, increase awareness,
and get measurable, actionable results.
- Is recognized as an expert and leader in the marketing communications
discipline by other professionals and executives, on a worldwide
basis. Provides expert advice and counsel that influences executive
management when making complex and difficult business decisions.
- Operates with significant autonomy in managing assigned marketing
communications activities, taking the lead in bringing together
relevant functions within IBM as needed.
- Contributes to setting direction and vision for the brand unit and/or
business unit marketing communications function.
- May discharge the basic management responsibilities common to all IBM
manages
Impact on Business/Scope
- Is accountable for complex to very complex marketing communications
programs that support the brand unit and/or business unit strategic
business objectives.
- Is accountable for directing the activities which directly affect the
achievement of the geography or major brand unit and/or business unit
objectives, performance, profitability and customer satisfaction.
- Activities directly influence how executive management views the
marketing communications function in the brand/business unit and
contribute to the perception of IBM's marketing communications
externally.
- Commits financial resources and coordinates human resources at levels
which significantly impact budgets and other activities. Is
responsible for ensuring project completion within identified cost,
schedule and functional requirements.
2.6.10 Marketing Communications Specialty Descriptions
Subtopics:
2.6.10.1 Specialty Title: Advertising
Specialty Summary:
Individuals working in this Marketing Communications specialty initiate
and direct advertising programs in support of IBM's goal to become the
industry leader in key market segments. They assist marketing executives
in refining marketing plans and from these plans develop effective
advertising plans. They develop close working relationships with marketing
executives as well as the senior management in the business units
supported. They maintain contacts with these senior executives to ensure
advertising strategy and execution are consistent with marketing
strategies. They direct the efforts of IBM's advertising agency and
provide leadership and guidance in order to keep them motivated,
productive and on schedule. Individuals in this specialty routinely
conduct research to understand communications and marketing effectiveness
of advertisements.
Responsibilities:
- Analyzes marketing plans for the marketing function and develops
advertising recommendations and strategies that visibly contribute to
the accomplishment of marketing goals as defined by the business
plans.
- Analyzes customer wants and needs and incorporates them into
long-range advertising strategies and plans that establish effective
dialogue with customers and prospects.
- Establishes advertising plans in support of sales objectives and
issues. Manages and directs advertising programs to achieve optimum
advertising effectiveness.
- Presents advertising strategies, plans and executions to all levels of
management up through the corporate level.
- Is proactive with internal IBM audiences by routinely making
presentations to make them aware of advertising strategies and to gain
their feedback regarding the effectiveness of IBM's advertising
programs.
- Participates in research with marketing management, customers, dealers
and business partners to establish and validate new advertising
program direction and content, and to measure results of advertising
programs.
- Stays informed regarding competitive marketing strategies, advertising
programs and media expenditures.
- Is involved with agency selection and evaluation, and participates in
contract negotiations.
- Directs the daily activities of IBM's advertising agency, keeping them
fully apprised of current strategies. Provides leadership and guidance
in all aspects of advertising operations (e.g., develops agency
briefings, facilitates communications between IBM and the agency,
provides input on advertising content, etc.).
- Determines, in consultation with marketing management and the
advertising agency, appropriate media plans for advertising programs.
Provide input to media plan objectives, strategies, tactics, and
selection and ensure overall marketing and communication objectives
are met.
- Maintains current advertising campaigns. Recommends follow-up programs
to enhance advertising effectiveness.
- Is responsible for the content of all advertising programs executed by
the brand unit and/or business unit.
- Establishes financial targets for advertising programs. Manages
advertising production and media costs and tracks agency performance
to ensure targets are met.
- Maintains business relationships with professional organizations and
representatives of the advertising media.
- Participates with marketing communications colleagues in development
of integrated marketing communications programs.
- Consults with marketing management and collateral/sales promotion
departments on fulfillment plans.
- Employs negotiating skills and marketing knowledge to develop client
relationships.
2.6.10.2 Specialty Title: Collateral/Sales Promotion
Specialty Summary:
Individuals working in this Marketing Communications specialty initiate
and direct collateral/sales promotion programs in support of IBM's goals
to become the industry leader in key marketing segments. He/she assists
marketing executives in refining marketing plans. From these plans,
he/she develops solid collateral/sales promotion plans. The media used to
support these plans includes videos, diskettes, premiums, point-of-sale
materials and displays, slides, foils/foilmasters and product literature
(brochures, flyers, specification sheets, application briefs and
portfolios), and are used in support of offering/solution announcements,
dealer and dealer incentive programs, marketing programs and promotions.
In addition, the incumbent develops a close working relationship with all
levels of management, up through and including the Global Brand
Manager/Business Unit General Manager of the brand unit and/or business
unit supported.
Responsibilities:
- Develops collateral/sales promotion recommendations and strategies
that visibly contribute to the accomplishment of marketing goals as
defined in the client's business plans. Develops long-range
collateral/sales promotion strategies that establish effective
dialogue with customers and prospects.
- Presents collateral/sales promotion plans/strategies/executions to
senior management, business units and corporate.
- Is proactive with internal IBM audiences by routinely making
presentations to make them aware of collateral/sales promotion
strategies and to gain their feedback regarding the effectiveness of
IBM's collateral/sales promotion programs.
- Participates in research with marketing, customers, dealers and
business partners to establish and validate new collateral/sales
promotion program direction and content, and to measure results of
existing collateral/sales promotion and point-of-sales programs.
- Stays informed regarding competitive marketing strategies and
collateral/sales promotion programs.
- Directs agency selection and evaluation and participates in contract
negotiations.
- Directs the daily activities of IBM's collateral/sales promotion
agencies, keeping them fully apprised of current strategies.
- Directs the creative efforts of multiple collateral/sales promotion
agencies, by providing leadership and guidance in all aspects of
collateral/sales promotion operations.
- Develops appropriate point-of-sales materials and displays in support
of IBM's broad variety of channels, e.g., dealer promotions,
back-to-school promotions, business partners, etc. Recommends
follow-up programs to enhance collateral/sales promotion
effectiveness.
- Manages the sales promotion inventories, including negotiating with
marketing on appropriate actions for reprints, revisions, new stock,
and inventory reduction and obsolescence.
- Utilizes knowledge of layout/content, as well as copy and design
judgment, to guide the agency in development of creative.
- Establishes financial targets for deliverables and tracks agency
performance to ensure targets are met.
- Manages print production recommendations to ensure deliverables are
produced cost-effectively, and on time. Manages distribution
recommendations to ensure programs are delivered to appropriate
recipients cost-effectively, and on time.
- Determines, in consultation with marketing management, appropriate
media for each deliverable -- electronic, print, CD-ROM, diskette,
etc. Stays current on collateral/sales promotion-specific software
(e.g., PageMaker, Adobe Illustrator, PhotoShop, and Acrobat).
- Consults with marketing management and advertising on appropriate
fulfillment plans.
- Participates with marketing communications colleagues in development
of integrated marketing communications programs.
- Employs negotiating skills and marketing knowledge to develop client
relationships.
2.6.10.3 Specialty Title: Business Shows
Specialty Summary:
Business Shows/Special Events is responsible for planning, implementing,
producing, budgeting and measuring major meetings including national
business and trade shows. Provides show support of major
offering/solution announcements and marketing events in support of brand
unit and/or business unit objectives. Provides a vehicle for the delivery
of key marketing messages to customer decision makers attending national
shows and special events. Manages the allocation of funds among marketing
organizations to provide enhanced focus on key market segments. Develops
and implements measurement techniques to determine business effectiveness
and impact on sales volumes. Has regular contacts with all levels of
management to understand their objectives and to continually improve show
performance.
Responsibilities:
- Analyzes and contributes to the brand unit and/or business unit
business plans and strategies of a business unit that visibly
contribute to the accomplishment of marketing goals.
- Presents show strategies, designs, recommendations and results to all
levels of management.
- Manages and directs the implementation of these programs and
strategies to achieve optimum show effectiveness within an assigned
budget.
- Executes shows that presents IBM offerings/solutions to customers and
prospects.
- Directs the activities of vendors including design firms, display
houses, transportation firms and production companies.
- Manages a show budget and capital exhibit properties.
- Maintains a proactive position in the area of internal communications
by providing information to both marketing and communications
audiences to make them aware of the effectiveness of business/trade
shows and special events and how to continue to improve their
effectiveness and performance.
- Develops long-range strategies, to maximize the effectiveness of IBM's
participation in these events as well as capitalize on the
availability of key decision makers at these events.
- Maintains an ongoing knowledge of industry trends and practices.
- Maximizes the use of research to validate the performance of shows by
focusing on show attendees, to evaluate the success of business shows
and events, identify areas that require improvement and measure IBM's
effectiveness versus the competition.
- Manages multiple vendors in the area of design, display, electrical,
transportation, production, sound, lighting, etc.
- Coordinates with planning staffs to anticipate changes in future show
requirements.
2.6.10.4 Specialty Title: Corporate Sponsorships
Specialty Summary:
Responsible for the development of major corporate sponsorship projects on
a worldwide basis serving all brand units and/or business units, and for
the development and execution of external press and internal promotions.
Manages the allocation of funds among organizations to provide enhanced
focus on key management goals. Develops and implements measurement
programs to determine the effectiveness of a sponsorship and uses the
results to modify the sponsorship as appropriate. Has regular meetings
with all levels of management to understand their objectives and to
continually improve each sponsorship's impact.
Responsibilities:
- Executes sponsorship strategies and develops plans to outline
objectives and recommends new/alternative sponsorship opportunities.
- Serves as a supplier or agent on behalf of all brand units and/or
business units, and acts as the key contact in corporate marketing for
matters related to the development of sponsorship programs.
- Designs and implements advertising and promotion programs as well as
external press and internal programs to leverage sponsorships.
- Reads and reviews incoming proposals for sponsorships and prepares
executive summaries and recommendations. Appropriately handles
declines for sponsorships.
- Acts as the liaison between marketing and corporate support concerning
the understanding of viable sponsorships.
- Administers budgets related to sponsorship development,
implementation, promotions and associated activities.
- Designs and implements research related to sponsorship development as
well as research to measure the impact of sponsorships.
- Supervises vendors in connection with developing, implementing and
managing sponsorships as well as promotions (e.g., advertising
agencies, etc.) and maintains accurate records of time and
communications.
- Analyzes industry trends, providing sound advice and counsel regarding
effective and efficient sponsorship opportunities.
- Provides the business perspective on legal and contractual obligations
concerning sponsorships.
- Recommends creative solutions to enable worldwide participation in
unique sponsorship opportunities, particularly as they relate to an
enhanced value to the business unit's marketing strategy, or to unique
community relations interests.
2.6.10.5 Specialty Title: Sports Marketing
Specialty Summary:
Responsible for the creation and implementation of a worldwide sports
sponsorship strategy and supporting programs that provide measurable and
intuitive returns on investment. Directs all internal and external
activities relating to the sponsorship of sporting events within the
confines of the budget.
Responsibilities:
- Maintains a high level of worldwide contacts in the sports and TV
industries in order to establish sources for worldwide sponsorship
activities.
- Designs an IBM sports sponsorship strategy and plan outlining
opportunities and suggests new/alternative extensions of the
sponsorship media.
- Advises all brand units and/or business units, as well as key contacts
in corporate communications for matters related to the development of
sponsorship programming.
- Designs and implements external press and internal programs related to
sponsorships.
- Recommends creative solutions to enable worldwide participation in
unique sponsorship opportunities, particularly as they related to an
enhanced value to the brand unit and/or business unit business
strategy.
- Manages relationships with event/organizing body executives to ensure
IBM receives maximum marketing rights/value and provides appropriate
value-in-kind (VIK) per contract.
- Negotiates sponsorship contracts to ensure IBM benefits equal or
surpass IBM's investment, to increase IBM's marketing opportunities,
and to minimize IBM's cost and risk.
- Directs all vendor activity to insure flawless operation of IBM
technology, major and tasteful IBM visibility, and first-class
customer hosting.
- Analyzes industry trends, providing sound advice and counsel regarding
effective and efficient sponsorship opportunities.
- Designs and implements research related to sponsorship development.
- Designs and supervises legal and contractual obligations concerning
sponsorship developments and promotions.
- Reads and reviews incoming proposals for sponsorships and prepares
executive summaries and recommendation.
2.6.10.6 Specialty Title: Media Strategy, Planning & Buying
Specialty Summary:
Media strategy, planning and buying is concerned with communicating the
message to the target audience in the right media at the right time and
frequency, and at the best possible price/value relationship. This
involves selecting the right mix of media (e.g., TV, magazines, radio,
Internet, etc.), the right media vehicles (e.g., the specific TV program,
magazine, newspaper, web site, etc.) within the media options available
(e.g., full-page, half-page, 60-second commercial, etc.) and ensuring that
the placement is leveraged for maximum effect (e.g., pricing, positioning,
added value, etc.). It involves a complete understanding of the target
audience and their media consumption habits, developing a strategy and
plan (media maps) that incorporates customer buying behaviors, and their
wants and needs with message strategies. It also involves a complete
understanding of the media marketplace dynamics to effectively execute
that strategy and plan.
Responsibilities:
- Evaluates and approves all media plan objectives, strategies, tactics,
and selection to ensure that overall marketing and marketing
communications objectives are effectively addressed.
- Evaluates and approves all media buys and contracts to ensure that
maximum value is secured in return for the media investment. Presents
approved media plans and buys to all levels of management up through
the corporate level.
- Directs the media activities of the advertising agency, keeping them
fully apprised of current strategies.
- Establishes procedures and guidelines for ensuring proper reporting
and overall quality control.
- Communicates media strategies, plans and expenditures throughout the
marketing communications community within IBM.
- Manages the competitive media spending system through the advertising
agency.
- Secures and communicates competitive media expenditure data.
- Maintains primary advertising business relationships with
representatives of the advertising media.
2.7 Chapter 10. Direct Marketing Profession Discipline
Subtopics:
2.7.1 Direct Marketing Profession Discipline Overview
Direct Marketing (DM) is one of six profession disciplines within the
Marketing Profession.
The Direct Marketing profession discipline is a discipline family that
includes the original Direct Marketing and Database Marketing Professions.
Direct Marketing is a structured approach to acquiring and cultivating
lifetime customer relationships. Integrated and consistent messages
focused on retaining or reactivating customers and acquiring new customers
are developed and delivered over an extended period of time. Direct
Marketing also supports the on-going development and maintenance of a
marketing information database that is designed to provide a competitive
advantage through the use of empirically-based and analytically-derived
conclusions about the market and customers. As a discipline within the
Marketing Profession, Direct Marketing is responsible for the strategy,
planning, development and implementation of a message and data plan that
supports a brand and/or customer set business unit's marketing plan.
Although both Direct Marketing and Database Marketing are described in
this overview section, the remainder of this document will focus on Direct
Marketing. Refer to Chapter 11, "Database Marketing Profession
Discipline" in topic 2.8 for the career path for Database Marketing.
DIRECT MARKETING:
Professionals who specialize in direct marketing, i.e., demand generation,
assist brand and/or customer set business units in translating marketing
strategies into effective direct marketing campaigns, programs and tactics
that are designed to create demand, i.e., measurable responses and
opportunities for sales channels. Direct Marketing professionals create
demand by orchestrating the delivery of effective messages and offers to
the market through the use of cost-effective media alternatives, which
include, but are not limited to, direct response advertising, mail,
catalogs, telemarketing, telecoverage and interactive.
Direct Marketing professionals generally begin their career as a Direct
Marketing Specialist. Direct Marketing Specialists are focused on
development and implementation activities associated with brand and/or
customer set message plans. In addition to direct marketing skills, they
must have an understanding of database marketing, project management,
business planning, and customer satisfaction processes. Daily activities
may include, but are not limited to catalog management, creative design,
project management, print production, literature fulfillment, and
opportunity (lead) management. With experience, a Direct Marketing
Specialist may become a Direct Marketing Strategist. The Direct Marketing
Strategist is responsible for the strategy and planning of messages that
support brand and/or customer set business plans. The Direct Marketing
Manager is an expert in direct marketing techniques and plays a leadership
role in the strategy, planning, development and implementation of messages
that support a large or multiple brand and/or customer set business units.
A Direct Marketing Manager typically leads a team/project or is a manager
of people.
The following positions are defined for the Direct Marketing Profession
Discipline:
Development and Implementation
- Direct Marketing Specialist
- Direct Marketing Specialist-Advisory
- Direct Marketing Specialist-Senior
Strategy and Planning
- Direct Marketing Strategist-Advisory
- Direct Marketing Strategist-Senior
Strategy, Planning, Development and Implementation
- Direct Marketing Manager
- Senior Direct Marketing Manager
The Direct Marketing Manager and Senior Direct Marketing Manager positions
are intended for non-manager employees who have successfully completed the
Direct Marketing certification program, and for managers with people
management responsibilities. Managers with people management
responsibilities also have the option to complete the Direct Marketing
certification program.
When a non-manager employee is approved for certification by a
certification review board, he/she is expected to perform the job
responsibilities of the Direct Marketing Manager or Senior Direct
Marketing Manager. Non-manager employees should not be promoted to Direct
Marketing Manager or Senior Direct Marketing Manager until they have
completed the certification process.
DATABASE MARKETING:
Professionals who specialize in database marketing develop and maintain
operational and analytical market information databases that support
creative and innovative direct marketing programs, as well as provide a
competitive advantage for brand and/or customer set business units.
Database marketing is designed to develop empirically-based and
analytically-derived conclusions about the market and customers. Analytic
capabilities such as modeling, RFM (receny, frequency methodology)
scoring, and sophisticated reporting are used to link multiple sources of
information related to the customer for the purpose of understanding
customer purchase behavior, improving market segmentation, and delivering
the right market messages to the right customer at the right time.
Direct Marketing professionals who specialize in database marketing
generally begin their career as a Database Marketing Specialist. Database
Marketing Specialists are focused on development and implementation
activities associated with brand and/or customer set data plans. They are
proficient in the use of message, contact database, and/or decision
support tools. Daily activities may include, but are not limited to, data
acquisition and integration, end user support services, data maintenance
and preparation, measurements and reporting, list preparation, decision
support services, and business process support. With experience, a
Database Marketing Specialist may become a Database Marketing Strategist.
The Database Marketing Strategist is responsible for the strategy and
planning of data plans that support brand and/or customer set business
plans. The Database Marketing Manager is an expert in database marketing
techniques and plays a leadership role in the strategy, planning,
development and implementation of data plans that support a large or
multiple brand and/or customer set business units. A Database Marketing
Manager typically leads a team/project or is a manager of people.
The following positions are defined for those in the Database Marketing
profession discipline:
Development and Implementation
- Database Marketing Specialist
- Database Marketing Specialist-Advisory
- Database Marketing Specialist-Senior
Strategy and Planning
- Database Marketing Strategist-Advisory
- Database Marketing Strategist-Senior
Strategy, Planning, Development & Implementation
- Database Marketing Manager
- Senior Database Marketing Manager
The Database Marketing Manager and Senior Database Marketing Manager
positions are intended for non-manager employees who have successfully
completed the Database Marketing certification program and for managers
with people management responsibilities. Managers with people management
responsibilities also have the option to complete the Database Marketing
certification program.
When a non-manager employee is approved for certification by a
certification review board, he/she is expected to perform the job role
responsibilities of the Database Marketing Manager or Senior Database
Marketing Manager. Non-manager employees should not be promoted to
Database Marketing Manager or Senior Database Marketing Manager until they
have completed the certification process.
Measurement of the Direct Marketing profession discipline will include
qualified opportunities (leads), return on investment, revenue, expense
management, business unit (internal client/sponsor) and customer
(external) satisfaction.
2.7.2 Profession Discipline Structure
Figure 10-1 through Figure 10-3 summarize the requirements of each
position of the profession discipline and the developmental requirements
for progression within the profession discipline. Detailed position
descriptions can be found in "Direct Marketing Position Descriptions" in
topic 2.7.10.
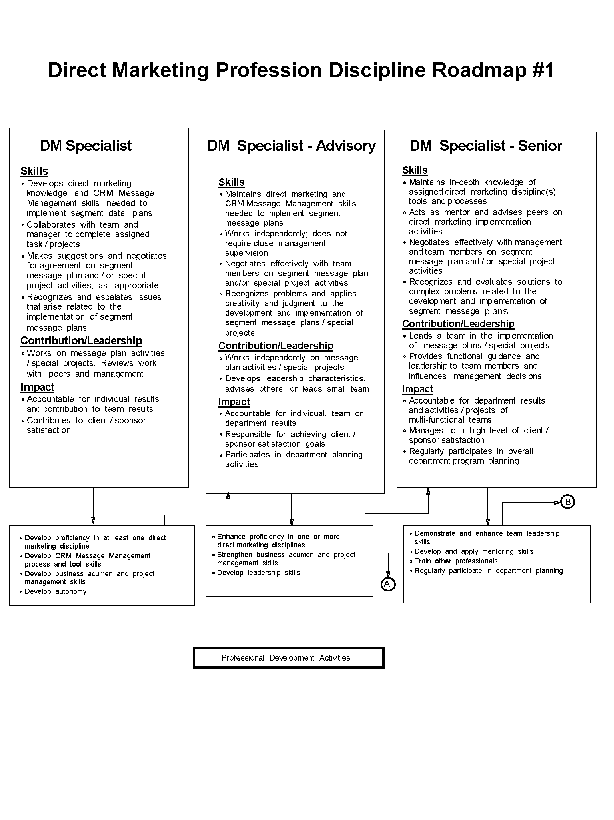
Figure 10-1. Direct Marketing Profession Discipline Roadmap - #1
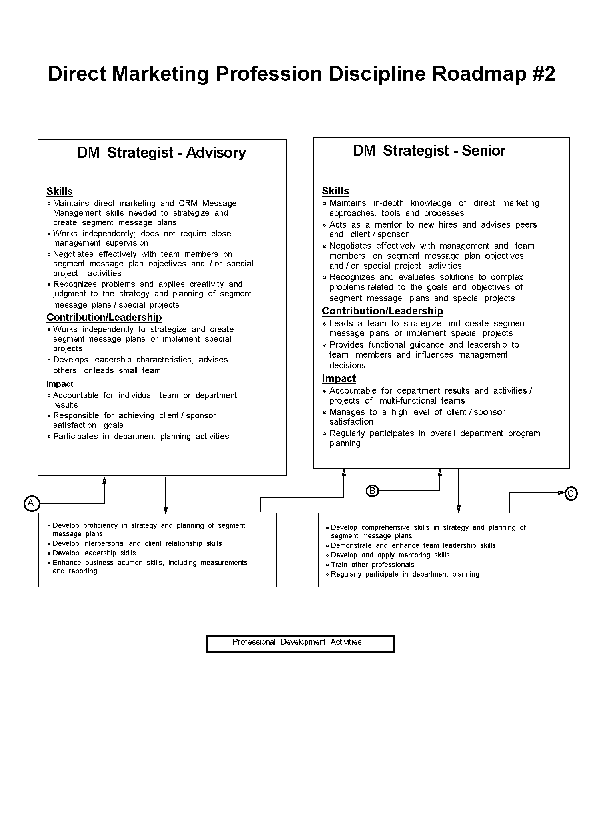
Figure 10-2. Direct Marketing Profession Discipline Roadmap - #2
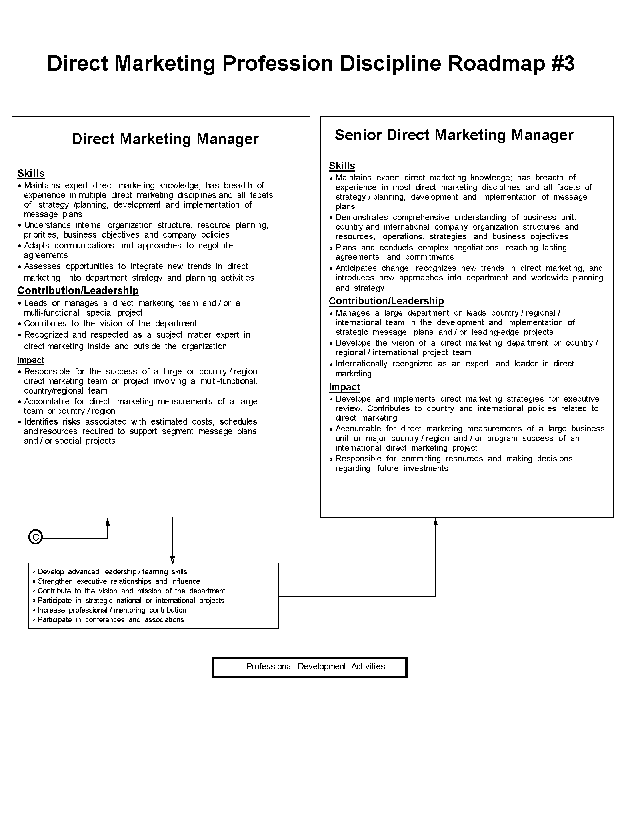
Figure 10-3. Direct Marketing Profession Discipline Roadmap - #3
2.7.3 Characteristics of the Profession Discipline
Direct Marketing professionals have the following characteristics:
- Understanding of the Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Process
- Skilled in direct marketing strategies and activities
- Knowledgeable about database marketing
- Knowledgeable about CRM Message Management Process
- Knowledgeable about Market Management Process and segment management
tools, techniques and methodologies
- Effective in coordinating internal and external resources in order to
implement a direct marketing plan
- Effective in the development and implementation of direct marketing
campaigns/programs that contribute to business unit/segment results
- Skilled in project management methods and tools
- Self-motivated in maintaining currency in the dynamic industry of
direct marketing, i.e., maintain and develop direct marketing and
database marketing skills
- Strong leadership and teamwork skills
The Direct Marketing Manager and Senior Direct Marketing Manager have the
following specific characteristics:
- Demonstrated consultative skills
- Proven analytical skills
- Skilled in CRM Message Management Process
- In-depth direct marketing skills and experience
- Proven skills in the development and implementation of direct
marketing campaigns/programs and successful business results
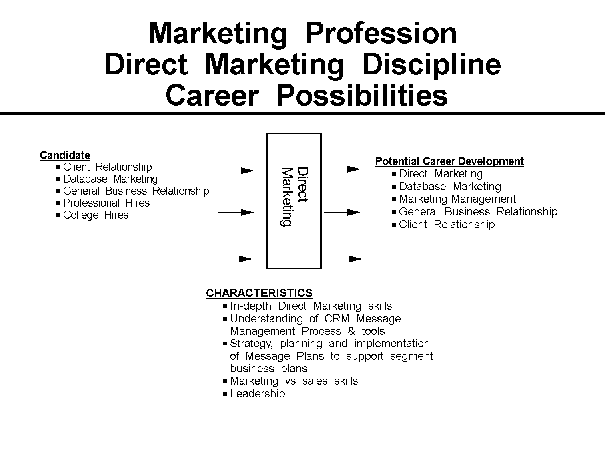
Figure 10-4. Direct Marketing Profession Discipline: Career Possibilities
2.7.4 Potential Candidates
Direct Marketing professionals may be sourced from current IBM employees
who represent a wide array of backgrounds and experience, i.e., marketing,
sales, database marketing, or other positions in a direct marketing
organization.
Direct Marketing professionals may also be sourced from professional hires
who have direct marketing, and/or database marketing experience.
More information on movement from other professions is available in Direct
Marketing Career Possibilities.
Figure 10-4 in topic 2.7.3 illustrates the the possibilities for movement
to and from the Direct Marketing profession discipline.
2.7.5 Career Growth
The difference between a Direct Marketing Specialist, Direct Marketing
Strategist and a Direct Marketing Manager is a function of increasing
skill, capability, experience, and responsibility.
The entry position to the profession discipline is the Direct Marketing
Specialist who focuses on direct marketing/message development and
implementation activities. Direct Marketing Specialists can develop their
career to advisory and senior or become a Direct Marketing Strategist.
Direct Marketing Strategists can occupy positions from advisory to senior.
No entry position is available because some direct marketing experience is
required before engaging with a segment/business unit (internal
client/sponsor) in direct marketing/message planning and strategy
activities. Additional positions exist beyond Direct Marketing
Strategist-Senior, but those are achieved only by successfully completing
the Direct Marketing certification process. The profession provides a
career path to the certified position of Direct Marketing Manager or
Senior Direct Marketing Manager. This allows an employee with expert
direct marketing skills to advance through the profession.
The first step in the certification process is qualification, i.e
attainment of the skills required of the certified position of Direct
Marketing Manager. Upon completion of the qualification process, the
professional's manager should facilitate an individual development plan
that includes mentoring activities and work experiences required by the
certified position, Direct Marketing Manager. Once the appropriate skill
level and other criteria have been met, and a business need for a
certified professional has been identified, the candidate may submit a
nomination package for certification.
2.7.6 Certification Nomination Guide
The Worldwide Direct Marketing Certification Nomination Guide contains the
criteria, required documentation, and process for certification in the
profession discipline.
2.7.7 Performance Elements
The direct marketing professional is an individual who generates demand,
i.e., direct response or qualified opportunities (leads), and contributes
to resulting revenue. A direct marketing professional is expected to
deliver a high level of satisfaction to both the the segment/business unit
(internal client/sponsor) and the customer.
2.7.8 Direct Marketing Profession Discipline Skills Profile
The skills required of a direct marketing professional include generic
professional skills such as client environment, business acumen, project
management, personal leadership etc., as well as direct marketing and
database marketing skills. The following chart summarizes the skills
required, within job levels, for a Direct Marketing Specialist, Direct
Marketing Strategist and Direct Marketing Manager.
____________________________________ ___________________________________
| | Profession Discipline Positions, |
| | with Associated Skill Levels |
| DIRECT MARKETING SPECIALIST SKILLS |________ ________ ________ ________|
| | DM | DM | DM | Key |
| | Spec | Spec | Spec | Skill |
| | | Adv | Sr | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| BUSINESS ACUMEN |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Understand Segment Business Plan | 1 | 2 | 2 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand Solution Marketing Plan | 1 | 2 | 2 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Customer Satisfaction Management | 2 | 2 | 3 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Consulting Methods | 2 | 2 | 3 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Message Management | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand Response Plan | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand Information Fulfillment | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Process | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand Direct Marketing | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand DB Marketing | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| INDUSTRY |
|________________________________________________________________________|
| You should select/assign to your job role the appropriate industry |
| customer classification templates and the appropriate industry |
| solution templates. |
|________________________________________________________________________|
| IBM ENVIRONMENT |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| IBM Organization | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Articulate IBM | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
| Offerings/Technology | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand WW CRM Processes | 1 | 2 | 2 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand WW CRM Opportunity | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
| Management Process | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand Relationship Plan | 1 | 2 | 2 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand WW CRM Request | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Management Process | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| PRODUCT/TECHNOLOGY/SERVICES |
|________________________________________________________________________|
| You should select/assign to your job role the appropriate |
| product/brand templates. |
|________________________________________________________________________|
| PERSONAL |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Leadership | 2 | 2 | 3 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Coaching | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Foster Teamwork/Enable Teams | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Mentoring | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Interpersonal Communication | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Negotiation | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Problem Solving, Decision-Making | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Quality/Problem Prevention | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Perform Time Management | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
_________________________________________ ______________________________
| | Profession Discipline |
| | Positions, with Associated |
| DIRECT MARKETING STRATEGIST SKILLS | Skill Levels |
| |_________ __________ _________|
| | DMSt | DMSt Sr | Key |
| | Adv | | Skill |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| CLIENT ENVIRONMENT |
|_________________________________________ _________ __________ _________|
| Client Relationships | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Client Strategy & Planning | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| BUSINESS ACUMEN |
|_________________________________________ _________ __________ _________|
| Market Management | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Perform Primary Research | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Perform Secondary Research | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Perform Marketplace Situation Analysis | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Perform Analytics to Gain Marketing | 2 | 2 | |
| Intelligence | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Analyze & Interpret Marketing | 3 | 3 | |
| Information/Data | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Synthesize Marketing Information/Data | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Segment Business Plan | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Solution Marketing Plan | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Apply Basic Financial Concepts | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Provide Investment Advice | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Customer Satisfaction Management | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Consulting Methods | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Message Management | 4 | 5 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Use Market Research & DB Info-Message | 3 | 4 | |
| Strategy | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Analyze Message & Message Plan Results | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Develop Message Data Strategy | 2 | 2 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Use Message Management Tools | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Message Template | 4 | 5 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Track & Measure Marketplace Changes | 2 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Message Plan | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Select Among Media Alternatives-Message | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Message Creation & Delivery | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Develop Marketing Messages | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Ensure IBM Communication Compliance | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Copy & Visual Point Analysis | 3 | 4 | |
| Issues | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Develop Contextual Design | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Select Among Message Alternatives | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Design Market Test-Message | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Use Non-Verbal Communication Technique | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Translate Concept/Idea Into Visual Form | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Response Plan | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Information Fulfillment | 3 | 3 | |
| Process | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Direct Marketing | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand DB Marketing | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| INDUSTRY |
|________________________________________________________________________|
| You should select/assign to your job role the appropriate industry |
| customer classification templates, and the appropriate industry |
| solution templates. |
|________________________________________________________________________|
| IBM ENVIRONMENT |
|_________________________________________ _________ __________ _________|
| IBM Organization | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Articulate IBM Offerings/Technology | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand WW CRM Processes | 2 | 2 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand WW CRM Skills Management | 3 | 3 | |
| Process | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand WW CRM Offerings Information | 3 | 4 | |
| Process | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand WW CRM Information | 2 | 3 | |
| Management Process | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand WW CRM Opportunity | 3 | 3 | |
| Management Process | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand WW CRM Relationship | 3 | 4 | |
| Management Process | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Relationship Plan | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand WW CRM Supplier Management | 3 | 3 | |
| Process | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand WW CRM Request Management | 3 | 3 | |
| Process | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| PROJECT MANAGEMENT |
|_________________________________________ _________ __________ _________|
| Initiate Projects | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Manage Project Resource Requirements | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Manage Contracted Resource & Services | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Apply Project Management Techniques | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| PRODUCT/TECHNOLOGY/SERVICES |
|________________________________________________________________________|
| You should select/assign to your job role the appropriate |
| product/brand templates. |
|________________________________________________________________________|
| PERSONAL |
|_________________________________________ _________ __________ _________|
| Leadership | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Coaching | 2 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Foster Teamwork/Enable Teams | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Mentoring | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Creativity/Breakthru Thinking | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Interpersonal Communication | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Negotiation | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Problem Solving, Decision-Making | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Risk Awareness/Taking | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Quality/Problem Prevention | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
_________________________________________ ______________________________
| | Profession Discipline |
| | Positions, with Associated |
| DIRECT MARKETING MANAGER SKILLS | Skill Levels |
| |_________ __________ _________|
| | DM Mgr | Sr DM | Key |
| | | Mgr | Skill |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| CLIENT ENVIRONMENT |
|_________________________________________ _________ __________ _________|
| Client Relationships | 5 | 5 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Client Strategy & Planning | 4 | 5 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| BUSINESS ACUMEN |
|_________________________________________ _________ __________ _________|
| Market Management | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Perform Primary Research | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Perform Secondary Research | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Perform Marketplace Situation Analysis | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Perform Analytics to Gain Marketing | 2 | 2 | |
| Intelligence | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Analyze & Interpret Marketing | 4 | 4 | |
| Information/Data | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Synthesize Marketing Information/Data | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Segment Business Plan | 5 | 5 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Solution Marketing Plan | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Apply Basic Financial Concepts | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Provide Investment Advice | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Customer Satisfaction Management | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Consulting Methods | 4 | 5 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Value-Add Selling | 4 | 5 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Message Management | 5 | 5 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Use Market Research & DB Info-Message | 4 | 4 | |
| Strategy | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Analyze Message & Message Plan Results | 5 | 5 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Develop Message Data Strategy | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Use Message Management Tools | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Message Template | 5 | 5 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Track & Measure Marketplace Changes | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Message Plan | 5 | 5 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Select Among Media Alternatives-Message | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Message Creation & Delivery | 5 | 5 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Develop Marketing Messages | 5 | 5 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Ensure IBM Communication Compliance | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Copy & Visual Point Analysis | 4 | 4 | |
| Issues | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Develop Contextual Design | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Select Among Message Alternatives | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Design Market Test-Message | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Use Non-Verbal Communication Technique | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Translate Concept/Idea Into Visual Form | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Response Plan | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Information Fulfillment | 3 | 3 | |
| Process | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Direct Marketing | 5 | 5 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand DB Marketing | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| INDUSTRY |
|________________________________________________________________________|
| You should select/assign to your job role the appropriate industry |
| customer classification templates and the appropriate industry |
| solution templates. |
|________________________________________________________________________|
| IBM ENVIRONMENT |
|_________________________________________ _________ __________ _________|
| IBM Organization | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| IBM Vision/Mission/Strategy | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Articulate IBM Offerings/Technology | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| IBM Management System | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand WW CRM Processes | 2 | 2 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand WW CRM Skills Management | 3 | 3 | |
| Process | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand WW CRM Offerings Information | 4 | 4 | |
| Process | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand WW CRM Information | 3 | 3 | |
| Management Process | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand WW CRM Opportunity | 3 | 3 | |
| Management Process | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand WW CRM Relationship | 4 | 4 | |
| Management Process | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Relationship Plan | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand WW CRM Supplier Management | 3 | 3 | |
| Process | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand WW CRM Request Management | 3 | 3 | |
| Process | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| PROJECT MANAGEMENT |
|_________________________________________ _________ __________ _________|
| Initiate Projects | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Manage Project Resource Requirements | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Manage Contracted Resource & Services | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Apply Project Management Techniques | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| PRODUCT/TECHNOLOGY/SERVICES |
|________________________________________________________________________|
| You should select/assign to your job role the appropriate |
| product/brand templates. |
|________________________________________________________________________|
| PERSONAL |
|_________________________________________ _________ __________ _________|
| Leadership | 5 | 5 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Coaching | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Foster Teamwork/Enable Teams | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Mentoring | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Creativity/Breakthru Thinking | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Interpersonal Communication | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Negotiation | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Problem Solving, Decision-Making | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Risk Awareness/Taking | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Quality/Problem Prevention | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
Subtopics:
2.7.8.1 Direct Marketing Specialty Skills Templates
Note: SKILLS V2 refers to these templates as 'Discipline' Templates.
When SKILLS V3 is available, they will be renamed to 'Specialty'
Templates.
Direct Marketing Specialty Skills Templates have been created to support
specialized skills. These specialty templates may include additional
skills, or may simply require a proficiency level that is higher or lower
than a skill within the job role template. A Direct Marketing Specialist
will be directed to select one or more Direct Marketing Specialty Skills
Templates, in addition to their Profession Discipline/Job Role Skills
Template, to better reflect his/her responsibilities. A Direct Marketing
Strategist and Direct Marketing Manager will have the option to select one
or more Direct Marketing Specialty Skills Templates. (In smaller Direct
Marketing organizations, it is feasible that a Direct Marketing Strategist
may also have the job responsibilities of the Direct Marketing
Specialist).
The Direct Marketing Specialties are as follows:
(sub-bullets reflect general responsibilities within a specialty, not
specific skills)
- DM-Catalog Management
- Agency management
- Copywriting
- Layout, design
- Mechanical artwork
- Photos, Illustration
- Resource coordination
- Vendor management
- Measurements & reporting
- DM-Creative Concept & Design
- Agency relationship & mgmt.
- Copywriting
- Layout, design
- Mechanical artwork
- Photos, illustration
- Resource coordination
- Vendor management
- Measurements & reporting
- DM-Project Management
- Project plan
- Resource requirements & scheduling
- Vendor management
- Traffic management
- Results tracking
- Expense projection & tracking
- Measurements & reporting
- DM-Print Production
- List definition
- Letter shop
- Mailing
- Testing
- Production facility coordination
- Resource coordination
- Vendor management
- Measurements & reporting
- DM-Literature Fulfillment
- Request processing
- Customer service
- Inventory management
- Resource coordination
- Vendor management
- Measurements & reporting
- DM-Opportunity (Lead) Management
- Response plan
- Request management
- Opportunity qualification criteria
- Scripting
- Channel linkage & training
- Call Center Sales & Services
- Client Reps & BPs
- Measurements & Reporting
The Direct Marketing Specialty Skills Templates are as follows:
____________________________________ ___________________________________
| | Skill Levels |
| DIRECT MARKETING SPECIALTY |________ ________ ________ ________|
| - CATALOG MANAGEMENT | (Base) | Adv | Sr | Key |
| | | | | Skill |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| CLIENT ENVIRONMENT |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Client Relationships | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| BUSINESS ACUMEN |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Apply Basic Financial Concepts | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Use Message Management Tools | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand Message Template | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand Message Plan | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Select Among Media | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Alternatives-Message | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand Message Creation & | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Delivery | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Develop Marketing Messages | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Use Copywriting Techniques | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Ensure IBM Communication | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Compliance | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand Copy & Visual Point | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Analysis Issues | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Develop Contextual Design | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Use Non-Verbal Communication | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Technique | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Translate Concept/Idea Into Visual | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Form | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| IBM ENVIRONMENT |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Understand WW CRM Skills | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
| Management Process | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand WW CRM Offerings | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
| Information Process | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand WW CRM Supplier | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
| Management Process | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| PROJECT MANAGEMENT |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Track & Report Status | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Record Project Resource & Schedule | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Data | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Manage Project Resource | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Requirements | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Manage Project Change | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Manage Contracted Resource & | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Services | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Apply Project Management | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
| Techniques | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| PERSONAL |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Creativity/Breakthru Thinking | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
____________________________________ ___________________________________
| | Skill Levels |
| DIRECT MARKETING SPECIALTY |________ ________ ________ ________|
| - CREATIVE CONCEPT & DESIGN | (Base) | Adv | Sr | Key |
| | | | | Skill |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| CLIENT ENVIRONMENT |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Client Relationships | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| BUSINESS ACUMEN |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Apply Basic Financial Concepts | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Use Message Management Tools | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand Message Template | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand Message Plan | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Select Among Media | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Alternatives-Message | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand Message Creation & | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Delivery | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Develop Marketing Messages | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Use Copywriting Techniques | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Ensure IBM Communication | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Compliance | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand Copy & Visual Point | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Analysis Issues | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Develop Contextual Design | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Use Non-Verbal Communication | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Technique | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Translate Concept/Idea Into Visual | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Form | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| IBM ENVIRONMENT |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Understand WW CRM Skills | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
| Management Process | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand WW CRM Offerings | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| Information Process | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand WW CRM Supplier | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
| Management Process | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| PROJECT MANAGEMENT |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Track & Report Status | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Record Project Resource & Schedule | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Data | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Manage Project Resource | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Requirements | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Manage Project Change | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Manage Contracted Resource & | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Services | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Apply Project Management | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
| Techniques | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| PERSONAL |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Creativity/Breakthru Thinking | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
____________________________________ ___________________________________
| | Skill Levels |
| DIRECT MARKETING SPECIALTY |________ ________ ________ ________|
| - PROJECT MANAGEMENT | (Base) | Adv | Sr | Key |
| | | | | Skill |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| CLIENT ENVIRONMENT |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Client Relationships | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| BUSINESS ACUMEN |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Apply Basic Financial Concepts | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Track Message & Message Plan | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Results | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Use DB Applications & | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Tools-Message Plans | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Use Message Management Tools | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand Message Template | 1 | 2 | 2 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand Message Plan | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand Message Creation & | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
| Delivery | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| IBM ENVIRONMENT |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Understand WW CRM Skills | 1 | 2 | 2 | |
| Management Process | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand WW CRM Offerings | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
| Information Process | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand WW CRM Supplier | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
| Management Process | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| PROJECT MANAGEMENT |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Initiate Projects | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Develop Project Cost Structures | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Define/Estimate Work Tasks | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Use Estimating Planning Tools | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Develop Project Plans | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Project Track/Report/Deliver | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Track & Report Status | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Record Project Resource & Schedule | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Data | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Manage Project Resource | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Requirements | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Manage Project Risk | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Manage Project Change | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Manage Contracted Resource & | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Services | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
____________________________________ ___________________________________
| | Skill Levels |
| DIRECT MARKETING SPECIALTY |________ ________ ________ ________|
| - PRODUCTION & PRINTING | (Base) | Adv | Sr | Key |
| | | | | Skill |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| BUSINESS ACUMEN |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Apply Basic Financial Concepts | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Use Message Management Tools | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand Message Plan | 1 | 2 | 2 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand Message Creation & | 1 | 2 | 2 | |
| Delivery | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Ensure IBM Communication | 1 | 2 | 2 | |
| Compliance | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| IBM ENVIRONMENT |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Understand WW CRM Skills | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
| Management Process | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand WW CRM Offerings | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
| Information Process | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand WW CRM Supplier | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
| Management Process | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| PROJECT MANAGEMENT |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Track & Report Status | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Record Project Resource & Schedule | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Data | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Manage Project Resource | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Requirements | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Manage Project Change | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Manage Contracted Resource & | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Services | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Coordinate Project Facilities | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Apply Project Management | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Techniques | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
____________________________________ ___________________________________
| | Skill Levels |
| DIRECT MARKETING SPECIALTY |________ ________ ________ ________|
| - LITERATURE FULFILLMENT | (Base) | Adv | Sr | Key |
| | | | | Skill |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| BUSINESS ACUMEN |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Apply Basic Financial Concepts | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Use DB Applications & | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
| Tools-Message Plans | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand Information Fulfillment | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Process | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| IBM ENVIRONMENT |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Understand WW CRM Offerings | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
| Information Process | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand WW CRM Supplier | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Management Process | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| PROJECT MANAGEMENT |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Manage Contracted Resource & | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Services | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Coordinate Project Facilities | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Apply Project Management | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
| Techniques | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
____________________________________ ___________________________________
| | Skill Levels |
| DIRECT MARKETING SPECIALTY |________ ________ ________ ________|
| - OPPORTUNITY (LEAD) MANAGEMENT | (Base) | Adv | Sr | Key |
| | | | | Skill |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| CLIENT ENVIRONMENT |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Client Relationships | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| BUSINESS ACUMEN |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Use DB Applications & | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
| Tools-Message Plans | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Use Message Management Tools | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand Message Plan | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand Response Plan | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| IBM ENVIRONMENT |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Understand WW CRM Opportunity | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Management Process | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand Relationship Plan | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand WW CRM Request | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Management Process | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| PROJECT MANAGEMENT |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Apply Project Management | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
| Techniques | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
2.7.9 Professional Development
Many forms of education exist that can help to increase skill proficiency
levels, including:
- IBM Internal Education and Training
- External Education and Training
- College & University Continuing Education
- Fee Seminars and Workshops
- Professional Associations / Conferences
- National Associations
- Regional Associations
- Self Education / Reference Reading
- Articles
- Books
- DM WEB Sites
- Journals & Reports
- Newsletters
- Subscriptions & Publications
- Videos
- Research Libraries
For an overview of the Worldwide Professions and links to the Common
Skills Categories and Professions Roadmaps, refer to the Education Roadmap
page of the IEC Course Catalog at
http://w3.lahulpe.ibm.com/roadmap/index.htm.
In support of the Worldwide CRM Message Management Process, additional
skills were created and integrated into the Direct Marketing profession
discipline skills templates. Skills development roadmaps and activities
are also being developed to support the new and revised skills templates.
These roadmaps will be published in the Direct Marketing/Database
Marketing Profession & Skills Development Reference Guide.
2.7.10 Direct Marketing Position Descriptions
The following position descriptions describe the basic work of each of the
positions within the Marketing Profession. Formal descriptions which may
contain legally mandated language necessary for classifying employees in a
geography should be obtained through the approved on-line job library, if
available in the geography, or by contacting the appropriate H.R.
personnel within the geography.
Subtopics:
2.7.10.1 Position Title: Direct Marketing Specialist
Position Concept:
The Direct Marketing Specialist works closely with Direct Marketing
Strategists/Managers and other direct marketing/database marketing
professionals, and assists in implementing message plans that support
client/sponsor segment business plans (market or brand). The Direct
Marketing Specialist is usually assigned to a team and is guided by senior
team members and management. The Direct Marketing Specialist focuses on
developing direct marketing skills and professional effectiveness. Work is
reviewed with peers and management for developmental purposes. The Direct
Marketing Specialist is proficient in at least one direct marketing
discipline, which includes, but is not limited to, catalog management,
project management, creative concept and design, print production,
literature fulfillment, and/or opportunity management. All activities
support the Message Management process (delivery of marketing messages to
customers), and associated processes within Customer Relationship
Management (CRM).
Skills
- Develops marketing, business acumen, analytical, direct marketing/
database marketing, Message Management process, and associated
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) process skills needed to
develop and implement message plans created by a Direct Marketing
Strategist/Manager and client/sponsor, or participate in an assigned
direct marketing project. Demonstrates required skill proficiency
levels for this position.
- Collaborates with direct marketing and database marketing team members
to complete assigned tasks/projects, e.g., creative design,
project/work plan development, print production, measurement and
reporting.
- Makes suggestions and negotiates to gain agreement with other
professionals on segment message plan and/or special project
activities, as appropriate.
- Recognizes and escalates issues that arise related to the development
and implementation of segment message plans and/or assigned direct
marketing projects.
- Analyzes issues related to the use of the Message Management tool
(MMTool), and other tools (e.g., MSM), and assists with preparation
and recommendation for solution alternatives and enhancements.
- Challenges Message Management and associated processes within Customer
Relationship Management (CRM), and/or department procedures with the
intention of enhancing and improving them.
- Generally requires a BA/BS degree or equivalent.
Contribution/Leadership
- Works on assigned segment message plans and/or direct marketing
projects. Delivers work on time and to the satisfaction of the Direct
Marketing Manager and segment client/sponsor.
- Reviews work for completeness with a manager and other members of the
team.
- Understands the mission of the assigned team/unit and its relation-
ship to the direct marketing and database marketing departments.
- May influence other direct marketing/database marketing team members
regarding project or segment message plan implementation activities.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Accountable for individual results and contributes to team results
(e.g., campaign/program revenue, response rates).
- Contributes to client/sponsor satisfaction (e.g., on time delivery).
- Supports activities that impact campaign/program or project costs.
2.7.10.2 Position Title: Direct Marketing Specialist-Advisory
Position Concept:
The Direct Marketing Specialist-Advisory works closely with Direct
Marketing Strategists/Managers and other direct marketing/database
marketing professionals to develop and implement message plans that
support client/ sponsor segment business plans (market or brand). The
Direct Marketing Specialist-Advisory works independently as a productive
member of a team or leader of a small team. The Direct Marketing
Specialist-Advisory develops leadership skills and uses analytical skills
and business/ professional knowledge to generate solutions (e.g., quality
deliverables), and achieve the agreed upon objectives of a segment message
plan or direct marketing project. The Direct Marketing Specialist-Advisory
demonstrates proficiency in one more direct marketing disciplines, which
include, but are not limited to catalog management, project management,
creative concept and design, print production, literature fulfillment,
and/or opportunity management. All activities support the Message
Management process (delivery of marketing messages to customers), and
associated processes within Customer Relationship Management (CRM).
Skills
- Maintains marketing, business acumen, analytical, direct marketing/
database marketing, Message Management process, and associated
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) process skills needed to
develop and implement message plans created by a Direct Marketing
Strategist/Manager and client/sponsor, or participate in an assigned
direct marketing project. Demonstrates required skill proficiency
levels for this position.
- Works independently as a direct marketing professional and does not
require close management supervision.
- Articulates and evaluates alternative approaches for developing and
implementing segment message plans.
- Negotiates effectively with team members, including vendors and
subcontractors, on segment message plan and/or special project
activities in support of statement of work objectives.
- Recognizes problems associated with the goals and objectives of
segment message plans or statements of work.
- Applies creativity and judgement to the development and implementation
activities for assigned segment message plans, direct marketing
projects, and other activities.
- Independently generates solutions based on analytical skills and
business knowledge.
- Challenges existing department procedures, or company processes,
(e.g., Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Message Management) for
the purpose of enhancing and improving them and recommends/ develops
alternative approaches.
Contribution/Leadership
- Works independently and/or leads small team of other direct marketing
professionals to develop and implement segment message plans, or
participates in special direct marketing projects.
- Develops leadership characteristics, e.g., advises others in the use
of tools, works on a special direct marketing project, or leads a
small team in operational activities.
- Controls own work priorities and methods for assigned tasks/projects
and makes necessary trade-offs.
- Understands and articulates the mission and vision of the assigned
functional unit and department.
- Provides advice to the Direct Marketing Strategist/Manager regarding
project or segment message plan objectives and implementation
activities.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Accountable for individual, team or departmental results (e.g.,
campaign/program results, direct marketing revenue) and impact of the
results on direct marketing functional activities (e.g., additional
(funding and investment initiatives).
- Responsible for achieving client/sponsor satisfaction goals (e.g.,
on-time delivery, assessment of business risks).
- Participates in department planning activities.
- Analyzes the impact of activities on costs in relation to the revenue
and expense objectives of segment message or business plans.
2.7.10.3 Position Title: Direct Marketing Specialist-Senior
Position Concept:
The Direct Marketing Specialist-Senior works closely with Direct Marketing
Strategists/Managers and other direct marketing/database marketing
professionals to develop and implement message plans that support complex
client/sponsor segment business plans (market or brand). The Direct
Marketing Specialist-Senior is self-directed, perceived as a leader,
provides advice and guidance to other professionals, and is often assigned
as a team leader or to a special project. The Direct Marketing
Specialist-Senior drives the implementation of segment message plans and
achievement of the agreed upon objectives of a segment message plan or
direct marketing project. The Direct Marketing Specialist-Senior
demonstrates comprehensive knowledge in one or marketing disciplines,
which include, but are not limited to, catalog management, project
management, creative concept and design, print production, literature
fulfillment, and/or opportunity management. The Direct Marketing
Specialist-Senior influences others in the effective implementation of the
Message Management process (delivery of marketing messages to customers),
and associated processes within Customer Relationship Management (CRM).
In addition to the attributes of the Direct Marketing Specialist-Advisory,
the Direct Marketing Specialist-Senior has responsibility to act as a
mentor to at least one less-experienced Direct Marketing Specialist.
Skills
- Maintains in-depth knowledge of assigned direct marketing
discipline(s), direct marketing tools (e.g., the Message Management
Tool, MMTool), Message Management and associated processes within
Customer Relationship Management (CRM). Delivers the effective
development and implementation of client/sponsor segment message
plans. Demonstrates required skill proficiency levels for this
position.
- Acts as a mentor to new hires and/or advises peers within direct
marketing and/or database marketing.
- Negotiates effectively with management and team members, including
vendors and subcontractors, on segment message plan and/or special
project activities in support of statement of work objectives.
- Recognizes and evaluates solutions to complex problems related to the
development and implementation of segment message plans, statements of
work, and/or direct marketing special projects.
- Analyzes problem situations and challenges. Takes the initiative to
develop and implement solutions.
- Applies creativity and sound business judgement to the development and
implementation activities for segment message plans, direct marketing
projects, and other assigned activities.
Contribution/Leadership
- Leads a team of direct marketing specialists, vendors, and/or
subcontractors in the development and implementation of segment
message plans, or leads a special project team.
- Understands and supports the mission and vision of the assigned
department and functional unit, and can articulate the linkages to
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and impact on client/sponsor
satisfaction.
- Directly influences the statement of work related to the development
and implementation of segment message plans and/or assigned direct
marketing projects.
- Defines and sets objectives related to the development and
implementation of segment message plans and/or direct marketing
projects.
- Has responsibility for providing functional guidance and leadership to
team members throughout a project's life cycle, and often influences
management decisions and/or activities of a multi-functional team.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Accountable for department results (e.g., campaign/program results,
direct marketing revenue), and for activities and/or projects
involving multi-functional teams (e.g., additional client/sponsor
funding and investments).
- Manages to a high level of client/sponsor customer satisfaction by
analyzing feedback and modifying plans or approaches.
- Regularly participates in overall departmental and functional program
planning.
2.7.10.4 Position Title: Direct Marketing Strategist-Advisory
Position Concept:
The Direct Marketing Strategist-Advisory is responsible for creating
segment message strategies/plans that support client/sponsor segment
business plans (market or brand). The Direct Marketing Strategist-Advisory
works independently as a productive member of a team, or leader of a small
team. The Direct Marketing Strategist-Advisory develops leadership skills
and uses analytical skills, creativity, and business/professional
knowledge to generate strategies and solutions. The Direct Marketing
Strategist-Advisory demonstrates proficiency in strategy and planning
activities, including translating market or brand strategies into messages
and deliverables for products, services and/or solutions for the purpose
of generating transaction opportunities, building customer loyalty, and/or
maintaining customer relationships. Activities include the selection and
use of multiple direct marketing techniques, (e.g., catalog, direct mail,
telemarketing), and the use of data analytics to understand customer
purchase behavior and target opportunities. All activities support the
Message Management process (delivery of marketing messages to customers),
and associated processes within Customer Relationship Management (CRM).
Skills
- Maintains marketing, business acumen, creative, analytical, direct
marketing/database marketing, Message Management process, and
associated Customer Relationship Management (CRM) process skills
needed to create segment message strategies and plans to support
client/sponsor segment business plans. Demonstrates required skill
proficiency levels for this position.
- Works independently as a direct marketing professional and does not
require close management supervision.
- Articulates and evaluates alternative approaches for strategizing and
creating segment message plans.
- Negotiates effectively with team members, including vendors and
subcontractors, on segment message plan objectives and/or special
activities, e.g., a statement of work that includes outputs, target
completion dates, data requirements, resource requirements.
- Recognizes problems associated with the goals and objectives of
segment message plans/special projects and statements of work.
- Applies creativity and judgement to the strategy and planning
activities for assigned segment message plans, direct marketing
projects, and other activities.
- Independently generates strategies and solutions based on creativity,
analytical skills and business knowledge.
- Challenges existing department procedures, or company processes (e.g.,
Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Message Management) for the
purpose of enhancing and improving them and recommends/ develops
alternative approaches.
Contribution/Leadership
- Works independently and/or leads small team of other direct marketing
professionals to create segment message plans, or participates in
special direct marketing projects.
- Develops leadership characteristics, e.g., advises others in the use
of tools, works on a special direct marketing project, or leads a
small team in strategy and planning activities.
- Controls own work priorities and methods for assigned tasks/projects
and makes necessary trade-offs.
- Understands and articulates the mission and vision of the assigned
functional unit and department.
- Provides advice to the Direct Marketing Strategist/Manager and
client/sponsor regarding segment message plan objectives, segment
opportunities, and/or segment message strategies.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Accountable for individual, team or departmental results (e.g.,
campaign/program results, direct marketing revenue), and for the
impact of the results on functional activities (e.g., additional
funding and investment initiatives).
- Responsible for achieving client/sponsor satisfaction goals (e.g.,
on-time delivery, assessment of business risks).
- Participates in department planning activities.
- Analyzes the impact of activities on costs in relation to the revenue
and expense objectives of segment message or business plans.
2.7.10.5 Position Title: Direct Marketing Strategist-Senior
Position Concept:
The Direct Marketing Strategist-Senior is responsible for creating segment
message strategies/plans that support complex client/sponsor segment
business plans (market or brand). The Direct Marketing Strategist-Senior
is self-directed, perceived as a leader, provides advice and guidance to
other professionals, and is often assigned as a team leader or to a
special project. The Direct Marketing Strategist-Senior demonstrates
comprehensive knowledge in all strategy and planning activities, including
translating market or brand strategies into messages and deliverables for
products, services and/or solutions for the purpose of generating
transaction opportunities, building customer loyalty, and/or maintaining
customer relationships. The Direct Marketing Strategist-Senior drives the
selection and effective use of direct marketing techniques (e.g., catalog,
direct mail, telemarketing), and the use of data analytics to understand
customer purchase behavior and target opportunities. The Direct Marketing
Strategist-Senior influences others in the effective implementation of the
Message Management process (delivery of marketing messages to customers),
and associated processes within Customer Relationship Management (CRM).
In addition to the attributes of the Direct Marketing Strategist-Advisory,
the Direct Marketing Strategist-Senior has responsibility to act as a
mentor to at least one less-experienced Direct Marketing Strategist or
Specialist.
Skills
- Maintains in-depth knowledge of direct marketing approaches, processes
and tools (e.g., the Message Management tool, MMTool) to effectively
create segment message strategies and plans that support
client/sponsor business plans. Demonstrates required skill proficiency
levels for this position.
- Acts as a mentor to new hires and/or advises peers within direct
marketing and database marketing. Advises Direct Marketing Managers
and/or client/sponsor on direct marketing techniques, message plan
strategies and contributes to the overall strategy and planning of
segment business plans, or special projects.
- Negotiates effectively with management and team members, including
vendors and subcontractors, on segment message plan objectives and/or
special project activities, e.g., a statement of work that includes
outputs, target completion dates, data requirements, resource
requirements.
- Recognizes and evaluates solutions to complex problems related to the
goals and objectives of segment data plans, segment message plans,
statements of work, and/or direct marketing special projects.
- Analyzes problem situations and challenges, takes the initiative to
recommend alternatives, and develops and implements solutions.
- Applies creativity and sound business judgement to the strategy and
planning activities for segment message plans, direct marketing
projects, and other assigned activities.
Contribution/Leadership
- Leads a team of direct marketing strategists, specialists, vendors,
and/or subcontractors in creating segment message plans, or leads a
special project team.
- Understands and supports the mission and vision of the assigned
department and functional unit, and can articulate the linkages to
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and impact on client/sponsor
satisfaction.
- Directly influences the definition of objectives for segment message
plans and/or direct marketing projects.
- Has responsibility for providing functional guidance and leadership to
team members throughout a project's life cycle, and often influences
management decisions and/or activities of a multi-functional team.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Accountable for department results (e.g., campaign/program results,
direct marketing revenue), and for activities and/or projects
involving multi-functional teams (e.g., additional client/sponsor
funding and investments).
- Manages to a high level of client/sponsor satisfaction by analyzing
feedback and modifying plans or approaches.
- Regularly participates in overall departmental and functional program
planning.
2.7.10.6 Position Title: Direct Marketing Manager
Position Concept:
The Direct Marketing Manager leads a direct marketing team or manages a
unit/department focused on building and implementing message
strategies/plans that support client/sponsor segment business plans
(market or brand). The Direct Marketing Manager is guided by worldwide
direct marketing strategies, has latitude to set priorities and determine
resources, and has a breadth of business and direct marketing knowledge.
The Direct Marketing Manager is recognized as an expert in translating
market or brand strategies into messages and deliverables for products,
services, and/or solutions. The Direct Marketing Manager has experience in
all facets of strategy/planning, development and implementation of segment
message plans, including the use of analytics to profile customer purchase
behavior and target opportunities. The Direct Marketing Manager is
responsible for the client/sponsor relationship and satisfaction, and is
accountable for all agreed upon objectives (e.g., revenue, expense
budgets, schedules) with department executives and/or client/sponsors.
The Direct Marketing Manager plays a leadership role in implementing the
Message Management process (delivery of marketing messages to customers),
Customer Relationship Management (CRM), and worldwide direct marketing
initiatives.
In addition to the attributes of the Direct Marketing Specialist-Senior
and the Direct Marketing Strategist-Senior, the Direct Marketing Manager
has responsibility to act as a mentor to one or more direct marketing
professionals.
Skills
- Maintains expert direct marketing knowledge; has a breadth of
experience in multiple direct marketing disciplines and all facets of
strategy planning, development, and implementation of segment message
plans. Demonstrates required skill proficiency levels for this
position.
- Understands internal organization structure, resource planning,
priorities, business objectives and company policies. Manages
effectively in the matrix environment to meet department and
client/sponsor objectives.
- Leads and guides other direct marketing professionals. Initiates and
effectively advises client/sponsors, department managers and
executives on direct marketing techniques and approaches (e.g., the
use of data analytics to target new opportunities, integration of
direct marketing with other routes to market strategies).
- Adapts communications and approaches to negotiate agreement with
department management, direct marketing and database marketing peers,
client/sponsors, and/or vendor resources (e.g., staffing requirements
to meet direct marketing demand and client/sponsor objectives).
- Anticipates and analyzes problems associated with message plans or
special projects. Contains risk and develops and manages the
implementation of direct marketing strategies and solutions. Assesses
business impact of solutions.
- Assesses opportunities to integrate new trends in direct marketing
into department planning and strategy activities. Develops
leading-edge direct marketing strategies and solutions.
Contribution/Leadership
- Leads or manages a direct marketing team and/or a multi-functional
special project team.
- Has considerable latitude and accountability for decisions concerning
tool selection/usage, processes, priorities, and resources to support
client/sponsor objectives, direct marketing campaigns/programs, and/or
special direct marketing projects.
- Contributes to the vision of the department and how its mission
supports the worldwide direct marketing strategies, goals and
objectives. Initiates communication of vision and mission to
client/sponsors and other internal organizations.
- Frequently influences department executives and managers on
complex/difficult issues.
- Is recognized and respected as a subject matter expert in direct
marketing inside and outside the organization.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Responsible for the success of a large or country/region direct
marketing team or project involving a multi-functional, country or
regional team (e.g., future funding or investments).
- Accountable for direct marketing measurements of a large team or
country/region, i.e., direct marketing revenue, high level of
client/sponsor satisfaction.
- Identifies risks associated with estimated costs, schedules and
resources required to support segment message plans and/or special
projects.
- Initiates activities that impact client/sponsor satisfaction, customer
satisfaction, and future decisions regarding direct marketing
investments.
2.7.10.7 Position Title: Senior Direct Marketing Manager
Position Concept:
The Senior Direct Marketing Manager leads a large direct marketing team or
manages a unit/department focused on building and implementing message
strategies/plans that support multiple and/or complex client/sponsor
segment business plans (market or brand). The Senior Direct Marketing
Manager develops innovative direct marketing strategies, has input to
policy-making, and is considered an expert and leader by other authorities
inside and outside the company. The Senior Direct Marketing Manager is
considered a person of vision, anticipates change, recognizes new trends
in direct marketing/database marketing, and is the expert in translating
market or brand strategies into messages and effective deliverables for
products, services, and/or solutions. The Senior Direct Marketing Manager
has expert knowledge and breadth of experience in all facets of
planning/strategy, development and implementation of segment message
plans, and drives the use of data analytics to profile customer purchase
behavior and target opportunities. The Senior Direct Marketing Manager is
responsible for one or more client/sponsor relationships and satisfaction,
and is accountable for all agreed upon objectives, (e.g., expense budgets,
schedules, revenue) with client/sponsors and/or department executives. The
Senior Direct Marketing Manager is a unit/department/functional leader in
implementing the Message Management process, (delivery of marketing
messages to customers), Customer Relationship Management (CRM), and
worldwide direct marketing initiatives.
The Senior Direct Marketing Manager has responsibility to act as a mentor
to one or more direct marketing professionals, and to facilitate the use
of a mentoring program within the unit/department.
Skills
- Maintains expert direct marketing knowledge; has a breadth of
experience in most direct marketing disciplines, and demonstrates
expertise in all facets of strategy/planning, development, and
implementation of segment message plans. Defines and drives the
development of new skills in direct marketing throughout the
organization.
- Demonstrates a comprehensive understanding of business unit, country,
and international company organization structures and resources,
operations, strategies, and business objectives.
- Plans and conducts complex negotiations reaching lasting agreements
and commitments.
- Develops and implements direct marketing concepts and strategies with
executive review.
- Anticipates change, recognizes new trends in direct marketing, and
introduces new approaches into department and worldwide planning and
strategy.
Contribution/Leadership
- Develops the vision of a direct marketing department or
country/regional/international project team, and how its mission
supports worldwide direct marketing strategies, goals and objectives.
Facilitates communication of vision and mission to client/sponsor
executives, functional executives, and other internal organizations.
- Internationally recognized as an expert and leader in direct
marketing. Sought out by peers, client/sponsors, and executive
management to resolve complex/difficult issues and to develop
innovative segment message and direct marketing strategies.
- Manages a department, or leads country/regional/international teams in
the development and implementation of strategic, and often
leading-edge direct marketing projects (e.g., the CRM Message
Management process and tool - MMTool).
Impact on Business/Scope
- Develops and implements direct marketing strategies for executive
review. Contributes to country and international policies related to
direct marketing.
- Accountable for direct marketing measurements of a large business unit
or major country/region, and/or program success of an international
direct marketing project.
- Responsible for committing resources, making decisions regarding
future direct marketing investments, and overall direct marketing
success/measurements, e.g., direct marketing revenue, client/sponsor
satisfaction, customer satisfaction.
- Responsible for quality output and value add for highly visible market
segments, strategic direct marketing projects, and future business
development.
2.8 Chapter 11. Database Marketing Profession Discipline
Subtopics:
2.8.1 Database Marketing Profession Discipline Overview
Direct Marketing (DM) is one of six profession disciplines within the
Marketing Profession.
The Direct Marketing profession discipline is a discipline family that
includes the original Direct Marketing and Database Marketing Professions.
Direct Marketing is a structured approach to acquiring and cultivating
lifetime customer relationships. Integrated and consistent messages
focused on retaining or reactivating customers and acquiring new customers
are developed and delivered over an extended period of time. Direct
Marketing also supports the on-going development and maintenance of a
marketing information database that is designed to provide a competitive
advantage through the use of empirically-based and analytically-derived
conclusions about the market and customers. As a discipline within the
Marketing Profession, Direct Marketing is responsible for the strategy,
planning, development and implementation of a message and data plan that
supports a brand and/or customer set business unit's marketing plan.
Although both Direct Marketing and Database Marketing are described in
this overview section, the remainder of this document will focus on
Database Marketing. Refer to Chapter 10, "Direct Marketing Profession
Discipline" in topic 2.7 for the career path for Direct Marketing.
DATABASE MARKETING:
Professionals who specialize in database marketing develop and maintain
operational and analytical market information databases that support
creative and innovative direct marketing programs, as well as provide a
competitive advantage for brand and/or customer set business units.
Database marketing is designed to develop empirically-based and
analytically-derived conclusions about the market and customers. Analytic
capabilities such as modeling, RFM (receny, frequency methodology)
scoring, and sophisticated reporting are used to link multiple sources of
information related to the customer for the purpose of understanding
customer purchase behavior, improving market segmentation, and delivering
the right market messages to the right customer at the right time.
Direct Marketing professionals who specialize in database marketing
generally begin their career as a Database Marketing Specialist. Database
Marketing Specialists are focused on development and implementation
activities associated with brand and/or customer set data plans. They are
proficient in the use of message, contact database, and/or decision
support tools. Daily activities may include, but are not limited to, data
acquisition and integration, end user support services, data maintenance
and preparation, measurements and reporting, list preparation, decision
support services, and business process support. With experience, a
Database Marketing Specialist may become a Database Marketing Strategist.
The Database Marketing Strategist is responsible for the strategy and
planning of data plans that support brand and/or customer set business
plans. The Database Marketing Manager is an expert in database marketing
techniques and plays a leadership role in the strategy, planning,
development and implementation of data plans that support a large or
multiple brand and/or customer set business units. A Database Marketing
Manager typically leads a team/project or is a manager of people.
The following positions are defined for those who specialize in database
marketing within the Direct Marketing profession discipline:
Development and Implementation
- Database Marketing Specialist
- Database Marketing Specialist-Advisory
- Database Marketing Specialist-Senior
Strategy and Planning
- Database Marketing Strategist-Advisory
- Database Marketing Strategist-Senior
Strategy, Planning, Development and Implementation
- Database Marketing Manager
- Senior Database Marketing Manager
The Database Marketing Manager and Senior Database Marketing Manager
positions are intended for non-manager employees who have successfully
completed the Database Marketing certification program and for managers
with people management responsibilities. Managers with people management
responsibilities also have the option to complete the Database Marketing
certification program.
When a non-manager employee is approved for certification by a
certification review board, he/she is expected to perform the job role
responsibilities of the Database Marketing Manager or Senior Database
Marketing Manager. Non-manager employees should not be promoted to
Database Marketing Manager or Senior Database Marketing Manager until they
have completed the certification process.
DIRECT MARKETING:
Professionals who specialize in Direct Marketing, i.e., demand generation,
assist brand and/or customer set business units in translating marketing
strategies into effective direct marketing campaigns, programs and tactics
that are designed to create demand, i.e., measurable responses and
opportunities for sales channels. Direct Marketing professionals create
demand by orchestrating the delivery of effective messages and offers to
the market through the use of cost-effective media alternatives, which
include, but are not limited to, direct response advertising, mail,
catalogs, telemarketing, telecoverage and interactive.
Direct Marketing professionals who specialize in demand generation
generally begin their career as a Direct Marketing Specialist. Direct
Marketing Specialists are focused on development and implementation
activities associated with brand and/or customer set message plans. In
addition to direct marketing skills, they must have an understanding of
database marketing, project management, business planning, and customer
satisfaction processes. Daily activities may include, but are not limited
to catalog management, creative design, project management, print
production, literature fulfillment, and opportunity (lead) management.
With experience, a Direct Marketing Specialist may become a Direct
Marketing Strategist. The Direct Marketing Strategist is responsible for
the strategy and planning of messages that support brand and/or customer
set business plans. The Direct Marketing Manager is an expert in direct
marketing techniques and plays a leadership role in the strategy,
planning, development and implementation of messages that support a large
or multiple brand and/or customer set business units. A Direct Marketing
Manager typically leads a team/project or is a manager of people.
The following positions are defined for the Direct Marketing profession
discipline:
Development and Implementation
- Direct Marketing Specialist
- Direct Marketing Specialist-Advisory
- Direct Marketing Specialist-Senior
Strategy and Planning
- Direct Marketing Strategist-Advisory
- Direct Marketing Strategist-Senior
Strategy, Planning, Development and Implementation
- Direct Marketing Manager
- Senior Direct Marketing Manager
The Direct Marketing Manager and Senior Direct Marketing Manager positions
are intended for non-manager employees who have successfully completed the
Direct Marketing certification program, and for managers with people
management responsibilities. Managers with people management
responsibilities also have the option to complete the Direct Marketing
certification program.
When a non-manager employee is approved for certification by a
certification review board, he/she is expected to perform the job
responsibilities of the Direct Marketing Manager or Senior Direct
Marketing Manager. Non-manager employees should not be promoted to Direct
Marketing Manager or Senior Direct Marketing Manager until they have
completed the certification process.
Measurement of the Direct Marketing profession discipline will include
qualified opportunities (leads), return on investment, revenue, expense
management, business unit (internal client/sponsor) and customer
(external) satisfaction.
2.8.2 Profession Discipline Structure
Figure 11-1 in topic 2.8.3 through Figure 11-3 in topic 2.8.3 summarize
the requirements of each position of the profession discipline and the
developmental requirements for progression within the profession
discipline. Detailed position descriptions can be found in "Database
Marketing Position Descriptions" in topic 2.8.10.
2.8.3 Characteristics of the Profession Discipline
Database marketing professionals have the following characteristics:
- Understanding of the Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Process
- Skilled in database marketing and direct marketing strategies
- Skilled in database marketing tools and techniques
- Knowledgeable about CRM Message Management Process
- Knowledgeable about Market Management Process
- Effective in coordinating internal and external resources in order to
implement a database marketing plan and contribute to segment business
results
- Skilled in project management
- Self-motivated in maintaining currency in the dynamic industry of
database marketing; i.e., maintain and develop database marketing and
direct marketing skills
- Strong leadership and teamwork skills
The Database Marketing Manager and Senior Database Marketing Manager have
the following specific characteristics:
- Demonstrated consultative skills
- Proven analytical skills
- Skilled in CRM Message Management Process
- In-depth database marketing skills and experience in the following
categories: Infrastructure, Content, Deployment, and Analytics,
Measurement and Reporting
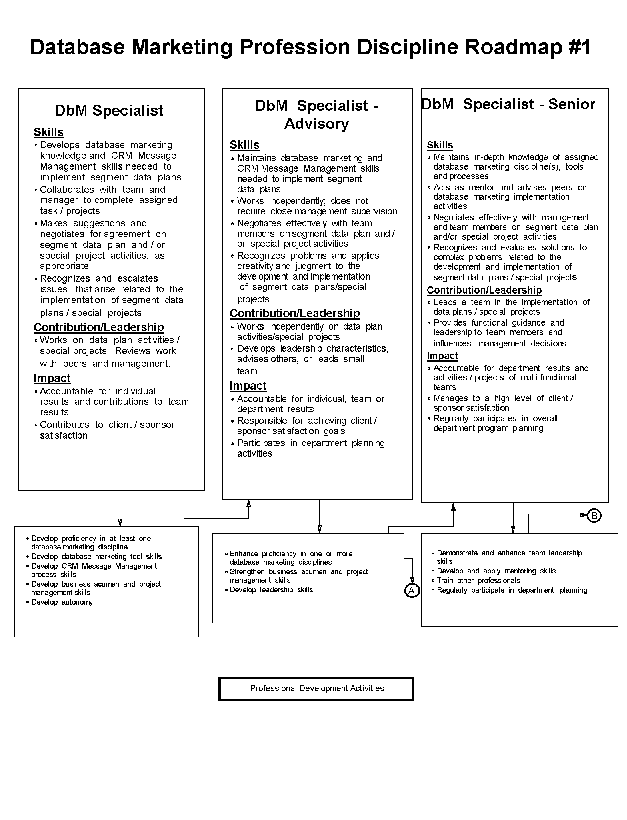
Figure 11-1. Database Marketing Profession Discipline Roadmap - #1
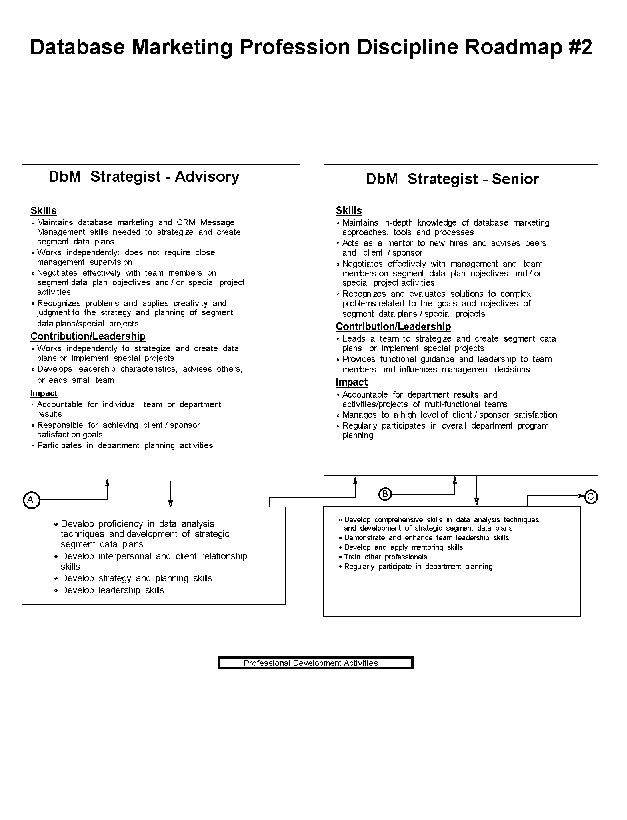
Figure 11-2. Database Marketing Profession Discipline Roadmap - #2
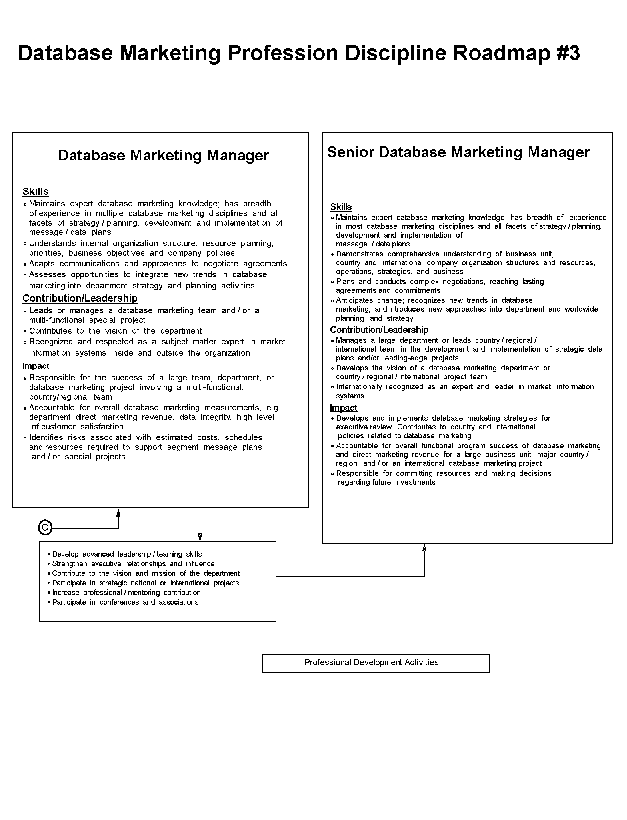
Figure 11-3. Database Marketing Profession Discipline Roadmap - #3
2.8.4 Potential Candidates
Database Marketing professionals may be sourced from current IBM employees
who represent a wide array of backgrounds and experience; i.e., marketing,
sales, I/T, technical services and/or project management. Employees in
the Direct Marketing profession discipline may also be interested in
pursuing a career in database marketing.
Database Marketing professionals may also be sourced from professional
hires who have database marketing and/or direct marketing experience.
More information on movement from other professions is available in
Database Marketing Career Possibilities.
Figure 11-4 illustrates the the possibilities for movement to and from the
Database Marketing profession discipline.
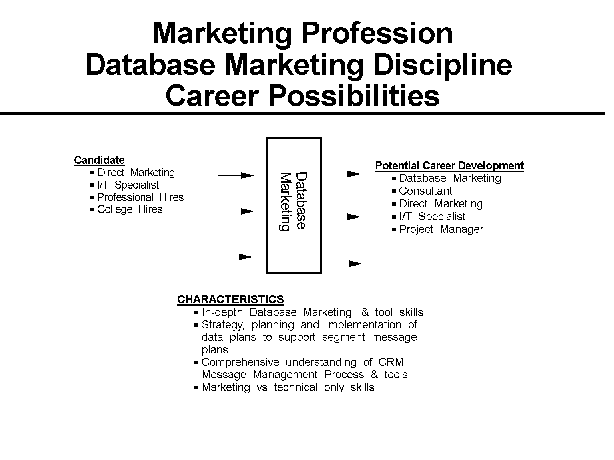
Figure 11-4. Database Marketing Profession Discipline: Career
Possibilities
2.8.5 Career Growth
The difference between a Database Marketing Specialist, Database Marketing
Strategist and a Database Marketing Manager is a function of increasing
skill, capability, experience, and responsibility.
The entry position to the profession is the Database Marketing Specialist
who focuses on data plan development and implementation activities.
Database Marketing Specialists can develop their career to advisory and
senior or become a Database Marketing Strategist.
Database Marketing Strategists can occupy positions from the advisory to
senior level. No entry position is available because some database
marketing experiences is required before engaging with a segment/business
unit (internal client/sponsor) in data planning and strategy activities.
Additional positions exist beyond the Database Marketing Strategist-Senior
level, but those are achieved only by successfully completing the Database
Marketing certification process. This allows an employee with expert
database marketing skills to advance through the profession.
The first step in the certification process is qualification, i.e
attainment of the skills required for certification. Upon completion of
the qualification process, the professional's manager should facilitate an
individual development plan that includes mentoring activities and work
experiences required by the certified position of Database Marketing
Manager. Once the appropriate skill level and other criteria have been
met, and a business need for a certified professional has been identified,
the candidate may submit a nomination package for certification.
2.8.6 Certification Nomination Guide
The Worldwide Database Marketing Certification Nomination Guide contains
the criteria, required documentation, and process for certification in the
profession discipline.
2.8.7 Performance Elements
The database marketing professional is an individual who partners with
other marketing/direct marketing professionals to generate demand, i.e.,
direct response or qualified opportunities (leads) and contributes to
resulting revenue. A database marketing professional focuses on data
accuracy, completeness and recency, return on investment, client/sponsor
(internal) satisfaction and customer (external) satisfaction.
2.8.8 Database Marketing Profession Discipline Skills Profile
The skills required of a database marketing professional include generic
professional skills such as client environment, business acumen, project
management, personal leadership etc., as well as database marketing and
direct marketing skills. The following charts summarize the skills
required, within job levels, for a Database Marketing Specialist, Database
Marketing Strategist and a Database Marketing Manager.
____________________________________ ___________________________________
| | Profession Discipline Positions, |
| | with Associated Skill Levels |
| DATABASE MARKETING SPECIALIST |________ ________ ________ ________|
| SKILLS | DBM | DBM | DBM | Key |
| | Spec | Spec | Spec | Skills |
| | | Adv | Sr | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| BUSINESS ACUMEN |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Market Management | 1 | 2 | 2 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand Segment Business Plan | 1 | 2 | 2 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand Solution Marketing Plan | 1 | 2 | 2 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Apply Basic Financial Concepts | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Customer Satisfaction Management | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Consulting Methods | 0 | 1 | 2 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Message Management | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Develop Message Data Strategy | 1 | 2 | 2 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Use DB Applications & Tools - | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Message Plans | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Use Message Management Tools | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand Message Template | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand Message Plan | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand Message Creation & | 1 | 2 | 2 | |
| Delivery | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand Response Plan | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Manage Data Quality | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand Direct Marketing | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand DB Mktg | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Design Specifications for | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Marketing DB System | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| INDUSTRY |
|________________________________________________________________________|
| You should select/assign to your job role the appropriate industry |
| customer classification templates and the appropriate industry |
| solution templates. |
|________________________________________________________________________|
| IBM ENVIRONMENT |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| IBM Organization | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Articulate IBM | 1 | 2 | 2 | |
| Offerings/Technology | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand WW CRM Processes | 1 | 2 | 2 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand WW CRM Information | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Management Process | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| PROJECT MANAGEMENT |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Apply Project Management | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Techniques | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| PRODUCT/TECHNOLOGY/SERVICES |
|________________________________________________________________________|
| You should select/assign to your job role the appropriate |
| product/brand templates. |
|________________________________________________________________________|
| PERSONAL |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Leadership | 2 | 2 | 3 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Coaching | 0 | 2 | 3 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Foster Teamwork/Enable Teams | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Mentoring | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Interpersonal Communication | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Negotiation | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Problem Solving, Decision-Making | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Quality/Problem Prevention | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Perform Time Management | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
_________________________________________ ______________________________
| | Profession Discipline |
| | Positions, with Associated |
| | Skill Levels |
| DATABASE MARKETING STRATEGIST SKILLS |_________ __________ _________|
| | DBM | DBM | Key |
| | Strat | Strat Sr | Skill |
| | Adv | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| CLIENT ENVIRONMENT |
|_________________________________________ _________ __________ _________|
| Client Relationships | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Client Strategy & Planning | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| BUSINESS ACUMEN |
|_________________________________________ _________ __________ _________|
| Market Management | 2 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Perform Secondary Research | 2 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Perform Marketplace Situation Analysis | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Perform Analytics to Gain Marketing | 3 | 4 | |
| Intelligence | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Analyze & Interpret Marketing | 4 | 5 | |
| Information/Data | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Synthesize Marketing Information/Data | 4 | 5 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Develop Statistical Query Programs - | 3 | 4 | |
| Analytics | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Segment Business Plan | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Solution Marketing Plan | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Apply Basic Financial Concepts | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Provide Investment Advice | 2 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Customer Satisfaction Management | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Consulting Methods | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Message Management | 4 | 5 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Use Market Research & DB Info - Message | 2 | 3 | |
| Strategy | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Analyze Message & Message Plan Results | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Develop Message Data Strategy | 4 | 5 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Use DB Applications & Tools - Message | 4 | 4 | |
| Plans | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Use Message Management Tools | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Message Template | 4 | 5 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Track & Measure Marketplace Changes | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Message Plan | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Message Creation & Delivery | 2 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Ensure IBM Communication Compliance | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Response Plan | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Manage Data Quality | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Build & Implement Data Plans - Message | 3 | 4 | |
| Data Strategy | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Direct Marketing | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand DB Mktg | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Design Specifications for Marketing DB | 3 | 4 | |
| System | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Mailing List Strategies | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| INDUSTRY |
|________________________________________________________________________|
| You should select/assign to your job role the appropriate industry |
| customer classification templates and the appropriate industry |
| solution templates. |
|________________________________________________________________________|
| IBM ENVIRONMENT |
|_________________________________________ _________ __________ _________|
| IBM Organization | 2 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Articulate IBM Offerings/Technology | 2 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand WW CRM Processes | 2 | 2 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand WW CRM Skills Management | 2 | 3 | |
| Process | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand WW CRM Information | 3 | 3 | |
| Management Process | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand WW CRM Relationship | 2 | 3 | |
| Management Process | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Relationship Plan | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand WW CRM Supplier Management | 2 | 3 | |
| Process | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand WW CRM Request Management | 2 | 3 | |
| Process | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| PROJECT MANAGEMENT |
|_________________________________________ _________ __________ _________|
| Initiate Projects | 2 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Manage Contracted Resource & Services | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Apply Project Management Techniques | 2 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| PRODUCT/TECHNOLOGY/SERVICES |
|________________________________________________________________________|
| You should select/assign to your job role the appropriate |
| product/brand templates. |
|________________________________________________________________________|
| PERSONAL |
|_________________________________________ _________ __________ _________|
| Leadership | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Coaching | 2 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Foster Teamwork/Enable Teams | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Mentoring | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Creativity/Breakthru Thinking | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Interpersonal Communication | 2 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Negotiation | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Problem Solving, Decision-Making | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Risk Awareness/Taking | 2 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Quality/Problem Prevention | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
_________________________________________ ______________________________
| | Profession Discipline |
| | Positions, with Associated |
| DATABASE MARKETING MANAGER SKILLS | Skill Levels |
| |_________ __________ _________|
| | DBM | Sr DBM | Key |
| | Mgr. | Mgr | Skill |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| CLIENT ENVIRONMENT |
|_________________________________________ _________ __________ _________|
| Client Relationships | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Client Strategy & Planning | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| BUSINESS ACUMEN |
|_________________________________________ _________ __________ _________|
| Market Management | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Perform Marketplace Situation Analysis | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Perform Analytics to Gain Marketing | 4 | 4 | |
| Intelligence | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Analyze & Interpret Marketing | 5 | 5 | |
| Information/Data | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Synthesize Marketing Information/Data | 5 | 5 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Segment Business Plan | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Solution Marketing Plan | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Apply Basic Financial Concepts | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Provide Investment Advice | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Customer Satisfaction Management | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Consulting Methods | 4 | 5 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Value-Add Selling | 3 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Message Management | 5 | 5 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Use Market Research & DB Info - Message | 3 | 3 | |
| Strategy | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Analyze Message & Message Plan Results | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Develop Message Data Strategy | 5 | 5 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Message Template | 5 | 5 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Message Plan | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Message Creation & Delivery | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Ensure IBM Communication Compliance | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Response Plan | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Manage Data Quality | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Build & Implement Data Plans - Message | 5 | 5 | |
| Data Strategy | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Direct Marketing | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand DB Mktg | 5 | 5 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Design Specifications for Marketing DB | 4 | 4 | |
| System | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Mailing List Strategies | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| INDUSTRY |
|________________________________________________________________________|
| As appropriate, you should select/assign the appropriate industry |
| customer classification templates and the appropriate industry |
| solution templates. |
|________________________________________________________________________|
| IBM ENVIRONMENT |
|_________________________________________ _________ __________ _________|
| IBM Organization | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| IBM Vision/Mission/Strategy | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Articulate IBM Offerings/Technology | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| IBM Management System | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand WW CRM Processes | 2 | 2 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand WW CRM Skills Management | 3 | 3 | |
| Process | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand WW CRM Information | 4 | 4 | |
| Management Process | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand WW CRM Relationship | 3 | 3 | |
| Management Process | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand Relationship Plan | 3 | 3 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand WW CRM Supplier Management | 3 | 3 | |
| Process | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Understand WW CRM Request Management | 3 | 3 | |
| Process | | | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| PROJECT MANAGEMENT |
|_________________________________________ _________ __________ _________|
| Initiate Projects | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Manage Project Resource Requirements | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Manage Contracted Resource & Services | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Apply Project Management Techniques | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| PRODUCT/TECHNOLOGY/SERVICES |
|________________________________________________________________________|
| You should select/assign the appropriate product/brand templates. |
|________________________________________________________________________|
| PERSONAL |
|_________________________________________ _________ __________ _________|
| Leadership | 5 | 5 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Coaching | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Foster Teamwork/Enable Teams | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Mentoring | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Creativity/Breakthru Thinking | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Interpersonal Communication | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Negotiation | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Problem Solving, Decision-Making | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Risk Awareness/Taking | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
| Quality/Problem Prevention | 4 | 4 | |
|_________________________________________|_________|__________|_________|
Subtopics:
2.8.8.1 Database Marketing Specialty Skills Templates
Note: SKILLS V2 refers to these templates as 'Discipline' Templates.
When SKILLS V3 is available, they will be renamed to 'Specialty'
Templates.
Database Marketing Speciality Skills Templates have been created to
support specialized skills. These specialty templates may include
additional skills, or may simply require a proficiency level that is
higher or lower than a skill within the job role template. A Database
Marketing Specialist will be directed to select one or more Database
Marketing Speciality Skills Templates, in addition to their Profession
Discipline/Job Role Skills Template, to better reflect his/her
responsibilities. A Database Marketing Strategist and Database Marketing
Manager will have the option to select one or more Specialty Skills
Templates. (In smaller Direct Marketing organizations, it is feasible
that a Database Marketing Strategist may also have the job
responsibilities of the Database Marketing Specialist).
The Database Marketing Specialties are as follows:
(sub-bullets reflect general responsibilities within a speciality, not
specific skills)
- DbM-Architecture / Infrastructure
- Business processes
- Data acquisition & integration
- Data quality
- End user support services
- Technology & tools
- Measurements and reporting
- DbM-Data Management & Operations
- Data maintenance & preparation
- Measurements and reporting
- DbM-Decision Support
- Decision support tools
- Measurements and reporting
- DbM-List Selection & Management
- Data source identification
- List rental/acquisition
- Cost analysis
- Data integration
- List security
- Measurements and reporting
The Database Marketing Specialty Skills Templates are as follows:
____________________________________ ___________________________________
| | Skill Levels |
| DATABASE MARKETING SPECIALTY |________ ________ ________ ________|
| - ARCHITECTURE/INFRASTRUCTURE | (Base) | Adv | Sr | Key |
| | | | | Skill |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| BUSINESS ACUMEN |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Track Message & Message Plan | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
| Results | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Ensure IBM Communication | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Compliance | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand Information Fulfillment | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Processes | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Build & Implement Data Plans - | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Message Data Strat | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| IBM ENVIRONMENT |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Understand WW CRM Opportunity | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Management Process | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand WW CRM Relationship | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Management Process | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand WW CRM Supplier | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Management Process | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand WW CRM Request | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Management Process | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| PROJECT MANAGEMENT |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Manage Contracted Resource & | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Services | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
____________________________________ ___________________________________
| | Skill Levels |
| DATABASE MARKETING SPECIALTY |________ ________ ________ ________|
| - DATA MANAGEMENT & OPERATIONS | (Base) | Adv | Sr | Key |
| | | | | Skill |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| BUSINESS ACUMEN |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Track Message & Message Plan | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Results | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand Information Fulfillment | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Process | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| IBM ENVIRONMENT |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Understand WW CRM Opportunity | 2 | 2 | 3 | |
| Management Process | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand WW CRM Request | 2 | 2 | 3 | |
| Management Process | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
____________________________________ ___________________________________
| | Skill Levels |
| DATABASE MARKETING SPECIALTY |________ ________ ________ ________|
| - DECISION SUPPORT | (Base) | Adv | Sr | Key |
| | | | | Skill |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| BUSINESS ACUMEN |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Perform Analytics to Gain | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Marketing Intelligence | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Develop Statistical Query Programs | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| - Analytics | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| IBM ENVIRONMENT |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Understand WW CRM Supplier | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Management Process | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| PROJECT MANAGEMENT |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Manage Contracted Resource & | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Services | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
____________________________________ ___________________________________
| | Skill Levels |
| DATABASE MARKETING SPECIALTY |________ ________ ________ ________|
| - LIST SELECTION & MANAGEMENT | (Base) | Adv | Sr | Key |
| | | | | Skill |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| BUSINESS ACUMEN |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Ensure IBM Communication | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
| Compliance | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Build & Implement Data Plans - | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Message Data Strat | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Understand Mailing List Strategies | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| IBM ENVIRONMENT |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Understand WW CRM Supplier | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Management Process | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| PROJECT MANAGEMENT |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Manage Contracted Resource & | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Services | | | | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
2.8.9 Professional Development
Many forms of education exist that can help to increase skill proficiency
levels, including:
- IBM Internal Education and Training
- External Education and Training
- College & University Continuing Education
- Fee Seminars and Workshops
- Professional Associations / Conferences
- Self Education / Reference Reading
- Articles
- Books
- DM WEB Sites
- Journals & Reports
- Newsletters
- Subscriptions & Publications
- Videos
- Research Libraries
For an overview of the Worldwide Professions and links to the Common
Skills Categories and Professions Roadmaps, refer to the Education Roadmap
page of the IEC Course Catalog at
http://w3.lahulpe.ibm.com/roadmaps/index.html
In support of the Worldwide CRM Message Management Process, additional
skills were created and integrated into the Direct Marketing profession
discipline skills templates. Skills development roadmaps and activities
are also being developed to support the new and revised skills templates.
These roadmaps will be published in the Direct Marketing/Database
Marketing Profession & Skills Development Reference Guide.
2.8.10 Database Marketing Position Descriptions
The following position descriptions describe the basic work of each of the
positions within the Marketing Profession. Formal descriptions which may
contain legally mandated language necessary for classifying employees in a
geography should be obtained through the approved on-line job library, if
available in the geography, or by contacting the appropriate H.R.
personnel within the geography.
Subtopics:
2.8.10.1 Position Title: Database Marketing Specialist
Position Concept:
The Database Marketing Specialist works closely with Database Marketing
Strategists/Managers and direct marketing professionals, and assists in
implementing data plans that support client/sponsor segment message plans
(market or brand). The Database Marketing Specialist is usually assigned
to a team and is guided by senior team members and management. Work is
reviewed with peers and management for developmental purposes. The
Database Marketing Specialist focuses on developing database marketing
skills and professional effectiveness. Primary activities include using
message and contact database tools to support the enhancement of the
marketing information database and implementation of segment data plans.
The Database Marketing Specialist is proficient in at least one database
marketing discipline, which includes, but is not limited to, database
architecture/infrastructure, data operations, decision support, and/or
list selection and management. All activities support the Message
Management process (delivery of marketing messages to customers), and
associated processes within Customer Relationship Management (CRM).
Skills
- Develops marketing, business acumen, analytical, database marketing/
direct marketing, Message Management process, and associated Customer
Relationship Management (CRM) process skills needed to implement data
plans that support segment message plans created by Database Marketing
Strategists/Managers and Direct Marketing Strategists/ Managers, or
participate in an assigned Database Marketing project. Demonstrates
required skill proficiency levels required for this position.
- Collaborates with database marketing and direct marketing team members
to complete assigned tasks/projects, e.g., provide end user support
services, integrate data sources, prepare data lists, use decision
support tools for data analytics, develop project/work plan.
- Makes suggestions and negotiates to gain agreement with other
professionals on segment data plan and/or special project activities,
as appropriate.
- Recognizes and escalates issues that arise related to the
implementation of segment data plans and enhancement of the marketing
information database.
- Analyzes issues related to the use of the Message Management tool
(MMTool), and other marketing database tools (e.g., MSM), and assists
with preparation and recommendation for solution alternatives and
enhancements.
- Challenges CRM Message Management and/or Information Management
processes and/or department procedures with the intention of enhancing
and improving them.
- Generally requires a BA/BS degree or equivalent.
Contribution/Leadership
- Works on assigned segment data plans, and/or database marketing
projects. Delivers work on time and to the satisfaction of the
Database Marketing Manager and/or segment client/sponsor.
- Reviews work for completeness with a manager and other members of the
team.
- Understands the mission of the assigned team/unit and its relation-
ship to the database marketing and direct marketing departments.
- May influence other database marketing/direct marketing team members
regarding project or segment data plan implementation activities.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Accountable for individual results and contributes to team results,
e.g., data integrity, campaign/program business results.
- Contributes to client/sponsor satisfaction.
- Supports activities that impact campaign/program or project costs.
2.8.10.2 Position Title: Database Marketing Specialist - Advisory
Position Concept:
The Database Marketing Specialist-Advisory works closely with Database
Marketing Strategists/Managers and direct marketing professionals to
develop and implement data plans that support client/sponsor segment
message plans (market or brand). The Database Marketing
Specialist-Advisory works independently as a productive member of a team,
or leader of a small team. The Database Marketing Specialist-Advisory
focuses on developing leadership skills, using analytical skills,
enhancing the marketing information database, and developing/implementing
segment data plans. The Database Marketing Specialist-Advisory
demonstrates proficiency in one or more database marketing disciplines,
which include, but are not limited to, database
architecture/infrastructure, data operations, decision support, and/or
list selection and management. All activities support the Message
Management process (delivery of marketing messages to customers), and
associated processes within Customer Relationship Management (CRM).
Skills
- Maintains marketing, business acumen, analytical and database
marketing/direct marketing, Message Management process, and associated
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) process skills needed to
implement data plans that support segment message plans created by
Database Marketing Strategists/Managers and Direct Marketing
Strategists/Managers. Demonstrates required skill proficiency levels
for this position.
- Works independently as a database marketing professional and does not
require close management supervision.
- Articulates and evaluates alternative approaches for implementing
segment data plans and enhancing a marketing information database.
- Negotiates effectively with team members, including vendors and
subcontractors, on segment data plan and/or special project activities
in support of statement of work objectives.
- Recognizes problems associated with the goals and objectives of
segment data plans, statements of work, and/or special projects.
- Applies creativity and judgement to the development and implementation
activities for assigned segment data plans, database marketing
projects, and other activities.
- Independently generates solutions based on analytical skills and
business knowledge.
- Challenges existing department procedures, or company processes (e.g.,
Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Message Management) for the
purpose of enhancing and improving them and recommends/ develops
alternative approaches.
Contribution/Leadership
- Works independently and/or leads small team of other database
marketing professionals to strategize and create segment data plans or
special database marketing projects.
- Develops leadership characteristics, e.g., advises others in the use
of tools, works on a special database marketing project, or leads a
small team in operational activities.
- Controls own work priorities and methods for assigned tasks/projects,
and makes necessary trade-offs.
- Understands and articulates the mission and vision of the assigned
team/unit and department.
- Provides advice to the Database Marketing Strategist/Manager regarding
project or segment data plan objectives and/or implementation
activities.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Accountable for individual, team or departmental results (e.g.,
on-time delivery, data integrity, or direct marketing revenue), and
impact of the results on direct marketing functional activities (e.g.,
additional funding and investment initiatives).
- Responsible for achieving client/sponsor satisfaction goals (e.g.,
creative ideas, completion targets, assessing business risks).
- Participates in department planning activities.
- Analyzes the impact of activities on costs in relation to the revenue
and expense objectives of segment message or business plans.
2.8.10.3 Position Title: Database Marketing Specialist - Senior
Position Concept:
The Database Marketing Specialist-Senior works closely with Database
Marketing Strategists/Managers and direct marketing professionals to
develop and implement data plans that support complex client/sponsor
segment message plans (market or brand). The Database Marketing
Specialist-Senior is self-directed, perceived as a leader, provides advice
and guidance to other professionals, and is often assigned as a team
leader or to a special project. The Database Marketing Specialist-Senior
drives the enhancement of the marketing information database, and
development a implementation of segment data plans. The Database Marketing
Specialist Senior demonstrates comprehensive knowledge in one or more
database marketing disciplines, which include, but are not limited to,
database architecture /infrastructure, data operations, decision support,
and/or list selection and management. The Database Marketing
Specialist-Senior influences others in the effective implementation of the
Message Management process (delivery of marketing messages to customers),
and associated processes within Customer Relationship Management (CRM).
In addition to the attributes of the Database Marketing
Specialist-Advisory, the Database Marketing Specialist-Senior has
responsibility to act as a mentor to at least one less-experienced
Database Marketing Specialist.
Skills
- Maintains in-depth knowledge of the assigned database marketing
discipline(s), database marketing tools, and processes. Delivers
quality data plans that support a client/sponsor's segment message
plans. Demonstrates required skill proficiency levels for this
position.
- Acts as a mentor to new hires and/or advises peers within database
marketing and direct marketing. Advises a Direct Marketing Strategist/
Manager on target opportunities through the use of data analytics and
contributes to the overall strategy and planning of segment message
plans and/or special projects.
- Negotiates effectively with management and team members, including
vendors and subcontractors, on segment data plan and/or special
project activities in support of statement of work objectives.
- Recognizes and evaluates solutions to complex problems related to the
development and implementation of segment data plans, statements of
work, and/or database marketing special projects.
- Analyzes problem situations and challenges, and takes the initiative
to develop and implement solutions.
- Applies creativity and sound business judgement to development and
implementation activities for segment data plans, database marketing
projects, and other assigned activities.
Contribution/Leadership
- Leads a team of database marketing specialists, vendors, and/or
subcontractors in the implementation of segment data plans, or leads a
special project team.
- Understands and supports the mission and vision of the assigned
department and functional unit, and can articulate the linkages to
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and impact on client/sponsor
satisfaction and customer satisfaction.
- Directly influences the statement of work related to the development
and implementation of segment data plans and/or assigned database
marketing projects.
- Has responsibility for providing functional guidance and leadership to
team members throughout a project's life cycle, and often influences
management decisions and/or activities of a multi-functional team.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Accountable for department results (e.g., campaign/program results,
direct marketing revenue), and for activities and/or projects
involving multi-functional teams (e.g., additional client/sponsor
funding and investments).
- Manages to a high level of client/sponsor satisfaction by analyzing
feedback and modifying plans or approaches.
- Regularly participates in overall departmental and functional program
planning.
2.8.10.4 Position Title: Database Marketing Strategist - Advisory
Position Concept:
The Database Marketing Strategist-Advisory is responsible for creating
data strategy/plans that support client/sponsor segment message plans
(market or brand). The Database Marketing Strategist-Advisory works
independently as a productive member of a team, or leader of a small team.
The Database Marketing Strategist-Advisory focuses on developing
leadership skills, and using analytical skills and business/professional
knowledge to generate strategies and solutions. The Database Marketing
Strategist-Advisory demonstrates proficiency in strategy and planning
activities, including the use of marketing information and data analysis
techniques to understand customer purchase behavior, target business
opportunities, and to assist Direct Marketing Strategists/Managers in the
development of segment message strategies and deliverables. The Database
Marketing Strategist-Advisory determines the requirements for customer
contact data, and ensures those requirements are met. All strategy and
planning activities support the Message Management process (delivery of
marketing messages to customers), and associated processes within Customer
Relationship Management (CRM).
Skills
- Maintains marketing, business acumen, analytical, and database
marketing/direct marketing, Message Management process, and associated
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) process skills needed to
strategize and create segment data plans that support segment message
plans created by Direct Marketing Strategists/ Managers and
client/sponsors. Demonstrates required skill proficiency levels for
this position.
- Works independently as a database marketing professional and does not
require close management supervision.
- Articulates and evaluates alternative approaches for strategizing and
creating segment data plans, and enhancing a market information
database.
- Negotiates effectively with team members, including vendors and
sub-contractors, on segment data plan objectives and/or special
project activities, e.g., a statement of work that includes outputs,
target completion dates, data requirements, resource requirements.
- Recognizes problems associated with the goals and objectives of
segment data plans or statements of work.
- Applies creativity and judgement to the strategy and planning
activities for assigned segment data plans, database marketing
projects, and other activities.
- Independently generates solutions based on analytical skills and
business knowledge.
- Challenges existing department procedures, or company processes (e.g.,
Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Message Management) for the
purpose of enhancing and improving them and recommends/ develops
alternative approaches.
Contribution/Leadership
- Works independently and/or leads small team of other database
marketing professionals to strategize and create segment data plans,
or implement special database marketing projects.
- Develops leadership characteristics, e.g., advises others in the use
of tools, works on a special database marketing project, or leads a
small team in strategy and planning activities.
- Controls own work priorities and methods for assigned tasks/projects
and makes necessary trade-offs.
- Understands and articulates the mission and vision of the assigned
functional unit and department.
- Provides advice to the Direct Marketing Strategist/Manager and
client/sponsor regarding segment opportunities, and data and message
strategies.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Accountable for individual, team or departmental results (e.g.,
campaign/program results, direct marketing revenue, and impact of the
results on direct marketing functional activities (e.g., additional
funding and investment initiatives).
- Responsible for achieving client/sponsor satisfaction goals (e.g.,
creative ideas, completion targets, assessing business risks).
- Participates in department planning activities.
- Analyzes the impact of activities on costs in relation to the revenue
and expense objectives of segment message or business plans.
2.8.10.5 Position Title: Database Marketing Strategist - Senior
Position Concept:
The Database Marketing Strategist-Senior is responsible for creating data
strategy/plans that support complex client/sponsor segment message plans
(market or brand). The Database Marketing Strategist-Senior is
self-directed, perceived as a leader, provides advice and guidance to
other professionals, and is often assigned as a team leader or to a
special project. The Database Marketing Strategist-Senior demonstrates
comprehensive knowledge in marketing information and data analysis
techniques to understand customer purchase behavior, target business
opportunities, and to support Direct Marketing Strategists/Managers in the
development of segment message strategies and deliverables. The Database
Marketing Strategist-Senior drives the requirements for customer contact
data, defines objectives, and ensures those requirements and objectives
are met. The Database Marketing Strategist-Senior influences others in the
effective implementation of the Message Management process (delivery of
marketing messages to customers), and associated processes within Customer
Relationship Management (CRM).
In addition to the attributes of the Database Marketing
Strategist-Advisory, the Database Marketing Strategist-Senior has
responsibility to act as a mentor to at least one less-experienced
Database Marketing Strategist or Specialist.
Skills
- Maintains in-depth knowledge of database marketing approaches,
database marketing tools, and processes. Delivers the effective
strategy, planning and creation of segment data plans that support
client/sponsor segment message plans. Demonstrates required skill
proficiency levels for this position.
- Acts as a mentor to new hires and/or advises peers within database
marketing and direct marketing. Advises a Direct Marketing
Strategist/Manager on target opportunities through the use of data
analytics and contributes to the overall strategy and planning of
segment message plans and/or special projects.
- Negotiates effectively with management and team members, including
vendors and subcontractors, on segment data plan objectives and/or
special project activities, e.g., a statement of work that includes
outputs, target completion dates, data requirements, resource
requirements.
- Recognizes and evaluates solutions to complex problems related to the
goals and objectives of segment data plans, segment message plans,
statements of work and/or database marketing special projects.
- Analyzes problem situations and challenges, takes the initiative to
recommend alternatives, and develops and implements solutions.
- Applies creativity and sound business judgement to the strategy and
planning activities for segment data plans, database marketing
projects, and other assigned activities.
Contribution/Leadership
- Leads a team of database marketing strategists, specialists, vendors,
and/or subcontractors in creating segment data plans, or leads a
special project team.
- Understands and supports the mission and vision of the assigned
department and functional unit, and can articulate the linkages to
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and impact on client/sponsor
satisfaction.
- Directly influences decisions concerning tool selection/usage,
processes, priorities, and resources to support client/sponsor
objectives, and/or special database marketing projects.
- Has responsibility for providing functional guidance and leadership to
team members throughout a project's life cycle, and often influences
management decisions and/or activities of a multi-functional team.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Accountable for department results (e.g., campaign/program results,
direct marketing revenue), and for activities and/or projects
involving multi-functional teams (e.g., additional client/sponsor
funding and investments).
- Manages to a high level of client/sponsor satisfaction by analyzing
feedback and modifying plans or approaches.
- Regularly participates in overall departmental and functional program
program planning.
2.8.10.6 Position Title: Database Marketing Manager
Position Concept:
The Database Marketing Manager leads a database marketing team or manages
a unit/department focused on building and implementing data
strategies/plans that support client/sponsor segment business and message
plans (market or brand). The Database Marketing Manager is guided by
worldwide database marketing strategies, has latitude to set priorities
and determine resources, and has a breadth of business and database
marketing knowledge. The Database Marketing Manager is recognized as an
expert in the use of market information and data analysis techniques to
profile customer purchase behavior and target business opportunities. The
Database Marketing Manager partners with Direct Marketing
Strategists/Managers to develop and implement segment message/ strategies.
The Database Marketing Manger has experience in all facets of
planning/strategy, development and implementation of message/ data plans,
and is accountable for all agreed to objectives (e.g., expense budgets,
data integrity, schedules) with Direct Marketing Strategists/ Managers
and/or client/sponsors. The Database Marketing Manager plays a leadership
role in implementing the Message Management process, (delivery of
marketing messages to customers), Customer Relationship Management (CRM),
and worldwide database marketing initiatives.
In addition to the attributes of the Database Marketing Specialist-Senior
and the Database Marketing Strategist-Senior, the Database Marketing
Manager has responsibility to act as a mentor to one or more database
marketing professionals.
Skills
- Maintains expert database marketing knowledge; has a breadth of
experience in multiple database marketing disciplines and all facets
of strategy/planning, development, and implementation of message/data
plans. Demonstrates required skill proficiency levels for this
position.
- Understands internal organization structure, resource planning,
priorities, business objectives and company policies. Manages
effectively in the matrix environment to meet department and
client/sponsor objectives.
- Leads and guides other database marketing professionals. Initiates and
effectively advises Direct Marketing Strategists/Managers,
client/sponsors, department managers and executives on database
marketing techniques and approaches, and is considered a partner in
the overall strategy and planning of segment message strategies.
- Adapts communications and approaches to negotiate agreement with
department management, direct marketing peers, client/sponsors, and/or
vendor resources (e.g., staffing requirements and/or tools to meet
demand and client/sponsor objectives).
- Anticipates and analyzes problems associated with segment message
plans, segment data plans, or special projects. Contains risk and
develops and manages the implementation of database marketing
strategies and solutions. Assesses business and technical impact of
solutions.
- Assesses opportunities to integrate new trends in database marketing
into department planning and strategy activities. Develops
leading-edge database marketing strategies and solutions.
Contribution/Leadership
- Leads or manages a database marketing team and/or a multi-functional
special project team.
- Has considerable latitude and accountability for decisions concerning
tool selection/usage, processes, priorities, and resources to support
client/sponsor objectives, and/or special database marketing projects.
- Contributes to the vision of the department and how its mission
supports the worldwide database marketing strategies, goals and
objectives. Initiates communication of vision and mission to
client/sponsors and other internal organizations.
- Frequently influences department executives and managers on
complex/difficult issues.
- Is recognized and respected as a subject matter expert in market
information systems inside and outside the organization.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Responsible for the success of a large database marketing
team/department, or database marketing project/program involving a
multi-functional, country or regional team (e.g., future funding or
investments).
- Accountable for overall database marketing measurements, e.g.,
department direct marketing revenue, data integrity, high level of
client/sponsor satisfaction.
- Identifies risks associated with estimated costs, schedules and
resources required to support segment data plans and/or special
projects.
- Initiates activities that impact client/sponsor satisfaction, customer
satisfaction, and future decisions regarding database marketing
investments.
2.8.10.7 Position Title: Senior Database Marketing Manager
Position Concept:
The Senior Database Marketing Manager leads a large database marketing
team or manages a unit/department focused on building and implementing
data strategies/plans that support multiple and/or complex client/sponsor
segment business and message plans (market or brand). The Database
Marketing Manager develops innovative database marketing/direct marketing
strategies, has input to policy-making, and is considered an expert and
leader by other authorities inside and outside the company. The Senior
Database Marketing Manager is considered a person of vision, anticipates
change, recognizes new trends in database marketing/direct marketing and
is the expert in the use of marketing information and data analysis
techniques to profile customer behavior and target business opportunities.
The Senior Database Marketing Manager partners with Direct Marketing
Strategists/Managers to develop and implement innovative segment
message/data strategies. The Senior Database Marketing Manager has expert
knowledge and breadth of experience in all facets of planning/ strategy,
development and implementation of message/data plans, and is accountable
for all agreed to objectives (e.g., expense budgets, data integrity,
schedules) with Direct Marketing Strategists/Managers, client/ sponsors,
and/or department executives. The Senior Database Marketing Manager is a
unit/department/functional leader in implementing the Message Management
process, (delivery of marketing messages to customers), Customer
Relationship Management (CRM), and worldwide database marketing
initiatives.
The Senior Database Marketing Manager has responsibility to act as a
mentor to one or more database marketing professionals, and to facilitate
the use of a mentoring program within the unit/department.
Skills
- Maintains expert database marketing knowledge; has a breadth of
experience in most database marketing disciplines, and demonstrates
expertise in all facets of strategy/planning, development, and
implementation of segment message/data plans. Defines and drives the
development of new skills in database marketing throughout the
organization.
- Demonstrates a comprehensive understanding of business unit, country,
and international company organization structures and resources,
operations, strategies, and business objectives.
- Plans and conducts complex negotiations reaching lasting agreements
and commitments.
- Develops and implements database marketing concepts and strategies
with executive review.
- Anticipates change; recognizes new trends in database marketing, and
introduces new approaches into department and worldwide planning and
strategy.
Contribution/Leadership
- Manages a large department, or leads country/regional/international
team in the development and implementation of strategic, and often
leading-edge database marketing projects (e.g., the design or
implementation of an analytic database).
- Develops the vision of a database marketing department or country/
regional/international project team, and how its mission supports
worldwide database marketing strategies, goals and objectives.
Facilitates communication of vision and mission to client/sponsor
executives, functional executives, and other internal organizations.
- Internationally recognized as an expert and leader in market
information systems. Sought out by peers, client/sponsors, and
executive management to resolve complex/difficult issues and develop
innovative database marketing strategies.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Develops and implements database marketing strategies for executive
review. Contributes to country and international policies related to
database marketing.
- Accountable for the overall functional program success of database
marketing, direct marketing revenue for a business unit, major country
or region, and/or an international database marketing project.
- Responsible for committing resources, making decisions regarding
future database marketing investments and large special projects.
- Responsible for quality output and value add for highly visible market
segments, strategic database marketing projects, and future business
development.
3.0 Sales Professions
Subtopics:
3.1 Chapter 12. Client Relationship Profession
Subtopics:
3.1.1 Client Relationship Profession Overview
Understanding customers' values and needs and properly attending to their
requirements, locally as well as globally, is extremely critical to
success. The Client Relationship Professional is responsible for
understanding business requirements and influencing the inner circle of
top management.
The Client Relationship Professional is responsible for the overall
Customer/IBM relationship and the execution of associated business
strategies. He/she monitors key IBM activities within the client
environment. He/she identifies and qualifies IBM opportunities, shares
information with appropriate members of the extended team supporting the
customer, gains customer commitment to solutions and ensures overall
customer satisfaction.
The following positions are defined within the Client Relationship
profession:
- Client Representative
- Advisory Client Representative
- Senior Client Representative
- Consulting Client Representative (where announced)
- Client Manager
- Client Executive
The major differences among these positions are experience, skill levels
and business contribution.
The certified positions demand higher skill requirements and are
differentiated primarily by the complexity of the client environment and
the level of experience required to excel. The Consulting Client
Representative position recognizes and leverages high-level industry and
leadership skills.
There are three profession disciplines within the Client Relationship
profession:
- Client Relationship Profession - I/T
- Client Relationship Profession - International
- Client Relationship Profession - Business Partner
A discipline is a specified area within the profession that focuses on a
specialized business activity and the development of skills that support
the role.
Client Relationship professionals work in industry specific areas and
develop an extensive knowledge of the client's industry and the operation
of the extended enterprise.
The Client Relationship Profession - I/T discipline focuses on the
Information Technology in support of business and functional requirements
within the client's extended enterprise. In this discipline, the Client
Relationship Representative develops and maintains a working relationship
with senior I/T executives and managers. This specialty requires in-depth
skills in technology, industry solutions and/or services offerings.
The Client Relationship Profession - International discipline is designed
to ensure focus on special requirements of global customers. In this role,
the Client Relationship Representative - International must development
the skills required to sell solutions and manage issues particular to the
international marketplace.
The Client Relationship Profession - Business Partner discipline focuses
on marketing to and through Business Partners and maintains fruitful
relationships with third party business executives and managers. It
requires a high level partnership skills, with the ability to strike a
business balance among:
- The needs and satisfaction of Business Partners,
- Concern for high end user satisfaction, and
- IBM's business interests
3.1.2 Profession Structure
The Client Relationship Relationship Profession consists of 6 positions:
- Client Representative
- Advisory Client Representative
- Senior Client Representative
- Consulting Client Representative (where announced)
- Client Manager
- Client Executive
The Client Manager and Client Executive positions are certified positions.
Figure 12-1, Figure 12-2 and Figure 12-3 summarize the requirements of
each position of the profession and the developmental requirements for
progression within the profession. Detailed position descriptions can be
found in "Client Relationship Position Descriptions" in topic 3.1.10.
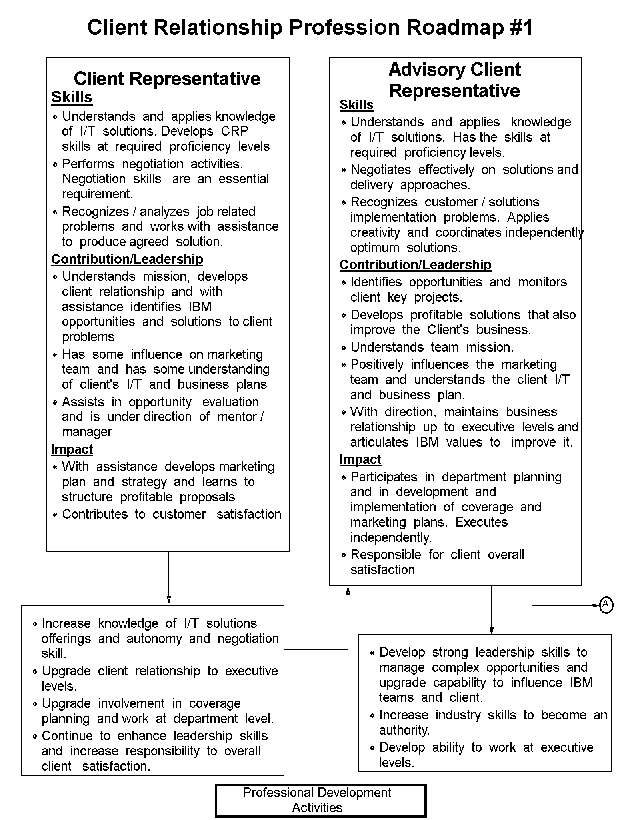
Figure 12-1. Client Relationship Profession Roadmap
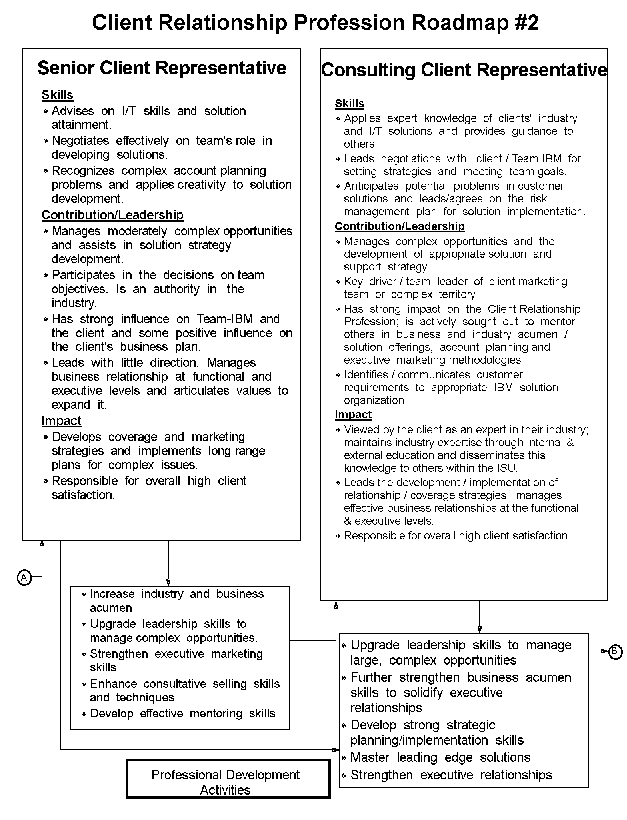
Figure 12-2. Client Relationship Profession Roadmap
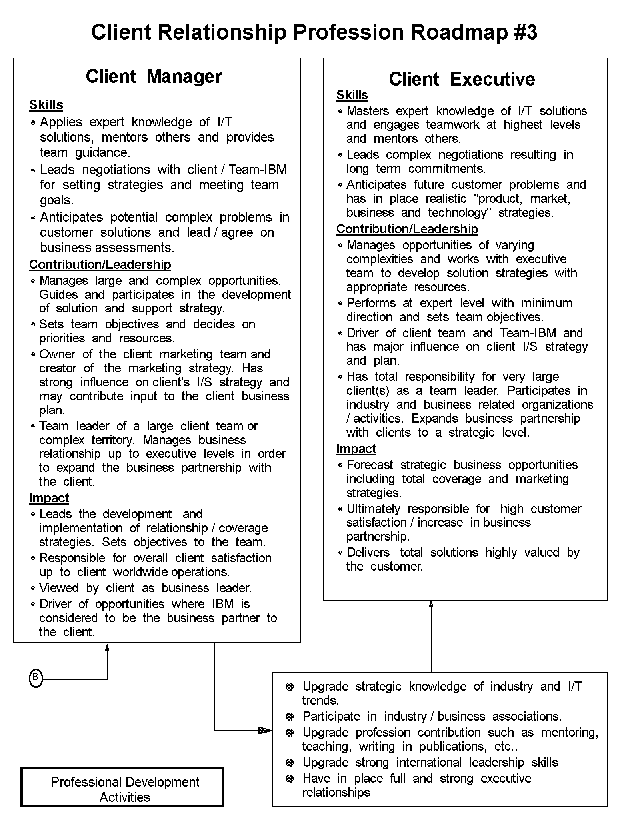
Figure 12-3. Client Relationship Profession Roadmap
3.1.3 Characteristics of the Profession
IBM competes in a market-driven environment and is focused on satisfying
each customer's unique business needs. To be successful, the Client
Relationship Professional must understand each customer's business, where
they place value, develop expertise and deliver on promised results.
- Client Representatives focus on understanding the business goals and
objectives of the client including client business strategies,
industry position, measurement of success and management processes, in
order to identify IBM business opportunities for application
solutions, services and products.
- The Client Relationship Representative is a non-management
professional position responsible for establishing and maintaining the
IBM business relationship with one or more clients.
- The Client Relationship Representative may be the owner of a large
account, part of a large account team, or the owner of a few
individual large accounts within the same industry.
- The Client Relationship Representative is NOT expected to be a product
or solutions expert and should engage the appropriate IBM sales
specialist or consultant to address the client's specific
requirements.
- Complementing the responsibilities described above, the Client
Relationship Representative/Executive - I/T also addresses client
business requirements but works more closely with I/T executives and
managers. The Client Relationship Representative/Executive -
International focuses on the client's worldwide requirements,
international executives and operations. These two disciplines, I/T
and International, are implemented in two environments:
- Large accounts that warrant a dedicated focus on I/T and/or
International functions.
- Selected accounts with a single industry where an I/T and/or
International Client Relationship Representative/Executive is
required.
- The Client Relationship Representative/Executive - Business Partner
addresses the requirements of Business Partners who have potential to
significantly increase IBM revenue and facilitate the expansion of the
Business Partner's activities with the proper level of IBM resources.
In summary, the Client Relationship professional has the mission of
nurturing the customer relationships. Their success is dependent on the
value that they bring to their client(s). It is the Client Relationship
Professional's responsibility to register business opportunities in the
CRM Opportunity Management system.
3.1.4 Potential Candidates
The concept of this profession is based on the principle that customer
valued opportunities are best recognized and solutions proposed by
individuals who have broad based and in-depth knowledge of the client's
business.
The Client Relationship Representative/Executive is a skill-based
position. Strong personal leadership, communication, problem-solving and
project management skills are required for success. In addition, sound
business acumen and a working understanding of the client's industry are
fundamental. Furthermore, the Client Relationship professional must be an
effective coordinator of projects and resources in support of the client.
(Please refer to section "Skill Requirements by Position" below).
Since the profession spans positions from client representative through
certified levels, opportunity exists at multiple entry points assuming
skills proficiency and experience requirements are satisfied.
Figure 12-4 shows some possible candidates for the Client Relationship
Profession and possible career movement from a client relationship
position.
Additional information on moving from another profession into the Client
Relationship Profession is available in Client Relationship Career
Movement Possibilities.
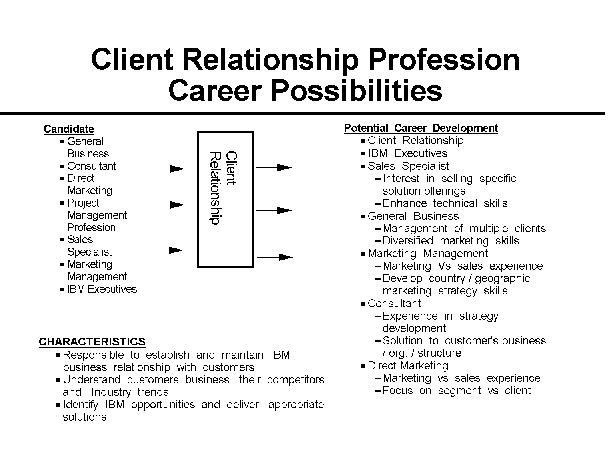
Figure 12-4. Client Relationship Profession Career Possibilities
3.1.5 Career Growth
The Client Relationship professional career growth is linked to the
individual's ability to understand their client's key business
requirements and effectiveness with senior management. These required
skills are not acquired overnight, but are the result of several years of
working with and understanding the customers' industry and environment.
Career growth is fundamentally based on business need, skill development
and business/professional contribution.
The Client Relationship Representative career positions span from client
representative through the consulting level. The Client Manager/Executive
roles assume greater responsibility and require certification. The major
difference among these positions is a function of demonstrated skill,
experience and business contribution. The Consulting Client Representative
demonstrates industry leadership and expertise. The Client Manager and
the Client Executive positions have similar skill requirements as the
client representative positions; however, the positions are differentiated
by certain classification criteria that reflect the complexity of the
client environment and the individual's business contribution.
As a Client Relationship Representative develops skills and experience,
he/she can aspire to higher levels of responsibility and compensation.
The Consulting Client Representative is an alternative career step for
Client Representatives with the appropriate industry skills and is not a
required step for certification nomination. More information on
certification can be found in the following section, Certification
Nomination Guide. Refer to Figure 12-1 in topic 3.1.2, Figure 12-2 in
topic 3.1.2 and Figure 12-3 in topic 3.1.2.
A Client Relationship Representative qualifies for each level of the
professional career when management assesses that prerequisite skills
levels (see Skills Requirements Table which lists in detail the skills and
proficiency requirements by position) and other professional standards
have been met. Professional skills are achieved through experience and
participation in a variety of skills development activities. The
activities (see Training/Education Roadmaps section of this guide) include
classroom, readings, self-study arrangements, industry associations,
conferences, mentoring and internships.
3.1.6 Certification Nomination Guide
A Client Relationship Representative may seek certification when the
business requires a Client Manager/Executive to support client
relationship activity, and management concludes that his/her experience
and skills are sufficient. Once a business need for a certified
professional has been identified, the candidate will submit a nomination
package for certification, with approvals from management. Guidance for
certification can be found in the Worldwide Client Relationship
Certification Nomination Guide.
3.1.7 Performance Elements
The client relationship profession is designed to ensure the IBM sales
team has the skills necessary to work as business partners with our
customers. The Client Relationship professional has the mission to
nurture the customer relationship and identify client projects and
opportunities where IBM has a solution and can bring value.
Accordingly, the key measurement of the IBM business relationship with the
client will be the level of satisfaction the client has with the Client
Relationship Representative's contribution to his business and the degree
of involving the Representative in his plans and projects. Additionally,
and as IBM's focal point with the client, all revenue for services,
products and solutions and associated profit are the other key performance
factors.
3.1.8 Client Relationship Profession Skills Profile
The skills required for a Client Relationship position include
professional skills, IBM environment skills, personal skills, and project
management skills. The following table lists the skills required of a
Client Relationship professional at the Client Representative, Advisory,
Senior, Consulting, Client Manager and Client Executive positions within
the profession.
Position templates are found on the Skills tool and include for each
position template a section on extended descriptions and a list of the
required skills. An example of a template extended description is that of
the Client Representative position as follows: (Other position templates
extended descriptions in the skills tool are similar to this) :
Client Representative
Template Owner - Colleen Brunton
Template Number - 06073
Description
TEMPLATE NAME: Client Representative
USERS OF THIS TEMPLATE: This template is used by a Client
Representative.
OVERVIEW: The Client Representative is responsible for the overall
customer/IBM relationship and associated strategies. This individual is
involved in identifying and qualifying IBM opportunities, sharing the
information among the extended team members, gaining customer
commitment to solutions as appropriate and ensuring overall customer
satisfaction.
RELATED TEMPLATES:
* Client Representative-Adv
* Client Representative-Sr
* Client Representative-Cons
* Client Manager
* Client Executive
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION:
More information on the Client Relationship profession can be found in
the Worldwide Guide to IBM Sales & Distribution Professional Careers.
If you are unfamiliar with local procedures for obtaining this
document, you can obtain instructions by issuing the following from an
OV/VM command line:
For AP: Request WWGUIDAP from WWSSPROF at RHQVM15
For EMEA: Request WWGUIDEM from WWSSPROF at RHQVM15
For LA: Request WWGUIDLA from WWSSPROF at RHQVM15
For NA: Request WWGUIDNA from WWSSPROF at RHQVM15
OWNER: Colleen Brunton IBMUSM02/CBRUNTON December 1997
_____________________ __________________________________________________
| | Profession Positions, with Associated Skill |
| CLIENT RELATIONSHIP | Levels |
| SKILLS |______ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| | CR | Adv | Sr | Cons | CL | CL | Key |
| | | CR | CR | CR | Mgr | Exec | Skill|
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| PROFESSIONAL SKILLS |
|_____________________ ______ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| Client Management | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
| System & Culture | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Client | | | | | | | |
| Information/Data | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
| Infrastructures | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Develop & Implement | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
| Account Plan | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Develop & Maintain | | | | | | | |
| Client | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | Y |
| Relationships | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Apply Knowledge of | | | | | | | |
| Client's Business | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | Y |
| Strategies | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Apply Knowledge of | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 5 | Y |
| Client's Industry | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Apply Knowledge of | | | | | | | |
| Multi-Industry | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Solutions | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Deploy the IBM | | | | | | | |
| Coverage/Relationshi| 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
| Plan | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Manage Customer | | | | | | | |
| Satisfaction & | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
| Loyalty | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Consultative | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | Y |
| Selling | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Analyze & Select | | | | | | | |
| Target | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
| Opportunities | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Apply Appropriate | | | | | | | |
| Financial Strateges | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| to Client | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Apply Knowledge of | | | | | | | |
| Business Processes | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| to Client | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Understand | | | | | | | |
| Appropriate | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Consulting | | | | | | | |
| Techniques | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Articulate the | | | | | | | |
| Impact of | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | Y |
| Information | | | | | | | |
| Technology | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| IBM ENVIRONMENT SKILLS |
|_____________________ ______ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| Understand IBM | | | | | | | |
| Organization/Managem|nt 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | Y |
| System | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Apply Business | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Conduct Guidelines | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Articulate IBM | | | | | | | |
| Business Strategies | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
| & Initiatives | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Understand IBM | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Y |
| Architectures | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Know & Explain IBM | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Products/Technologie|/Servi|es | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| PERSONAL SKILLS |
|_____________________ ______ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| Leadership | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | Y |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Negotiation | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Interpersonal | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
| Communication | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Demonstrate | | | | | | | |
| Effective | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
| Problem-Solving | | | | | | | |
| Techniques | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Team Building | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | Y |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Creativity/Breakthro|gh 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
| Thinking | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Mentoring | | | | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| PROJECT MANAGEMENT SKILLS |
|_____________________ ______ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| Initiate Projects | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Plan Projects | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Track & Report on | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Client Projects | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Manage Risk & | | | | | | | |
| Change on Client | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| Projects | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Manage | | | | | | | |
| Contractors/Vendors | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| on Client Projects | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
3.1.9 Professional Development
For more information about Client Relationship profession skills, refer to
the Education Roadmap page of the IEC Course Catalog at
http://w3.lahulpe.ibm.com/roadmaps/index.html for an overview of the
Worldwide Professions and links to the Common Skills Categories and
Professions Roadmaps.
Also refer to Client Relationship Professional Development Activities.
In addition, use of mentoring is encouraged to improve skills with the
support of more experienced professions.
3.1.10 Client Relationship Position Descriptions
The following position descriptions describe the basic work of each of the
positions within the Professions. Formal descriptions which may contain
legally mandated language necessary for classifying employees in a
geography should be obtained through the approved on-line job library, if
available in the geography, or by contacting the appropriate H.R.
personnel within the geography.
Subtopics:
3.1.10.1 Position Title: Client Representative
Position Concept:
In the Client Representative position the individual develops skills under
the guidance of a team leader or manager and is provided assistance in
accomplishing his/her responsibilities. The Client Rep performs tasks that
include developing relationships within the client's account and
identifying viable client business problems which may translate into IBM
opportunities.
Skills
- Understands and applies knowledge of information technology and
associated solutions related to the Client's business to attain
his/her position and team objectives. Develops the required
proficiency levels of the CRP skills.
- Draws upon concepts and knowledge of information technology to
collaborate with team members and other IBM functions under the
guidance and assistance of a team leader or manager to accomplish
his/her responsibilities.
- Uses and attends to negotiation sessions as an entry team member,
involving other IBM functions and clients in order to attain position
objectives. Negotiation skills are an essential requirement.
- Recognizes job-related problems in account planning and solution
implementation and works to produce solutions with the assistance of a
team leader or manager. Analyzes causes using available methods and
procedures related to information technology and the client
profession.
- Analyzes client problems using available methodologies and prepare
alternative solutions for discussion with team leader or manager/other
IBM functions towards adoption of agreed solution to the client.
Contribution/Leadership
- Workscope
With assistance, identifies and qualifies IBM opportunities based on
an understanding of the client's business and strategy. Manages a few
simple projects.
- Autonomy
Work is reviewed with team members or team leader or management.
Gathers customer requirements and helps to translate them into
potential solutions.
- Vision
Understands the standard team mission he/she belongs to, and the
proper job mission. He/She develops relationship with the client
account and identifies viable client business problems which may turn
into IBM opportunities. Influence
On Large account team or owner of few individual accounts-Has some
influence on client marketing team, "team IBM" and the client.
Understands client team strategy and begins to cause those he/she
comes in contact with to align their contributions with this strategy.
Has some understanding of the client's information systems strategy
and business plan.
- Leadership
Assists in determining the priority position of an opportunity on the
client value system. Is under the direction of a mentor or manager.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Accountability
Accountable for individual results and contributes to team results
including revenue objectives and operational customer satisfaction
objectives.
- Planning
With assistance, develops and implements a marketing plan and the
supporting strategy for specific opportunities. With assistance,
works with the client and IBM resources to establish and implement
coverage/marketing plans to achieve business objectives and customer
satisfaction. Helps to implement long range plans and learns to
structure profitable proposals. Assists in execution as directed by
others.
- Business Measurement
Helps to make IBM business objectives including revenue and customer
satisfaction.
- Customer Satisfaction
Assists in making decisions regarding, and contributes to, customer
satisfaction. Contributes to team efforts.
- Financials
Helps meet the team business objectives.
- Value-Add
Maintains an awareness of IBM/Client activities and represents client
issues throughout team/IBM.
3.1.10.2 Position Title: Advisory Client Representative
Position Concept:
The Advisory Client Representative works independently, with general
direction, or as a member of a large team. At this position he/she is
expected to be proficient in establishing and maintaining an IBM
relationship with one or more clients. The Advisory Client Representative
has substantial marketing, business, technical and professional skills and
takes initial responsibility for the success of the relationship. This
involves identifying and qualifying IBM opportunities gaining client
commitment to solutions, and ensuring overall client satisfaction. The
Advisory Client Representative understands the client's business and is
able to determine areas where IBM solutions improve the client's business
effectiveness.
Skills
- Understands and applies knowledge of information technology and
associated solutions related to the Client's business to attain
departmental or functional area objectives . Has and demonstrates the
required skills proficiency levels of the Client Relationship
Profession.
- Engaged as an independent client representative in the attainment of
functional objectives and the evaluation of alternative solutions
towards the adoption of optimum approaches to meet client
requirements.
- Negotiates effectively with the client representatives team, customers
and other IBM functions on account planning, solution implementation
and problem-solving requirements and approaches to deliver them.
- Recognizes account planning/solution implementation problems related
to CRP project/department objectives and works towards solving them by
producing new client offerings/solutions or adjusting IBM procedures.
- Creativity and judgement applied in adapting solutions to customer
situations within the business environment, involving IBM functions,
subcontractors if needed and clients.
- Independently generates and coordinates client solutions with other
IBM functions and client r, based on analytical skills and information
technology knowledge.
Contribution/Leadership
- Workscope
Works on special projects : Identifies and qualifies IBM opportunities
and may assist in the development of the solution and support strategy
based on an understanding of the client's business, industry trends
and directions, the client's competitors, their relative position in
the industry and IBM's capability in the client's environment.
Monitors and maintains awareness of the client's key projects and
manages opportunities well.
- Autonomy
Generally controls own work priorities and methods requiring
trade-offs between different alternatives to reach optimum client
solutions. Evaluates critical customer requirements and develops
mutually profitable solutions by working with others.
- Vision
Understands departmental mission and vision for proper implementation.
Also, understands the client's business and is able to determine areas
where IBM solutions improve the client's business effectiveness.
- Influence
On large account team or owner of few individual accounts- Positively
influences the client marketing team, "team IBM" and the client.
Understands the client team strategy, client information system
strategy and client business plan.
- Leadership
Is a member of a large client team or has independently a small number
of accounts and can be a team leader. With direction, establishes and
maintains effective business relationships at both the functional and
executive levels by referencing successful IBM engagements and
articulating the value IBM can bring to the relationship.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Accountability
Accountable for individual, team, or department results for objectives
including revenue and customer satisfaction, and for the impact of the
results on functional areas.
- Planning
Participates in overall departmental program planning. Evaluates
critical client requirements. Working with clients and IBM resources,
participates in the development and implementation of relationship,
coverage and marketing plans to achieve business objectives. Leverages
channels of distribution to maintain and improve customer satisfaction
and maximize revenue and profit. Implements long range plans and
executes independently.
- Business Measurement
Supports activities that are subject to business measurement against
assigned objectives like revenue, profit and customer satisfaction.
- Customer Satisfaction
Significantly supports activities that contribute to customer
satisfaction. Is responsible for the client's overall satisfaction
with the business relationship. Makes regular independent decisions
regarding customer satisfaction and develops and executes plans on
time with positive results.
- Financials
May have budgetary responsibility and has significant influence on
revenue and profit.
- Value-Add
Monitors and maintains an awareness of key IBM/client activities and
represents client issues, needs and concerns throughout IBM. Delivers
complete solutions which meet the client business needs and which are
considered strategic by both the client and IBM.
3.1.10.3 Position Title: Senior Client Representative
Position Concept:
The Senior Client Representative works independently or as a member of a
large team or leader of a small team. He/she is proficient in establishing
and maintaining an IBM relationship with one or more clients. The Senior
Client Representative has in-depth marketing, business, technical and
professional skills and has primary responsibility for the success of the
relationship. This involves identifying and qualifying IBM opportunities,
gaining client commitment to IBM solutions and ensuring overall client
satisfaction. He/She has an in-depth understanding of the client's
business and is able to determine areas where IBM's functional business
segments can complement the client's business.
Skills
- Understands and applies knowledge of information technology and
associated solutions related to the Client's business to attain
function and business unit objectives. Demonstrates and advises on the
required proficiency levels of the CRP skills.
- Advises other professionals in the CRP team on the attainment of
required proficiency levels and on achieving business objectives.
- Works effectively with other team members to understand and anticipate
customer needs and to develop solutions which meet those needs. Has
influence on team members, clients and other IBM functions towards
accomplishing the team goals.
- Negotiates effectively on account planning with team members, clients
and other IBM functions to identify the team's role in developing
solutions and agree on specific client problem solving needs and
approaches to produce them.
- Recognizes complex account planning problems related to CRP functional
objectives.
- Creativity and judgement applied to solution development work to
clients on different projects within the business environment
involving IBM functions, subcontractors and clients.
- Supervises the adequate implementation of clients solutions and if
necessary stimulates the creation of new procedures and processes.
- Challenges the validity of given procedures and processes to enhance
and improve or develop complementary solutions to clients.
Contribution/Leadership
- Workscope
Conducts special projects : Creates and qualifies IBM opportunities
and may assist in development of the solution and support strategy
based on an in-depth understanding of the client's business, industry
trends and directions, the client's competitors, their relative
position in the industry and IBM's capability in the client's
environment. Anticipates and escalates client's concerns on key
projects. Manages moderately complex opportunities.
- Autonomy
Defines and participates in the decision on objectives within
specified business concepts for the CRP team and/or department.
Usually recognized as an authority in their client's business and
industry. Is able to develop creative solutions by leveraging
resources.
- Vision
Understands department/function mission and vision for effective
implementation and has in-depth understanding of the the client's
business and is able to determine areas where IBM's solutions
complement the client's business.
- Influence
On large account team or owner of few individual accounts- Owns or has
strong influence on the client marketing team, "team IBM", and the
client. Has input to the client team strategy, client information
systems strategy and some positive influence on the client's business
plan.
- Leadership
Leads with little direction multiple middle size clients or a large
account. May manage a department. Establishes, maintains and manages
effective business relationships at both the functional and executive
business levels referencing successful IBM engagements, understanding
and articulating the value IBM can bring to the relationship and
developing new ideas that expand the business partnership.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Accountability
Accountable for department results for objectives usually involving
revenue and profit, customer satisfaction etc..., and as required for
specific activities and/or projects involving multi-functional teams.
- Planning
Regularly participates in overall functional operating planning;
builds and executes plans. Works with clients and IBM resources to
develop and implement relationship, coverage and marketing strategies
to achieve business objectives and customer satisfaction. Leverages
channels of distribution to maintain and improve customer satisfaction
and maximize revenue and profit. Implements long range plans for
complex business issues.
- Business Measurement
Activities are subject to business measurement against assigned
objectives usually involving customer satisfaction, revenue and
profit.
- Customer Satisfaction
Activities impact customer satisfaction. The Senior Client
Representative is viewed by the client as reliable and highly valued
resource on solving client problems and in meeting his expectations.
Is responsible for the client's overall satisfaction with the business
relationship. Determines severity level in critical situations that
affect customer satisfaction. Comprehensive plan developed with the
client. Consistently should show positive results.
- Financials
Performance of activities has significant impact on generating revenue
and profit, to exceed objectives thus minimizing costs and expenses
impact on the business.
- Value-Add
Monitors and maintains awareness of all key IBM related activities
with the client's environment, including the representation of the
client issues, needs and concerns throughout IBM. Delivers complete
solutions which are highly valued by client and IBM and are considered
as high impact and strategic by both.
3.1.10.4 Position Title: Consulting Client Representative (where announced)
Position Concept:
The Consulting Client Representative is a key contributor within the ISU
organization, demonstrating proficiency and leadership within a specific
industry. He/She is actively engaged in external and internal industry
associations, industry education and related activities and is responsible
for disseminating this industry expertise / knowledge to others within the
ISU.
The Consulting Client Representative is a lead individual contributor on
large important/strategic accounts or on large portions of very large
strategic accounts. He/She is proficient in establishing and maintaining
an IBM relationship with one or more important strategic clients and makes
calls on policy level customer executives within their accounts or area of
responsibility. He/She has expert marketing business, technical and
professional skills and has primary responsibility for the success of the
relationship. This involves identifying and qualifying IBM opportunities,
engaging the appropriate IBM resources, gaining client commitment to
solutions when appropriate, and ensuring overall client satisfaction. The
Consulting Client Representative has an in-depth understanding of the
client's business and is able to determine areas where IBM's functional
business segments can complement the client's business. In addition, the
Consulting Client Representative often provides guidance and direction to
others. He/She often assists others in the development of their
strategies and plans and in identifying and qualifying opportunities.
Skills
- Understands and applies in-depth knowledge of the industry, including
trends and directions, forces driving the industry and its players,
competitive environment, extended enterprise relationships, etc., and
takes an active, leadership role in external industry associations /
organizations.
- Applies expert knowledge of information technology and associated
leading edge solutions related to the Client's business to attain
function, business unit or regional operations objectives. Has the
required proficiency levels of the CRP skills.
- Understands organizational resources, priorities, needs and policies.
- Mentors others and provides guidance on the attainment of the required
skills proficiency levels and on achieving business objectives.
Directly influences the team, clients and other IBM functions to
attain team goals.
- Leads negotiations effectively with clients and other IBM functions on
project/team goals for definition and setting of strategies to
reach/exceed them.
- Anticipates potential problems associated with account planning and/or
customer solutions and leads/agrees on the risk management plan for
implementation of solutions.
- Analyzes new and complex industry, technology, economic and
competitive situations taking into consideration real client needs and
problems. Evaluates potential solutions involving IBM functions,
subcontractors and clients. Gains team agreement on business
assessment of solutions.
- Ensures that Client and IBM functions agree on the steps involved to
develop and implement client solutions including the set-up of a
project management plan to ensure timely success.
Contribution/Leadership
- Workscope
Creates, qualifies and manages IBM opportunities, guides and
participates in the development of the solution and support strategy
based on an in-depth understanding of the client's business, industry
trends and directions, their competitors, their relative position in
the industry and IBM capabilities in the clients environment.
Anticipates and responds to/escalates client's concerns on key
projects. Manages complex opportunities.
- Autonomy
A recognized expert in their client's industry/business. Secures
commitment and agreement on client/solutions. Responsible for complex
projects and decides on priorities and resources following general
business unit directives by setting team objectives.
- Vision
Has strategic vision of functional or business unit mission for
effective implementation and has an in-depth understanding of the
client's business and is able to determine areas where IBM's
functional business segments can complement the client's business.
- Influence
On large important account team or as owner of one or more important
accounts-- has responsibility for on the client marketing team.
Utilizes all internal IBM resources well and has strong influence on
the client's information systems strategy. Contributes possible
inputs for the client's business strategy/plan. Influences the client
on ways IBM can become their strategic IS partner.
Has positive impact and influence on the client relationship
profession as well as other team members. Is actively sought out to
mentor other client rep professionals in industry acumen and industry
solutions / offerings from IBM and competitors.
- Leadership
Key driver/team leader of client marketing team or complex territory.
Establishes, maintains and manages effective business relationships at
both the functional and executive levels referencing successful
business engagements, understanding and articulating what value IBM
can bring to the relationship and creating new ideas to expand the
business partnership. Is sought by the client's management team for
input and direction.
Is regarded as an industry role model with recognized impact within
the ISU.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Accountability
Maintains industry expertise through internal and external education
and disseminates this knowledge to others within the ISU.
Responsible for overall department results involving revenue, profit
and customer satisfaction, and as required for specific activities
and/or projects involving country-wide, regional, or multifunctional
teams.
- Planning
Develops creative plans broad in scope and impact. Works with clients
and IBM resources and leads the development and implementation of
relationship, coverage and marketing strategies to achieve business
objectives and assists others. Leverages channels of distribution to
maintain and improve customer satisfaction and maximize revenue and
profit. Sets/drives objectives for the team to exceed IBM business
objectives.
- Business Measurement
Activities are directly subject to business measurement including
revenue, profit, customer satisfaction, market share, share of
applicable client IT budget and installed base which directly affect
revenue and profit.
- Customer Satisfaction
Is viewed by the client as a reliable, valuable resource. Is
responsible for the client's overall satisfaction with the business
relationship. Proactive in improving customer satisfaction year to
year wherever customer makes business.
- Financials
Applies creativity to enhance revenues and profitability and to reduce
department/team costs and expenses, thereby having favorable impact on
functional and Business Unit objectives.
- Value-Add (additional)
Monitors and maintains an awareness of all key IBM/Client activities,
including the representation of client issues, needs concerns
throughout IBM.
Communicates customer requirements to appropriate IBM solutions
organization in a professional, efficient and timely manner.
Consistently delivers solutions which are highly valued by client and
IBM and are considered as high impact, complex and strategic by both.
Driver of opportunities in which IBM is considered to be the client's
strategic business partner.
3.1.10.5 Position Title: Client Manager
Position Concept:
The Client Manager works as a member/leader of a large team. He/She is
proficient in establishing and maintaining an IBM relationship with one
strategic or several important clients. He/She has expert marketing,
business, technical and professional skills and has ultimate
responsibility for the success of the relationship. This involves
identifying and qualifying IBM opportunities, engaging the appropriate IBM
resources, gaining client commitment to solutions when appropriate, and
ensuring overall client satisfaction. The Client Manager has an in-depth
understanding of the client's business and is able to determine areas
where IBM's functional business segments can complement the client's
business. In addition, the Client Manager often provides guidance and
direction to others. He/She often assists others in the development of
their strategies and plans identifying and qualifying opportunities,
making executive calls and professional skills development.
Skills
- Applies expert knowledge of information technology and associated
leading edge solutions related to the Client's business to attain
function, business unit or country/ regional operations objectives.
Has the required proficiency levels of the CRP skills.
- Understands organizational resources, priorities, needs and policies.
- Mentors others and provides guidance to the team on the attainment of
the required skills proficiency levels and on achieving business
objectives. Directly influences the team, clients and other IBM
functions to attain team goals.
- Leads negotiations effectively with clients and other IBM functions on
projects/team goals for definition and setting of strategies to
reach/exceed them.
- Anticipates potential problems associated with account planning and/or
customer solutions and lead/agree on the risk management plan for
implementation of solutions.
- Analyzes new and complex industry, technology, economic and
competitive situations taking into consideration real client needs and
problems. Evaluates potential solutions and leads IBM functions
towards the adoption of optimum solutions. Agree on business
assessment of solutions.
- Agree with client and IBM functions on the steps involved to develop
and implement client solutions including the set-up of a project
management plan to ensure timely success.
Contribution/Leadership
- Workscope
Qualifies and manages IBM opportunities. Guides and participates in
the development of the solution and support strategy based on an
in-depth understanding of the client's business, industry trends and
directions, their competitors, their relative position in the industry
and IBM capabilities in the client's environment. Manages large and
complex opportunities.
- Autonomy
A recognized expert inside and outside the client geography. Secures
commitment and agreement on client solutions. Responsible for complex
projects and decides on priorities and resources following general
business unit directives by setting team objectives.
- Vision
Has strategic vision of functional or business unit mission for
effective implementation and has an in-depth understanding of the
client's business and is able to determine areas where IBM's
functional business segments can complement the client's business.
- Influence
On large account- Owner of the client marketing team and creator of of
the marketing strategy. Utilizes all internal IBM resources well and
has strong influence on client's information systems strategy, often
considered a teammate to the client's IS organization. Contributes
possible inputs for the client's business strategy and plan. Has
contributed to the client as a thought leader. Is influencing the
client on ways IBM can become their strategic IS partner.
- Leadership
Is the team leader of a large multifunctional client team or complex
territory. Establishes , maintains and manages effective business
relationships at both the functional and executive levels referencing
successful business engagements, understanding and articulating what
value IBM can bring to the relationship and creating new ideas to
expand the business partnership. Is sought by the client executive
team for input and direction . Leads multifunctional teams.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Accountability
Directly responsible for overall department results involving revenue,
profit and customer satisfaction, and for multifunction, country-wide
or geographic teams projects.
- Planning
Develops creative plans broad in scope and impact. Works with clients
and IBM resources, leads the development and implementation of
relationship, coverage and marketing strategies to achieve business
objectives and assist others. Leverages channels of distribution to
maintain and improve customer satisfaction and maximize revenue and
profit. Sets objectives for the team to exceed IBM business
objectives.
- Business Measurement
Activities are directly subject to business measurement including
revenue, profit, customer satisfaction, market share, share of
applicable client IT budget and installed base. which directly affect
revenue and profit.
- Customer Satisfaction
Is viewed by the client as a business leader, a reliable and highly
valued resource, and is responsible for the client's overall
satisfaction with the business relationship. Proactive in improving
customer satisfaction year to year wherever customer makes business.
- Financials
Apply creativity to reduce department/team costs and expenses
impacting functional and geographic achievements. Has a major impact
on functional and Business Unit revenue and profit objectives.
- Value-Add (additional)
Monitors and maintains an awareness of all key IBM/Client activities,
including the representation of client issues, needs concerns
throughout IBM. Consistently delivers solutions which are highly
valued by client and IBM and are considered as high impact, complex
and strategic by both. Driver of opportunities in which IBM is
considered to be the client's strategic business partner.
3.1.10.6 Position Title: Client Executive
Position Concept:
The Client Executive develops a long term business relationship with one
strategic or several important clients, providing total solutions to the
client's business needs. The Client Executive maintains effective
business relationships at the senior level with key decision makers and
influencers. The Client Executive identifies IBM opportunities and
develops solutions strategies. He/She is accountable for total client
satisfaction, IBM market share, revenue and profit earned from the client,
and is the responsible IBM interface with the client nationally and/or
internationally.
Skills
- Masters and applies expert knowledge of information technology and
associated leading edge solutions and strategies related to the
client's business to attain business unit, country/ area or
international objectives. Masters the required proficiency levels of
the CRP skills.
- Understands and masters organizational resources, priorities, needs
and policies.
- Mentors others and engages in teamwork at the highest management and
technical levels of IBM, client and other business parties if needed
to attain personal, team and IBM business objectives.
- Plans and conducts complex negotiations between IBM, client and other
parties which result in appropriate and often long-term agreements and
commitments.
- Anticipates future client problems in account planning, industry and
information technology trends and develops realistic visions and
strategies based on risk management plans and copes with them by
involving IBM geographic and global organizations.
- Has in place successful product, market, business and/or technology
strategies which meet IBM and client objectives.
Contribution/Leadership
- Workscope
Identifies opportunities and develops IBM solution strategies.
Manages and monitors many opportunities of varying complexities.
Works with the executive team to position long term strategic issues
and solutions. Works with resource coordinators/managers to ensure
that appropriate quantity and quality of technical and services
resources are deployed.
- Autonomy
Performs at expert level with little/no management direction.
- Vision
Has vision of overall IBM and client strategies. Develops accordingly
a long term business relationship with the client providing total
solutions to the client business needs.
- Influence
Driver of client team and "team IBM" at all levels. Utilizes IBM
resources as Key Client Value Add component. Major influencer of the
client's information systems strategy and plan. Considered key
thought leader by Client's senior management team and virtual
teammate. Understands client's business, industry, strategy, and
competition. Is sought out by client for advice on how IS can leverage
the client's business problems and opportunities and how IBM can
become a strategic IS partner to the client.
- Leadership
Has total responsibility for very large client(s) which might be an
international account(s). Establishes, maintains and coordinates an
effective relationship with the client's executive management team and
key decision makers/influencers. Considered peer manager and
contributor within client's executive team.
Leads business unit, country, or international teams. Participates in
industry and business related organizations, societies, conferences
and other client related activities to maintain professional
credibility and leadership. Leads by example and demonstrates the
highest level of teamwork and professional qualities in all activities
to enhance IBM's position in the marketplace.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Accountability
Directly responsible for Business unit, country, or international
assigned projects/objectives including revenue, profit and customer
satisfaction.
- Planning
Forecasts tactical and strategic business opportunities. Works with
clients and IBM resources, leads the development and implementation of
coverage and marketing strategies for the entire account or large
multiple accounts to achieve business and client objectives and
assists others. Leverages channels of distribution and resources
across the enterprise geographically or globally, to maintain and
improve customer satisfaction and maximize revenue and profit.
Ensures overall linkages and execution of strategies developed on all
customer locations. Sets objectives for the team.
- Business Measurement
Activities are directly subject to business measurement including, in
addition to resources, customer satisfaction, costs, expenses,
revenue, profit, market share, share of client IT budget and installed
base.
- Customer Satisfaction
Has ultimate responsibility for high customer satisfaction. Results
include increase in partnerships with and acquisitions from IBM and
clients willingness to influence others to be partners with IBM.
- Financials
Apply executive empowerment to optimize costs and expenses and revenue
and profit.
- Value-Add
Successfully markets and installs entire IBM portfolio of solutions of
Hardware, Software, Services, Consulting and Financing Options.
Consistently delivers solutions which are highly valued by Client and
IBM and are considered as high impact, complex and strategic by both.
Key driver of opportunities in which IBM is considered to be the
Client's Strategic IS Partner and positions IBM to deploy core
competencies and resources to the client's benefit in a highly visible
way.
3.2 Chapter 13. General Business Relationship Profession
Subtopics:
3.2.1 General Business Relationship Profession Overview
Over the past several years, General Business has embarked on a strategy
that provides a dedicated focus to general business customers through
management and the execution of segment-specific go-to-market plans,
optimizing efficient sales and marketing methods in each phase of the
selling cycle.
The focus on General Business improving the efficiency of the coverage
model has resulted in the following 1997 coverage-based market
segmentation model.
____________________________________ ___________________________________
| Key Accounts (Q1) | Small Accounts (Q2) |
|____________________________________|___________________________________|
| 20% of Customers | 80% will have Telecoverage |
| Face to Face Selling | (Inside Sales Reps) |
| Industry Specialized | Industry Specialized |
|____________________________________|___________________________________|
| Winback Accounts (Q3) | Very Small/New Business (Q4) |
|____________________________________|___________________________________|
| Named Accounts | Two-Tier Distribution |
| Winback Reps | Cross-Functional Teams |
| | Solutions Portfolios |
|____________________________________|___________________________________|
Q1: The primary coverage in this quadrant is face-to-face General
Business Territory Reps, segmented by major industry groupings. The
intent is to ensure that the appropriate resources are focused on the
appropriate opportunities.
Q2: Telecoverage with solution sourcing and fulfillment primarily through
business partners and ISVs, with IBM resources deployed only as
required. The strategy is to align telecoverage by industry.
Q3: Primary coverage is competitive winback reps segmented by major
industry groupings; and direct marketing for demand generation.
Q4: Leads are generated by direct marketing campaigns with business
partners and ISVs providing solutions, primarily through two-tier
distributors.
Based upon this model, the primary focus of General Business Territory
Reps is in the Key Account/Opportunities (Q1) and the Competitive Winback
(Q3) quadrants.
The General Business relationship professional is required to develop
client relationships and execute an industry aligned territory coverage
plan that is responsible for revenue, profit and customer satisfaction.
The professional develops a territory plan to maximize revenue and
customer satisfaction while minimizing IBM's sales expense. They
establish, develop and build IBM relationships with the client's executive
team. These relationships are developed in a number of accounts as well
as through other channels.
This highly skilled professional must evaluate various distribution
methods to market, develop and direct an effective strategy based on
customer requirements within the segment. This model includes IBM
Representatives, Business Partners, Call Centers and Telesales.
Developing IBM relationships by managing a seamless movement of customers
through this hybrid model is critical to both IBM's success and that of
the customer.
In addition to territory management and relationship skills, the General
Business Professional must have extensive industry and solution skills in
order to work effectively with the client and satisfy their needs. This
professional works closely with Segment Management professionals to
execute the segment go-to-market plan, and develop an effective territory
plan. This in turn will provide the most efficient and effective coverage
plan.
The skills required by territory manager/executives working in a
customer-driven environment are far different from the skills required in
traditional roles.
Territory relationship positions require:
- Outstanding in-depth knowledge of the client's vision, business
objectives, strategies, organization plans and management system.
- Exceptional business acumen that includes superior understanding of
business, industry and economic trends.
- High-level leadership, communication and problem-solving skills to
command the confidence and respect of the client.
- Knowledge of current and future IBM offerings and technologies.
- Ability to work closely with the Segment Manager to ensure execution
of market plans.
- Skills in developing and applying telecoverage and telesales
techniques in managing multiple clients within the territory.
These skills are acquired as the result of an extended working
relationship with customers and understanding their business. Along with
this tenure comes a trust, so much so that the General Business
Relationship Professional is viewed as a partner more so than a vendor.
Continuity and skills are both key elements of this relationship
profession.
Prior to the Professional Careers announcement, much of the internal
reward and recognition system was based on breaking this continuity with
the customer. The foundation of the General Business Relationship
Profession is to reward this continuity with career growth tied to
customer and territory growth.
The territory representative positions span entry through senior levels
with the major differences being skill level and business contribution.
The Territory Manager/Executive position is an expert position and
requires certification. At appointment time, the Territory
Manager/Executive must complete an initial nomination package highlighting
how these skills have been demonstrated. Certification requires expansion
of these skills which is further supported by completion of external and
internal education programs.
3.2.2 Profession Structure
The General Business Relationship Profession consists of 5 positions:
- Territory Representative
- Advisory Territory Representative
- Senior Territory Representative
- Consulting Territory Representative
- Territory Manager
- Territory Executive
The Territory Manager and Territory Executive positions are certified
positions. Figure 13-1 and Figure 13-2 summarize the requirements of each
position of the profession and the developmental requirements for
progression within the profession. Detailed position descriptions can be
found in "General Business Relationship Position Descriptions" in
topic 3.2.9.
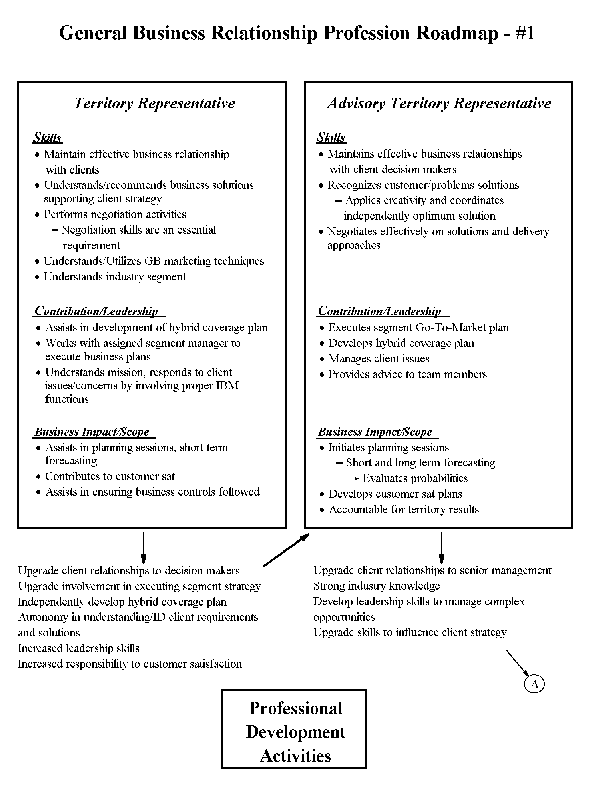
Figure 13-1. General Business Relationship Profession Roadmap - #1
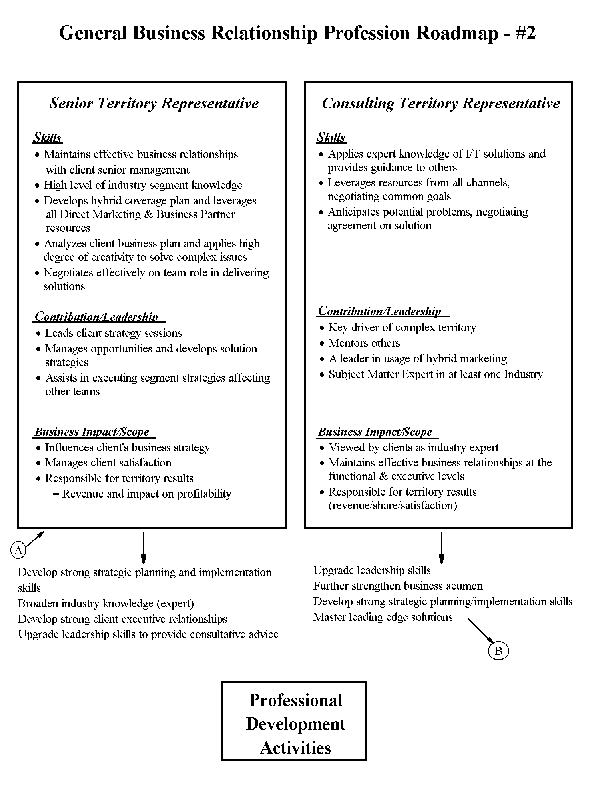
Figure 13-2. General Business Relationship Profession Roadmap - #2

Figure 13-3. General Business Relationship Profession Roadmap - #3
3.2.3 Characteristics of the Profession
The characteristics of a General Business Relationship Professional are as
follows:
- Strong leadership ability
- Effective communicator
- Displays business acumen
- Provides value add consulting
- Oriented to client satisfaction
- Understands internal IBM processes
- Strong negotiation ability
- Effective problem solving ability
- Able to maintain territory control
- Capable of developing a deep understanding of clients' business
strategy / environment / competitors
- Able to balance IBM and non-IBM resources
- Capable of delegating account coverage to direct marketing
- Able to rebalance the territory and change key account focus based on
changes of potential opportunity.
- Can represent IBM in the community and geography across many accounts
and several industries.
3.2.4 Potential Candidates
To participate in the General Business Relationship Profession, one must
be actively performing in the role of the General Business Relationship
Representative / Manager / Executive, and have direct account relationship
responsibility. There must also be a business need in order to be
nominated for certification. Any of the following may be candidates for
this profession:
- Current representatives / managers
- Current channels business units representatives
- Sales specialists
- New hires - campus
- Marketing oriented headquarters staff
- Professional hires
- Inside sales representatives
- Direct marketing
Figure 13-4 shows some possible candidates for the General Business
Relationship Profession.
More information on moving from another profession into the General
Business Relationship Profession is available in General Business Career
Possibilities.
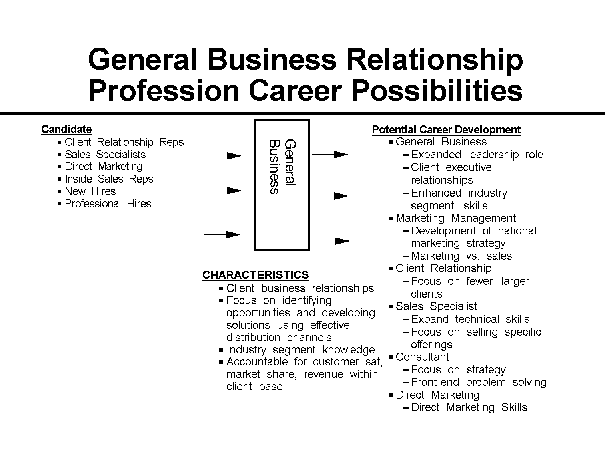
Figure 13-4. General Business Relationship Profession Career Possibilities
3.2.5 Career Growth
Specialization and expert careers have been implemented in IBM to provide
skills and support to clients of all sizes. In general business,
specialization and expert careers support the general business strategy.
For those currently in the GB Relationship Profession, the following are
examples of career growth possibilities:
- Relationship
- Territory Representative - (GB) General Business
This position may lead to certification in the expert levels of
Territory Manager/Executive
- Client Representative - ISU
A GB Relationship Professional may elect, at some point within
their career, to move to the Client Relationship Profession, and
focus on fewer, larger clients.
- Marketing/Sales
- Market Management
A GB Relationship Professional with interest and skills in
marketing in a particular industry or segment may choose to move
to the Marketing Profession and pursue this career path.
- Direct Marketing Manager
Although not in the General Business organization, Direct
Marketing is an integral part of the General Business team, and a
career opportunity in Direct Marketing may be a growth opportunity
for GB relationship professionals.
- Sales Specialist
This position can lead to certification and supports general
business in several disciplines:
- Products (mid-range or intermediate systems)
- Industry solutions
- Services
- Consulting
- Consultant Profession
Another potential career development plan would be to move to the
Consultant Profession, and focus more on strategy and front-end
problem solving.
3.2.6 Certification Nomination Guide
As someone working in this relationship profession, you may qualify for
certification as a Territory Manager/Executive if you meet the
certification criteria, skill proficiency levels required, and there is a
business need. Guidance for certification can be found in the Worldwide
General Business Certification Nomination Guide.
The key performance criteria for this profession include the ability for
the Territory Rep/Manager/Executive to professionally manage IBM and
non-IBM sales coverage resources to maximize coverage, revenue and profit.
It is essential these professionals optimize the use of call centers,
business partners, and other channels. They should display the ability to
effectively review and re-balance their territory periodically to move
less active accounts to direct marketing centers while moving accounts
with new potential to their "top 20 list". Therefore, optimizing coverage
and maximizing territory management will be significant considerations for
a candidate who applies to become a certified territory manager/executive.
Additional criteria include the ability to represent IBM in large
geographies, to grow market share profitably, to display industry
leadership and assure the highest level of customer satisfaction.
3.2.7 General Business Relationship Profession Skills Profile
The general business profession incorporates an expert career called
Territory Manager/Executive which requires the highest, most advanced
levels of skills and capabilities. Developing and enhancing your skills
through education and experience are fundamental to career growth and
requires focus, discipline and clear goals.
The key skill categories for the profession are:
- Client Environment
- Business Acumen
- Industry
- IBM Environment
- Project Management
- Product/Technology/Services
- Personal
The following relationship templates are used in the GB relationship
profession:
- Territory Representative
- Territory Representative - Adv
- Territory Representative - Sr
- Territory Representative - Cons
- Territory Manager
- Territory Executive
Industry/Product Templates
To customize the relationship template for your particular job role, you
should do the following (select only those which are appropriate for your
territory):
- Select the appropriate INDUSTRY Customer Classification (CC) and
INDUSTRY Solution Area (SA) Discipline Template(s) for your
environment, and add them to your Job Role Profile.
- If you require additional skills in Products/Technology/Services,
select and assign the appropriate Product-Specific Product Skills
template(s), for example: "AS/400 PRODS-GENERAL PRODUCT SKILLS"
For a complete listing of the relationship skills templates for the
General Business Relationship Profession, please access the SKILLS
application.
_____________________ __________________________________________________
| | Profession Positions, with Associated Skill |
| TERRITORY REP / | Levels |
| MANAGER / EXECUTIVE |______ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| GENERAL BUSINESS | Terr | Adv | Sr | Cons | Terr | Terr | Key |
| SKILLS | Rep | Terr | Terr | Terr | Mgr | Exec | Skill|
| | | Rep | Rep | Rep | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| CLIENT ENVIRONMENT |
|_____________________ ______ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| Client | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | Y |
| Relationships | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Relationships with | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 5 | Y |
| Client Execs | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Relationships with | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 5 | Y |
| End Users | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Relationships with | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | Y |
| Client I/T | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Client Strategy and | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | Y |
| Planning | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Client Critical | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | Y |
| Success Factors | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Client Planning | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | Y |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Use Business | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | Y |
| Partners | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Client Management | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | Y |
| Sys/Culture | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Client Info/Data | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | Y |
| Infrastruct | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Know Client | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | Y |
| Compet/Econ Environ | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| BUSINESS ACUMEN |
|_____________________ ______ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| Market Management | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | N |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Use Dir Mkt | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | Y |
| Processes / Service | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Coverage / | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | Y |
| Relationship Plan | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Consultive Sales | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | Y |
| Call | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Financial Skills | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | N |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Advise on Financing | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | N |
| Choices | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Customer | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | Y |
| Satisfaction Mgmt | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Facilitate | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | N |
| Organization Change | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Consulting Methods | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | Y |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Value-add Selling | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | Y |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Potential | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | Y |
| Opportunity to Real | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Client Issue | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | Y |
| Identification | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Frame Client | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | Y |
| Solution | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Close Opportunity | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | Y |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Measure Client | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | N |
| Results | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| INDUSTRY |
|_____________________ ______ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| Industry | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 4 | Y |
| Segments/Industries | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| IBM ENVIRONMENT |
|_____________________ ______ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| IBM Organization | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Y |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| IBM Vision / | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Y |
| Mission / Strategy | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| IBM Management | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Y |
| System | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Operate Channel | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Y |
| Strategies | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| PROJECT MANAGEMENT |
|_____________________ ______ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| Initiate Projects | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | N |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Plan Projects | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | N |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Project | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | N |
| Track/Report/Deliver| | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Manage Project Risk | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | N |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| PRODUCT/TECHNOLOGIES/SERVICES |
|_____________________ ______ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| Platforms | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | Y |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Applications | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | Y |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Architectures | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | N |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Methodologies | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | N |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| I/T Related | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Y |
| Services | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Position Lotus | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | N |
| Notes | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Understand Network | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | N |
| Comp. Tech. | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| PERSONAL |
|_____________________ ______ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| Leadership | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | Y |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Mentoring | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | N |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Communication | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | Y |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Negotiation | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | Y |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| PROBLEM SOLVING |
|_____________________ ______ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| Problem Solving, | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | Y |
| Decision Making | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
3.2.8 Professional Development
Growing your skills requires a combination of experience, education,
training, coaching and mentoring. these elements are called Skill
Development Activities. Education and training can be separated into
several forms ranging from self study, distance learning, internships,
classroom, and seminars. The integration of these delivery methods can be
an efficient and cost effective say to build your skills. Refer to the
Education Roadmap page of the IEC Course Catalog at
http://w3.lahulpe.ibm.com/roadmaps/index.html for an overview of the
Worldwide Professions and links to the Common Skills Categories and
Professions Roadmaps.
3.2.9 General Business Relationship Position Descriptions
The following position descriptions describe the basic work of each of the
positions within the Professions. Formal descriptions which may contain
legally mandated language necessary for classifying employees in a
geography should be obtained through the approved on-line job library, if
available in the geography, or by contacting the appropriate H.R.
personnel within the geography.
Subtopics:
3.2.9.1 Position Title: Territory Representative
Position Concept:
The role of the Territory Representative is to develop an IBM relationship
with clients in an assigned territory, thereby providing business
solutions to their business needs. Understands an industry segment in a
selected market. Participates on a cross-functional team, taking
advantage of all marketing resources available to General Business.
Maintains an effective business relationship with client contacts and
identifies marketing opportunities. Assists in the selection of the
appropriate offering and distribution channel that will meet the client's
business objectives and provide a financial return to IBM. Builds a
working relationship with members of other IBM marketing functions. The
primary measurements are customer satisfaction and revenue.
Skills
- Utilizes knowledge of the General Business function to maintain an
effective business relationship with customer accounts within an
assigned industry or geographic segment.
- Receives guidance in identifying marketing opportunities by
understanding the client's business, and its competitors.
- Collaborates with others to understand business solutions and
recommends solutions that support the successful implementation of a
client's business strategy.
- Requires the use of negotiation skills to reach general agreements
with staff members and clients.
- Reviews business solutions and offers alternatives that enhance and
improve them.
- Utilizes established marketing techniques to provide business
solutions for assigned clients.
- Reviews the client's business issues and recommends solutions or
alternatives.
- Demonstrates the skill proficiency levels for this profession
position.
Contribution/Leadership
- When assigned, works closely with their segment manager and other
marketing professionals to execute business plans which are at a
professional level.
- Assists in the development of a hybrid coverage plan based on
validated customer buying habits. Plans are reviewed by management or
senior professionals. These reviews are considered part of their
professional development.
- Assists in the direction of activities of the hybrid marketing process
ensuring quality resources are deployed to delight the customer,
increasing IBM's market share and revenue.
- Responds to client issues and concerns by ensuring the involvement of
the proper IBM functions and has an influence on other members of the
department by addressing these client issues.
- Understands the department mission and vision as it applies to the
incumbent's assignments.
Impact On Business/Scope
- Participates in planning sessions, evaluates IBM's competitive
advantages, and identifies potential areas of improvement. Assists in
forecasting for short-term business volumes by using tools such as
OMSYS, CRM processes, etc.
- Develops customer satisfaction plans that identify dissatisfiers and
develops plans to address those issues.
- Assists in ensuring, that business controls - i.e., A/R, backlog
management, bill accuracy, ship and install on time etc., are closely
followed.
- Utilizes quality principles in the development and assessment of all
assignments.
3.2.9.2 Position Title: Advisory Territory Representative
Position Concept:
The role of the Advisory Territory Representative is to develop an ongoing
IBM relationship with many clients in an assigned territory, thereby
providing solutions to their business needs. This requires an
understanding of industry segment(s) in a selected market. Implements the
General Business industry marketing plans in the territory. Advisory
Territory Representatives may form or lead a small cross-functional team,
taking advantage of all marketing resources available within General
Business. Independently selects the appropriate offering and distribution
channels that will meet the client's business objectives and provide a
financial return to IBM. The Advisory Territory Representative maintains
an effective business relationship with the client decision makers,
identifies marketing opportunities, and is accountable for customer
satisfaction for all assigned accounts. Builds working relationships with
members of other IBM marketing functions (i.e., Sales Specialists, I/T
Architects, Consultants, etc.), Direct Marketing, Business Partners and
other channels. The primary measurements are customer satisfaction,
revenue and profitability.
Skills
- On a professional level utilizes knowledge of the General Business
function in order to maintain relationships with the decision makers
of accounts within an assigned industry or geographic segment(s).
- Independently identifies and creates opportunities by understanding
the client's business, competitors and position within the industry.
- Articulates various approaches to business plans by recommending
solutions that support the successful implementation of the client's
business strategy.
- Negotiates with specific objectives, client requests, commensurate
with client expectations and consistent with IBM's delegation of
authority.
- Analyzes General Business client concerns and uses creative approaches
in developing solutions.
- Challenges the validity of business solutions and uses creative
approaches to develop new solutions when needed.
- Demonstrates the skill proficiency levels for this profession
position.
Contribution/Leadership
- Works closely with a segment manager and other marketing professionals
to execute the segment go-to-market plan.
- Develops a hybrid coverage plan based on validated customer buying
behaviors.
- Coordinates the activities of the hybrid marketing process by engaging
the expertise of a small team of Sales Specialists, inside sales,
Business Partners, direct marketing solutions reps/mgrs and all other
marketing functions within the area.
- Provides appropriate feedback to General Business management relative
to client requirements and inputs to industry/product functions all
pertinent information and trends that will enhance IBM's position in
the marketplace.
- Sets own priorities in managing client issues and concerns and ensures
the involvement of the proper IBM functions, thereby bringing added
value and cultivating a continuing customer relationship.
- Provides advice to other marketing team members as required in order
to meet business objectives.
- Understands the General Business' mission and vision.
Impact On Business/Scope
- Initiates and may lead planning sessions, evaluates IBM's competitive
advantages, and identifies potential areas for improvement. Forecasts
long- and short-term business volumes by using tools such as OMSYS,
CRM processes, etc. Also will include the probability of a win or
loss and the profitability to IBM.
- Develops customer satisfaction plans that identify key dissatisfiers
and plans to address those issues and sets goals to improve.
- Ensures, that business controls, - i.e., A/R, backlog management,
billing accuracy, ship and install on time, etc.- are closely followed
and is held accountable for results that impact account activities.
- May have budget responsibilities for special teams of marketing
professionals.
- Utilizes quality principles in the development and assessment of all
assignments.
3.2.9.3 Position Title: Senior Territory Representative
Position Concept:
The role of the Senior Territory Representative is to develop an on-going
IBM business relationship with clients and provide solutions to their
business needs. This requires a through understanding of an assigned
industry segment of a major industry. Leads cross-functional marketing
teams, taking advantage of all marketing resources within General
Business. Selects the appropriate offerings and distribution channels
that are designed to meet the client's business objectives and provide an
optimum financial return to IBM.
The Senior Territory Representative has the authority to make commitments
on behalf of IBM, including terms and conditions, resources and financial
arrangements. Maintains an effective business relationship with the
client's management team. Responsible for identifying opportunities and
developing solutions using effective distribution channels. Accountable
for total customer satisfaction, market share, IBM profit and revenue
within the client base, and acts as the IBM interface with focus accounts
within a General Business industry segment.
Skills
- Develops new approaches to establish and maintain an effective
relationship with clients by contacting senior management.
- Utilizing an in-depth knowledge of segments and General Business
techniques and develops hybrid coverage plans based on validated
customer buying behaviors.
- Leverages all Direct Marketing and Business Partner resources and
negotiates goals and approaches to optimize profit and customer
satisfaction and is held accountable for the results.
- Analyzes a number of clients' business plans and applies a high degree
of creativity to solve complex issues.
- Advises other marketing professionals on General Business strategies
and plans.
- Identifies and executes solutions for complex problems associated with
the General Business function.
- Demonstrates the skill proficiency levels for this profession
position.
Contribution/Leadership
- Leads client strategy and planning sessions, evaluates IBM's
competitive advantages and identifies potential areas for improvement.
Identifies marketing opportunities and develops IBM solutions,
including distribution and support strategies.
- Works closely with segment managers and other marketing professionals
to execute the segment strategy and go-to-market plan that affect
other General Business teams. Understands the issues and makes
trade-offs to accommodate other team members.
- Defines activities and directs the activities of the hybrid marketing
process by employing effective management techniques in order to
ensure that the appropriate quantity and quality of technical and
service resources are deployed.
- Provides technical direction to less experienced professionals based
on General Business marketing techniques.
- Understands the General Business mission and vision.
Impact On Business/Scope
- Influences the client's business strategies and the results are
subject to business measurements established by the General Business
management team.
- Accountable for return-on-investment evaluations for a General
Business senior management team on all General Business products and
services. Provides appropriate feedback to IBM executives concerning
client requirements.
- Negotiates customer contracts involving others as necessary and
ensures compliance by all parties (IBM, customer, partner). Has a
significant impact on customer satisfaction.
- Manages financial issues for IBM as they relate to pricing tools, cost
formulation, profit generation and asset/resource utilization by using
CRM processes.
- Participates in the planning of General Business programs and
strategies.
- Utilizes quality principles in the development and assessment of all
assignments.
3.2.9.4 Position Title: Consulting Territory Representative (if available)
Position Concept:
The Consulting Territory Representative is a key contributor within the
Small and Medium Business organization, demonstrating proficiency and
leadership within a specific industry. He/She is actively engaged in
external and internal industry associations, industry education and
related activities and takes a leadership role in disseminating this
industry expertise/knowledge to others within Small and Medium Business.
The Consulting Territory Representative is a lead individual contributor
in a significant Small and Medium Business Territory with
important/strategic accounts. He/She is proficient in establishing and
maintaining an IBM relationship with important, strategic clients. The
Consulting Territory Representative has the relationship which grants
access to policy level customer executives within his/her set of accounts.
He/She has expert marketing, business, technical and professional skills
and has primary responsibility for the success of the relationships with
the clients. This responsibility involves identifying and qualifying IBM
opportunities, engaging the appropriate IBM resources, gaining client
commitment to solutions when appropriate, and ensuring overall client
satisfaction. The Consulting Territory Representative is proficient in a
specific industry and is actively engaged in external and internal
industry associations/organizations and related activities. The
representative holding this position has an in-depth understanding of the
client's business and is able to determine areas where IBM's functional
business segments and business partners can complement the client's
business. In addition, the Consulting Territory Representative often
provides guidance and direction to others. He/She often assists others in
the development of their strategies and plans and in identifying and
qualifying opportunities.
Skills
- Understands and applies in-depth knowledge of the assigned industries,
including trends and directions, forces driving the industries and
their players, competitive environment, and extended enterprise
relationships. Takes an active, leadership role in external industry
associations/organizations.
- Applies expert knowledge of information technology and associated
leading edge solutions related to the clients' business to attain
function, business unit or area objectives. Has the required
proficiency levels of the Territory Relationship Profession skills.
- Understands organizational resources, priorities, needs and policies.
- Mentors others, providing guidance on the attainment of the required
skills, their proficiency levels and on achieving business objectives.
Directly influences the team, clients and other IBM functions to
attain team goals.
- Leads negotiations effectively with clients and other IBM functions on
project/team goals for definition and setting of strategies to
reach/exceed them.
- Anticipates potential problems associated with account planning or
customer solutions and leads/agrees on the risk management plan for
implementation of solutions.
- Analyzes new and complex industry, technology, economic and
competitive situations, taking into consideration real client needs
and problems. Evaluates potential solutions involving IBM functions,
subcontractors, business partners and clients. Gains team agreement
on business assessment of solutions.
- Ensures that the client and IBM team agree on the steps involved to
develop and implement client solutions including the set-up of a
project management plan to ensure timely success.
Contribution/Leadership
- Creates, qualifies and manages IBM opportunities. Guides and
participates in the development of the solution and support strategy
based on an in-depth understanding of the clients' business, industry
trends and directions, their competitors, their relative position in
the industry and IBM capabilities in the clients' environments.
Engages various distribution channels effectively. Anticipates and
responds to or escalates the clients' concerns on key projects.
Manages complex opportunities.
- A recognized expert in their clients' industry/business. Secures
commitment and agreement on client solutions. Responsible for complex
projects. Decides on priorities and resources; follows business
unit's directives by setting team objectives commensurately.
- Has strategic vision of functional or business unit mission for
effective implementation and has an in-depth understanding of the
clients' business and is able to determine areas where IBM's
functional business segments or business partners can complement the
clients' business.
- Has responsibility for strategy and results on the sales teams with
which he/she works. Utilizes all internal IBM resources well and has
strong influence on the clients' information systems strategy.
Contributes possible inputs for the clients business strategies/plans.
Influences the clients on tways IBM can become their strategic IS
partner.
- Has positive impact and influence on the General Business Territory
Relationship Profession as well as other team members. Is actively
sought out to mentor other Territry Rep Professionals in industry
acumen and industry solutions/offerings from IBM, its partners and
competitors.
- Key driver/team leader of complex territory. Establishes, maintains
and manages effective business relationships at both the functional
and executive levels referencing successful business engagements,
understanding and articulating what value IBM can bring to the
relationship and creating new ideas to expand the business
partnership. Is sought by his/her clients' management teams for input
and direction.
- Is regarded as an industry role model with recognized impact within
SMB. For at least one key industry, maintains industry expertise
through internal and external education and disseminates this
knowledge to others within SMB.
Impact On Business/Scope
- Responsible for overall territory results involving revenue, profit
and customer satisfaction, and as required for specific activities
and/or projects involving country-wide, regional, or multifunctional
teams.
- Develops creative plans broad in scope and impact. Works with
clients, business partners, and IBM resources and leads the
development and implementation of relationship, coverage and marketing
strategies to achieve business objectives; assists others in doing so,
also. Leverages channels of distribution to maintain and improve
customer satisfaction and maximize revenue and profit. Sets/drives
objectives for his/her team to exceed IBM business objectives.
- Activities are directly subject to business measurement (including
revenue, profit, customer satisfaction, market share, share of
applicable client IT budget, and installed base) and directly affect
revenue and profit.
- Is viewed by the clients as a reliable, valuable resource. Is
responsible for the clients' overall satisfaction with their business
relationship with IBM. Proactive in improving customer satisfaction
year to year regardless of customers' buying decisions.
- Uses creativity to enhance revenues and profitability and to reduce
department/team costs and expenses, thereby having a favorable impact
on functional and Business Unit objectives.
- Monitors and maintains an awareness of all key IBM/Client/Business
Partner activities. Represents client issues, needs, and concerns
throughout IBM. Communicates customer requirements to appropriate IBM
solutions organizations in a professional, efficient and timely
manner. Consistently delivers solutions which are highly valued by
client and IBM and are considered as high impact, complex and
strategic by both. Drives opportunities in which IBM is considered to
be the clients' strategic business partner.
3.2.9.5 Position Title: Territory Manager
Position Concept:
The role of the Territory Manager is to develop an ongoing IBM business
relationship with major clients and provide solutions to their business
needs that impact their financial success. This requires a through
understanding of a number of assigned industry segments. Leads
cross-functional marketing teams made up of senior professionals, taking
advantage of all marketing resources within General Business, and is aware
of resources in other geographies. Selects the appropriate offerings and
distribution channels that are designed to meet the client's business
objectives and provide an significant financial return to IBM.
The Territory Manager has the authority, with executive review, to make
all commitments on behalf of IBM, including terms and conditions,
resources and financial arrangements. Maintains effective business
relationships with senior management and influences client executive
management. Responsible for identifying marketing opportunities and
developing complex solutions/support strategies, including the number and
size of distribution channels. Accountable for total customer
satisfaction, market share, IBM profit and revenue within the client base
and acts as the senior IBM interface with the largest accounts within
General Business. The incumbent is recognized as an expert within one or
more industries and gives advice and counsel to other professionals as
needed.
Skills
- Establishes, maintains and coordinates an effective relationship with
clients by understanding their priorities, policies and needs of the
executive management team.
- Utilizing an expert professional knowledge of the General Business
function develops a hybrid marketing coverage plan for a major company
or area.
- Leverages all Direct Marketing and Business Partner resources and
negotiates common goals and approaches to optimize profit and
satisfaction. Negotiations result in agreements of all areas
involved.
- Gives guidance to other marketing professionals on General Business
policies, strategies, and practices.
- Anticipates future trends and potential problems associated with the
General Business function and assesses their impact on the financial
objectives for an area.
- Demonstrates the skills proficiency levels for this profession
- Identifies and analyzes unique and complex situations for major
General Business clients and provides appropriate solutions.
Contribution/Leadership
- Leads major client strategy sessions made up of multiple functions,
evaluates IBM's competitive advantages and identifies areas of
improvement. Identifies opportunities and develops IBM solutions,
distribution and support strategies.
- Has considerable latitude in directing the activities of the hybrid
marketing process by employing effective management techniques in
order to ensure that the appropriate quantity and quality of technical
and service resources are deployed.
- Works with and may give advice to segment managers in the execution of
segment strategies and go-to-market plans.
- Participates in the establishment of the General Business' mission and
vision.
- Acts as mentor to senior-level General Business professionals.
- Influences client executives and exercises authority appropriate to
client requests and consistent with IBM delegation of authority.
Requires considerable tact and diplomacy.
- Recognized throughout the General Business function as an expert.
Impact On Business/Scope
- Impacts the client's General Business strategy by suggesting changes
based on the partnership between IBM and the client. Results are
subject to measurements established by the client and IBM.
- Develops return-on-investment evaluations for the area's executive
management team of all General Business products and services.
Provides appropriate feedback to IBM executives concerning client
requirements.
- Manages multi-functional teams and programs that ensures an assigned
General Business Area or a major company's marketing objectives are
met.
- Negotiates customer contracts for large complex accounts involving
others as necessary and ensures compliance by all parties (IBM,
customer, partner). Negotiations have considerable impact on customer
satisfaction.
- Manages major financial issues for IBM as they relate to pricing
tools, cost formulation, profit generation and asset/resource
utilization by using CRM processes.
- Utilizes quality principles in the development and assessment of all
assignments.
3.2.9.6 Position Title: Territory Executive
Position Concept:
The role of the Territory Executive is to develop an on-going strategic
IBM business relationship with the largest clients throughout a business
unit. Provides solutions to their business needs that may determine their
financial success. This requires a through understanding of all assigned
industry segments within the General Business function. Leads
cross-functional marketing teams, made up of senior professionals from a
number of geographies, taking advantage of all marketing resources within
General Business and utilizes all available marketing resources throughout
the world. Selects the appropriate offerings and distribution channels
that are designed to meet the client's business objectives and provide a
considerable financial return to IBM.
The Territory Executive has the authority, without review, to make all
commitments on behalf of IBM, including terms and conditions, resources
and financial arrangements. Maintains effective business relationships
with client executive management and influencers of executive management.
Responsible for identifying marketing opportunities and developing leading
edge support strategies, using effective distribution channels.
Accountable for total customer satisfaction, market share, IBM profit and
revenue within the client base and acts as the senior IBM interface with
accounts that have considerable impact on the General Business
organization. The incumbent is recognized as an expert in one or more
industries and gives advice and counsel to senior professionals within
General Business on a worldwide basis.
Skills
- Establishes, maintains and coordinates an effective relationship with
major clients by advising the executive management team of leading
edge programs and strategies.
- Leverages all Direct Marketing and Business Partner resources and
negotiates goals and approaches to optimize profit and customer
satisfaction. Conducts complex negotiations with other marketing
functions resulting in lasting agreements.
- Creates innovative concepts that impact the business results in
General Business.
- Fosters a teamwork approach at the highest levels in order to achieve
General Business goals and objectives.
- Demonstrates the skill proficiency levels for this profession
position.
Contribution/Leadership
- Leads major client strategy sessions made up of senior professionals,
evaluates the IBM's competitive advantages and identifies unique areas
of improvement.
- Has considerable latitude directing the activities of a complex hybrid
marketing process by employing effective management techniques in
order to formulate leading edge solutions that address issues that are
critical to the General Business function.
- Acts as mentor to senior level General Business professionals and
develops mentorship programs for the General Business that may be used
internationally.
- Has considerable insight of General Business Strategies and is able to
articulate them to senior IBM and senior client management.
Contributes to the formulation of General Business' policies and
practices.
Impact On Business/Scope
- Has considerable impact on General Business and major client's
long-term business strategies. These clients are typically operate
internationally.
- Develops return-on-investment evaluations for major product lines and
advises executive management teams on all General Business products
and services. Provides appropriate feedback to IBM executives
concerning client requirements.
- Negotiates customer contracts for major international accounts
involving others and ensures compliance by all parties (IBM, customer,
partner). Negotiations have considerable impact on customer
satisfaction.
- Contributes to the formulation of General Business area policies,
practices, and strategies.
- Utilizes quality principles in the development and assessment of all
assignments.
3.3 Chapter 14. Sales Specialist Profession
Subtopics:
3.3.1 Sales Specialist Profession Overview
Sales specialist professionals are responsible for selling IBM offerings
directly to customers. IBM offerings include hardware, software, services
and industry solutions. A sales specialist professional specializes in a
set of related offerings, called a discipline. Sales specialist
professionals are assigned to specific opportunities where they possess
the sales and technical expertise required to conduct all phases of the
sales cycle. They are responsible for winning the business and the
customer's satisfaction with the engagement and the offering.
A primary measurement for this profession is revenue contribution.
The sales specialist professional understands the offerings of our
competitors and is capable both of successfully engaging them directly and
of developing sales strategies to increase IBM market share in the
assigned territory. A sales specialist professional is a partner to the
client relationship and general business relationship professionals.
The Sales Specialist Profession is intended to complement and enable IBM's
overall strategy to be more responsive to our customers' needs. As experts
in their offerings, sales specialists can best match IBM solutions to
customer requirements.
Sales specialist professionals carry quota for their set of offerings,
contributing directly to IBM's revenue achievement or other offering
measurements, and to the overall success of their offerings.
3.3.2 Profession Structure
The following positions, from low to high, are defined within the Sales
Specialist Profession:
- Sales Specialist
- Advisory Sales Specialist
- Senior Sales Specialist
- Consulting Sales Specialist
- Senior Consulting Sales Specialist
The Consulting Sales Specialist and Senior Consulting Sales Specialist
positions are intended for those employees who have successfully completed
the profession certification process. They are the "certified" positions.
Figure 14-1 in topic 3.3.3 and Figure 14-2 in topic 3.3.3 summarize the
requirements of each position of the profession and the developmental
requirements for progression within the profession. Detailed position
descriptions can be found in "Sales Specialist Position Descriptions" in
topic 3.3.11.
Subtopics:
3.3.2.1 Disciplines within the Profession
The Sales Specialist Profession is made up of many specialized
disciplines. Each discipline focuses on IBM's offerings in a particular
area -- products (hardware or software), services, or Industry solutions.
Within a discipline, there may be defined subsets of offerings called
specialties.
The following are the disciplines currently defined in the Sales
Specialist Profession; however, some of them may not be fully implemented
yet:
- AS/400
- Network Computing (formerly Client/Server)
- Networking Systems (hardware and software)
- Personal Systems (PC Company, PC Server)
- Printing Systems
- RS/6000 (RS/6000, AIX, SP)
- Storage Systems
- System/390
- Software (specialties listed below)
- Application Development
- Data Management
- Personal Systems
- Systems Management
- Transaction Systems
- Workgroup (office, publishing systems)
- Availability Services
- Customer Financing (formerly Financial Services)
- Managed Operations / Business Recovery Services
- Networking Services
- Systems Integration/Application Development Services
- Industry Solutions (aligned with industry units, specialties listed
below)
- Banking, Finance, and Securities
- Distribution
- Education
- Government
- Healthcare
- Insurance
- Manufacturing
- Petroleum
- Process
- Telecommunications and Media
- Travel and Transportation
- Utility and Energy Services
- Cross Industry
3.3.3 Characteristics of the Profession
- Sales specialists are focused on offerings. They work with client
relationship or general business professionals, other professionals,
and IBM Business Partners to match IBM solutions to the business needs
of the customer. Their prime responsibility is to engage and close
sales opportunities in their discipline or specialty area.
- A sales specialist has the technical depth to understand IBM offerings
and their application to specific customer projects. This
professional also has the sales skill to develop strategy and present
the value of the discipline offerings in appropriate detail to all
levels of customer management, and to close business.
- This professional is not expected to perform billable work.
- This professional should have very strong discipline offering skills.
At the lowest profession position, a sales specialist may first focus
on a single offering, then broaden those skills to multiple offerings
as experience is gained. This professional must also have very strong
personal skills, particularly in communications and negotiation, and
should have strengths in business acumen, particularly in applying
financial sales strategies.
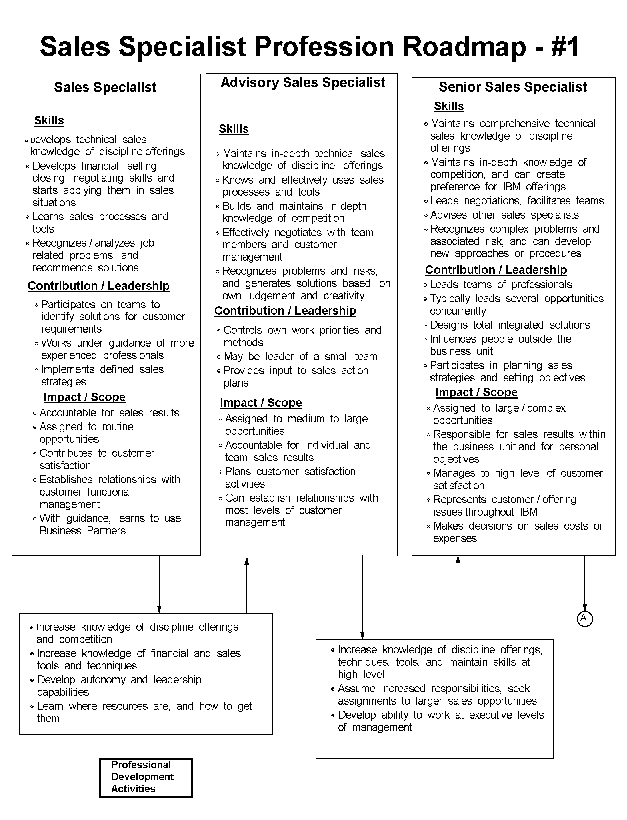
Figure 14-1. Sales Specialist Profession Roadmap - #1

Figure 14-2. Sales Specialist Profession Roadmap - #2
3.3.4 Potential Candidates
People in sales or services organizations today with both sales and
technical expertise are potential candidates for the Sales Specialist
Profession. These might include client relationship or general business
professionals with strong technical skills or I/T specialists with strong
sales skills. People from other IBM organizations with appropriate skills
and expertise would also be candidates.
Since the Sales Specialist Profession spans five positions from the Sales
Specialist position through the Senior Consulting Sales Specialist
position, opportunities exist for multiple entry points into the
profession, assuming that the skill proficiency requirements and other
requirements are satisfied.
The expert positions of the profession -- Consulting or Senior Consulting
-- are most likely to be filled by candidates already within the Sales
Specialist Profession, who have attained the necessary skills and
experience to meet the expert position criteria, when a business need is
identified.
Although the lower level sales specialist positions are directly linked to
the Consulting and Senior Consulting sales specialist positions, some
sales specialists may choose to pursue other professions or careers, where
the required skills and experiences are similar to the Sales Specialist
Profession. These include the consultant profession, a general management
| career as a sales manager, positions within the brand or development
| organizations, or one of the relationship professions. Or, sales
specialists who have deep technical skills and who may assist the sales
effort, but who do not have ownership of the opportunity or responsibility
for closing the sales, may consider the I/T Specialist positions.
Figure 14-3 shows some possible candidates for the Sales Specialist
Profession and possible career movement from a sales specialist position.
More information on movement from other professions to the Sales
Specialist Profession is available in Sales Specialist Career
Possibilities.
Charts in this document describe in more detail some of the possibilities
for making a career change from one of the other Worldwide Sales &
Services Professions to the Sales Specialist Profession. For each
Profession pair, there is a summary of the commonalities and deltas for
skills, contribution / leadership, and scope of responsibility / impact on
the business, that should be considered when making a career change.
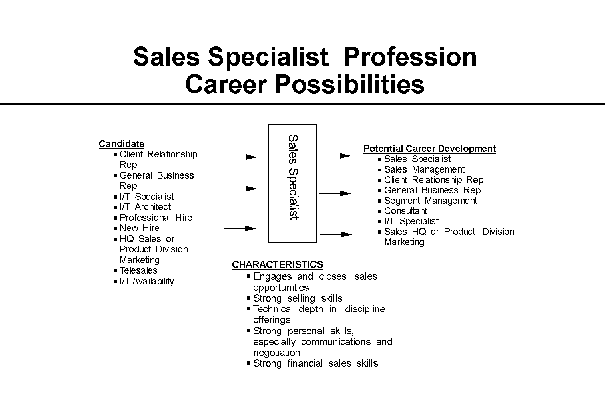
Figure 14-3. Sales Specialist Profession Career Possibilities
3.3.5 Career Growth
The difference between a Sales Specialist and a Senior Consulting Sales
Specialist is a function of increasing skill, capability, experience, and
responsibility. As a sales specialist professional develops skills and
assumes more responsibility, that individual can aspire to higher levels
of both compensation and status.
Sales specialists can occupy positions from Sales Specialist to Senior
Sales Specialist. Additional positions exist beyond the senior level, but
those are achieved only by successfully completing the certification
process.
The profession provides a direct career path from the lowest sales
specialist position to the highest sales specialist position. This allows
an employee with exceptional sales and technical skills to advance through
the career.
As with all IBM Certified Professionals, the sales specialist professional
may seek certification when that person achieves the level of skills and
experience required to enter the expert positions (Consulting Sales
Specialist and Senior Consulting Sales Specialist) within the profession.
The candidate for certification will hone those skills through a
combination of education, mentoring, and most importantly, experience.
Once the appropriate skill level and other criteria have been met, and a
business need for a certified professional has been identified, the
candidate will submit a nomination package for certification, with
approvals from management. The candidate achieves at least the Consulting
Sales Specialist position within the profession by successfully gaining
the approval of a Certification Review Board.
In the last step of the process, the position of the Certified
Professional -- either Consulting or Senior Consulting -- is assigned
based on certain classification criteria. These criteria include the
level of skills, revenue attainment or other quantifiable business
contribution, leadership, impact on the business, and scope of
responsibility.
3.3.6 Certification Nomination Guide
The Worldwide Sales Specialist Certification Nomination Guide contains the
criteria, required documentation, and process for certification in the
profession.
3.3.7 Performance Elements
The sales specialist professional is an individual who generates sales and
the resulting revenue. A sales specialist is expected to deliver a high
level of satisfaction both to the customer and to the client team which
identifies the opportunity to the professional. For each discipline or
specialty offering set, there may be specific, established quotas or
objectives that can be applied as performance elements. The professional
will be expected to win against competition and generate profit for the
IBM Corporation.
In summary, the performance elements are as follows:
- Revenue contribution
- Satisfaction of client and client team
- Offerings objectives
- Wins / losses
- Profit
In certain situations, other quantifiable business measurements may apply,
such as year-to-year growth or results from an investment territory.
3.3.8 Sales Specialist Profession Skills Profile
The skills required of a sales specialist include generic professional
skills in the categories of client environment, business acumen, industry,
IBM environment, project management, product/technology/services, and
personal, as well as detailed skills within the discipline area. The
following chart summarizes the skills required of a sales specialist at
the different positions within the profession.
____________________________ ___________________________________________
| | Profession Positions, with Associated |
| | Skill Levels |
| |_______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| SALES SPECIALIST SKILLS | | Adv | Sr | Cons | Sr | |
| | Sales | Sales| Sales| Sales | Cons | Key |
| | Spec | Spec | Spec | Spec | Sales| Skill|
| | | | | | Spec | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| CLIENT ENVIRONMENT |
|____________________________ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| Client Relationships | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | Y |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Client Strategy & Planning | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | Y |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Client Management | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | Y |
| System/Culture | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| BUSINESS ACUMEN |
|____________________________ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| Market Management | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | Y |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Use Business Partners | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | Y |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Finance Skills/Technique | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | Y |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Use Value-Added Finance | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | Y+ |
| Method | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Consulting Methods | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Y |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Value-Add Selling | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | Y |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Client Issue ID | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | Y |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Consultative Sales Call | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | Y+ |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Potential Opportunities to | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | Y |
| Real | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Frame Client Solutions | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | Y+ |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Close Opportunity | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | Y+ |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Measure Client Results | 1 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Y |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Customer Satisfaction | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | Y+ |
| Management | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| INDUSTRY |
|____________________________ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| Industry | | | | | | |
| Segments/Industries (1) | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | Y |
| (Any Sales Specialist) | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Industry | | | | | | |
| Segments/Industries (1) | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | Y |
| (Industry Solutions Sales | | | | | | |
| Specialist) | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| IBM ENVIRONMENT |
|____________________________ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| IBM Organization | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | Y |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| IBM | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Y |
| Vision/Mission/Strategy | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| IBM Management System | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | Y |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| PROJECT MANAGEMENT |
|____________________________ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| Initiate Projects | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | Y |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Plan Projects | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | Y |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Project | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | Y |
| Track/Report/Deliver | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Manage Project Risk | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | Y |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| PRODUCT/TECHNOLOGY/SERVICES |
|____________________________ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| Platforms | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Y |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Applications | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | Y |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| I/T Related Services | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Y |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Architectures | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Y |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Methodologies | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | Y |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Discipline | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5** | Y+ |
| products/services (2) | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| PERSONAL |
|____________________________ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| Leadership | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | Y |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Communication | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | Y |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Interpersonal | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | Y |
| Communication | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Business-to-Business | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | Y+ |
| Communication | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Negotiation | 2 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | Y+ |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Problem Solving & | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | Y |
| Decision-Making | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Risk Awareness/Taking | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | Y |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| 4 skills have been deleted from the templates -- 2 business acumen
| financial, 2 personal
(1) Replaced by an industry customer classification template.
(2) Replaced by a discipline-specific template. Proficiency level is
overall proficiency required for discipline skills.
** At Sr Cons position, must have expert knowledge in multiple
disciplines / specialties.
+ Indicates critical skill for the profession.
Skill templates for the Sales Specialist Profession are found in the
SKILLS tool. The profession templates have the following names:
- Sales Specialist
- Sales Specialist-Adv
- Sales Specialist-Sr
- Sales Specialist-Cons
- Sales Specialist-Sr Cons
The sales specialist discipline templates are generally named Sales
Spec-"discipline"-"position", where "discipline" is the name or
abbreviation of the discipline (or discipline/specialty), and "position"
is an abbreviation for the relative position within the profession.
Industry customer classification templates are generally named
"Industry"-CC-"other identifiers", where "Industry" is the name or
abbreviation of the industry and "other identifiers" may include the
abbreviation of an industry segment and/or an indication of which
professionals should use the template.
3.3.9 Professional Development
Many forms of education or developmental activities exist that can help to
increase skill proficiency levels, including formal classroom training,
self-study, outside reading, courses outside IBM, and also experience on
the job. A sales specialist is expected to focus on general professional
skills, selling skills, and skills specific to the discipline offerings.
Figure 14-1 in topic 3.3.3 summarizes developmental activities from one
position in the profession to the next. For an overview of the Worldwide
Professions and links to the Common Skills Categories and Professions
Roadmaps, refer to the Education Roadmap page of the IEC Course Catalog at
http://w3.lahulpe.ibm.com/roadmaps/index.html
3.3.10 Additional Information
Questions about the Sales Specialist Profession may be sent to the
following ID for your geography:
_________________ _________________
| | Asia Pacific | IBMAU(SUEBODDY) |
|_________________|_________________|
| | EMEA | NHBVM9(CHILDJM) |
|_________________|_________________|
| | Latin America | ARG(GONZALER) |
|_________________|_________________|
| North America | HQVMIC1(MSQA) |
|_________________|_________________|
3.3.11 Sales Specialist Position Descriptions
The following position descriptions describe the basic work of each of the
positions within the Professions. Formal descriptions which may contain
legally mandated language necessary for classifying employees in a
geography should be obtained through the approved on-line job library, if
available in the geography, or by contacting the appropriate H.R.
personnel within the geography.
Subtopics:
3.3.11.1 Position Title: Sales Specialist
Position Concept:
Sales specialist professionals are responsible for selling IBM offerings
(hardware, software, services, and industry solutions) directly to
customers.
Sales Specialists become specialized in a set of related offerings known
as a discipline. They are assigned to specific opportunities where they
possess the sales and technical expertise required to conduct the phases
of the sales cycle. For assigned opportunities, the Sales Specialist is
responsible for closing the sale and positively impacting the customer's
satisfaction with the engagement and the offerings. The Sales Specialist
works under the guidance of a team leader or more experienced sales
specialist, or may work independently for specific assignments. The Sales
Specialist is expected to establish proficiency in the products or
services of the assigned discipline, and to learn how these are included
in total solutions. The Sales Specialist is typically assigned small to
medium size opportunities within a business unit, area/country, or
industry unit.
Skills
- Develops and maintains technical sales knowledge of offerings in the
discipline, along with financial and selling skills, to effectively
handle routine assignments and to assist on more complex assignments,
for opportunities within the territory. Demonstrates required
proficiency levels for technical and sales skills, as defined for
Sales Specialist.
- Develops an understanding of sales processes, techniques and tools in
the discipline, for the assigned territory. Examples of these
techniques include, but are not limited to -- opportunity / territory
management, availability management, network management, application
development, cost justification, recovery services, acquisition
management, performance management, service business management
processes. With guidance, can apply these to specific customer
situations.
- Develops the ability to plan and execute an effective sales call,
either individually or with others.
- Acquires new information on selling techniques or discipline offering
capabilities quickly, to enhance sales and professional effectiveness.
- For selected offerings within the discipline, differentiates them from
competitive alternatives.
- Collaborates and negotiates with other local team members in matching
IBM offerings to customer business requirements. Solutions are based
on own discipline offerings, and include other offerings and
appropriate terms and conditions, resulting in a final customer
proposal. Helps to define acquisition alternatives which result in
winning financial strategies.
- With guidance, negotiates with customers to close the sale, in routine
situations.
- Assists in communicating new developments or announcements in the
discipline / specialty to client relationship teams, IBM Business
Partners and to customers within the assigned territory.
- Recognizes job-related problems with discipline offerings, solutions,
customer negotiations, or team relationships. Uses existing
techniques or tools to analyze causes, and prepares and recommends
solution alternatives to more senior sales specialists or local
management.
Contribution/Leadership
- Participates on teams of other related professionals to identify
solutions to meet customer requirements.
- Work is reviewed by more senior professionals and management for
developmental purposes.
- Understands the mission of the department in which assigned, and how
the activities of sales specialists contribute to its success.
- Implements defined sales activities in the discipline for the
assigned territory or opportunity.
Impact On Business/Scope
- Accountable for individual or team sales results, such as revenue or
profit in the discipline, for the assigned territory.
- Typically assigned to routine customers / opportunities.
- Performs activities which positively impact customer satisfaction with
solutions sold.
- Establishes relationships with customers at the functional and higher
levels within customer organizations.
- Develops an understanding of the capabilities of IBM agents and other
IBM Business Partners in the discipline, and with guidance uses them
in appropriate situations.
3.3.11.2 Position Title: Advisory Sales Specialist
Position Concept:
Sales specialist professionals are responsible for selling IBM offerings
(hardware, software, services, and industry solutions) directly to
customers.
Advisory Sales Specialists maintain in-depth skills in the discipline
offerings, and are assigned to discipline-specific opportunities where
they possess the sales and technical expertise required to conduct all
phases of the sales cycle. They are responsible for closing the sale and
winning the customer's satisfaction with the engagement and the offerings.
The Advisory Sales Specialist works independently, as a member of a large
team, or the leader of a small team. The Advisory Sales Specialist is
typically assigned to medium to large size opportunities within a business
unit, area/country, or industry unit.
Skills
- Maintains in-depth technical sales knowledge of offerings in the
discipline, along with financial and selling skills, that can be
applied to most opportunities in the territory. Demonstrates required
proficiency levels for technical and sales skills, as defined for
Advisory Sales Specialist.
- Maintains an understanding of sales processes, techniques and tools in
the discipline, and uses them appropriately. Examples of these
techniques include, but are not limited to -- opportunity / territory
management, availability management, network management, application
development, cost justification, recovery services, acquisition
management, performance management, service business management
processes.
- Performs independently, without supervision, in engaging and closing
assigned sales opportunities.
- Understands the competition's offerings and plans. Can differentiate
IBM offerings from competition to ensure winning in engagements.
- Negotiates with team members to match discipline and other offerings
to customer business problems, articulating and comparing alternative
approaches, to design a total solution. Identifies most appropriate
channels for delivery and support of solution. Recognizes
opportunities to integrate other discipline offerings into a total
solution. Knows when to transfer the opportunity to another IBM sales
specialist or other resource if another discipline offering or
resource is the most appropriate for the customer. Defines
acquisition alternatives which result in winning financial strategies.
- Negotiates with customer management, resulting in successfully closing
the sale.
- Communicates new developments or announcements in the discipline /
specialty to client relationship teams, IBM Business Partners and to
the customers within the assigned territory.
- Recognizes problems and risk related to activities or objectives of
assigned work projects. Independently generates solutions, based on
own analytical skills and business judgements.
- Applies creativity and judgment to solving customer business problems,
in designing and selling solutions, and in other assigned activities.
- Challenges the validity of given procedures and processes, such as
those related to selling, opportunity management, etc., to enhance and
improve them, or to develop complementary adjustments or solutions.
Contribution/Leadership
- Works independently, or is a member of a large team, or leads small
teams of other professionals (such as sales specialists, client
relationship professionals, I/T specialists, IBM Business Partners) to
design solutions for assigned customer opportunities.
- Controls own work priorities and methods, and makes necessary
trade-offs.
- Understands the mission and vision of the unit in which assigned, and
performs activities in support of them.
- Provides input to and implements sales action plans in the discipline
offering set for the assigned territory.
Impact On Business/Scope
- Accountable for individual, team, or unit sales results, such as
revenue and profit.
- May be assigned to large customers / opportunities.
- Plans and performs activities which have a positive impact on customer
satisfaction.
- Establishes relationships with customers at most levels of management.
Advises customers on matters related to the discipline offerings.
- Uses IBM agents and other IBM Business Partners in appropriate
situations for opportunities in the discipline.
- Recognizes and communicates offering requirements to IBM management or
more senior sales specialists.
3.3.11.3 Position Title: Senior Sales Specialist
Position Concept:
Sales specialist professionals are responsible for selling IBM offerings
(hardware, software, services, and industry solutions) directly to
customers.
The Senior Sales Specialist works independently or is the leader of a team
of sales specialists, providing advice and guidance to other specialists.
The Senior Sales Specialist has comprehensive knowledge of the
discipline's offerings and is responsible for the success of those
offerings within the business unit. This professional typically leads
large and/or complex opportunities, where customers are national or
otherwise significant, and is responsible for winning the business. The
Senior Sales Specialist has in-depth sales, business, and professional
skills to work with any level of customer management. With a perspective
beyond the assigned territory, this professional provides input to sales
objectives and strategies for the business unit.
Skills
- Develops and maintains comprehensive technical sales knowledge in the
discipline offerings, along with financial and selling skills, that
can be applied to opportunities across the business unit.
Demonstrates required proficiency levels for technical and sales
skills, as defined for Senior Sales Specialist.
- Maintains an in-depth knowledge of the discipline sales processes,
techniques, and tools, and advises others on their use. Examples of
these include, but are not limited to -- opportunity / territory
management, availability management, network management, application
development, cost justification, recovery services, acquisition
management, performance management, service business management
processes.
- Advises other sales specialists within the discipline.
- Maintains in-depth knowledge of competition's offerings, strategies,
and plans. Effectively differentiates IBM offerings from competitive
alternatives and creates customer preference for IBM offerings, based
on that differentiation.
- Negotiates with team members to define approaches and goals,
especially as it relates to designing solutions to meet customer needs
or defining sales action plans. Facilitates teams, where members have
diverse backgrounds.
- Effectively negotiates with multiple levels of customer management,
resulting in successful closing of the sale.
- Designs total integrated solutions including hardware, software and
services, including offerings from other disciplines, to meet complex
customer business requirements. Combines solutions with terms and
conditions to create a final customer proposal. Ensures that the
proposal delivered to the customer provides a workable solution.
- Develops business and sales strategies for communicating new
developments or announcements in the discipline to client teams, IBM
Business Partners and to the customers within the assigned territory.
- Recognizes complex problems relating to discipline offerings, customer
sales engagements, business unit measurements. Analyzes situation and
implements solutions, or develops new approaches or procedures.
Assesses risk in terms of value and exposure to both IBM and
customers.
- Applies creativity and judgement in developmental work on complex
opportunities, defining sales activities, or other projects within the
business environment.
Contribution/Leadership
- Leads teams of professionals (such as sales specialists, client
relationship professionals, I/T specialists, IBM Business Partners),
and provides ongoing technical and sales guidance, to design solutions
for large or complex opportunities. Typically leads several
opportunities concurrently.
- Initiates selling activity where no relationship team or agent is
involved. May be assigned to develop customer solutions where no
precedent exists.
- Understands the mission and vision of the sales function within the
business unit and geography.
- Utilizes expertise to directly influence people outside the business
unit, such as in sales headquarters, product divisions.
- Regularly participates in planning of sales strategies and objectives
for the territory / business unit.
Impact On Business/Scope
- Accountable for business unit sales results, and specific personal
objectives, including revenue and profit, and for activities and
project results of cross-functional sales teams.
- Typically assigned to large/complex opportunities, where customers may
be national, or otherwise significant.
- Manages to a high level of customer satisfaction. Designs and
implements plans to increase customer satisfaction with sales
engagements and solutions.
- Identifies new IBM agents and other IBM Business Partners appropriate
to the discipline / specialty.
- Represents customer issues and market requirements on discipline
offerings to product divisions, service lines, or industry solution
units.
- Makes decisions on project costs or expenses relating to sales
activities.
3.3.11.4 Position Title: Consulting Sales Specialist
Position Concept:
Sales specialist professionals are responsible for selling IBM offerings
(hardware, software, services, and industry solutions) directly to
customers.
The Consulting Sales Specialist works independently or is the leader of a
team of sales specialists, guiding and mentoring others. This sales
specialist is an expert in the offerings of the discipline, with breadth
of knowledge in other disciplines. In addition to achieving personal
business objectives, the Consulting Sales Specialist assures that sales of
the set of discipline offerings meets assigned objectives within the
business unit, area/country, or industry unit. This professional leads
multi-functional teams covering large, complex opportunities, negotiating
with the highest levels of customer management. This professional is
responsible for the unit sales strategy and gathering requirements, and
provides advice to sales and development executives. This sales
specialist anticipates potential problems, is generally guided by business
directives, and has latitude to define priorities and resources for sales
opportunities.
This is a non-management position. However, people management
responsibility may be assigned, if it is incidental to the other
responsibilities.
Skills
- Maintains expert technical sales knowledge of discipline / specialty
offerings, and has breadth of knowledge in related disciplines /
specialties and other IBM and IBM Business Partner offerings.
Maintains expert skills in engaging and closing sales opportunities,
including in-depth financial acquisition skills. Demonstrates
required proficiency levels for technical and sales skills, as defined
for Consulting Sales Specialist.
- Maintains expert knowledge of the management and/or sales processes,
techniques, and tools associated with the discipline offerings, and
guides others in their use. Identifies and implements improvements to
them. Examples of these techniques and tools include, but are not
limited to -- opportunity / territory management, availability
management, network management, application development, cost
justification, recovery services, acquisition management, performance
management, service business management processes.
- Guides and mentors less experienced sales specialists within the
discipline.
- Demonstrates expert knowledge of competition in the discipline -- the
company, its strategies and its products / services. Effectively
differentiates IBM offerings from competitive alternatives and creates
customer preference for IBM offerings on that differentiation. Is the
primary source of competitive knowledge within the assigned discipline
and business unit.
- Adapts communications and approaches to conclude negotiations with
various teams of IBM, IBM Business Partner, and/or vendor resources,
resulting in common agreements, to solve customer business
requirements. Ensures that the relationship teams and IBM agents have
a reasonable and sufficient knowledge of the discipline / specialty to
help determine the preferred IBM offerings for customer requirements.
- Applies creativity and judgement in designing total solutions to meet
customer business requirements, based on own discipline offerings, and
including those of other disciplines. This requires the coordination
of any IBM resources, IBM Business Partner resources and/or outside
vendors necessary to deliver the proposal.
- Leads negotiations with the highest levels of customer management for
the acquisition of the solution.
- In-depth knowledge of business operations of area/country and
geography. Understands organization resources, priorities, needs and
policies that relate to staffing, engaging, and winning sales
opportunities, and provides advice to management.
- Analyzes complex/new sales situations, anticipating potential problems
and future trends. Assesses risk and designs customer solutions /
contracts or sales strategies to minimize risk to IBM and to the
customer.
Contribution/Leadership
- Leads multi-functional teams of other professionals (such as sales
specialists, client relationship professionals, I/T specialists, I/T
architects, and IBM Business Partners) to design solutions to meet
complex or leading edge customer requirements. These opportunities
are often one-of-a-kind, where it is possible to create and
demonstrate value. Recognized within the geography or worldwide as an
expert in the discipline, with significant knowledge in disciplines
outside the area of expertise.
- Based on business unit directives, has considerable latitude to define
and decide on tools, processes, priorities, and resources required to
design customer solutions and meet sales objectives. Often no
precedent exists.
- Has vision of the business unit mission and geography mission.
- Represents complex / difficult customer issues and requirements,
relating to the discipline offerings, throughout IBM. Influences
people and organizations, including executive management, when issues
require considerable diplomacy.
- Anticipates direction of future discipline offerings, and future
customers. Assesses opportunities, impacts, and risks of the new
offerings on current and new customers.
- Leads development of sales strategies for the business unit.
Impact On Business/Scope
- Accountable for success of sales engagements involving multi-
functional, area/country teams. Leads several opportunities at the
same time.
- Responsible for the overall success of the discipline offerings within
the business unit. Assists in setting sales objectives for assigned
business unit.
- Assigned to customers / opportunities that are highly complex,
competitive, leading edge, or difficult, or to development of
strategic new territories.
- Develops and implements strategies to build and maintain high customer
satisfaction with sales engagements and IBM. Accountable for customer
satisfaction with solutions sold.
- Decisions on resources, revenue and profit from sales engagements
impact business unit or area/country costs and expenses.
- Maintains awareness of activities performed by, and high level
relationships with, all IBM Business Partners and consultants within
the territory. Advises IBM Business Partners on which offerings and
skills can impact productivity and revenue attainment, and enhance
solutions.
3.3.11.5 Position Title: Senior Consulting Sales Specialist
Position Concept:
Sales specialist professionals are responsible for selling IBM offerings
(hardware, software, services, and industry solutions) directly to
customers.
The Senior Consulting Sales Specialist is the expert in the discipline /
specialty offerings, both within the geography and internationally, and
has in-depth knowledge in other disciplines / specialties. This sales
specialist leads very large multi-functional teams to develop and close
the most complex, leading-edge, high-risk opportunities, planning and
leading negotiations with the highest levels of customer management. The
Senior Consulting Sales Specialist is accountable for teams and results in
large business units or geographies, where customers are international or
worldwide. This professional anticipates, creates and defines innovative
sales strategies and customer solutions in strategic environments, with
executive review, and provides input to policy-making for discipline
offerings. This sales specialist is considered as an expert and leader by
others inside and outside IBM.
This is a non-management position. However, people management
responsibility may be assigned, if it is incidental to the other
responsibilities.
Skills
- Maintains expert technical and sales knowledge in multiple disciplines
/ specialties. Recognized as the expert by executives within the
geography and within the discipline's worldwide development
organization. Demonstrates required proficiency levels for technical
and sales skills, as defined for Senior Consulting Sales Specialist.
- Maintains expert knowledge of the management and/or sales techniques
associated with the discipline offerings, along with the use of
appropriate tools. Develops and implements new techniques and tools.
Examples of these techniques include, but are not limited to --
opportunity / territory management, availability management, network
management, application development, cost justification, recovery
services, acquisition management, performance management, service
business management processes.
- Mentors less experienced sales specialists within and outside the
discipline, and other professionals.
- Recognized as the expert on the competition -- the companies or
industries, their products / services, strategies, and directions.
Effectively differentiates IBM offerings from competitive
alternatives, and IBM from competitors, and creates customer
preference, at the most strategic IBM customers, for the IBM company
and IBM offerings on that differentiation. Is a primary source of
competitive knowledge within the geography or globally, for the
discipline.
- Based on own knowledge of future trends, anticipates, creates and
defines innovative and visionary solutions for leading edge or
critical customer business requirements. Solutions address the most
strategic requirements of the customer.
- Exhibits teamwork at the highest levels of IBM and customer management
in developing and selling solutions.
- Plans and conducts complex negotiations, reaching lasting agreements
and commitments with team members or customers, in any activities
relating to discipline offerings. Plans and leads negotiations with
the highest levels of customer management, for the acquisition of
leading edge, total solutions.
- Anticipates direction of future discipline offerings and the I/T
industry, and assesses opportunities, impacts, and risks of the new
offerings on current and new customers. Represents complex /
difficult issues and requirements to executives throughout IBM.
Contribution/Leadership
- Assigned to customers / opportunities that are highly visible or
highly complex, competitive, leading edge, or difficult; or to develop
strategic new territories or business opportunities. Assigned
opportunities have executive visibility and review.
- Leads business unit, geography, or international sales teams including
sales specialists, client relationship professionals, I/T specialists,
I/T architects, and IBM Business Partners, and others, to design
international or worldwide solutions to meet the most demanding
customer requirements.
- Has vision of geography and worldwide IBM business strategies.
- Internationally recognized as an expert and leader. Sought out by
executive management. May be assigned to conduct strategic projects.
Impact On Business/Scope
- Accountable for business unit or major country or international sales
results. Ultimately responsible for the success of offerings from
multiple disciplines / specialties, within the business unit or
country.
- Contributes to policy making, as it relates to discipline offerings or
customer sales strategies, geography-wide or internationally.
- Responsible for committing multiple resources and achieving the
customer satisfaction, cost, expense, revenue, profit and other
business measurements of critical importance at the business unit
level, as they relate to selling customer solutions.
- Responsible for quality output and value add for highly visible
offerings within the discipline, and for future business development.
4.0 Services Professions
Subtopics:
4.1 Chapter 15. Consultant Profession
Subtopics:
4.1.1 Consultant Profession Overview
The mission of consulting is to help client organizations understand and
take the best advantage of business, organizational, functional, and
information technology strategies. Consultants provide advice and counsel
to clients for a fee. They use their skills, experience, intellectual
capital, and an integrated set of methodologies to solve client business
problems, translating their findings into written, actionable
recommendations. IBM consultants are hired by clients for a variety of
business and I/T related reasons, ranging from re-engineering a business
process to advising how to manage operations. Consultants work in an
unstructured environment creating, sharing, and reusing intellectual
capital to solve diverse, technology related issues that extend from the
Board Room to the Machine Room.
Subtopics:
4.1.1.1 Organizational Structure
The organizational structure through which consultants deliver services is
called a practice. The service(s) a practice delivers is defined by the
capabilities of the individuals, supported by the methodologies and tools
developed by service line (specialist areas) experts. Some examples of IBM
consulting services are Transformation Consulting Services, Information &
Technology Consulting Services, Object Technology Services, and Systems
Integration/Application Development Services. Consultant deliver services
working in teams on client "engagements". Engagement team activities
include research and data collection, analysis, preparation of
recommendations, presentation of the final report, and contribution and
reuse of intellectual capital. Throughout their careers, at various
stages, consultants are expected to contribute to the engagement either as
a team member performing engagement activities or as the engagement
manager with overall responsibility for engagement performance.
Furthermore, consultants are expected to grow, share, and reuse
intellectual capital for the benefit of the entire Consulting
organization.
4.1.1.2 Consultant Skills
Performing the responsibilities of a Consultant dictates the development
of a set of key skills. Consultants are expected to work with all levels
of the client organization including top executives. Therefore, they must
possess strong communication and interpersonal skills. A good
understanding of human behavior and organizational dynamics is also
important, as consultants must be able to deal with complex organizations
and act as agents of change. Given the engagement environment, consultants
must be strong team players, both as team builders and leaders; yet
consultants must be able to work autonomously with little supervision.
Because of the creative aspects of the work, strong analytical skills are
required. Business acumen and financial skills are needed to determine
the impact of their recommendations on the clients' business. In addition,
at the senior levels, leadership and people management skills are required
to manage client relationships and engagement responsibilities.
Consultants should possess a strong knowledge of I/T trends and
directions. They should also have technical expertise in a particular
industry and/or service line methodology.
Consultant skills are grouped into four categories: generic, service line
(specialist area), industry, and product. All consultants need to develop
some level of competency in generic and service line skills and possibly
industry and product skills. The level of skill competency required will
be dictated by the position, industry, and other related factors. In
general, Associate Consultants, Consultants, and Senior Consultants will
focus on developing generic skills, i.e., fact-finding, analysis, business
acumen, intellectual capital management and personal effectiveness skills,
as well as service line, and industry skills. Principals will need well
developed project management, client management, intellectual capital
creation, and leadership skills. People and practice management are
essential skills for Principals and Managing Principals. Executive
Consultants may have strong competencies in one or more service lines,
industries or technologies. They are regarded as critical thought leaders
in their specialist areas, and contribute intellectual capital.
IBM Professionals and professional hires with extensive consulting,
industry, marketing, and/or technology-specific skills are ideal
candidates for the consulting profession. Persons new to consulting can
acquire technology, industry, and service line skills through formal
education, mentoring, and on-the job training.
4.1.2 Profession Structure
The Consultant Profession offers a dual career path. As consultants gain
skill and experience, they may progress along the consulting career path
into the Executive Consultant Levels (i.e., Associate Consultant,
Consultant, Senior Consultant, Executive Consultant - which has three
levels, a professional level equivalent to Principal and two executive
levels equivalent to Managing Principal and Vice President) or choose
business/people management, beginning with the Principal position (i.e.,
Associate Consultant, Consultant, Senior Consultant, Principal, Managing
Principal, Vice President, General Manager).
Figure 15-1 and Figure 15-2 summarize the requirements of each position of
the profession and the developmental requirements for progression within
the profession. Detailed position descriptions can be found in
"Consultant Position Descriptions" in topic 4.1.12.
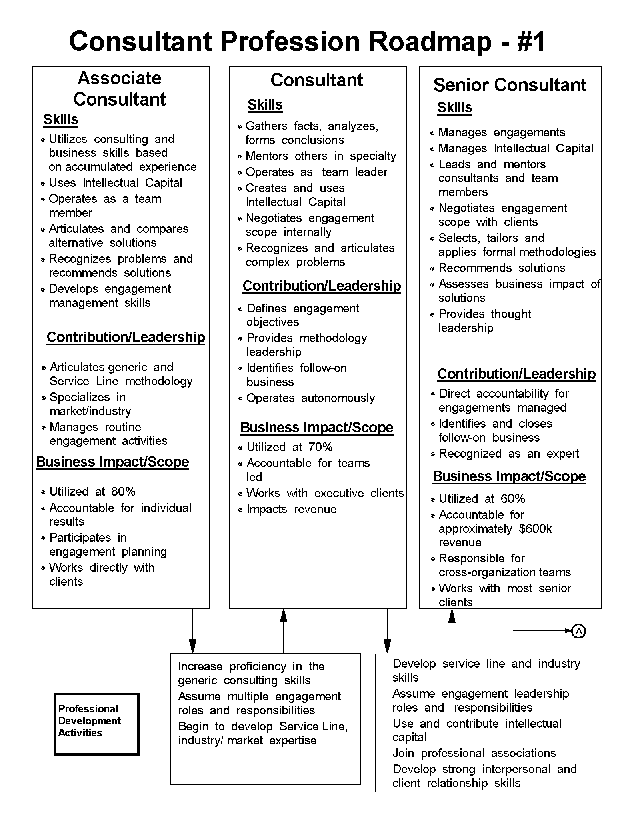
Figure 15-1. Consultant Profession Roadmap - #1
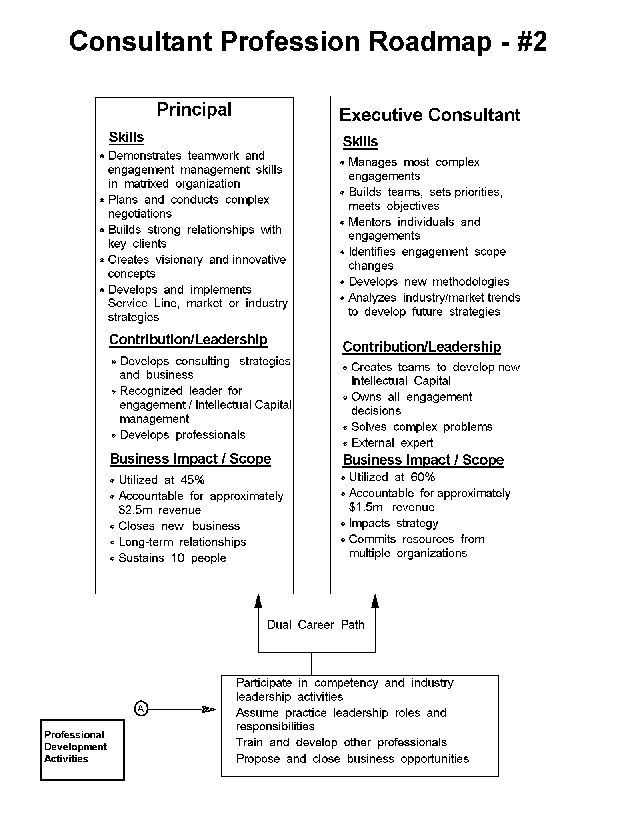
Figure 15-2. Consultant Profession Roadmap - #2
All consultants (The term "consultant" used in this context is intended to
describe all positions within the Consultant Professional Career) are
expected to perform engagement team activities. However, a typical
engagement team has an average size of four to five members and will
include a mix of Associate Consultants, Consultants, and Senior
Consultants, possibly supported by a Research Associate. Other IBM
professionals, such as I/T Architects, Project Managers, or I/T
Specialists may also be members of an engagement team. The Research
Associate and Associate Consultant are entry positions for the college
hire and experienced IBM service professional. Associate Consultants,
Consultants, and Senior Consultants all perform the same type of
engagement work. The difference in responsibility is based on skill and
experience level. Senior Consultants and Executive Consultants (and
occasionally Principals) usually play the role of the engagement manager
on large engagements. Principals usually also have people management and
business development responsibilities. Executive Consultants lead complex
engagements or may work on multiple engagements simultaneously and are
expected to contribute expertise and/or intellectual capital to
engagements, the practice, and the Consulting organization. Managing
Principals oversee all engagements in their practice and have profit and
loss, selling, client satisfaction, and people management
responsibilities. Key quantitative measurements for consultants are:
billable activity or utilization; personal revenue; profitability; new or
add-on business; and growth and reuse of intellectual capital for the
Consulting organization.
4.1.3 Characteristics of the Profession
The IBM Consulting Group is a global network of highly skilled
professionals dedicated to furthering the client's success by applying
industry, operational, and technical knowledge. The mission includes
developing and deploying the industry's best intellectual capital,
ensuring excellence in worldwide service quality, innovating with
technology, and providing the best local and global resource for the
client's business challenges.
Consultants share a common set of values which include: Clients first,
people contributing through teams are a key asset, extraordinary
environment for professional growth, and superior results in everything
Individuals who aspire to become consultants should possess a variety of
skills. They are grouped below in two categories: basic consulting skills
for those entering the profession and advanced consulting skills for those
desiring advancement in the profession.
- Basic Consulting Skills
Fact finding and data collection, analysis, report writing,
presentation skills, business acumen, ability to work well in a team
based engagement environment, intellectual curiosity, good
interpersonal skills.
- Advanced Consulting Skills
Strong project management, client relationship skills, critical
thinking and writing, business development, thought leadership and
intellectual capital creation, practice development, communication
skills - both written and oral, leadership skills, understanding of
the financial impact of recommendations to a client's business,
ability to work and lead in a team based engagement environment,
strong business acumen.
All consultants use a set of IBM integrated methodologies to solve client
business problems. All consultants are expected to become certified in a
specific service line. Many consultants will have a specific industry
expertise.
4.1.4 Potential Candidates
Candidates for the Consultant Profession can come from a variety of
sources. Three specific sources are:
- College campus
- Experienced hires from consulting firms
- Internal transfers
Campus recruiting comes in two varieties: University hires predominantly
for the Research Associate position and Associate Consultant position and
advanced degree hires with prior work experience for the Associate
Consultant and Consultant positions. Experienced hires from other
consulting firms are generally sought after for Senior Consultant and
Principal positions. Internal IBM transfers may come from other units in
Global Services, M&D sites, IBM Research, or Sales and Services.
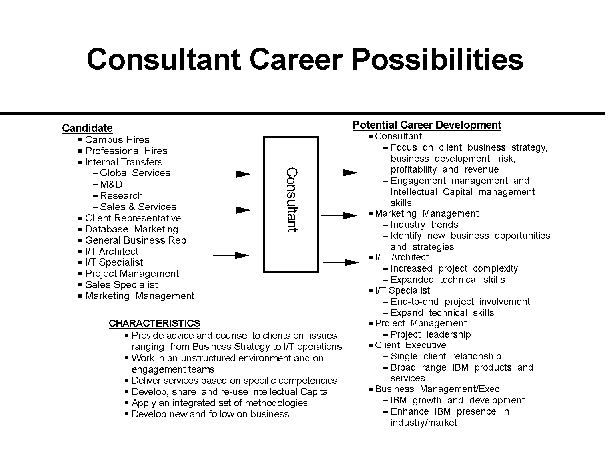
Figure 15-3. Consultant Profession Career Possibilities
Figure 15-3 shows possible candidates for the Consultant Profession and
possible career movement from a Consultant position.
More information on movement from other professions is available in
Consultant Career Possibilities.
4.1.5 Career Growth
The Consultant Profession offers a dual career path. A path which
includes management of a piece of the business or a path which results in
recognition primarily based on thought leadership and subject matter
expert skills. Progression up either side of the career ladder is
dependent on proven capabilities and business need. Figure 15-4 shows the
progression of the Dual Consulting Career Path and Figure 15-1 in
topic 4.1.2 shows an Overview of Consulting Roles and Responsibilities for
each position.
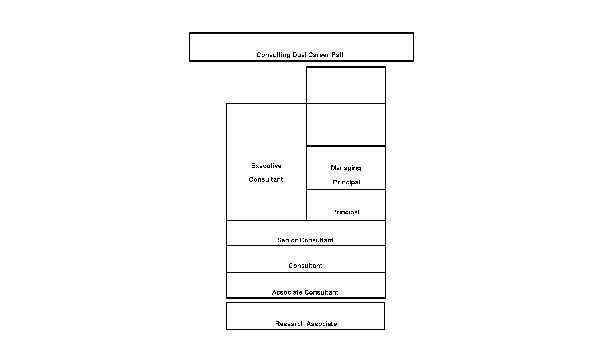
Figure 15-4. Dual Consulting Career Path
4.1.6 Certification Requirements
The certification process is intended to recognize IBM consultants who are
working at a defined standard of excellence. With the exception of the
Research Associate and Associate Consultant positions, which are not
certifiable positions, a person entering the consulting profession is
expected to be certified within two years. Normally (unless an
experienced hire), Consultants are expected to be certified prior to
promotion to the Senior Consultant position.
Consultant certification is somewhat different from other WW Professions.
It is more of a "license to practice". Consultants are expected to know
and apply the IBM issue based consulting methodology, and demonstrate
effective use of one of the service line (specialist area) methodologies.
Consultant certification is particularly important in a business where
many of its constituents join as experienced hires and may have used other
methodologies prior to joining. The vast majority of IBM consultants are
expected to be certified. Therefore certification takes place a little
earlier than some other WW Professions.
The certification process is designed to inspect and validate a candidates
credentials based on:
- Skills
- Experiences on Client Engagements (application of skills in client
situations)
- References of Client Satisfaction
- Professional/Intellectual Capital Contributions
Typically, to meet the Certification requirements, an individual would
have several years of consulting or related business experience, often
outside IBM. They would have a strong track record of sustained
contribution to their organization in terms of revenue and customer
satisfaction. They often have two academic qualifications, and if they
have been working in a consulting organization, their utilization would be
consistently high. Certification criteria are mapped to the consulting
industry, and the expectation is that IBM Certified Consultants would have
high market value.
To be eligible for certification, a consultant must:
- Be a member of an accepted practice in the IBM Consulting Group
- Meet the experience criteria for the service line i.e., formal
training and completion of three methodology-based engagements with
the appropriate client satisfaction and individual performance
evaluations.
- Be nominated by a confirmed Principal.
(Note: "Confirmed" in this context refers to the way that Practices are
set up within the IBM Consulting Group. When a Practice is first set up,
a Principal is appointed to manage business development activities. Once
it is clear that there is a viable business, the Practice itself is
accepted and the Principal confirmed.)
If you meet these criteria, you are ready to submit a nomination for
certification. This package must be approved by your principal. Then it
should be submitted to the certification representative for a preliminary
review. If your nomination application is accepted, your package will be
assessed and you will be interviewed. You will be approved based on board
recommendations. Certificates are signed and issued by the General Manager
of the geography. Certified Consultants must be re-certified every three
years - or after an absence from the profession of two or more years.
A Principal must be "confirmed" within eighteen months of appointment.
This requires meeting several criteria. You must:
- Be part of an accepted practice that is financially viable, delivering
IBM Consulting Group services,
- Be certifiable or already certified, as a Consultant, I/T Architect,
or Project Manager,
- Demonstrate skill proficiency, especially in engagement management,
intellectual capital management, selling, and professional staff
development,
- Understand your practice financial management, and competitive market
dynamics,
- Demonstrate commitment and contribution to the IBM Consulting Group
and its values, i.e., sending in client satisfaction forms, monthly
reports, engagement analysis summaries, and end-of engagement
evaluations, etc.
4.1.7 Certification Nomination Guide
The Worldwide Consultant Certification Nomination Guide contains the
criteria, required documentation, and process for certification in the
profession.
4.1.8 Performance Elements
Utilization and personal revenue are the key quantitative measures up
through the consultant level. Senior Consultants, Executive Consultants,
Principals and Executive level positions in the Consultant Profession are
measured on utilization personal revenue, follow-on and new business, and
engagement profitability. All consultants are expected to contribute to
the intellectual capital of the IBM Consulting Group.
4.1.9 Consultant Profession Skills Profile
Performing the responsibilities of a Consultant dictates the development
of a set of key skills. Consultants are expected to work with all level
of the client organization including top executives. Therefore, they must
possess strong communication and interpersonal skills. A good
understanding of human behavior and organizational dynamics is also
important, as consultants must be able to deal with complex organizations
and act as agents of change.
Given the engagement environment, consultants must be strong team players,
both as team builders and leaders; yet consultants must be able to work
autonomously with little supervision. Because of the creative aspects of
the work, analytical skills are required. Business acumen and financial
skills are needed to determine the financial impact of their
recommendations on the clients' business. In addition, at the senior
levels, leadership and people management skills are required to manage
client relationships and engagement responsibilities. Consultants should
possess a strong knowledge of I/T trends and directions. They should also
have technical expertise in a particular industry and/or service line
methodology.
4.1.10 Consulting Templates
There are different types of templates corresponding to the different
categories of consulting skills.
- Generic templates include what are commonly referred to as intangible
skills, such as leadership and negotiation skills. Generic templates
are also referred to as "fixed" templates. There is one generic
template for the Consulting Profession which contains skills and skill
levels for Research Associate, Associate Consultant, Consultant,
Senior Consultant, Principal, and Executive Consultant.
- Service line templates include service-line-specific skills. There is
one set for each service line.
- Industry templates include industry-specific skills. There is one set
for each industry.
- Product templates include product-specific skills. There is one set
for each of the key product areas. This includes networking, personal
systems, client server, systems software, and others.
The various types of templates are selected in combination to form a
consultant's skill profile. A consultant's profile describes the complete
"suite" of consulting skills, e.g., generic, service line skills,
industry, etc. required for specific position and job role, i.e., senior
consultant in a Transformation Consulting practice in the manufacturing
industry.
Proficiency levels in the generic templates are "standards" and represent
fixed skill requirements for all consultants worldwide. Required
proficiency levels for service line skills are determined based on the
specific need of the business or practice.
Subtopics:
4.1.10.1 Generic Template
The generic template includes "Professions" skills which are common to all
of the "IBM Professional Careers" and skills that are specific to the
consulting profession. (Refer to the PROFESSIONS TEMPLATE at the end of
this chapter for the twenty-four "professions-specific" skills.) This
generic template is also referred to as "fixed" because, unlike other
types of templates, it can not be customized. The generic template
represents a worldwide standard that all consulting professionals will
recognize and use.
For simplicity, both "profession-specific" and "consulting-specific"
generic skills are combined and organized by key job responsibilities
(identified as activity groups) as described below.
- Business/Project Management
- Finding Facts, Analysis, and Conclusions
- Managing Client Relationships
- Business Development (Selling)
- Practice/Professional Development
- Service Line, Industry, and Product Expertise ("Product" added since
publishing the Career Guide)
- Leadership/Personal Effectiveness
Every consultant will use a generic (or "fixed") template corresponding to
their position (i.e associate consultant, consultant, etc.). Generic
templates are described in the following tables. Note that each column in
the table represents a consulting position template:
- "RA" refers to Research Associate, template name Consultant-Research
Associate
- "AS" refers to Associate Consultant, template name
Consultant-Associate
- "CO" refers to Consultant, template name Consultant
- "SC" refers to Senior Consultant, template name Consultant-Senior
- "PR" refers to Principal, template name Consultant-Principal
- "EX" refers to Executive Consultant, template name
Consultant-Executive
4.1.10.2 Skill Template for IBM Consultant - Generic Template
_____________________ __________________________________________________
| | Profession Positions, with Associated Skill |
| CONSULTANT | Levels |
| PROFESSION SKILLS |______ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| | RA | AS | CO | SC | PR | EX | Key |
| | | | | | | | Skill|
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| BUSINESS/ENGAGEMENT MANAGEMENT |
|_____________________ ______ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| Manage Consulting | 0 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
| Engagements | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Initiate Projects | 0 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Plan Projects | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Project Track, | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
| Report, and Deliver | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Manage Project Risk | 0 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| FINDING FACTS, ANALYSIS, AND CONCLUSIONS |
|_____________________ ______ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| (Employ) Consulting | 1 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Methods | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Employ Generic | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
| Consulting Methods | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| (Apply) Financial | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 4 | |
| Skills | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Apply Basic | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Financial Concepts | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Use Value-Added | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 3 | |
| Finance Method | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| MANAGING CLIENT RELATIONSHIPS |
|_____________________ ______ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| (Develop) Client | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 4 | |
| Relationships | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| (Develop) | | | | | | | |
| Relationships with | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| client execs | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| (Develop) | | | | | | | |
| Relationships with | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
| end-users | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| (Develop) | | | | | | | |
| Relationships with | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
| client I/T | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| (Understand) Client | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 4 | |
| Strategy and Plan | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| (Understand) | | | | | | | |
| Client's Management | 1 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| System and Culture | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| BUSINESS DEVELOPMENT (SELLING) |
|_____________________ ______ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| (Perform) Market | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 3 | |
| Management | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Perform Market | 0 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 3 | |
| Analysis | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Develop Segment | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 3 | |
| Mkt/Bus Plan | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Client Issue | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
| Identification | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| (Execute) | | | | | | | |
| Consultative Sales | 0 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Calls | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| (Convert) Potential | | | | | | | |
| Opportunities to | 0 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
| Real | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Frame Client | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 4 | |
| Solution | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Close Opportunity | 0 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 4 | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| PRACTICE/PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT |
|_____________________ ______ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| Coaching (Coach) | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Mentoring (Mentor) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Give Career Advice | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 3 | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Delegate Tasks and | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Responsibilities | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Manage Performance | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 5 | |
| of People | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Acknowledge | | | | | | | |
| Employee | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Contribution | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| PRODUCT/INDUSTRY/SERVICE LINE SKILLS |
|_____________________ ______ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| (Understand) | | | | | | | |
| Industry | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 4 | |
| Segments/Industries | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| (Understand) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
| Platforms | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| (Understand) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
| Applications | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| (Understand) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
| Architectures | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| (Understand) | 1 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 5 | |
| Methodologies | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| (Understand) I/T | 1 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Related Services | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| LEADERSHIP/PERSONAL EFFECTIVENESS |
|_____________________ ______ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| (Demonstrate) | 1 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Leadership | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Show Thought | 1 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
| Leadership | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Foster Teamwork / | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
| Enable Teams | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Facilitate Meetings | 1 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 3 | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Communication | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 4 | |
| (Communicate) | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Negotiate | 1 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 4 | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Use Problem Solving | | | | | | | |
| and Decision Making | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
| Techniques | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Understand IBM | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Organization | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| (Explain) IBM | | | | | | | |
| Vision / Mission / | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Strategy | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| (Describe) IBM | 1 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Management Systems | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Use IBM Client | 1 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Satisfaction System | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Use IBM | | | | | | | |
| Intellectual | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
| Capital System | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Use IBM Opportunity | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Management System | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Use IBM CG | | | | | | | |
| Consulting | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | | |
| Workbench | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
Subtopics:
4.1.10.2.1 Service Line Templates
The following service line templates map to the eleven (11) consulting
service lines.
These templates will be updated in early 1997 to reflect changes in
service line direction, methodologies, tools, and techniques. Templates
can be found in SKILLS V2/3 by searching "CONSULTANT-" or "SL-". The
resulting list will include the specific service line/ competency name.
An individual's required proficiency level on service line and depends on
the overall needs of the consulting business and local practice
requirements.
- Business Transformation (BT)
- Information Technology Strategy (ITS)
- Workflow Management
- Management Technologies
- Information Systems Management (ISM)
- Networking
- Business Recovery
- Application Development Effectiveness (ADE)
- Rapid Solutions (SI/AD)
- Redevelopment/Year 2000 (SI/AD)
- Object Technology (OT)
4.1.10.3 Skill Template for IBM Consultant - Service Line Templates
TRANSFORMATION CONSULTING
(consultant in TC must be proficient in at least one of the competencies
highlighted below)
__________ ____________________________________________ ________________
| | SKILL | See Note Below |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| TRANSFORMATION CONSULTING |
|__________ ____________________________________________ ________________|
| PT26-01 | Do Architect Transformation and | |
| | Reengineering | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-02 | Employ Dynamic Stability Concepts | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-03 | Perform Customer Value Management | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-04 | Perform Customer Market Segmentation | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-05 | Perform Customer Wants, Needs, & | |
| | Requirements | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-06 | Perform Customer Satisfaction and Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-07 | Perform Customer Capability Enabler | |
| | Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-08 | Perform Customer Management Process | |
| | Development | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-09 | Perform Process Assessment, Redesign, & | |
| | Management | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-10 | Perform Process Assessment/Analyze | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-11 | Perform Process Improvement | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-12 | Perform Process Redesign | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-13 | Perform Process Re-engineering | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-14 | Perform Process Measurements | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-15 | Perform Change Management and Organization | |
| | Dynamics | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-16 | Do Performance Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-17 | Do Business Culture Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-18 | Do Job & Work Group Design and Alignment | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-19 | Do Change Barrier Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-20 | Do Change Enabler Alignment and Deployment | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-21 | Do Organization/Enterprise Design & | |
| | Restruct. | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-22 | Do Management & Leadership Team Building | |
| | and Coaching | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-23 | Do Performance Comp. & Modeling | |
| | Application for Perf Improvement | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-24 | Do Enterprise Management System Modeling | |
| | Application | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-25 | Do HR Program Design and Alignment | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-26 | Perform Business Economic Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-27 | Analyze Business Processes | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-28 | Do Activity Based Costing | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-29 | Apply Simulation Techniques | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-30 | Apply Experimental Design Techniques | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-31 | Apply Cost-Benefit Analysis Techniques | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-32 | Apply Scale Curve Analytics | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-33 | Apply Experience Curve Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-34 | Apply Scope Economy Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-35 | Apply Option Theory Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-36 | Perform Product Lifecycle Management | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-37 | Perform Product Engineering Sub-Process | |
| | Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-38 | Perform Product Cost Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-39 | Perform Engineering Data Management | |
| | Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-49 | Make (Build)/Buy Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-41 | Design for Manufacturability | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-42 | Perform Order Fulfillment | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-43 | Perform Order Fulfillment Sub-Process | |
| | Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-44 | Perform Inventory Reduction Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-45 | Perform Quick Response Techniques | |
| | Application | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-46 | Perform MRP Requirements Assessment | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-47 | Perform Transformation Modes and Policies | |
| | Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-48 | Perform Operations Management | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-49 | Perform Operations Process Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-50 | Perform Value-Add Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-51 | Perform TQM Program Design and | |
| | Implementation | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-52 | Perform Manufacturing Line Modeling & | |
| | Simulation | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-53 | Perform Factory Automation Requirements | |
| | Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| Note: Individual required proficiency level of service line depends |
| on the overall needs of the consulting business and local |
| practice requirements. |
|________________________________________________________________________|
IT STRATEGY (ITS)
(A consultant in ITS must be proficient in at least one of the
competencies highlighted below.)
__________ ____________________________________________ ________________
| | SKILL | See Note Below |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| TRANSFORMATION CONSULTING |
|__________ ____________________________________________ ________________|
| PT26-55 | Determine Strategic Choices | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-56 | Use Infrastructure Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-57 | Use Strategic Alignment | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-58 | Employ Dynamic Stability | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-59 | Do Process Assessment/Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-60 | Use Technology Evaluation and Impact | |
| | Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-61 | Determine Business System Architecture | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-62 | Use Strategic Alignment | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-63 | Use Technology Evaluation and Linkages | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-64 | Use Value Delivery Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-65 | Use IT Services Applications | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| Note: Individual required proficiency level of service line depends |
| on the overall needs of the consulting business and local |
| practice requirements. |
|________________________________________________________________________|
WORKFLOW MANAGEMENT
__________ ____________________________________________ ________________
| | SKILL | See Note Below |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| WORKFLOW MANAGEMENT |
|__________ ____________________________________________ ________________|
| PT26-66 | Use Emerging Technologies | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-67 | Perform Emerging Technology Assessment | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-68 | Perform Emerging Technology Cost/Benefit | |
| | Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-69 | Perform Activity Based Costing | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-70 | Perform Emerging Technology Risk | |
| | Assessment | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-71 | Perform Emerging Technology Impact | |
| | Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-72 | Perform Emerging Technology Design and | |
| | Implementation | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-73 | Perform Emerging Technology Platform & | |
| | Architecture Selection | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| Note: Individual required proficiency level of service line depends |
| on the overall needs of the consulting business and local |
| practice requirements. |
|________________________________________________________________________|
MANAGEMENT TECHNOLOGIES
__________ ____________________________________________ ________________
| | SKILL | See Note Below |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| MANAGEMENT TECHNOLOGIES |
|__________ ____________________________________________ ________________|
| PT26-74 | Do Mathematical Modeling and Simulation | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-75 | Use Object-Oriented Architecture, Design, | |
| | & Implementation | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-76 | Use Discrete Event Simulation | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-77 | Use Linear Programming | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-78 | Use Non-Linear Programming | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-79 | Use Stochastic Programming | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-80 | Use Differential Equations | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-81 | Use Neural Network Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-82 | Use Expert Systems | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-83 | Use Genetic Optimization | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-84 | Use Simulated Annealing | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| Note: Individual required proficiency level of service line depends |
| on the overall needs of the consulting business and local |
| practice requirements. |
|________________________________________________________________________|
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY PLANNING (ITP)
(A consultant in ITP is expected to be proficient in at least one of each
of the skill areas below.)
__________ ____________________________________________ ________________
| | SKILL | See Note Below |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY PLANNING (ITP) |
|__________ ____________________________________________ ________________|
| PT26-85 | Develop Architectures | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-86 | Develop Business Architectures | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-87 | Develop Data Architecture | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-88 | Develop Object Architecture | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-89 | Develop Technology Architecture | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-90 | Ensure Inter-Architecture Integration | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-91 | Perform Business Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-92 | Perform CSF Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-93 | Perform Business Impact Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-94 | Perform Gap Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-95 | Define I/T Values and Principals | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-96 | Define I/T Standards | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-97 | Define Evaluation Criteria | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-98 | Perform Financial Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-99 | Perform Situation Assessment | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-100 | Perform Solution Definition | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-101 | Perform Valuation and Justification | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-102 | Perform Transition Planning | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| Note: Individual required proficiency level of service line depends |
| on the overall needs of the consulting business and local |
| practice requirements. |
|________________________________________________________________________|
INFORMATION SYSTEMS MANAGEMENT (ISM) (A consultant in ISM is expected to
be proficient in at least one of the skill areas below.)
__________ ____________________________________________ ________________
| | SKILL | See Note Below |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| INFORMATION SYSTEMS MANAGEMENT (ISM) |
|__________ ____________________________________________ ________________|
| PT26-103 | Assess and Design Restructuring and | |
| | Consolidation | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-104 | Assess and Design Problem Management | |
| | Systems | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-105 | Assess and Design Availability Management | |
| | Systems | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-106 | Perform IT Assessment | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-107 | Design Systems Management Framework | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-108 | Assess and Design IT Customer Satisfaction | |
| | Management Systems | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-109 | Assess and Design Security Management | |
| | Systems | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-110 | Assess and Design IT Change Management | |
| | System | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-111 | Assess and Design Performance Management | |
| | Systems | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-112 | Assess and Design Help Desks | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-113 | Assess and Design Capacity Management | |
| | Systems | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-114 | Define I/T Management Systems | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| Note: Individual required proficiency level of service line depends |
| on the overall needs of the consulting business and local |
| practice requirements. |
|________________________________________________________________________|
APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT EFFECTIVENESS (ADE)
__________ ____________________________________________ ________________
| | SKILL | See Note Below |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT EFFECTIVENESS (ADE) |
|__________ ____________________________________________ ________________|
| PT26-115 | Perform ADE Effectiveness Consulting | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-116 | Employ ADE Project Review Intervention | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-117 | Employ ADE Process Formalization | |
| | Intervention | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| Note: Individual required proficiency level of service line depends |
| on the overall needs of the consulting business and local |
| practice requirements. |
|________________________________________________________________________|
BUSINESS RECOVERY
__________ ____________________________________________ ________________
| | SKILL | See Note Below |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| BUSINESS RECOVERY |
|__________ ____________________________________________ ________________|
| PT26-118 | Perform Business Recovery Consulting | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-119 | Perform Enterprise Solutions Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-120 | Perform Customer Environment Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-121 | Perform Business Impact Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-122 | Develop Recovery Plan | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-123 | Perform Integrated Risk Management | |
| | Analysis | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-124 | Develop Enterprise-Wide Recovery Strategy | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| Note: Individual required proficiency level of service line depends |
| on the overall needs of the consulting business and local |
| practice requirements. |
|________________________________________________________________________|
NETWORKING
__________ ____________________________________________ ________________
| | SKILL | See Note Below |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| NETWORKING |
|__________ ____________________________________________ ________________|
| PT26-125 | Assess and Design Network and Systems | |
| | Management | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-126 | Perform Network Trends and Directions | |
| | Studies and Surveys | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-127 | Assess and Design Network Operations | |
| | Policies and Procedures | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-128 | Assess and Design Network | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-129 | Assess and Design Network Architecture | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-130 | Assess and Develop Network Strategy | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-131 | Define Network Requirements | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-132 | Perform Network Assessment & Audit | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| Note: Individual required proficiency level of service line depends |
| on the overall needs of the consulting business and local |
| practice requirements. |
|________________________________________________________________________|
RAPID SOLUTIONS (SI/AD)
__________ ____________________________________________ ________________
| | SKILL | See Note Below |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| RAPID SOLUTIONS (SI/AD) |
|__________ ____________________________________________ ________________|
| PT26-133 | Employ Rapid Solutions Consulting | |
| | Methodology | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-134 | Employ Project Management Methodology | |
| | (e.g., MITP) | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| Note: Individual required proficiency level of service line depends |
| on the overall needs of the consulting business and local |
| practice requirements. |
|________________________________________________________________________|
REDEVELOPMENT/YEAR 2000 (SI/AD)
__________ ____________________________________________ ________________
| | SKILL | See Note Below |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| REDEVELOPMENT/YEAR 2000 (SI/AD) |
|__________ ____________________________________________ ________________|
| PT26-133 | Employ Application Redevelopment | |
| | Methodology | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-134 | Employ Project Management Methodology | |
| | (i.e., MITP) | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| Note: Individual required proficiency level of service line depends |
| on the overall needs of the consulting business and local |
| practice requirements. |
|________________________________________________________________________|
OBJECT ORIENTED TECHNOLOGY
__________ ____________________________________________ ________________
| | SKILL | See Note Below |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| OBJECT ORIENTED TECHNOLOGY |
|__________ ____________________________________________ ________________|
| PT26-143 | Build Object Model | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-144 | Define Object Technology Transition Plan | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-145 | Build Re-usable assets | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| PT26-146 | Use Object Foundry | |
|__________|____________________________________________|________________|
| Note: Individual required proficiency level of service line depends |
| on the overall needs of the consulting business and local |
| practice requirements. |
|________________________________________________________________________|
Subtopics:
4.1.10.3.1 Consulting Template -- Example
A consultant's template will consist of one or more of the template types
shown below.
____________________________________ ___________________________________
| | Same For All Consultants |
| GENERIC SKILLS | (Includes Profession Template) |
|____________________________________|___________________________________|
| SERVICE LINE SKILLS | At Least 1 Service Line Template |
|____________________________________|___________________________________|
| INDUSTRY SKILLS | 0 Or More Industry Templates |
|____________________________________|___________________________________|
| PRODUCT SKILLS | 0 Or More Product Templates |
|____________________________________|___________________________________|
At a minimum, your job role template would consist of the generic and
appropriate service line templates corresponding to your position and it
may contain one or more industry and/or product templates based on your
job responsibilities. For example, if you are a Senior Consultant in a
Networking practice in the Finance industry. Your profile would include
the professional skills for CONSULTANT-SENIOR, networking service line,
finance industry, and networking product templates.
Using the example above, proficiency levels for the generic template
represent what is required of a Senior Consultant regardless of service
line, industry, and/or product expertise. These levels are not
negotiable. However, the proficiency levels shown in the service line
templates are guidelines. You (the consultant) will customize the service
line skills in your template to represent the unique requirements of your
business. It would be up to you/the Consultant and the Principal to
determine what is appropriate.
4.1.10.4 Skill Template for IBM Consultant - Profession Template
Profession Template -- 24 skills common to all professions. These skills
are integrated with key consulting skills in the generic template.
_____________________ __________________________________________________
| | Profession Positions, with Associated Skill |
| CONSULTANT | Levels |
| PROFESSION SKILLS |______ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| | RA | AS | CO | SC | PR | EX | Key |
| | | | | | | | Skill|
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| PROFESSION TEMPLATE |
|_____________________ ______ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| (Develop) Client | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 4 | |
| Relationships | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| (Understand) Client | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 4 | |
| Strategy and Plan | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| (Understand) | | | | | | | |
| Client's Management | 1 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| System and Culture | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| (Apply) Financial | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 4 | |
| Skills | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| (Employ) Consulting | 1 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Methods | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| (Perform) Market | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 3 | |
| Management | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| (Execute) | | | | | | | |
| Consultative Sales | 0 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Calls | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| (Understand) | | | | | | | |
| Industry | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 4 | |
| Segments/Industries | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Understand IBM | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Organization | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| (Explain) IBM | | | | | | | |
| Vision / Mission / | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Strategy | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| (Describe) IBM | 1 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Management Systems | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Initiate Projects | 0 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Plan Projects | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Project Track, | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
| Report, and Deliver | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Manage Project Risk | 0 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| (Understand) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
| Platforms | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| (Understand) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
| Applications | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| (Understand) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
| Architectures | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| (Understand) | 1 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 5 | |
| Methodologies | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| (Understand) I/T | 1 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Related Services | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| (Demonstrate) | 1 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Leadership | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Communication | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 4 | |
| (Communicate) | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Negotiate | 1 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 4 | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Use Problem Solving | | | | | | | |
| and Decision Making | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
| Techniques | | | | | | | |
|_____________________|______|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
4.1.11 Professional Development
Growing your skills requires a combination of experience, on the job
training, education, coaching and mentoring. The Consulting Profession
emphasizes a range of skill development activities to grow skills.
Education and training can be separated into several forms including self
study, distance learning, internships, classroom and seminars. The
integration of these delivery methods can be an efficient and cost
effective way to build your skills. For an overview of the Worldwide
Professions and links to the Common Skills Categories and Professions
Roadmaps, refer to the Education Roadmap page of the IEC Course Catalog at
http://w3.lahulpe.ibm.com/roadmaps/index.html.
Also, refer to the Consulting Profession Career Planning Guide.
4.1.12 Consultant Position Descriptions
The following position descriptions describe the basic work of each of the
positions within the Professions. Formal descriptions which may contain
legally mandated language necessary for classifying employees in a
geography should be obtained through the approved on-line job library, if
available in the geography, or by contacting the appropriate H.R.
personnel within the geography.
Subtopics:
4.1.12.1 Position Title: Research Associate
Position Concept:
Research Associates support engagement activities, primarily through data
research and analysis, and administration of engagement activities (e.g.,
creation of charts/graphs and other reports, data entry, etc.) under
supervision. Research Associates are expected to be proficient in the use
of the analysis and graphics tools on the Consultant Work- bench, and the
Intellectual Capital System. Research Associates may work on client
premises and may occasionally assist with client presentations. A
Research Associate is the entry level for the Consulting Profession, and
presumes skills of a college graduate or equivalent. Research Associates
are expected to be billable.
Skills
- Develops analytical, logical, verbal and written communication, and
negotiation materials, based on accumulated skills, experience and
education, aligned to specific engagement requirements. Demonstrates
required skills proficiencies.
- Has a basic understanding of consulting methodologies and business
processes. Collaborates with engagement team members to carry out
assigned duties.
- Makes creative suggestions and negotiates with other professionals to
present research findings in appropriate ways to support the
engagement objectives.
- Recognizes and articulates issues that arise during research or
analysis for an engagement.
- Is proficient in the use of the Consultant Workbench to perform data
analysis, report writing or presentation material.
- Has a thorough understanding of the Intellectual Capital Management
system, and uses material to assist with preparation and
recommendation of solution alternatives.
- Relates findings to relevance of engagements. Challenges given
procedures and processes with the intent to enhance and improve.
Contribution/Leadership
- Works on assigned projects and specific engagements.
- Work is often reviewed by Associate Consultants and other members of
the engagement team for developmental purposes.
- Understands the mission of the engagement team or practice, its
market/Industry positioning, in relationship to own area of
competence.
- Operates as an effective and enthusiastic team member. May directly
influence people in own engagement/team, in structure of analysis,
report structure and content etc.
- May coordinate the activities of support staff (e.g., graphics
reproduction), or people from other departments during client
engagements.
Impact on Business/Job Scope
- Accountable for individual results, and for contributing to engagement
results through production of accurate research and data.
- Performs activities such as data gathering and analysis and report
preparation that impact business results and/or client satisfaction.
- Supports activities that impact engagement costs or expenses in
relation to methods of collecting, analyzing and presenting data.
4.1.12.2 Position Title: Associate Consultant
Position Concept:
Associate Consultants gather facts (through research, structured and
unstructured interviews, surveys, etc.) in support of specific
engagements, typically one engagement at a time. They develop leadership
skills through ownership of specific tasks or projects within an
engagement. Associate Consultants perform primary and secondary research
and are responsible for the design, analysis and presentation of data.
Associate Consultants are expected to use key analysis and graphics tools
on the Consultant Workbench, and the Intellectual Capital System.
Associate Consultants are expected to establish relationships within
client organizations and deliver timely, high quality service to the
client. Associate Consultant level utilization rates and approved
business development activities are expected to be in the 80% range.
In addition to the attributes of Research Associate, typical attributes of
this position include the following:
Skills
- Utilizes consulting skills and business knowledge based on accumulated
experience and education, aligned to practice business objectives.
Demonstrates required skill proficiencies.
- Acts as an independent professional, including interaction with
clients and does not require close management supervision on IBM or
client premises.
- Operates as a team member, drawing upon the experience of other
professionals within the engagement team and from other functions.
- Is able to articulate and compare alternative approaches drawing from
previous engagements, and recommend solutions. Draws upon existing
intellectual capital and improves it. May create new intellectual
capital.
- Negotiates effectively with specific (given) objectives. Contributes
to the definition of the engagement scope of work and outputs.
- Recognizes problems related to the engagement objectives and suggests
solutions.
- Creativity, judgement and engagement management skills are applied to
consulting engagements or phases of medium/large engagements in
drawing conclusions from fact gathering and guiding clients.
- Independently generates solutions, based on strong quantitative and
analytical skills and business knowledge, and contributes to
intellectual capital.
- Challenges the validity of given procedures and processes to enhance
and improve or develop complementary adjustments/ solutions.
Contribution/Leadership
- Controls own work priorities and methods, for example tasks within
engagement schedules, and analysis methods.
- Understands and can articulate generic and Service Line methodology to
client and engagement team members.
- Understands practice business objectives. Is alert to opportunities
for follow-on business with the client.
- Specializes in a market/Industry. Provides advice in specialist
market/Industry and Service Line (for example Transformation
Consulting, Object Technology etc).
- Manages routine engagement activities and leads small teams which may
include people from other departments. Likely to be directing the
activities of Research Associates.
Impact on Business/Job Scope
- Accountable for individual results, (for example delivery of research,
interview data, and presentations), and those of teams led.
- Participates in engagement planning. Identifies, estimates and
presents costs, schedules, and business risks associated with specific
tasks or activities.
- Works directly with clients to middle management levels. Supports
activities that affect client satisfaction.
- Supports activities that impact engagement costs or expenses in
relation to the execution of client relationship skills, methods of
conducting and presentation of data, identification of follow-on work.
- May have budget responsibility for tracking costs/expenses on specific
parts of engagements.
- Associate Consultants are expected to be utilized in the 80% range.
4.1.12.3 Position Title: Consultant
Position Concept:
The Consultant performs the bulk of the engagement work as defined by the
client contract. They lead major portions of large or medium engagements,
and lead small engagements autonomously. Consultants gather facts
(through research, interviewing, surveys, etc.) analyze the client's
business, draw conclusions, prepare final reports, and give presentations.
Consultants are expected to be proficient in the use of key analysis and
graphics tools on the Consultant Workbench, and the Intellectual Capital
System. Consultants are expected to establish relationships with key
client personnel and deliver timely, high quality service to the client.
Consultant level utilization rates and approved business development
activities are expected to be in the 70% range.
In addition to the attributes of the Associate Consultant, typical
attributes of this position include the following:
Skills
- Uses in depth consulting skills and business knowledge based on
accumulated experience and education, aligned to practice business
objectives and processes. Uses knowledge to formulate hypotheses and
test conclusions to determine appropriate solutions. Demonstrates
required skill proficiencies.
- Acts as a coach for Associate Consultants, Research Associates, peers,
new hires and engagement participants from other IBM organizations.
Specifically coaches in application of Service Line methodology, issue
or hypothesis based consulting methods and intellectual capital
creation and management.
- Operates as a team member and team leader. Reports milestone or
engagement phase progress to the Engagement Manager, and demonstrates
leadership in the engagement team. Creates new intellectual capital,
and improves existing intellectual capital. Consultants are expected
to create more new intellectual capital than draw on existing
material.
- Negotiates effectively with the engagement manager and team members to
define engagement scope of work and outputs, and contract-based phased
approaches to achieving client objectives.
- Recognizes and articulates complex problems related to the engagement
and creates solutions to the hypothesis being developed.
- Creativity and judgement are applied to consulting engagements in
drawing conclusions from fact gathering.
- Applies knowledge gained from each engagement to execute future tasks
or engagements and contributes as intellectual capital.
Contribution/Leadership
- Conducts projects defined by Principal/Practice Leader on special
topics related to business objectives, such as market analysis,
creation and management of intellectual capital etc.
- Defines and decides, with the engagement manager, engagement
objectives. Leads and guides the efforts of others in specific areas.
Provides methodological leadership.
- Understands department/function mission and vision. Is alert to
opportunities for follow-on business with the client, including those
outside the Consulting Group.
- Influences people outside the immediate department/practice, through
work with clients, business partners and other IBM organizations, and
special projects or presentations to IBM and client management.
- Operates autonomously with regard to complex issues, and leads and
guides the efforts of others during client engagements.
Impact on Business/Job Scope
- Accountable for results of teams led and for activities involving
multi-functional teams.
- Regularly participates in overall department planning. Identifies,
estimates and presents costs, schedules, and business risks associated
with specific client situations.
- Works directly with clients to lower executive levels. Activities
affect client satisfaction through face to face interaction with
clients, quality of deliverables, etc.
- Activities impact engagement costs or expenses in relation to the
execution of client relationship skills, development of hypotheses,
identification of follow-on work and presentation of the final report
- Utilization is expected to be in the 70% range.
4.1.12.4 Position Title: Senior Consultant
Position Concept:
Senior Consultants manage engagement work as defined by the client
contract. They lead medium to large complex engagements and major phases
of very large engagements. Senior Consultants manage the fact finding,
analysis, development of hypotheses/conclusions, production of final
reports and delivery of presentations. They are responsible for ensuring
that the engagement delivers to client expectations on time and to budget,
as well as delivering planned profit to IBM. They recognize and track
changing requirements and renegotiate contracts with the client. Senior
Consultants are responsible for managing the intellectual capital
throughout the engagement. They are expected to invest time in the
professional development of other consultants and act as mentors. Senior
consultants are expected to establish relationships with executive client
personnel and develop a reputation within their market/industry. Senior
Consultants are expected to have extremely strong engagement management
skills. Senior Consultant level utilization rates and approved business
development activities are expected to be in the 60% range.
In addition to the attributes of a Consultant, typical attributes of this
position include the following:
Skills
- Has expert knowledge of practice, Consulting Group and matrixed
organization operations and business objectives. Has in depth
knowledge of market/Industry and Service Line. This knowledge is
applied to engagements to ensure they are managed profitably to meet
client expectations. Demonstrates required skill proficiencies.
- Understands and can manage organizational resources, priorities,
business objectives and policies; in the context of the matrix
environment, to meet engagement deadlines.
- Leads and mentors other Consultants, peers, experienced hires, and
engagement participants from other IBM organizations.
- Operates as a Engagement Manager. Presents engagement (phase)
results to clients. Contributes to and manages the intellectual
capital for the engagement.
- Negotiates with clients to incorporate changes to client requirements
in contracts and engagement scope. Negotiates with IBM organizations
for resources.
- Uses in depth knowledge of the client to develop sophisticated
hypotheses and test various conclusions. Tests for depth,
completeness, relevance.
- Analyzes complex/new situations. Selects, tailors and applies formal
methodologies to analyze client requirements, develop hypotheses, and
draws conclusions/recommend solutions. Assesses business and
technical impact of solutions. Applies previous engagement
experiences to deduce future industry/market trends and possible
solutions.
Contribution/Leadership
- Manages projects on special topics such as intellectual capital
creation and management, engagement management skills development etc
related to business objectives
- Direct accountability for the definition of and decisions concerning
processes, priorities and resources for all engagements responsible
for, in the matrix environment.
- Defines and has vision of practice business strategy. Identifies and
closes opportunities for follow-on business with the client, including
those outside the Consulting Group.
- Influences people and organizations, including executive management,
when issues are complex/difficult and require considerable diplomacy.
- Recognized as an expert in their field inside IBM across different
organizations, and in their market/industry and Service Line.
- Manages engagement teams including members from many IBM organizations
and potentially other business partners. Sets engagement scope,
timescales and deliverables and ensures all objectives are met
profitably. Ensures fit with overall strategy.
Impact on Business/Job Scope
- Accountable for engagements or programs involving multi-functional,
international or cross-organizational teams.
- Responsible for overall engagement success and profitability.
- Manages engagement planning. Identifies, estimates and presents
costs, schedules, and business risks associated with business
development in specific segments.
- Works directly with clients to top executive levels. Activities
affect client satisfaction, as engagements represent significant
investment by clients in services and changes in strategy.
- Activities impact practice, business unit, Consulting Group or
multiple departments' costs or expenses in relation to the execution
of client relationship skills, engagement management, identification
of follow-on work within the client and in the market/industry, and
closing new opportunities.
- Senior Consultant level utilization rates are expected to be in the
60% range. They are expected to identify opportunities and
participate in closing contracts resulting in revenue equating to 60%
x 2080 x hourly rate x 2. In the US, this would equate to
approximately 600k US dollars.
4.1.12.5 Position Title: Principal
(This is a management position. The equivalent non-management position is
an Executive Consultant, described in the next job description.
Position Concept:
Principals are responsible for developing new business and building
practices - revenue/profit and critical skills. They are expected to have
very strong engagement management skills, but their focus is on building
profitable IBM Consulting business and developing client relationships.
Principals have overall responsibility for practice and business results,
including engagement deliverables, client satisfaction and profit.
Principals' focus will change depending on the maturity of the business.
They manage pre-engagement work (defining and closing opportunities,
determining engagement scope and cost projections, formulating initial
hypotheses). They have responsibility for and may be involved in all
aspects of the engagement, including renegotiation of client contracts in
line with changing client requirements. Principals are responsible for
business development - follow-on work with specific clients, and new
business in particular markets/industries. Principals are responsible for
professional development of Consultants and often have specific people
management responsibilities. They are responsible for developing their
practice. This position is very visible, within IBM and client
organizations. They are expected to achieve utilization rates and
business development activities in the 45% range.
In addition to the attributes of a Senior Consultant, typical attributes
of this position include the following:
Skills
- Business unit, country, or international professional mastery related
to operations, strategies, and objectives in leading edge or critical
situations. Demonstrates required skill proficiencies.
- Demonstrates teamwork and engagement management skills at the highest
levels within Practice, across IBM organizations, and in client
organizations.
- Plans and conducts complex negotiations reaching lasting agreements
and commitments.
- Builds strong, long-lasting relationships with key client individuals.
- Anticipates, creates and defines innovative and visionary concepts for
clients and the practice, in a strategic environment.
- Develops and implements Service Line, market, business or technology
strategies with executive review.
Contribution/Leadership
- Develops and communicates overall strategies for practice, Service
Line, Consulting Group and other organizations as appropriate
- Recognized as an expert and leader by practice members, related
organizations, and multi-country organizations, often in several
disciplines. Provides leadership for intellectual capital management.
- Manages major engagements, practices or strategic departments.
- Leads practice, country or international teams.
Impact on Business/Job Scope
- Accountable for practice, major country, or international projects or
engagements, with excellent client relationships at the highest
levels.
- Develops and implements Service Line, market, business or technology
strategies with executive review.
- Contributes to policy making across multiple IBM organizations, using
consulting skills.
- Responsible for committing multiple resources and achieving customer
satisfaction, cost, expense, revenue, profit - any business
measurements of critical importance.
- Responsible for quality output/value add for highly visible leading
edge engagements, services and future business development.
- Principals are expected to be utilized in the 45% range. They are
expected to identify opportunities and participate in closing
contracts resulting in revenue of up to 45% x 2080 x hourly rate x 8.
In the US, this would equate to approximately 2.5M US dollar revenue
revenue per annum. Principals should generate business to utilize at
least ten people.
4.1.12.6 Position Title: Executive Consultant
(This is a non-management position. The equivalent management position is
a Principal, described in the previous job description.)
Position Concept:
Executive Consultants at professional levels, and growing through the
Executive positions, are principally responsible for managing complex
engagements, developing intellectual capital, defining methodologies, and,
increasingly as they attain IBM executive positions, acting as mentor to
complex engagements. Executive Consultants are responsible for ensuring
that all deliverables meet client requirements and timescales, and that
hypotheses and conclusions are tested through experience gained on
previous engagements and through the development of intellectual capital.
They are responsible for qualifying client expectations and ensuring that
the engagement team work effectively together to meet expectations. They
identify and close new business. They regularly review client contracts
and plan and agree changes in scope with the clients to meet IBM profit
objectives. Executive Consultants have the primary responsibility for
assessing intellectual capital gained through engagements, contributing
new intellectual capital, and developing an asset based consultancy. They
may be involved in development of new Service Lines and supporting
methodologies and education, especially in IBM executive positions. They
act as mentors to individual consultants, but also to total engagements.
They are expected to establish relationships with clients at all levels,
but particularly with individuals in clients who have expert knowledge of
their own and industry/market processes. Executive Consultant utilization
rates are expected to be in the 60% range.
In addition to the attributes of a Senior Consultant, typical attributes
of this position include the following:
Skills
- Practices expert engagement management skills combined with in depth
knowledge of market/Industry and Service Line. This knowledge is
applied to engagements, in the use of existing intellectual capita and
in the creation of new intellectual capital to meet and exceed client
expectations. Demonstrates required skill proficiencies.
- Has responsibility for building engagement teams, utilizing resources
from several organizations, setting priorities, and meeting business
objectives and policies; in the context of the matrix environment.
- Actively mentors individuals and total engagements, transferring
engagement and intellectual capital management skills to engagement
participants from many IBM organizations, often across national
borders. Assumes a key leadership role when in IBM executive
positions.
- Practices as an Engagement Manager. Presents engagement results to
clients. Owns and manages the intellectual capital for the
engagement.
- Identifies changes in contract scope and ensures required changes are
negotiated with clients and reflected in contracts to meet IBM profit
objectives. Agrees optimum use of resources with clients and multiple
IBM organizations.
- Uses knowledge gained from previous engagements, knowledge of the
market/industry, and own research to develop creative hypotheses and
formulate conclusions.
- Analyzes market/industry trends and economics to develop future
strategies for IBM and client organizations. Understands the business
impact of implementing future strategies.
Contribution/Leadership
- Creates teams to develop new intellectual capital. Leads development
of new methodologies to support IBM strategies, especially in IBM
executive positions.
- Owns all decisions regarding engagements, including issue definition,
selection of appropriate hypotheses, development of conclusions and
testing for financial viability.
- Participates in the development of practice and IBM Consulting
strategy. Identifies, qualifies and closes opportunities for
follow-on business within client, including those outside the
Consulting Group.
- Articulates complex problems in various business environments in
client and IBM organizations to affect change to meet market demands.
- Recognized as an expert in their market/industry. Publishes on a
regular basis and speaks at industry conferences. Has high visibility
outside IBM.
- Creates and manages engagement teams including members from many IBM
organizations, clients, and business partners. Owns responsibility
for all aspects of engagement success, and for ensuring that future
engagements benefit from intellectual capital and experience gained.
As an IBM executive, manages particularly complex engagement and
client relationships.
Impact on Business/Job Scope
- Accountable for engagements directly managed, and responsible for the
success of mentored engagements.
- Within the context of IBM business objectives, defines the scope, risk
and profitability of engagements, as well as the viability of entering
new markets/industries and geographies. Identifies and closes new
business.
- Develops lasting relationships based on mutual respect with clients to
top executive levels. Influences client satisfaction with IBM through
initial and follow on engagements representing significant investment
or major changes in business strategies of clients.
- Activities impact IBM Consulting strategy, especially in IBM executive
positions, within the matrixed organization, specifically in the
creation of new methodologies to support penetration of new markets.
- Executive Consultant level utilization rates are expected to be in the
60% range. They are expected to identify opportunities and
participate in closing contracts resulting in revenue equating to 60%
x 2080 x hourly rate x5. In the US, this would equate to
approximately 1.5M US dollars.
4.2 Chapter 16. Education Profession
Subtopics:
4.2.1 Education Profession Overview
The Education Profession was created to meet the demanding, changing needs
of customers. The Education Profession consists of Education Specialists,
both certified and non-certified. These educators work closely with IBM
organizations and IBM customers to learn their businesses and how they
function. This partnership enables educators to:
- Work proactively
- Consider solutions beyond the traditional curricula and course
response
- Translate business needs into performance needs and select the most
appropriate performance solutions.
The Education Specialists function as part of multi-disciplined
performance teams working closely with business units. Based on the
role(s) they play, they are responsible for performance analysis, solution
selection and integration, solution development, solution delivery,
portfolio management, and monitoring and measuring solution
implementation. Education Specialists employ specific methodologies and
tools which encompass performance technology, the Systems Approach to
Education (SATE), and other appropriate methodologies.
The Education Specialist consists of both non-consulting Education
Specialists and Consulting Education Specialists. They must have strong
education and training skills with a greater level of expertise than the
traditional "educator."
The Consulting Education Specialists must have strong product/offering
skills in their speciality area(s) of instruction, development,
performance management and/or curriculum management. They must also have
strong personal skills, particularly leadership and communications. The
Consulting Education Specialist may or may not have quota(s) such as
billable hours, number of teach days, development ratio, etc. The key
performance elements are performance quotas, client satisfaction and team
participation. A direct career path from the Education Specialist to the
Consulting Education Specialist is provided. Certification is dependant
on business need, first and foremost, and also attaining certification by
the Education Profession Review Board.
A major source for Education Specialists is from within the IBM community.
Subtopics:
4.2.1.1 Business Strategy Summary
Customers are undergoing profound changes as their marketplaces are driven
more and more by knowledge and information. Their firms must transform
into adaptive, learning organizations whose underlying characteristics
need to change to address these new market forces. As they go through
these fundamental and difficult changes they are looking for partners and
suppliers who have the knowledge, expertise, services and products that
best fit their needs.
Knowledge and expertise, and the ability to deliver it in many forms, are
becoming key difference-makers in the marketplace. Central to our
client's transformation is the ability to develop a knowledgeable,
high-performance workforce at all levels. Therefore, the mission of IBM
education and training is to improve the performance of our customers,
both internal and external. Education and training supports our
customers' business strategies and response to business issues by
facilitating the required human performance outcomes.
Education and training has expanded the instructional model to a
"performance model" as described in the following chart.
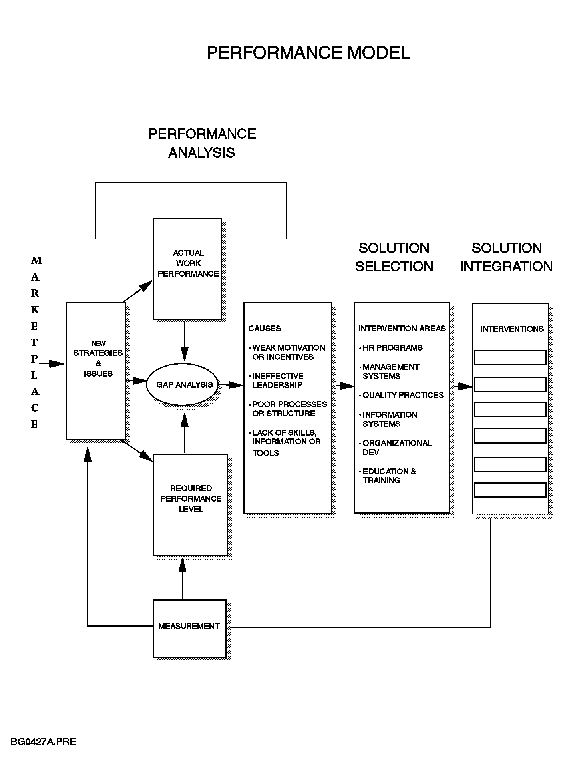
_______________ ________________________________ _______________________
| | INSTRUCTIONAL | PERFORMANCE MODEL |
| | MODEL | |
|_______________|________________________________|_______________________|
| Goals | Individual Knowledge & Skills | Business Outcomes |
|_______________|________________________________|_______________________|
| Target | The Individual | The Organization |
|_______________|________________________________|_______________________|
| Deliverables | Instructional Products & | Solution Systems |
| | Services | |
|_______________|________________________________|_______________________|
| Domain | The Classroom | The Workplace |
|_______________|________________________________|_______________________|
| Process | Systematic | Systematic & Systemic |
|_______________|________________________________|_______________________|
Both the instructional model and the performance model start with business
requirements. Under the instructional model, we analyze the "skills"
needed. In contrast, under the performance model, we analyze what "human
performance" is needed. That includes where we are today, what's causing
the "gap" and what set of additional interventions will best close that
gap. Interventions are selected based on the cause of the problem. For
example, if the performance gap results from a lack of skill or knowledge,
education and training are probably the answer. Process re-engineering,
changes to the measurement and compensation plans, new technologies or
tools, feedback instruments, organizational development techniques are
examples of additional interventions that can be applied.
4.2.2 Profession Structure
The Education Profession consists of 5 positions:
- Education Specialist
The Education Specialist applies experience and knowledge of one or
more IT disciplines and a basic professional knowledge of education
principles to increase the knowledge of clients. This would normally
be achieved by instructional delivery or occasionally through
development of basic educational materials.Is responsible for a
thorough understanding of concepts taught/developed, including
practical, hands-on experience with subject matter.
- Advisory Education Specialist
The Advisory Education Specialist is a seasoned, experienced
professional working on education services assignments of medium to
large complexity. Will normally be highly skilled in own discipline
in addition to at least one of the four areas of training
specialization. May also have program management responsibility.
- Senior Education Specialist
The Senior Education Specialist is an experienced Professional working
on education assignments of a large and/or complex nature, and will
have an outstanding record of success in this environment. Is
instrumental in helping to formulate Education & Training policy and
direction. Will have extensive experience in more than one of the
four areas of education specialization. May also have significant
program management responsibility.
- Consulting Education Specialist
The Consulting Education Specialist works on large complex education
assignments and is a key contributor to the success of the education
business unit.
- Senior Consulting Education Specialist
The Senior Consulting Education Specialist operates as an
exceptionally experienced professional working on multiple large
complex education assignments and is a key contributor to the success
of the education business unit. Is expected to have responsibility for
a very significant business stream from own personal activities.
Operation scope would normally be at business unit, country,
international or global projects level.
Note: The areas of education specialization referred to above are:
Instruction; Development; Performance Consultancy; Curriculum
Specialization
The Consulting and Senior Consulting positions are certified positions.
Figure 16-1 in topic 4.2.3 and Figure 16-2 in topic 4.2.3 summarize the
requirements of each position of the profession and the developmental
requirements for progression within the profession. Detailed position
descriptions can be found in "Education Position Descriptions" in
topic 4.2.10.
4.2.3 Characteristics of the Profession
An Education Specialist will perform in one or many areas of the Education
business. There are four area of Education Specialization:
- INSTRUCTION encompasses instructor facilitated training.
- DEVELOPMENT covers all tasks involved in preparing a training
intervention.
- PERFORMANCE CONSULTANCY involves working with clients to evaluate and
define job performance needs and to lead the activities to achieve
improvement.
- CURRICULUM SPECIALIZATION includes defining market/customer
requirements, determining training, and managing curriculum portfolio
and financial parameters.
As a foundation for the skills in a speciality area, the specialist will
use Performance Technology, SATE methodology and other methodologies as
appropriate in the speciality.
The Education Specialist will be the leading training provider of new
skills to professionals and management. They will:
- Perform in an education specialty area.
- Be effective change agents, developers, teachers, facilitators and/or
performance managers for their customers.
- Manage training and performance support projects from design to
development, delivery and measurement.
- Implement skill management strategies and programs.
To accomplish these tasks, the Education Specialist will:
- Use leadership skills to effectively manage the team(s).
- Manage projects/managements to successful conclusions.
- Provide in-depth expertise in the training and/or technical area of
expertise.
- Apply superior creative, analytical, written and verbal communication
skills to assignments.
- Incorporate appropriate methodologies in engagements/projects.
With these characteristics, an Education Specialist can provide insights
and leading-edge ideas which will help position our customers in the
global economy. This expertise, through training, will be a key "value
add" that influences the customer's preference in partnerships.
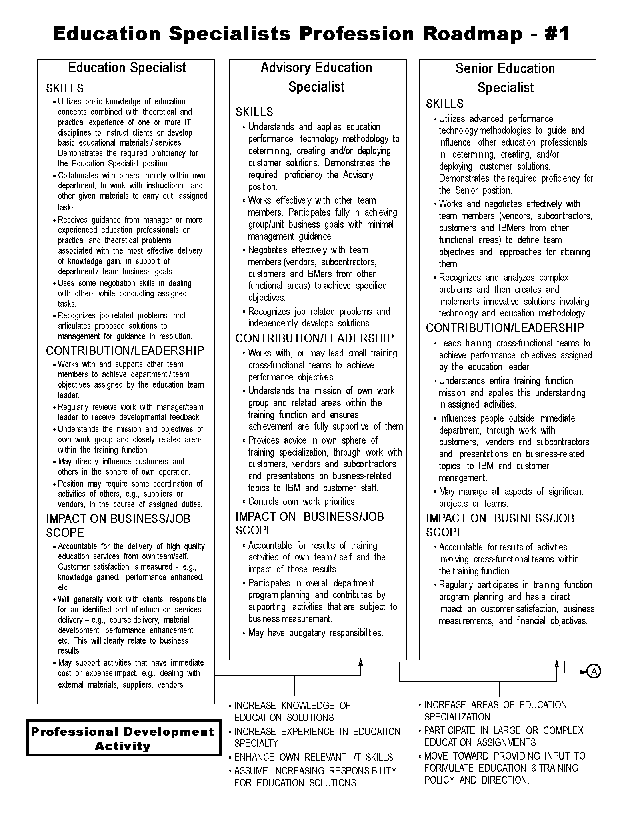
Figure 16-1. Education Specialist Profession Roadmap - #1

Figure 16-2. Education Specialist Profession Roadmap - #2
4.2.4 Potential Candidates
Education Specialist Candidates are in positions that grow strong
product/services/technical expertise and communications skills, such as:
- I/T Specialists
- Marketing Specialists
- Industry Specialists
- Software Service Representatives
- Programmers, Analysts
- Application Developers
These candidates can come from the following organizations:
- Service Organizations
- Field Operations
- Industry Sectors
- External IT Enterprise
Refer to Figure Figure 16-3 in topic 4.2.5 for more details on some
possible candidates for the Education Profession and possible career
movement from an education specialist position.
For the Consulting Specialist position, candidates would most likely come
from the education organizations and profession, although people with
relevant experience from other IBM professions could also be candidates.
More information on movement from other professions is available in
Education Career Possibilities.
4.2.5 Career Growth
Progression through the positions in the education specialist career path
from Associate to Senior is dependant on a number of factors. Individual
ability and experience, and also business need are two key factors.
Further details may be found on this in the following sections on skills
and in the appendix detailing the relevant position descriptions.
Within the Education Profession, there is provision for two levels of
certified professional, Consulting and Senior Consulting.
The focus in both positions is clearly supporting and adding value to the
education business, while operating effectively at a very senior level.
Job descriptions are to be found in the relevant section of this guide.
The establishment of any positions at the certified levels is a business
decision taken at unit level. Depending on a number of factors, chiefly
how the business is shaped and controlled in any one unit, there will be
varying requirements for the numbers of individuals in certified
positions. (It is possible that there may be a very limited requirement
in some cases.)
The differentiation between the two is essentially that of business volume
supported. Also, for the Senior Consulting, a skill level of five (5)
would be expected in all the Customer Environment, and Business Acumen
areas.
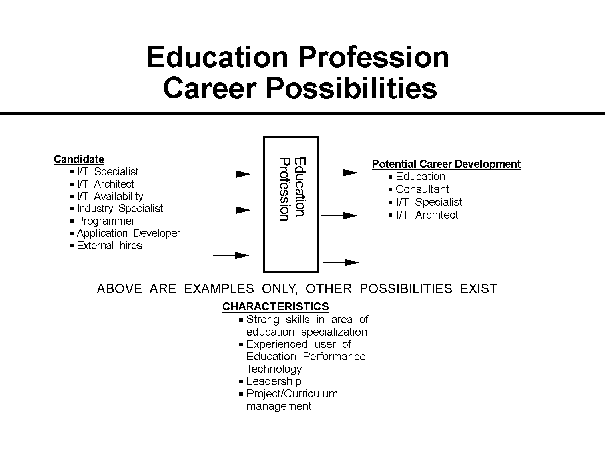
Figure 16-3. Education Profession Career Possibilities
An individual could progress from Consulting to Senior Consulting, firstly
by the business requirement, and secondly by achieving the standard and
having the track record of at least three years outstanding success as a
Consulting education specialist.
The certification requirement of being regularly assessed remains
unchanged in either position.
4.2.6 Certification Nomination Guide
The Worldwide Education Certification Nomination Guide contains the
criteria, required documentation, and process for certification in the
profession.
4.2.7 Performance Elements
________________________________________________________________________
| Education Specialist: Position Level Criteria |
|_________________ __________________ _________________ _________________|
| | Specialist | Advisory | Senior |
|_________________|__________________|_________________|_________________|
| Experience | Background in IT | Typically 4 | Typically a |
| | and Services | years in | minimum of 6 |
| | environment | IT/Services | years in IT / |
| | | environment At | Services / |
| | | least 3 years | Education |
| | | in education. | environment, |
| | | | significant |
| | | | industry |
| | | | related |
| | | | education |
| | | | experience. |
|_________________|__________________|_________________|_________________|
| Client | Limited with | Significant, | Extensive, will |
| Responsibility | guidance. | may control | lead complex |
| | | non-complex | assignments. |
| | | assignments. | |
|_________________|__________________|_________________|_________________|
| Technical | Practitioner | Practitioner | Practitioner |
| Expertise | skill in at | skills in at | skills in |
| | least 1 | least 1 | several |
| | specialist area. | specialist | specialist |
| | Good knowledge | area. Sound | areas. Expert |
| | of business | knowledge of | knowledge of |
| | environment in | business | business |
| | own area. Good | environment in | environment in |
| | range of | own area. Wide | own areas. |
| | education and | range of | Expert in |
| | training | education and | education and |
| | techniques. | training | training |
| | | techniques. | techniques. |
|_________________|__________________|_________________|_________________|
| Financial | Little direct. | Significant. | Extensive. May |
| Responsibility | Contributes to | May be assigned | have overall |
| | business | full | program |
| | targets. | responsibility | management |
| | | in areas. | control. |
|_________________|__________________|_________________|_________________|
Subtopics:
4.2.7.1 Performance Elements Detail
Depending on the area(s) of Education Specialization within which an
individual operates, the position may or may not be a quota position. The
areas of specialization are:
- INSTRUCTION encompasses instructor facilitated training.
- DEVELOPMENT covers all tasks involved in preparing a training
intervention.
- PERFORMANCE CONSULTANCY involves working with clients to evaluate and
define job performance needs and to lead the activities to achieve
improvement.
- CURRICULUM SPECIALIZATION includes defining market/customer
requirements, determining training, and managing curriculum portfolio
and financial parameters.
Typically, Key Performance Elements could be:
- Revenue
- Cost Control
- Performance Quotas
- Profit
- Education Product Delivery
- Project Management
- Customer Satisfaction
4.2.7.2 Role Comparison for Education Specialist
The following table compares various characteristics, performance
elements, and compensation among the Education Specialist, Education
Expert and Services Specialist tasks.
Note: Depending on the area(s) of specialization noted above, the items
marked * below, may differ in individual cases.
_________________ __________________ _________________ _________________
| | Education | Consulting | I/T Specialist |
| | Specialist | Education | |
| | | Specialist | |
|_________________|__________________|_________________|_________________|
| Focus * | Primarily | Primarily | Primarily |
| | education | contributing | billable |
| | product delivery | intellectual | |
| | / development / | capital to add | |
| | services revenue | value | |
|_________________|__________________|_________________|_________________|
| | Strong education | Very strong | Moderate |
| | and | education and | communication |
| | communication | communication | skills |
| | skills | skills | |
|_________________|__________________|_________________|_________________|
| | Strong | Very strong | Strong product |
| | product/IT | subject matter | skills |
| | skills | expertise | |
|_________________|__________________|_________________|_________________|
| | IBM education | Recognized as a | Generally |
| | focal point to | focal point | single customer |
| | multiple | within the | interface |
| | customers | education | |
| | | industry | |
|_________________|__________________|_________________|_________________|
| Key Performance | Financial | Revenue, | Revenue, |
| Elements * | targets: | profit, | personal |
| | cost/revenue, | business | utilization, |
| | profit, customer | targets, | customer |
| | satisfaction | customer | satisfaction |
| | | satisfaction | |
|_________________|__________________|_________________|_________________|
| Compensation | Specialist plan | Specialist plan | IT Specialist |
| | | | plan |
|_________________|__________________|_________________|_________________|
4.2.8 Education Profession Skills Profiles
Subtopics:
4.2.8.1 Skills Profiles Overview
____________________________ ___________________________________________
| | Profession Positions, with Associated |
| EDUCATION SPECIALIST | Skill Levels |
| - UNIVERSAL SKILLS |_______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| | Spec | Adv | Sr | Cons | Sr | Key |
| | | | | | Cons | Skill|
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| CUSTOMER ENVIRONMENT |
|____________________________ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| Client Relationships | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Client Strategy & Planning | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Client Management | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Sys/Culture | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| BUSINESS ACUMEN |
|____________________________ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| Market Management | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Financial Skills | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Consulting Methods | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Value-Add Selling | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| INDUSTRY |
|____________________________ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| Industry/Education | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| IBM ENVIRONMENT |
|____________________________ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| IBM Organization | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| IBM | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Vision/Mission/Strategy | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| IBM Management System | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| PROJECT MANAGEMENT |
|____________________________ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| Initiate Projects | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Plan Projects | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Project | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Track/Report/Deliver | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Manage Project Risk | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| PRODUCTS & TECHNOLOGY |
|____________________________ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| Platforms | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Applications | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| I/T Related Services | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Architectures | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Methodologies | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| PERSONAL |
|____________________________ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| Leadership | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Communication | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Negotiation | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Problem Solving/Decision | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
| Making | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
____________________________ ___________________________________________
| EDUCATION SPECIALIST | Profession Positions, with Associated |
| - DEVELOPMENT | Skill Levels |
| SPECIALIZATION SKILLS |_______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| | Assoc | Adv | Sr | Cons | Sr | Key |
| | | | | | Cons | Skill|
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Conduct Performance | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
| Analysis | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Use Perf Analysis Tools & | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
| Techniques | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Prescribe Solutions Based | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
| on Perf Analysis | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGN | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Analyze Delivery Methods & | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
| Techniques | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Plan Instructional Design | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Write Enabling Objectives | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Execute Syst Instructional | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
| Design Approach | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| INSTRUCTIONAL DEVELOPMENT | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Develop Courses | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Use Authoring Tools / | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
| Techniques | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| INSTRUCTIONAL DELIVERY | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Prepare for Training | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
| Events | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Deliver Training Events | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| EVALUATION | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Design Evaluation | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
| Instruments | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Apply Types of Evaluation | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Analyze Evaluation Results | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| SUBJECT MATTER EXPERTISE | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
____________________________ ___________________________________________
| EDUCATION SPECIALIST | Profession Positions, with Associated |
| - PERFORMANCE TECHNOLOGY | Skill Levels |
| SPECIALIZATION SKILLS |_______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| | Spec | Adv | Sr | Cons | Sr | Key |
| | | | | | Cons | Skill|
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Conduct Performance | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
| Analysis | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Use Perf Analysis Tools & | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
| Techniques | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Prescribe Solutions Based | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
| on Perf Analysis | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGN | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Analyze Delivery Methods & | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
| Techniques | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Plan Instructional Design | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Write Enabling Objectives | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Execute Syst Instructional | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
| Design Approach | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| INSTRUCTIONAL DEVELOPMENT | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Develop Courses | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Use Authoring Tools / | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Techniques | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| INSTRUCTIONAL DELIVERY | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Prepare for Training | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Events | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Deliver Training Events | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| EVALUATION | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Design Evaluation | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Instruments | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Apply Types of Evaluation | 2 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Analyze Evaluation Results | 2 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| SUBJECT MATTER EXPERTISE | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
____________________________ ___________________________________________
| EDUCATION SPECIALIST | Profession Positions, with Associated |
| - CURRICULUM | Skill Levels |
| SPECIALIZATION SKILLS |_______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| | Spec | Adv | Sr | Cons | Sr | Key |
| | | | | | Cons | Skill|
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Conduct Performance | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
| Analysis | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Use Perf Analysis Tools & | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
| Techniques | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Prescribe Solutions Based | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
| on Perf Analysis | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGN | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Analyze Delivery Methods & | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Techniques | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Plan Instructional Design | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Write Enabling Objectives | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Execute Syst Instructional | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Design Approach | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| INSTRUCTIONAL DEVELOPMENT | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Develop Courses | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Use Authoring Tools / | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
| Techniques | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| INSTRUCTIONAL DELIVERY | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Prepare for Training | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Events | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Deliver Training Events | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| EVALUATION | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Design Evaluation | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 5 | |
| Instruments | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Apply Types of Evaluation | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Analyze Evaluation Results | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| SUBJECT MATTER EXPERTISE | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
____________________________ ___________________________________________
| EDUCATION SPECIALIST | Profession Positions, with Associated |
| - INSTRUCTION | Skill Levels |
| SPECIALIZATION SKILLS |_______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| | Spec | Adv | Sr | Cons | Sr | Key |
| | | | | | Cons | Skill|
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Conduct Performance | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Analysis | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Use Perf Analysis Tools & | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
| Techniques | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Prescribe Solutions Based | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| on Perf Analysis | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGN | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Analyze Delivery Methods & | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
| Techniques | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Plan Instructional Design | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Write Enabling Objectives | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Execute Syst Instructional | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
| Design Approach | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| INSTRUCTIONAL DEVELOPMENT | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Develop Courses | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Use Authoring | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
| Tools/Techniques | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| INSTRUCTIONAL DELIVERY | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Prepare for Training | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
| Events | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Deliver Training Events | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| EVALUATION | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Design Evaluation | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
| Instruments | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Apply Types of Evaluation | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Analyze Evaluation Results | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| SUBJECT MATTER EXPERTISE | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
4.2.8.2 Skills Profile - Details
Universal Skills: Education Specialist
CUSTOMER ENVIRONMENT
_______________________________ ________________________________________
| Skills | Profession Positions, with Associated |
| | Skill Levels |
| |________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| | Spec. | Adv. | Senior| Cons. | Senior|
| | | | | | Cons. |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Client Relationships: | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Develop, maintain and manage | | | | | |
| client relationships | | | | | |
| (internal and external) at | | | | | |
| functional and executive | | | | | |
| levels throughout the | | | | | |
| organization. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Client Strategy and Planning: | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Understand the client's | | | | | |
| vision, goals, objectives, | | | | | |
| strategy, tactics and how | | | | | |
| they relate to IBM business | | | | | |
| objectives. Often work with | | | | | |
| client to formulate business, | | | | | |
| organization and/or | | | | | |
| information strategies to | | | | | |
| help them apply information, | | | | | |
| technology and/or services in | | | | | |
| support of their business. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Client Management | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Sys/Culture: | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| ° Understand the client's | | | | | |
| management structure, | | | | | |
| processes, formal and | | | | | |
| informal organization, | | | | | |
| and information | | | | | |
| infrastructure and | | | | | |
| culture. | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| ° Understand the key | | | | | |
| business processes needed | | | | | |
| to support the client's | | | | | |
| business (goals, | | | | | |
| objectives and critical | | | | | |
| success factors). | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| ° Understand the customs, | | | | | |
| protocols and business | | | | | |
| etiquettes in which the | | | | | |
| customer operates. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
Universal Skills: Education Specialist
BUSINESS ACUMEN
_______________________________ ________________________________________
| Skills | Profession Positions, with Associated |
| | Skill Levels |
| |________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| | Spec. | Adv. | Senior| Cons. | Senior|
| | | | | | Cons. |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Market Management: | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Understand the market | | | | | |
| management process steps; | | | | | |
| analyze and assess the | | | | | |
| marketplace; select | | | | | |
| attractive segments based on | | | | | |
| client wants and needs, | | | | | |
| market dynamics and IBM's | | | | | |
| core capabilities; | | | | | |
| build/assemble offerings | | | | | |
| (hardware, software, | | | | | |
| services); determine | | | | | |
| profitable delivery methods; | | | | | |
| and measure success and | | | | | |
| future needs. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Financial Skills: Analysis | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| of client finances and/or | | | | | |
| financial decision-making | | | | | |
| process for the purpose of | | | | | |
| recommending solutions. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Consulting Methods: Provide | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| client advice and guidance on | | | | | |
| what to do and/or how to do | | | | | |
| it in your area of expertise | | | | | |
| in a business context. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Value-Add Selling: | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| | | | | | |
| ° Use a selling process | | | | | |
| that replaces the | | | | | |
| traditional adversary | | | | | |
| buyer/seller relationship | | | | | |
| with a win-win | | | | | |
| partnership focused on | | | | | |
| value. | | | | | |
| ° Focus on selling the | | | | | |
| impact and value that | | | | | |
| you, and the products and | | | | | |
| services sold, have on a | | | | | |
| client's business. | | | | | |
| ° Sell solutions to a | | | | | |
| client's business | | | | | |
| problems that translate | | | | | |
| into a measurable return | | | | | |
| on the client's | | | | | |
| investment. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
Universal Skills: Education Specialist
INDUSTRY
_______________________________ ________________________________________
| Skills | Profession Positions, with Associated |
| | Skill Levels |
| |________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| | Spec. | Adv. | Senior| Cons. | Senior|
| | | | | | Cons. |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Industry/Education: | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| Understand and have influence | | | | | |
| within an industry. Have a | | | | | |
| general knowledge of the | | | | | |
| workings of an industry and | | | | | |
| form relationships within it. | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Ability to: | | | | | |
| ° Understand the framework | | | | | |
| within which an industry | | | | | |
| operates and the | | | | | |
| underlying competing | | | | | |
| strategies. | | | | | |
| ° Form, implement or | | | | | |
| understand IBM's industry | | | | | |
| strategy. | | | | | |
| ° Create solutions for an | | | | | |
| industry's wants and | | | | | |
| needs. | | | | | |
| ° Market and sell IBM | | | | | |
| solutions, products and | | | | | |
| services that are | | | | | |
| specific to an industry. | | | | | |
| ° Recruit partners, form | | | | | |
| and dissolve alliances in | | | | | |
| an industry. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
Universal Skills: Education Specialist
IBM ENVIRONMENT
_______________________________ ________________________________________
| Skills | Profession Positions, with Associated |
| | Skill Levels |
| |________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| | Spec. | Adv. | Senior| Cons. | Senior|
| | | | | | Cons. |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| IBM Organization: | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| | | | | | |
| ° Understand and be able to | | | | | |
| explain IBM's global | | | | | |
| operations, structure and | | | | | |
| its alignment to | | | | | |
| Industries in order to | | | | | |
| respond proactively to | | | | | |
| satisfy client | | | | | |
| requirements. | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| ° Understand and navigate | | | | | |
| IBM's formal and informal | | | | | |
| organizations to locate | | | | | |
| resources and assistance. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| IBM Vision/Mission/Strategy: | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Explain IBM's business | | | | | |
| strategies, tactical goals | | | | | |
| and corporate mission. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| IBM Management System: Use | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| the management system, its | | | | | |
| processes and practices. | | | | | |
| Refine the management system | | | | | |
| and ensure it is in step with | | | | | |
| the needs of business. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
Universal Skills: Education Specialist
PROJECT MANAGEMENT
_______________________________ ________________________________________
| Skills | Profession Positions, with Associated |
| | Skill Levels |
| |________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| | Spec. | Adv. | Senior| Cons. | Senior|
| | | | | | Cons. |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Project Management: | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Initiate Projects: Define | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| and prepare Statement of Work | | | | | |
| (SOW) and proposals that | | | | | |
| clearly identify objectives, | | | | | |
| scope, benefits, costs, | | | | | |
| responsibilities, | | | | | |
| assumptions, deliverables | | | | | |
| schedules, completion | | | | | |
| criteria and resource | | | | | |
| requirements needed to | | | | | |
| successfully start an | | | | | |
| engagement. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Plan Projects: | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| | | | | | |
| ° Identify and define | | | | | |
| standards, deliverables, | | | | | |
| work products and project | | | | | |
| procedures. | | | | | |
| ° Prepare plans at the task | | | | | |
| level and develop an | | | | | |
| organization structure | | | | | |
| for the project. | | | | | |
| ° Identify resource | | | | | |
| requirements in terms of | | | | | |
| personnel, hardware, | | | | | |
| software and facilities. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Project Track/Report/Deliver: | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| | | | | | |
| ° Execute the defined work | | | | | |
| tasks and produce the | | | | | |
| defined work products | | | | | |
| according to the detailed | | | | | |
| plans to the satisfaction | | | | | |
| of the client while | | | | | |
| meeting the defined | | | | | |
| project metrics | | | | | |
| (schedule, profit, | | | | | |
| budget, benefits, etc.). | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| ° Orchestrate all project | | | | | |
| components, internal and | | | | | |
| external to the project, | | | | | |
| in a manner which meets | | | | | |
| the prescribed objectives | | | | | |
| and benefits of the | | | | | |
| project. | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| ° Understand and accept | | | | | |
| sole and full | | | | | |
| responsibility for | | | | | |
| ensuring the successful | | | | | |
| achievement of the | | | | | |
| project. | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| ° Bring the project to | | | | | |
| completion according to | | | | | |
| the established criteria | | | | | |
| and accomplishing the | | | | | |
| metrics which were | | | | | |
| defined during project | | | | | |
| initiation and planning. | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| ° Define closure, clearly | | | | | |
| determine what | | | | | |
| constitutes successful | | | | | |
| closure for all parties | | | | | |
| and gain acceptance and | | | | | |
| sign-off by all parties | | | | | |
| when closure is attained. | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| ° Generate within the | | | | | |
| client the desire to do | | | | | |
| follow-on business. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Manage Project Risk: Define, | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| assess and evaluate risk | | | | | |
| factors and changes. Manage | | | | | |
| risk and change. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
Universal Skills: Education Specialist
PRODUCT/TECHNOLOGY/SERVICES
_______________________________ ________________________________________
| Skills | Profession Positions, with Associated |
| | Skill Levels |
| |________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| | Spec. | Adv. | Senior| Cons. | Senior|
| | | | | | Cons. |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Platforms: | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| | | | | | |
| ° Explain IBM's strategic | | | | | |
| product families, the | | | | | |
| hardware and software | | | | | |
| components. | | | | | |
| ° Relate the major | | | | | |
| differences between | | | | | |
| platforms for purposes of | | | | | |
| product positioning and | | | | | |
| addressing customer | | | | | |
| requirements. | | | | | |
| ° General knowledge of main | | | | | |
| IBM platform competitors. | | | | | |
| And, in platform(s) of | | | | | |
| your expertise, direct | | | | | |
| knowledge of OEM | | | | | |
| platform(s). | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Applications: | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| | | | | | |
| ° Explain IBM's strategic | | | | | |
| application offerings and | | | | | |
| their use in the | | | | | |
| marketplace. Relate the | | | | | |
| major differences between | | | | | |
| alternative offerings for | | | | | |
| the purpose of addressing | | | | | |
| customer requirements. | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| ° General knowledge of main | | | | | |
| IBM applications | | | | | |
| competitors. And, in | | | | | |
| application(s) of your | | | | | |
| expertise, direct | | | | | |
| knowledge of | | | | | |
| complementary and | | | | | |
| competitive applications. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| I/T Related Services: | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Create, differentiate, | | | | | |
| position and perform services | | | | | |
| and support offerings for | | | | | |
| IBM. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Architectures: Knowledge of | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| IBM's strategic architectures | | | | | |
| and their use in the | | | | | |
| marketplace. In | | | | | |
| architecture(s) of your | | | | | |
| expertise, knowledge of | | | | | |
| complementary and competitive | | | | | |
| architectures, and their use | | | | | |
| in the marketplace. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Methodologies: Knowledge of | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| IBM's strategic methodologies | | | | | |
| and their use in addressing | | | | | |
| customer requirements. In | | | | | |
| methodologies of your | | | | | |
| expertise, knowledge of | | | | | |
| complementary and competitive | | | | | |
| methodologies, and their use | | | | | |
| in the marketplace. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
Universal Skills: Education Specialist
PERSONAL
_______________________________ ________________________________________
| Skills | Profession Positions, with Associated |
| | Skill Levels |
| |________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| | Spec. | Adv. | Senior| Cons. | Senior|
| | | | | | Cons. |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Leadership: Set direction, | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| communicate, learn, and model | | | | | |
| effective leadership | | | | | |
| behaviors in dealing with | | | | | |
| individuals and teams and in | | | | | |
| managing business and/or | | | | | |
| processes. Empower, coach | | | | | |
| and lead change. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Communication: Effective | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| exchange of pertinent | | | | | |
| information. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Negotiation: Prepares for | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| and reaches agreement between | | | | | |
| or among parties. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Problem Solving/Decision | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| Making: Analyzes problems | | | | | |
| and activities. Specifies | | | | | |
| solutions and/or makes | | | | | |
| decisions. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
Subtopics:
4.2.8.2.1 Specialization Skills: Education Specialist - Development Specialization
EDUCATION SKILLS
_______________________________ ________________________________________
| Skills | Profession Positions, with Associated |
| | Skill Levels |
| |________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| | Spec. | Adv. | Senior| Cons. | Senior|
| | | | | | Cons. |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Conduct Performance Analysis: | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| | | | | | |
| ° Analyze the business | | | | | |
| problem/performance need | | | | | |
| and determine the | | | | | |
| solution - training or | | | | | |
| non-training. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Use Performance Analysis | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Tools and Techniques: | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| ° Use assessment tools, | | | | | |
| skills assessment tools | | | | | |
| and data gathering | | | | | |
| techniques. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Prescribe Solutions Based on | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Performance Analysis: | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| ° Prescribe solutions based | | | | | |
| on analysis results, | | | | | |
| documenting the findings. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGN | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Analyze Delivery Methods & | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Techniques: | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| ° Select the most | | | | | |
| appropriate and efficient | | | | | |
| delivery method that | | | | | |
| meets the expressed | | | | | |
| business need. | | | | | |
| ° Apply Adult Learning | | | | | |
| Principles. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Plan Instructional Design: | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| | | | | | |
| ° Define and develop plan | | | | | |
| for curriculum, program, | | | | | |
| course, lesson content, | | | | | |
| learning activities, | | | | | |
| learner interactions, | | | | | |
| learner options and | | | | | |
| performance levels. | | | | | |
| ° Estimate cost and perform | | | | | |
| justification. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Write Enabling Objectives: | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| | | | | | |
| ° Develop enabling | | | | | |
| objectives that meet task | | | | | |
| and task performance | | | | | |
| level requirements. | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| ° Create measurement items | | | | | |
| linked to terminal and | | | | | |
| enabling objectives. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Executive Systematic | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Instructional Design | | | | | |
| Approach: | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| ° Execute established | | | | | |
| systems approach to | | | | | |
| education (SATE) | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| INSTRUCTIONAL DEVELOPMENT | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Courses: | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| | | | | | |
| ° Create written materials | | | | | |
| from design documents, | | | | | |
| using instructional | | | | | |
| strategies that enable | | | | | |
| students to meet learning | | | | | |
| objectives. | | | | | |
| ° Create written technical | | | | | |
| materials about complex | | | | | |
| technical subjects. | | | | | |
| ° Create written scripts in | | | | | |
| conversational mode to | | | | | |
| express instructional and | | | | | |
| attitudinal information. | | | | | |
| ° Employ products, aids, | | | | | |
| methodologies and | | | | | |
| procedures/guidelines | | | | | |
| while writing | | | | | |
| instructional materials. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Use Authoring | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Tools/Technology: | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| ° Using authoring tools and | | | | | |
| technologies to create | | | | | |
| instructional materials. | | | | | |
| Note: Specific tools would | | | | | |
| be added here | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| INSTRUCTIONAL DELIVERY | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Prepare for Training Events: | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| | | | | | |
| ° Analyze previous course | | | | | |
| evaluations, prioritize | | | | | |
| changes needed and make | | | | | |
| adjustments required. | | | | | |
| ° Set up classrooms and/or | | | | | |
| labs to meet unique | | | | | |
| course needs. | | | | | |
| ° Mange all aspects of | | | | | |
| class coordination and | | | | | |
| delivery. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Deliver Training Events: | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| | | | | | |
| ° Take into account | | | | | |
| learning styles, teaching | | | | | |
| methods, student skill | | | | | |
| levels and student | | | | | |
| personalities when | | | | | |
| teaching. | | | | | |
| ° Evaluate self, instructor | | | | | |
| and student performance | | | | | |
| through questioning and | | | | | |
| giving feedback. | | | | | |
| ° Execute closed-loop | | | | | |
| feedback on any concerns. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| EVALUATION | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Design Evaluation | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Instruments: | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| ° Design evaluation | | | | | |
| instruments linked | | | | | |
| specifically to the | | | | | |
| objectives. | | | | | |
| ° Use a variety of formats, | | | | | |
| questions, etc., when | | | | | |
| designing evaluations at | | | | | |
| all levels. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Apply Types of Evaluations: | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| | | | | | |
| ° Apply the 4 levels of | | | | | |
| evaluation. | | | | | |
| ° Use formative and | | | | | |
| summative evaluations. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Analyze Evaluation Results | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| | | | | | |
| ° Draw conclusions and | | | | | |
| implications from | | | | | |
| evaluation data. | | | | | |
| ° Translate evaluation | | | | | |
| results into required | | | | | |
| actions. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
4.2.8.2.2 Specialization Skills: Education Specialist - Instruction Specialization
EDUCATION SKILLS
_______________________________ ________________________________________
| Skills | Profession Positions, with Associated |
| | Skill Levels |
| |________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| | Spec. | Adv. | Senior| Cons. | Senior|
| | | | | | Cons. |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Conduct Performance Analysis: | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| | | | | | |
| ° Analyze the business | | | | | |
| problem/performance need | | | | | |
| and determine the | | | | | |
| solution - training or | | | | | |
| non-training. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Use Performance Analysis | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| Tools and Techniques: | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| ° Use assessment tools, | | | | | |
| skills assessment tools | | | | | |
| and data gathering | | | | | |
| techniques. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Prescribe Solutions Based on | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Performance Analysis: | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| ° Prescribe solutions based | | | | | |
| on analysis results, | | | | | |
| documenting the findings. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGN | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Analyze Delivery Methods & | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Techniques: | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| ° Select the most | | | | | |
| appropriate and efficient | | | | | |
| delivery method that | | | | | |
| meets the expressed | | | | | |
| business need. | | | | | |
| ° Apply Adult Learning | | | | | |
| Principles. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Plan Instructional Design: | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| | | | | | |
| ° Define and develop plan | | | | | |
| for curriculum, program, | | | | | |
| course, lesson content, | | | | | |
| learning activities, | | | | | |
| learner interactions, | | | | | |
| learner options and | | | | | |
| performance levels. | | | | | |
| ° Estimate cost and perform | | | | | |
| justification. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Write Enabling Objectives: | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| | | | | | |
| ° Develop enabling | | | | | |
| objectives that meet task | | | | | |
| and task performance | | | | | |
| level requirements. | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| ° Create measurement items | | | | | |
| linked to terminal and | | | | | |
| enabling objectives. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Executive Systematic | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| Instructional Design | | | | | |
| Approach: | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| ° Execute established | | | | | |
| systems approach to | | | | | |
| education (SATE) | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| INSTRUCTIONAL DEVELOPMENT | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Courses: | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| | | | | | |
| ° Create written materials | | | | | |
| from design documents, | | | | | |
| using instructional | | | | | |
| strategies that enable | | | | | |
| students to meet learning | | | | | |
| objectives. | | | | | |
| ° Create written technical | | | | | |
| materials about complex | | | | | |
| technical subjects. | | | | | |
| ° Create written scripts in | | | | | |
| conversational mode to | | | | | |
| express instructional and | | | | | |
| attitudinal information. | | | | | |
| ° Employ products, aids, | | | | | |
| methodologies and | | | | | |
| procedures/guidelines | | | | | |
| while writing | | | | | |
| instructional materials. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Use Authoring | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| Tools/Technology: | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| ° Using authoring tools and | | | | | |
| technologies to create | | | | | |
| instructional materials. | | | | | |
| Note: Specific tools would | | | | | |
| be added here | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| INSTRUCTIONAL DELIVERY | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Prepare for Training Events: | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| | | | | | |
| ° Analyze previous course | | | | | |
| evaluations, prioritize | | | | | |
| changes needed and make | | | | | |
| adjustments required. | | | | | |
| ° Set up classrooms and/or | | | | | |
| labs to meet unique | | | | | |
| course needs. | | | | | |
| ° Mange all aspects of | | | | | |
| class coordination and | | | | | |
| delivery. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Deliver Training Events: | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| | | | | | |
| ° Take into account | | | | | |
| learning styles, teaching | | | | | |
| methods, student skill | | | | | |
| levels and student | | | | | |
| personalities when | | | | | |
| teaching. | | | | | |
| ° Evaluate self, instructor | | | | | |
| and student performance | | | | | |
| through questioning and | | | | | |
| giving feedback. | | | | | |
| ° Execute closed-loop | | | | | |
| feedback on any concerns. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| EVALUATION | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Design Evaluation | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Instruments: | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| ° Design evaluation | | | | | |
| instruments linked | | | | | |
| specifically to the | | | | | |
| objectives. | | | | | |
| ° Use a variety of formats, | | | | | |
| questions, etc., when | | | | | |
| designing evaluations at | | | | | |
| all levels. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Apply Types of Evaluations: | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| | | | | | |
| ° Apply the 4 levels of | | | | | |
| evaluation. | | | | | |
| ° Use formative and | | | | | |
| summative evaluations. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Analyze Evaluation Results | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| | | | | | |
| ° Draw conclusions and | | | | | |
| implications from | | | | | |
| evaluation data. | | | | | |
| ° Translate evaluation | | | | | |
| results into required | | | | | |
| actions. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
4.2.8.2.3 Specialization Skills: Education Specialist - Performance Technology Specialization
EDUCATION SKILLS
_______________________________ ________________________________________
| Skills | Profession Positions, with Associated |
| | Skill Levels |
| |________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| | Spec. | Adv. | Senior| Cons. | Senior|
| | | | | | Cons. |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Conduct Performance Analysis: | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| | | | | | |
| ° Analyze the business | | | | | |
| problem/performance need | | | | | |
| and determine the | | | | | |
| solution - training or | | | | | |
| non-training. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Use Performance Analysis | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Tools and Techniques: | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| ° Use assessment tools, | | | | | |
| skills assessment tools | | | | | |
| and data gathering | | | | | |
| techniques. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Prescribe Solutions Based on | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Performance Analysis: | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| ° Prescribe solutions based | | | | | |
| on analysis results, | | | | | |
| documenting the findings. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGN | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Analyze Delivery Methods & | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Techniques: | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| ° Select the most | | | | | |
| appropriate and efficient | | | | | |
| delivery method that | | | | | |
| meets the expressed | | | | | |
| business need. | | | | | |
| ° Apply Adult Learning | | | | | |
| Principles. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Plan Instructional Design: | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| | | | | | |
| ° Define and develop plan | | | | | |
| for curriculum, program, | | | | | |
| course, lesson content, | | | | | |
| learning activities, | | | | | |
| learner interactions, | | | | | |
| learner options and | | | | | |
| performance levels. | | | | | |
| ° Estimate cost and perform | | | | | |
| justification. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Write Enabling Objectives: | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| | | | | | |
| ° Develop enabling | | | | | |
| objectives that meet task | | | | | |
| and task performance | | | | | |
| level requirements. | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| ° Create measurement items | | | | | |
| linked to terminal and | | | | | |
| enabling objectives. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Executive Systematic | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Instructional Design | | | | | |
| Approach: | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| ° Execute established | | | | | |
| systems approach to | | | | | |
| education (SATE) | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| INSTRUCTIONAL DEVELOPMENT | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Develop Courses: | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| | | | | | |
| ° Create written materials | | | | | |
| from design documents, | | | | | |
| using instructional | | | | | |
| strategies that enable | | | | | |
| students to meet learning | | | | | |
| objectives. | | | | | |
| ° Create written technical | | | | | |
| materials about complex | | | | | |
| technical subjects. | | | | | |
| ° Create written scripts in | | | | | |
| conversational mode to | | | | | |
| express instructional and | | | | | |
| attitudinal information. | | | | | |
| ° Employ products, aids, | | | | | |
| methodologies and | | | | | |
| procedures/guidelines | | | | | |
| while writing | | | | | |
| instructional materials. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Use Authoring | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| Tools/Technology: | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| ° Using authoring tools and | | | | | |
| technologies to create | | | | | |
| instructional materials. | | | | | |
| Note: Specific tools would | | | | | |
| be added here | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| INSTRUCTIONAL DELIVERY | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Prepare for Training Events: | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| | | | | | |
| ° Analyze previous course | | | | | |
| evaluations, prioritize | | | | | |
| changes needed and make | | | | | |
| adjustments required. | | | | | |
| ° Set up classrooms and/or | | | | | |
| labs to meet unique | | | | | |
| course needs. | | | | | |
| ° Mange all aspects of | | | | | |
| class coordination and | | | | | |
| delivery. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Deliver Training Events: | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| | | | | | |
| ° Take into account | | | | | |
| learning styles, teaching | | | | | |
| methods, student skill | | | | | |
| levels and student | | | | | |
| personalities when | | | | | |
| teaching. | | | | | |
| ° Evaluate self, instructor | | | | | |
| and student performance | | | | | |
| through questioning and | | | | | |
| giving feedback. | | | | | |
| ° Execute closed-loop | | | | | |
| feedback on any concerns. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
4.2.8.2.4 Specialization Skills: Education Specialist - Curriculum Management
EDUCATION SKILLS
_______________________________ ________________________________________
| Skills | Profession Positions, with Associated |
| | Skill Levels |
| |________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| | Spec. | Adv. | Senior| Cons. | Senior|
| | | | | | Cons. |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| EVALUATION | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Design Evaluation | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 5 |
| Instruments: | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| ° Design evaluation | | | | | |
| instruments linked | | | | | |
| specifically to the | | | | | |
| objectives. | | | | | |
| ° Use a variety of formats, | | | | | |
| questions, etc., when | | | | | |
| designing evaluations at | | | | | |
| all levels. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Apply Types of Evaluations: | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| | | | | | |
| ° Apply the 4 levels of | | | | | |
| evaluation. | | | | | |
| ° Use formative and | | | | | |
| summative evaluations. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Analyze Evaluation Results | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| | | | | | |
| ° Draw conclusions and | | | | | |
| implications from | | | | | |
| evaluation data. | | | | | |
| ° Translate evaluation | | | | | |
| results into required | | | | | |
| actions. | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
4.2.9 Professional Development
Subtopics:
4.2.9.1 Core Skills Development
Refer to the Education Roadmap page of the IEC Course Catalog at
http://w3.lahulpe.ibm.com/roadmaps/index.html for an overview of the
Worldwide Professions and links to the Common Skills Categories and
Professions Roadmaps.
4.2.9.2 Technical Skills Development
There is further information in the I/T Specialist Profession on specific
IBM product and technical skills that are relevant in those areas for
education Specialists. These roadmaps should be used with management
guidance on specific skill development activities in the education
business.
4.2.9.3 Education Skills Development
Refer to the sections in this guide on Career Growth and Performance
Elements. Extensive Programs are being developed for release in 1996.
4.2.10 Education Position Descriptions
The following position descriptions describe the basic work of each of the
positions within the Professions. Formal descriptions which may contain
legally mandated language necessary for classifying employees in a
geography should be obtained through the approved on-line job library, if
available in the geography, or by contacting the appropriate H.R.
personnel within the geography.
Subtopics:
4.2.10.1 Position Title: Education Specialist
Position Concept:
There are four areas of Education specialization:
- INSTRUCTION encompasses instructor facilitated training.
- DEVELOPMENT covers all tasks involved in preparing a training
intervention
- PERFORMANCE CONSULTANCY involves working with clients to evaluate and
define job performance needs and to lead the activities to achieve
improvement.
- CURRICULUM SPECIALIZATION includes defining market/customer
requirements, determining training curriculum, and managing curriculum
portfolio and financial parameters.
An individual may operate in one or more of these areas of specialization
depending on local business need. However, the Education Specialist is
most likely to concentrate on Instruction, and Development.
The Education Specialist applies experience and knowledge of one or more
IT disciplines and a basic professional knowledge of education principles
to increase the knowledge of clients. This would normally be achieved by
instructional delivery or occasionally through development of basic
educational materials. The Education Specialist is responsible for a
thorough understanding of concepts taught/developed, including practical,
hands-on experience with subject matter.
Skills
- Utilizes basic knowledge of education concepts combined with
theoretical and practical experience of one or more IT disciplines to
instruct clients or develop basic educational materials/services.
Demonstrates the required proficiency level for the position.
- Collaborates with others, mainly within own department, to work with
instructional and other given materials to carry out assigned tasks.
- Receives guidance from manager or more experienced education
professionals on practical and theoretical problems associated with
the most effective delivery of knowledge gain, in support of
department / team business goals.
- Uses some negotiation skills in dealing with others while conducting
assigned tasks.
- Recognizes job-related problems, and articulates proposed solutions to
management for guidance in resolution.
Contribution/Leadership
- Works with and supports other team members to achieve department/team
objectives assigned by the education team leader.
- Regularly reviews work with manager/team leader to receive
developmental feedback.
- Understands the mission and objectives of own work group and closely
related areas within the training function.
- May directly influence customers and others in the sphere of own
operation.
- Position may require some coordination of activities of others, e.g.,
suppliers or vendors, in the course of assigned duties.
Impact on Business/Job Scope
- Accountable for the delivery of high quality education services from
own team/self. Customer satisfaction is measured - e.g., knowledge
gained, performance enhanced, etc.
- Will generally work with clients, responsible for an identified part
of education services delivery - e.g., course delivery, material
development, performance enhancement etc. This will clearly relate to
business results.
- May support activities that have immediate cost or expense impact,
e.g., dealing with external materials, suppliers, vendors.
4.2.10.2 Position Title: Advisory Education Specialist
Position Concept:
There are four areas of Education specialization:
- INSTRUCTION encompasses instructor facilitated training.
- DEVELOPMENT covers all tasks involved in preparing a training
intervention
- PERFORMANCE CONSULTANCY involves working with clients to evaluate and
define job performance needs and to lead the activities to achieve
improvement.
- CURRICULUM SPECIALIZATION includes defining market/customer
requirements, determining training curriculum, and managing curriculum
portfolio and financial parameters.
An individual may operate in one or more of these areas of specialization
depending on local business need.
The Advisory Education Specialist is a seasoned, experienced professional
working on education services assignments of medium to large complexity.
Will normally be highly skilled in own discipline in addition to at least
one of the four areas of training specialization. May also have program
management responsibility.
Skills
- Understands and applies education performance technology methodology
to determining, creating and/or deploying customer solutions.
Demonstrates the required proficiency level for the Advisory position.
- Works effectively with other team members. Participates fully in
achieving group/unit business goals with minimal management guidance.
- Negotiates effectively with team members (vendors, subcontractors,
customers and IBMers from other functional areas) to achieve specified
objectives.
- Recognizes job related problems and independently develops solutions.
Contribution/Leadership
- Works with, or may lead small training cross-functional teams to
achieve performance objectives.
- Understands the mission of own work group and related areas within the
training function and ensures achievements are fully supportive of
them.
- Provides advice in own sphere of training specialization, through work
with customers, vendors and subcontractors and presentations on
business-related topics to IBM and customer staff.
- Controls own work priorities.
Impact on Business/Job Scope
- Accountable for results of training activities of own team / self and
for the impact of those results.
- Participates in overall department program planning and contributes by
supporting activities that are subject to business measurement.
- May have budgetary responsibilities.
4.2.10.3 Position Title: Senior Education Specialist
Position Concept:
There are four areas of Education specialization:
- INSTRUCTION encompasses instructor facilitated training.
- DEVELOPMENT covers all tasks involved in preparing a training
intervention
- PERFORMANCE CONSULTANCY involves working with clients to evaluate and
define job performance needs and to lead the activities to achieve
improvement.
- CURRICULUM SPECIALIZATION includes defining market/customer
requirements, determining training curriculum, and managing curriculum
portfolio and financial parameters.
An individual may operate in one or more of these areas of specialization
depending on local business need.
The Senior Education Specialist is an experienced Professional working on
education assignments of a large and/or complex nature, and will have an
outstanding record of success in this environment. Is instrumental in
helping to formulate Education & Training policy and direction. Will have
extensive experience in more than one of the four areas of education
specialization. May also have significant program management
responsibility.
Skills
- Utilizes advanced performance technology methodologies to guide and
influence other education professionals in determining, creating,
and/or deploying customer solutions. Demonstrates the required
proficiency level for the Senior position.
- Works and negotiates effectively with team members (vendors,
subcontractors, customers and IBMers from other functional areas) to
define team objectives and approaches for attaining them.
- Recognizes and analyses complex problems and then creates and
implements innovative solutions involving technology and education
methodology.
Contribution/Leadership
- Leads training cross-functional teams to achieve performance
objectives assigned by the education leader.
- Understands entire training function mission and applies this
understanding in assigned activities.
- Influences people outside immediate department, through work with
customers, vendors and subcontractors and presentations on
business-related topics to IBM and customer management.
- May manage all aspects of significant projects or teams.
Impact on Business/Job Scope
- Accountable for results of activities involving cross-functional teams
within the training function.
- Regularly participates in training function program planning and has a
direct impact on customer satisfaction, business measurements, and
financial objectives.
4.2.10.4 Position Title: Consulting Education Specialist
Position Concept:
There are four areas of Education specialization:
- INSTRUCTION encompasses instructor facilitated training.
- DEVELOPMENT covers all tasks involved in preparing a training
intervention
- PERFORMANCE CONSULTANCY involves working with clients to evaluate and
define job performance needs and to lead the activities to achieve
improvement.
- CURRICULUM SPECIALIZATION includes defining market/customer
requirements, determining training curriculum, and managing curriculum
portfolio and financial parameters.
An individual may operate in one or more of these areas of specialization
depending on local business need.
The Consulting Education Specialist works on large complex education
assignments and is a key contributor to the success of the education
business unit.
Skills
- Understands and applies knowledge of function, business unit or
country objectives. Demonstrates the required proficiency level for
the Consulting position.
- Understands organizational resources, priorities, needs and policies.
- Guides other professionals. Mentors others in the Education
profession. Provides guidance to team members in area of new or
complex education activities and/or management techniques.
- Leads negotiations with engagement partners and team members (vendors,
subcontractors, customers, IBMers from other functional areas) to
define business goals and strategies for attaining them.
- Anticipates potential problems. Develops and leads execution of major
education business activities.
- Understands future customer, industry and information technology
trends. Applies this understanding to develop current business and to
identify opportunities for future business.
- Analyzes new and complex situations. Selects, tailors and applies a
wide range of techniques to analyze customer needs and develop
education solutions. Evaluates potential solution elements and selects
most appropriate elements. Assesses both short and medium term
business impact of solutions.
- Lead the implementation of solutions or provide expert guidance to the
education team(s) involved.
Contribution/Leadership
- Conducts special projects. Participates in exploratory activities in
new market sectors, application solutions, technologies and the use of
business partners.
- Leads selection of new education offerings in new markets
- Exhibits strategic vision of functional or unit mission and applies
vision in all activities.
- Influences people and organizations, including client and IBM
executive management, on issues related to education and business..
Is respected as a technical leader / subject matter expert inside and
outside own organization.
- Leads teams in the solution of new and complex problems. May serve as
project manager.
- Leads multifunctional teams. Identifies needs for expertise outside
own area, gets commitment of needed resources, and effectively applies
the expertise of team members to the enhancement of the education
business.
Impact on Business/Job Scope
- Accountable for projects or programs involving multifunctional,
country-wide or regional teams.
- Responsible for the successful implementation of a solution, or of a
major portion of a very large solution, within identified cost,
schedule and functional requirements.
- Leads assessment of cost, schedule and dependencies associated with
education solution development.
- Has overall responsibility for successful training solutions,
programs, and the performance model to achieve business measurements,
including financial and customer targets.
4.2.10.5 Position Title: Senior Consulting Education Specialist
Position Concept:
There are four areas of Education specialization:
- INSTRUCTION encompasses instructor facilitated training.
- DEVELOPMENT covers all tasks involved in preparing a training
intervention
- PERFORMANCE CONSULTANCY involves working with clients to evaluate and
define job performance needs and to lead the activities to achieve
improvement.
- CURRICULUM SPECIALIZATION includes defining market/customer
requirements, determining training curriculum, and managing curriculum
portfolio and financial parameters.
An individual may operate in one or more of these areas of specialization
depending on local business need.
The Senior Consulting Education Specialist operates as an exceptionally
experienced professional working on multiple large complex education
assignments and is a key contributor to the success of the education
business unit. Is expected to have responsibility for a very significant
business stream from own personal activities. Operation scope would
normally be at business unit, country, international or global projects
level.
Skills
- Applies professional mastery to develop solutions in leading edge or
critical situations, in education business of strategic significance.
Demonstrates the required proficiency level for the Senior Consulting
position.
- Fosters and engages in teamwork at the highest management and
technical levels of IBM, customer, vendor and subcontractor
organizations. This leads to lasting agreements and commitments
amongst all involved.
- Anticipates future customer, industry and information technology
trends. Applies this understanding to develop a strategic vision which
influences business area, country or international strategic
objectives.
Contribution/Leadership
- Develops and implements training offerings and strategies with
executive review.
- Articulates vision of long term IBM, industry and technology
directions which guides training business area strategy.
- Recognized as an expert and a leader by the training professionals and
multicountry organizations both within IBM, and outside.
- Leads business unit, functions, special projects country, or
international teams.
Impact on Business/Job Scope
- Accountable for business unit, major country and global projects and
programs.
- Contributes to policy-making, at a global level, and coordinates
executive review.
- Responsible for committing multiple resources and achieving customer
satisfaction, cost, expense, revenue and other critical business
measurements.
- Responsible for quality output / value add for highly visible
products and services and future business development.
4.3 Chapter 17. IT Architect Profession
Subtopics:
4.3.1 IT Architect Profession Overview
The IT Architect creates information technology solutions to clients'
business problems. These IT solutions may include systems, applications
or processes, and may involve the application and integration of a wide
variety of products, technologies and services. The IT Architect must
have extensive knowledge of systems, architectures, systems management,
networking and application design techniques, and must be able to
identify, evaluate and select the elements of the solution which best meet
the client's business needs.
The IT Architect's primary responsibilities include the following:
- Designs solutions to meet client requirements
- Identifies alternative solutions and solution elements.
- Evaluates alternatives for compliance with overall cost, schedule
and technical requirements.
- Ensures that the solution design meets client needs
- Directs and sizes design activities
- Influences client executives on design decisions
- Develops specifications for new products, applications and services
offerings
- Maintains a visible profile and respected reputation in the industry
- Acts as a mentor to future IT architects
- Represents IBM to the client and other external organizations on
technical matters
In the course of an engagement or as requested by the client, the IT
Architect may be required to work in other parts of the services
lifecycle, supporting and providing guidance to other services
professionals:
- Collaborates with consultants in defining business and integration
requirements and strategy
- Provides technical leadership to IT Specialists in the implementation
phase
- Collaborates with the project manager throughout the design,
implementation, or operation phases of a project
At all times, the IT Architect is responsible for developing and improving
his or her skills. He or she is also responsible for performing the role
of mentor to other technical professionals who aspire to become IT
Architects, sharing successful architectures and design techniques with
peers, reviewing the designs of other projects and representing IBM at
external events.
4.3.2 Profession Structure
The individual's career as an IT Architect begins at what is called the
"Senior" level in other services professions, and progresses through the
Consulting and Senior Consulting levels. This generally means that the IT
Architect developed his/her application and system skills in another
profession prior to becoming an IT Architect.
Responsibilities at the entry level generally involve growth from already
strong technical system / application implementation skills to
architectural problem-solving and decision making skills, either as lead
architect on a small to medium-sized project, or under the direction of a
more senior architect on a large or complex project. Certification, which
is generally a prerequisite to entry to the consulting level, marks the
validation by the IT Architect's professional peers that he/she has
attained the fundamental skills required of all members of the profession.
As the IT Architect develops architectural skills, he/she begins to take
on the solution of more difficult and complex client problems, and to take
increased project leadership responsibility. At the more senior levels,
the professional IT Architect may have marketing and/or business
responsibility. The IT Architect may be either management or
non-management.
As in other professions, certified and advanced professionals will be
expected to provide technology or competency leadership and mentoring to
less experienced members of the profession.
Figure 17-1 in topic 4.3.2.1 summarizes the requirements of each position
of the profession and the developmental requirements for progression
within the profession. Detailed position descriptions can be found in "IT
Architect Position Descriptions" in topic 4.3.11.
Subtopics:
4.3.2.1 IT Architect Areas of Specialization
The IT Architect profession requires broad skills in multiple technologies
and methodologies, but in addition it is expected that the IT Architect
will have specialized skills in one or more areas.
It is also expected that an IT Architect may master additional specialized
skill sets over time to remain competitive in a changing business and
technical environment. In very general terms, the IT Architect's current
specialization is determined by the major focus of the IT Architect's
current and recent assignments. The major areas of specialization
include:
_________________ ______________________________________________________
| Application | Focus is on customer-specific application design and |
| Development | implementation. |
|_________________|______________________________________________________|
| Networking | Focus is on system wide networking solutions design |
| | and implementation. |
|_________________|______________________________________________________|
| Systems | Focus is on multi-vendor hardware and software |
| Integration | design, integration and implementation |
|_________________|______________________________________________________|
| Systems | Focus is on the system hardware/software design and |
| Management | operational management. |
|_________________|______________________________________________________|
| Client/Server | Focus is on distributed computing solutions, |
| Architect | including hardware, software, and databases. |
|_________________|______________________________________________________|
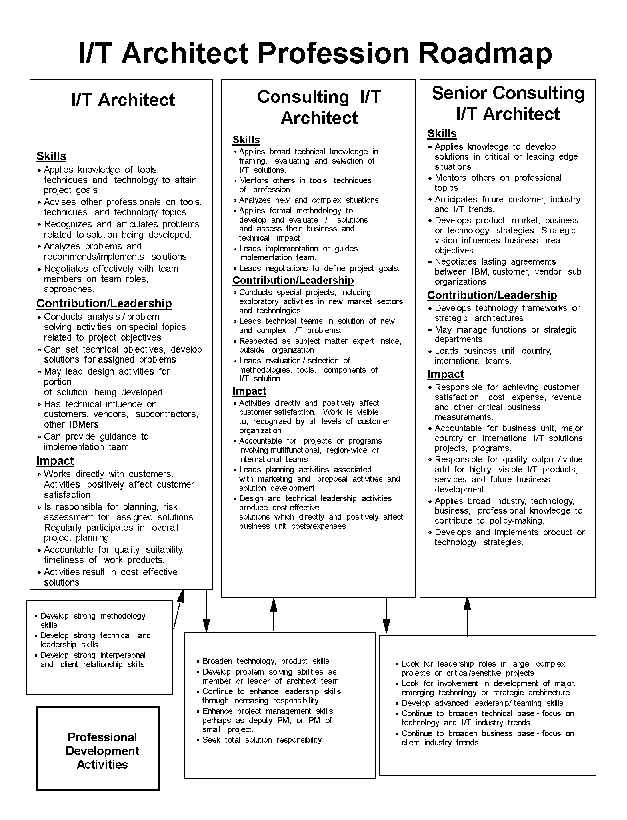
Figure 17-1. IT Architect Profession Roadmap
4.3.2.2 Application Development Architect
The Application Development Architect is responsible for supporting the
definition of business strategies, processes, IT architectures and
platforms for solution development, application maintenance and data
management activities.
The Application Development Architect is also responsible for transforming
client requirements and process models into plans, processes and IT
solutions which include hardware, software, network and data
specifications. Activities include technical planning, make vs. buy
assessment, reviews, development of architecture, and modification of
specifications for application solution components. Application
Development Architects, in addition to their broad technical background,
will have a tendency to focus their design and development efforts in one
of the following specialties and the tools required to operate in that
environment: Traditional (Host based) Development, Client/Server, Object
Oriented, Imaging Solutions, or Rapid Solutions.
4.3.2.3 Network Architect
The Network Architect is responsible for the development of networking
solutions, including definition of network strategies and architectures,
and of plans for installation and operation of network facilities.
In addition, responsibilities range from requirements analysis to
performing, directing, and managing the technical and business activities
associated with translating client requirements into an integrated network
solution. Activities include technology selection, network strategy
definition, analyzing client requirements, developing and managing the
network capacity plan, and providing marketing support for network
contracts.
4.3.2.4 Systems Integration Architect
The Systems Integration Architect is responsible for the analysis and
definition of a client's business problem. The SI Architect documents and
transforms those requirements into a comprehensive technical solution and
possesses a high degree of technical competence in designing solutions
that contain a wide mix of hardware, software, network and service
components. The SI Architect understands all the elements required to
architect, design, build, test, install, operate and maintain a complex
system that requires a variety of resources provided by IBM, IBM
subsidiaries, subcontractors, and clients.
In addition, responsibilities of the SI Architect include creating
solutions from standard product offerings and designing unique solutions
for highly complex client requirements. Activities include participating
in engagement teams, creating solution strategies, developing solutions,
reviewing proposed solutions, and mentoring less experienced personnel in
Systems Integration methodologies, disciplines, and processes.
4.3.2.5 Systems Management Architect
The Systems Management Architect is responsible for the definition of
strategies and architecture for complex information systems, including
central processors, peripherals, servers, end user systems, and system
management software. Activities include: managing the operation of
centralized and distributed systems, problem determination, scheduling,
and performance and capacity optimization.
Responsibilities range from large and moderately complex system designs,
development of implementation plans, analysis, and coordination of a
large, possibly distributed, information system environment to providing
technical guidance and recommendations while addressing client
requirements in a very large and complex, possibly distributed,
information system environment.
4.3.2.6 Client/Server Architect
The IT Architect specializing in Client/Server Solutions is responsible
for the definition of distributed systems solutions and strategies for
migration to these solutions.
The IT Architect Specializing in Client/Server solutions has a broad
knowledge of the Networking, Application Development, Systems Integration
and Systems Management Disciplines. Solutions begin with understanding of
client business problems and determination of the solution (client /
server or otherwise) which best addresses the client's present and future
IT needs.
In addition, responsibilities range from requirements analysis to
performing, directing, and managing the technical and business activities
associated with translating client requirements into an integrated
distributed solution. Activities include technology selection, migration
strategy definition, analyzing client requirements, developing and
managing capacity plans for the system, selection of development tools and
methodologies and providing marketing support for client/server contracts.
4.3.3 Characteristics of the Profession
The IT Architect's primary concern is the formulation of cost-effective
solutions which meet the client's business need and which can be
effectively implemented. In order to perform effectively, IT Architects
must have the following characteristics:
- Work effectively in the client environment.
In order to formulate effective solutions, the IT Architect must
understand the client's strategic goals and business processes. The
IT Architect must gain an understanding of the client's organization
and form relationships with end-users and decision-makers which allow
the IT Architect to gain knowledge of the client's real requirements
and to gain acceptance for proposed solutions.
- Work effectively in the IBM environment.
The IT Architect must know IBM products and services strategies and be
able to communicate them to the client in such a way as to help the
client make critical business decisions and to create confidence in
the robustness and quality of the proposed solution. The IT Architect
must have extensive relationships throughout IBM which can be used to
help solve technical and resource problems as they arise, and as a
source of knowledge which can be applied in the creation of solutions.
- Possess broad knowledge of the industry in which the client need
exists.
In addition to understanding the client's business processes, the IT
Architect must be knowledgeable about the industry in which the client
operates, including competitors, industry directions, and OEM products
and services within the industry which might contribute to a solution.
- Possess and apply business skills.
The IT Architect must understand the financial implications of
proposed solutions, both to the client and to IBM, and must be able to
assist the client in making an effective business case for the
proposed solution.
- Possess and apply project management skills.
The IT Architect must be able to assist the project manager in project
planning, tracking and reporting, and identification and management of
risk. On some engagements the IT Architect may, in fact, act as the
project manager, and therefore must possess extensive project
management skills.
- Have extensive knowledge of applicable products, technology, services
methodology and tools, and be able to apply this knowledge in the
formulation, evaluation and selection of solution alternatives.
The IT Architect's role demands extensive knowledge of components
(both IBM and OEM) of proposed solutions, their operational
characteristics and interoperability. The IT Architect must
understand relevant technologies, including their current
applicability and capacity to accommodate growth and change. Since
the IT Architect must discover client requirements, analyze them and
translate them into solutions, the IT Architect must be skilled in
requirements analysis methods and tools. Since the IT Architect must
develop total solutions which can be effectively implemented,
maintained and operated, he or she must have extensive knowledge of
development and test methods and systems management disciplines.
- Possess and apply excellent personal skills.
The IT Architect must be both a knowledge leader and a people leader,
and be able to persuade clients and team members that his or her
approaches and solutions are worthy of implementation. To do so, the
IT Architect must be able to clearly communicate complex technical and
business concepts, both to clients and to team members, and to
negotiate change, sometimes with multiple individuals or
organizations. Problem solving is a principle role of the IT
Architect, and he or she must be capable of effectively identifying
and framing problems, leading the collection of elements of
information and integrating this information to produce timely and
thoughtful decisions.
4.3.4 Potential Candidates
Most, though not all IT Architects begin their careers as IT Specialists,
since the IT Specialist profession has entry and staff levels within which
the aspiring technical person can acquire the skills and experience which
are prerequisite for starting a career as an IT Architect.
More senior people with strong technical and leadership backgrounds,
particularly those in the Consulting and IT Specialist professions, form
another pool of high potential IT Architect candidates.
Figure 17-2 shows possible candidates for the IT Architect Profession and
possible career movement from an IT Architect position. Additional
documentation on the normal possibilities for making a career change from
one of the other Worldwide Professions to the IT Architect profession is
available in I/T Architect Career Possibilities.
For each profession pair, a summary is presented of the common and delta
skills; contribution and leadership; and scope of responsibility /
contribution to the business; that is expected of members of each
profession.
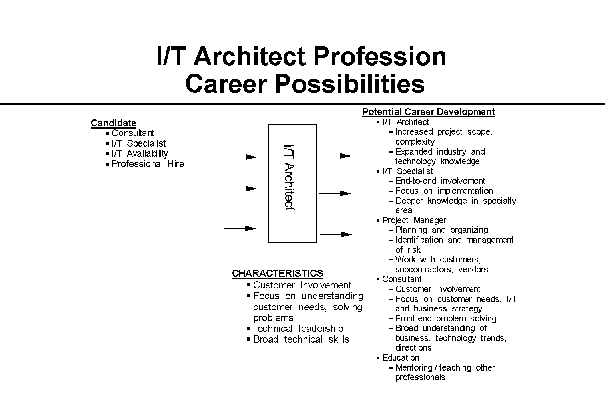
Figure 17-2. IT Architect Profession Career Possibilities
4.3.5 Career Growth
IT Architects can progress to the executive level within their profession,
applying their skills to the solution of increasingly complex client
problems. Many IT Architects choose to broaden their technical skills to
include extensive knowledge and experience in related IT Architect
disciplines, thus enlarging the range of engagements on which their skills
might be applied. Others, who enjoy the analysis of client business needs
and definition of requirements, may elect to enter the Consultant
profession. Still others become full time Project Managers.
4.3.6 Certification Nomination Guide
Refer to the Worldwide I/T Architect Certification Nomination Guide.
Additional information can also be found in Mentoring I/T Professionals.
4.3.7 Performance Elements
The key performance elements for the IT Architect profession are:
- Cost/Profit or Revenue/Share
- Customer Satisfaction
The depth and breadth of one's skills will be one of the factors which
determine the IT Architect's compensation, along with size and complexity
of the project/engagement/contract.
Measurement criteria will include project, solution or engagement profit
for services organizations, or personal revenue for services or cost
management in Internal IT organizations. Sales, services and industry
groups may include revenue or solution objectives (CAs) and share
objectives. Schedule or milestone objectives are common for services, IT
and sales organizations for proposal, requirements, design and
implementation projects/engagements. Most include external or internal
customer satisfaction measurements.
4.3.8 IT Architect Profession Skills Profile
The following profile describes skills and proficiency levels for all
members of the IT Architect profession.
____________________________________ ___________________________________
| | Profession Positions, with |
| | Associated Skill Levels |
| |________ ________ ________ ________|
| I/T ARCHITECT SKILLS | | Cons | Sr | |
| | I/T | I/T | Cons | Key |
| | Arch | Arch | I/T | Skills |
| | | | Arch | |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| CLIENT ENVIRONMENT |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Relationships | 3 | 4 | 4 | Y |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Strategy & Planning | 3 | 3 | 4 | Y |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Management Systems / Culture | 3 | 3 | 4 | Y |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| BUSINESS ACUMEN |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Market Management | 2 | 3 | 3 | Y |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Financial Skills | 2 | 3 | 3 | Y |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Consulting Methods | 3 | 3 | 4 | Y |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Value-Add Selling | 3 | 3 | 4 | Y |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| INDUSTRY |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Industry | 3 | 3 | 4 | Y |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| IBM ENVIRONMENT |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Organization | 3 | 4 | 4 | Y |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Vision / Mission / Strategy | 3 | 4 | 4 | Y |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Management Systems | 3 | 4 | 5 | Y |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| PROJECT MANAGEMENT |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Initiate Projects | 3 | 4 | 5 | Y |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Plan Projects | 4 | 4 | 4 | Y |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Project Track / Report / Deliver | 3 | 4 | 4 | Y |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Manage Project Risk | 3 | 4 | 4 | Y |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| PRODUCTS/TECHNOLOGY/SERVICES |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Platforms | 4 | 4 | 4 | Y |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Applications | 3 | 3 | 4 | Y |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| IT Related Services | 3 | 4 | 4 | Y |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Architectures | 4 | 4 | 5 | Y |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Methodologies | 4 | 5 | 5 | Y |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| PERSONAL |
|____________________________________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Leadership | 4 | 4 | 5 | Y |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Communication | 4 | 5 | 5 | Y |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Negotiation | 3 | 4 | 4 | Y |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
| Problem Solving/Decision Making | 4 | 5 | 5 | Y |
|____________________________________|________|________|________|________|
4.3.9 Skills Templates
The skills shown above are the basis for the Skills V2 templates for the
IT Architect profession. In order to work with these skills, you should
select two templates: the template containing profession-wide skills at
the appropriate level, and one of five specialization templates at that
level. V2 template names are as follows:
- I/T Architect
- I/T Architect-Appl Devel
- I/T Architect-Client/Server
- I/T Architect-Netwkg
- I/T Architect-Sys Integn
- I/T Architect-Sys Mgmt
- I/T Architect-Cons
- I/T Architect-Appl Devel-Cons
- I/T Architect-Client/Server-Cons
- I/T Architect-Netwkg-Cons
- I/T Architect-Sys Integn-Cons
- I/T Architect-Sys Mgmt-Cons
- I/T Architect-Sr Cons
- I/T Architect-Appl Devel-Sr Cons
- I/T Architect-Client/Server-Sr Cons
- I/T Architect-Netwkg-Sr Cons
- I/T Architect-Sys Integn-Sr Cons
- I/T Architect-Sys Mgmt-Sr Cons
4.3.10 Professional Development
Growing your skills requires a combination of experience, education,
training, coaching and mentoring. These elements are called Skill
Development Activities. Education and training can be separated into
several forms ranging from self study, distance learning, internships,
classroom, and seminars. The integration of these delivery methods can be
an efficient and cost effective way to build your skills. For an overview
of the Worldwide Professions and links to the Common Skills Categories and
Professions Roadmaps, refer to the Education Roadmap page of the IEC
Course Catalog at http://w3.lahulpe.ibm.com/roadmaps/index.html.
4.3.11 IT Architect Position Descriptions
The following position descriptions describe the basic work of each of the
positions within the Professions. Formal descriptions which may contain
legally mandated language necessary for classifying employees in a
geography should be obtained through the approved on-line job library, if
available in the geography, or by contacting the appropriate H.R.
personnel within the geography.
Subtopics:
4.3.11.1 Position Title: I/T Architect
Position Concept:
The I/T Architect participates in translation of the client's business
requirements into specific system, application or process designs. This
includes working as a team member with client personnel to identify
functional requirements and subsequently working with or in some instances
leading others in the identification, justification and design of the
client's solution. The I/T Architect participates in a wide range of
design activities, from requirements analysis through systems, application
and/or process design specification. At this level the position requires
knowledge across multiple platforms, processes or architectures.
The I/T Architect is at the entry level to the profession and is presumed
to have attained skills and responsibilities in prior technical
assignments equivalent to the Senior position or above.
Skills
- Applies knowledge of information technology and associated methods and
tools of the I/T Architect profession to attain project / business
unit objectives. Demonstrates the required proficiency levels for
technical skills.
- Advises other professionals (Project Managers, I/T Architects and I/T
Specialists) in team on tools, technology and methodology related to
the design and development of I/T solutions, and participates in
evaluation and selection. May be asked to research special topics as
part of team responsibilities.
- Works effectively with other team members to understand customer needs
and to design, evaluate and develop I/T solutions which meet those
needs. Guides and influences team members, including customer, vendor
and subcontractor personnel, and IBMers to accomplish the team's
technical and schedule goals.
- Negotiates effectively with team members (vendors, subcontractors,
customers and IBMers) to identify each member's role in solution
design and development, agree on specific problem-solving,
requirements analysis and design tasks and associated work products,
and to define approaches for producing them.
- Recognizes and articulates complex problems related to the solution
being developed.
- Applies creativity and judgment in development of multiple I/T
solutions related to project objectives.
- Analyzes problems and creates solutions involving I/T technology,
methodology, process, tools and solution components.
Contribution/Leadership
- Conducts analysis, problem-solving and evaluation activities on
special topics related to project objectives.
- May lead design activities. This includes leading all or portions of
the design project, recommending team members and organizing the team,
defining tasks, tracking and reporting progress, delivering on time
and within budget, and delivering results to the customer.
- Defines and determines solution design objectives related to the
project. May lead and guide the efforts of others in these areas.
- Understands department / function mission and applies this
understanding in project activities.
- Influences customers, vendors, subcontractors and IBMers inside and
outside project with presentations on project-related topics.
Influence extends to both management and non-management personnel.
- Provides technical guidance to implementation team members throughout
the project lifecycle. May lead implementation in a small project or
be responsible for subsystem implementation in a large project.
- Collaborates with the Consultant and/or Market Segment Manager in
defining the customer's business and integration
requirements/strategy.
Impact on Business/Job Scope
- Accountable for products of teams led / department managed in terms of
quality, timeliness and compliance with customer needs.
- Regularly participates in overall functional planning. Identifies,
estimates and presents cost, schedule, technical risk for solution
elements, both in marketing and proposal efforts and in implementation
planning.
- Works directly with customers. Activities affect customer
satisfaction.
- Activities lead to cost effective solutions which positively affect
project costs or expenses.
4.3.11.2 Position Title: Consulting I/T Architect
Position Concept:
The Consulting I/T Architect is responsible for translating the client's
business requirements into specific system, application or process
designs. This includes working with client personnel and executives to
identify functional requirements and subsequently working with and leading
others in the identification, justification and design of the client's
solution. The I/T Architect is responsible for a wide range of design
activities from requirements analysis through systems, application and/or
process design specification. At the Consulting level or higher the
position requires significant knowledge across multiple platforms,
processes or architectures, as well as broad knowledge of new
technologies, and will include directing the design efforts of less
experienced architects.
In addition to the attributes of the entry level I/T Architect position,
typical attributes of the Consulting I/T Architect position may include
the following:
Skills
- Understands and applies knowledge of function, business unit or
country objectives in framing, evaluating and selecting alternatives
for I/T solutions. Has the required proficiency levels for technical
skills and applies skills to the design of I/T solutions.
- Understands organizational resources, priorities, needs and policies.
- Mentors others in the I/T Architect profession. Provides guidance to
team members (Project Managers, I/T Architects and I/T Specialists,
among others) in new or complex solution design, implementation and/or
management tools and techniques.
- Leads negotiations with engagement partners and team members (vendors,
subcontractors, customers, IBMers) to define project goals and
strategies for attaining them.
- Anticipates potential problems associated with the solution being
developed. Develops and leads execution of the technical risk
management plan for the solution to be implemented.
- Understands future customer, industry and information technology
trends. Applies this understanding to develop robust solutions and to
identify opportunities for future business.
- Analyzes new and complex situations. Selects, tailors and applies
formal requirements, design and development methodologies to analyze
customer needs and develop requirements for I/T solutions. Evaluates
potential solution elements using a formal methodology and selects
most appropriate elements. Assesses business and technical impact of
solutions.
- Leads the implementation of solution or provides expert guidance to
the solution implementation team. Identifies development methodology
and supporting tools.
Contribution/Leadership
- Conducts special projects. Participates in exploratory activities
into new market sectors, application solutions, technologies and the
use of business partners.
- Leads selection of methodologies, tools and components of total I/T
solutions.
- Exhibits strategic vision of functional or unit mission and applies
vision in engagements.
- Influences people and organizations, including client and IBM
executive management, on issues related to the development of I/T
solutions. Is respected as a technical leader / subject matter expert
inside and outside organization.
- Leads technical teams in the solution of new and complex information
technology problems. May serve as project manager.
- Leads multifunctional teams. Identifies needs for specialized
expertise outside own area, gets commitment of needed resources, and
effectively applies the expertise of team members to the development
of I/T solutions.
Impact on Business/Job Scope
- Accountable for projects or programs involving multifunctional,
country-wide or regional teams.
- Responsible for the successful implementation of an I/T solution, or
of a major subsystem of a very large I/T solution, within identified
cost, schedule and functional requirements.
- Leads assessment of cost, schedule and dependencies associated with
marketing and proposal activities and with solution development.
- Activities directly affect customer satisfaction. Work is visible to
and recognized by all levels of customer organization. Works with
customers, from team members to executive levels, to ensure
understanding of, acceptance of and satisfaction with I/T solution and
development approach.
- Design and technical leadership activities produce cost effective I/T
solutions which directly affect functional, business unit or country
costs and expenses.
4.3.11.3 Position Title: Senior Consulting I/T Architect
Position Concept:
The Senior Consulting I/T Architect is responsible for translating the
client's business requirements into specific system, application or
process designs for very large, complex or leading-edge solutions. This
includes working with client personnel and executives to identify
functional requirements and subsequently working with and leading others
in the identification, justification and design of the client's solution.
It may also include the formation of partnerships among customer, vendor
and subcontractor organizations and the negotiation of lasting agreements
regarding goals and approaches. The I/T Architect is responsible for a
wide range of design activities from requirements analysis through
systems, application and/or process design specification. As is the case
for the Consulting I/T Architect, this position requires significant
knowledge across multiple platforms, processes or architectures and will
include directing the design efforts of less experienced architects. The
Senior Consulting I/T Architect is also expected to have an extensive
understanding of industry and technology trends, as well as of IBM
strategy, and to apply that understanding to articulate a strategic vision
which influences or guides business area, country or international
strategic directions.
In addition to the attributes of the Consulting I/T Architect position,
typical attributes of the Senior Consulting I/T Architect position may
include the following:
Skills
- Demonstrates the required levels of technical skills. Applies
professional mastery and industry-wide understanding of technology,
tools and methodologies to develop solutions in leading edge or
critical situations, on projects of strategic significance to business
unit, country or international objectives.
- Fosters and engages in teamwork at the highest management and
technical levels of IBM, customer, vendor and subcontractor
organizations, across all professions.
- Plans and conducts negotiations which result in lasting agreements and
commitments between IBM, customer, vendor and subcontractor
organizations.
- Anticipates future customer, industry and information technology
trends. Applies this understanding to develop a strategic vision
which influences business area, country or international strategic
objectives.
- Develops and implements product, market, business or technology
strategies with executive review.
Contribution/Leadership
- Articulates vision of long term IBM, industry and technology
directions which guides business area strategy. Develops technology
frameworks or strategic architectures at a corporate enterprise level
as well as being able to develop an architecture framework for a
multiapplication environment.
- Recognized as an expert and a leader by other members of the I/T
Architect profession, multicountry organizations within IBM, and by
customer, vendor and subcontractor organizations.
- May manage functions or strategic departments.
- Leads business unit, country or international teams.
Impact on Business/Job Scope
- Accountable for business unit, major country or international I/T
solutions, projects and programs.
- Develops and implements product or technology strategies with
executive review.
- Applies broad industry, technology, business and professional
knowledge to contribute to policy-making.
- Responsible for committing multiple resources and achieving customer
satisfaction, cost, expense, revenue and other critical business
measurements.
- Responsible for quality output / value add for highly visible I/T
products, services and future business development.
4.4 Chapter 18. I/T Availability Profession
Subtopics:
4.4.1 I/T Availability Profession Overview
As the complexity of the client's information systems has grown in recent
years, an increased demand for a broad range of system based skills has
arisen. Clients look for a single provider to support their
multi-platform, multi-vendor environments where the success of their
business depends on the availability of their information technology.
To become the premier services provider of choice, new requirements have
been incorporated into the Availability Services delivery strategy. These
new requirements include accepting responsibility and ownership for all
hardware systems, software, network and communication problems; developing
a partnership with clients and understanding their business priorities;
implementing pro-active, system-wide solutions, and responding in a
flexible and creative manner. Through this shift in focus, increased
services revenue can be attained, along with improved client trust and
confidence.
Subtopics:
4.4.1.1 Profession Concept
The I/T Availability Professional is a key contributor in maintaining IBM
as the Availability Services provider of choice. Their primary
responsibility is to ensure that the clients I/T goals are met. These
goals will be accomplished through the delivery of availability services
such as:
- Availability Services Consulting
- Installation and Migration
- Hardware and Software Maintenance
- Operational Enabling
- Performance Management
- Backup and Recovery
- Security Services
The I/T Availability Professional is accountable for management and growth
of services revenue and attainment of gross profit objectives.
The I/T Availability Profession disciplines provide the client with a
broad range of availability support. With in-depth client relationship
skills, the I/TAP understands the client's key availability goals and
strategies and address them with availability services solutions. Key
technical skills in the systems management practice address the client's
availability consulting and overall systems availability architecture
requirements. In addition, technical specialization by operational
environments provides the client with high value services and support.
These professionals have a high degree of analytical ability and
creativity in the development and implementation of plans and solutions to
client I/T requirements and problems. An individual in this position
functions independently with minimal direction and is recognized as an
expert in the availability services. The certified I/TAP is able to
provide expert advice to project managers or leaders as well as give
technical direction to team members, including IBM, subcontractors, or
client personnel.
4.4.2 Profession Structure
The I/T Availability Profession consists of 5 positions:
- I/T Availability Professional
- Advisory I/T Availability Professional
- Senior I/T Availability Professional
- Consulting I/T Availability Professional
- Senior Consulting I/T Availability Professional
The exception to the above positions is the I/TAP-Systems Services
Representative discipline which has six positions. These positions are
described in the "I/TAP Profession Position Descriptions" section of this
chapter.
Figure 18-1 in topic 4.4.2.1 to Figure 18-5 in topic 4.4.2.1 summarize the
requirements of each position of the profession and the developmental
requirements for progression within the profession.
Detailed position descriptions can be found in "I/TAP Profession Position
Descriptions" in topic 4.4.10
Subtopics:
4.4.2.1 Position Specifications
The following table highlights typical differences in experience and
responsibilities for the various positions within the I/T Availability
Profession.
______________ ______________ _______________ ______________ ______________________
| Experience | I/T | Advisory I/T | Senior I/T | Consulting / Sr |
| | Availability | Availability | Availability | Consulting I/T |
| | Professional | Professional | Professional | Availability |
| | | | | Professional |
|______________|______________|_______________|______________|______________________|
| IBM and I/T | 0-3 years | 3-6 years | 7-9 years | 10+ years |
| experience | | | | |
|______________|______________|_______________|______________|______________________|
| Revenue | | | | |
| responsi- | | | | |
| bility | | | | |
|______________|______________|_______________|______________|______________________|
| Note: Varies by discipline and geography. Amount increases at each higher |
| position. |
|______________ ______________ _______________ ______________ ______________________|
| IBM | 0-2 years | 2-3 years | 3-5 years | 4+ years |
| experience | | | | |
| in the | | | | |
| discipline | | | | |
| areas | | | | |
| (Software, | | | | |
| Availability,| | | | |
| etc) | | | | |
|______________|______________|_______________|______________|______________________|
| Territory | Assists in a | Independently | Independently| Is the technical |
| size | small to | has multiple | has large | discipline leader of |
| | medium size | small to | accounts | a large/complex |
| | territory | medium size | within the | territory or is |
| | | firms or is a | territory. | responsible for key |
| | | junior member | | client I/T executive |
| | | of a | | relationships |
| | | Availability | | |
| | | Services team | | |
| | | in a large | | |
| | | territory. | | |
|______________|______________|_______________|______________|______________________|
| Scope of | Limited | Works with | Communicates | Understands complex |
| influence | | staff and/or | issues to | problems and |
| | | product | staff and | proposes solutions |
| | | divisions. | product | to business unit, |
| | | | divisions. | staff product |
| | | | | divisions, other |
| | | | | professionals. Is |
| | | | | sought out by these |
| | | | | organizations. |
|______________|______________|_______________|______________|______________________|
| Success as a | Client | Client | Client | Client loyalty to |
| services | loyalty to | loyalty to | loyalty to | Availability |
| professional | Availability | Availability | Availability | Services. Revenue |
| | Services. | Services. | Services. | and profit |
| | Revenue and | Revenue and | Revenue and | objective. A |
| | profit | profit | profit | recognized expert |
| | objective. | objective. | objective. | inside and outside |
| | | Evaluates | Recognized | the territory. |
| | | critical | as an | Secures commitment |
| | | customer | authority in | and agreement. |
| | | requirements | the | Develops creative |
| | | and develops | discipline. | solutions and is |
| | | imaginative | Develops | sought out by |
| | | availability | creative | others. |
| | | services | availability | |
| | | solutions | services | |
| | | which evoke | solutions. | |
| | | negotiation. | | |
|______________|______________|_______________|______________|______________________|
| Customer | Assists in | With | Determines | Manages to a high |
| Satisfaction | making | guidance, | severity | customer |
| | decisions | makes regular | level in | satisfaction level. |
| | regarding | independent | critical | Pro-active in |
| | customer | decisions | situations | improving customer |
| | satisfaction.| regarding | that affect | satisfaction. |
| | Needs | customer | customer | Ultimate |
| | assistance | satisfaction. | satisfaction.| responsibility for |
| | in | | Positive | high customer |
| | developing | | influence on | satisfaction in |
| | and | | satisfaction.| offering set. |
| | executing | | | |
| | plans. | | | |
|______________|______________|_______________|______________|______________________|
| Availability | Assists in | Executes | Develops and | Develops for own |
| Services | executing, | independently.| executes for | territory, provides |
| Strategies | as directed | Assists in | own | input for the |
| | by others. | developing | territory. | Business unit. |
| | | locally. | | |
|______________|______________|_______________|______________|______________________|
| Competitive | Can | Works with | Understands | Competitive expert. |
| Strategies | differentiate| experienced | competition's| Always takes the |
| | IBM and | I/T | products, | initiative to engage |
| | competitive | Availability | plans and | the competition. |
| | offerings, | Professionals.| strategies. | In-depth knowledge |
| | with | Understands | Can | of competition's |
| | assistance. | competition's | differentiate| strategies, |
| | | products and | IBM | products, and plans. |
| | | services. | offerings | Achieves repeated |
| | | | from | wins against |
| | | | competition | competition. Sought |
| | | | to ensure | by others. |
| | | | winning in | |
| | | | engagements. | |
|______________|______________|_______________|______________|______________________|
| Communication| Good | Good | Strong; Can | Excellent; can |
| and skill | | | instruct/ment|rinstruct/mentor |
| transfer | | | others | others |
|______________|______________|_______________|______________|______________________|
| Communicating| Generally to | Business unit | Country | Drives business |
| offering | local team | level | level | unit, country, and |
| requirements | leader | | | influence on global |
|______________|______________|_______________|______________|______________________|

Figure 18-1. I/T Availability Profession Roadmap: Associate I/TAP

Figure 18-2. I/T Availability Profession Roadmap: Advisory I/TAP

Figure 18-3. I/T Availability Profession Roadmap: Senior I/TAP

Figure 18-4. I/T Availability Profession Roadmap: Consulting I/TAP

Figure 18-5. I/T Availability Profession Roadmap: Senior Consulting I/TAP
4.4.2.2 I/T Availability Profession Disciplines
Careers in the I/T Availability Profession consist of four disciplines:
- I/TAP-Availability Management - Position Concept
The Availability Manager (AM) is a client relationship role
responsible for delivering I/T Availability Management consultancy.
These professionals are accountable for total client satisfaction with
I/T availability management and support. AMs ensure that plans and
strategies are in place to address complex system availability needs
within an account. These plans and strategies include information
system services, client environment, client operations, total system
configuration and change management, all of which contribute to
application availability. Their primary responsibility is to ensure
that the client's overall system availability goals are met.
- I/TAP-Customer Services - Position Concept
The Customer Services Manager (CSM) is a client relationship role,
focused on I/T services, and is a key contributor in maintaining IBM's
presence as the service provider of choice. These professionals are
responsible for growing IBM Services and Availability Services revenue
through the ability to understand the client's industry, business
plans and strategies and to propose IBM solutions which deliver
business benefit to the client. CSMs are accountable for total client
satisfaction with IBM Availability Services.
- I/TAP-Systems Services Representative - Position Concept
The Systems Services Representative (SSR) performs technical service
and/or post sales support for hardware and software products in a
client's I/T environment. The SSR plans for and executes service
activities including systems assurance, installation planning, account
management, system problem determination, discontinuance, relocation,
diagnosis, and repair for IBM and non-IBM systems.
The SSR has the primary responsibility for hardware support. They also
contribute on software service delivery and other Availability
Services client solution engagements. The SSR discipline has six
positions which are described in the "I/TAP Profession Position
Descriptions" section of this chapter.
- I/TAP-Software Systems Specialist - Position Concept
The Software Systems Specialist (SSS) represents IBM software service
to the client and assumes responsibility for client service
satisfaction within the assigned area of responsibility. These
professionals understand the product impact on the client's business
and delivers efficient and effective problem resolution to ensure the
announced service level agreements are met or exceeded.
The SSS provides remote support to both clients and colleagues for
problem determination and resolution and could provide on-site support
to clients for complex support issues as required. The SSS acts as
the escalation point for product issues with the development centers.
Detailed discipline descriptions can be found in "I/TAP Discipline
Position Descriptions" in topic 4.4.11.
4.4.2.3 Discipline Comparison
________________ ________________ ________________ ________________ _______________
| | Availability | Customer | Systems | Software |
| | Management | Services | Services | Systems |
| | | | Representative | Specialist |
|________________|________________|________________|________________|_______________|
| Focus: | I/T Systems | Relationship | Primarily | Primarily |
| | Availability | with Client | HW/SW | Post-Install |
| | Management | Executive | Maintenance | Software |
| | | | Support and | Support |
| | | | Services | |
|________________|________________|________________|________________|_______________|
| | Relationship / | Relationship / | Relationship / | Broad |
| | Consulting IT | Consulting | Performance | Software |
| | Availability | Business | Systems | Support |
| | Perspective | Perspective | Services | Perspective |
| | | | Perspective | |
|________________|________________|________________|________________|_______________|
| | Broad Client | Broad Client | Operational | Operational |
| | Executive | Executive | Client | Software |
| | Interface | Interface | Interface | Client |
| | | | | Interface |
|________________|________________|________________|________________|_______________|
| Key | Client I/T | Services | Client | Client |
| Performance | Systems | Revenue & | Satisfaction | Satisfaction |
| Elements: | Availability | Profit | w/ Operational | w/ Software |
| | | | Support | Support |
|________________|________________|________________|________________|_______________|
| | Client | Client | Service | Service |
| | Satisfaction | Satisfaction | Quality | Quality |
| | w/ I/T Systems | w/ | | |
| | Availability | Availability | | |
| | | Services | | |
|________________|________________|________________|________________|_______________|
| | Client Loyalty | Client Loyalty | Service | Client |
| | | | Expense | Loyalty |
|________________|________________|________________|________________|_______________|
| | Profitability | Profitability | Client Loyalty | |
| | of Systems | of I/T | | |
| | Availability | Services | | |
| | Engagements | Solutions | | |
|________________|________________|________________|________________|_______________|
The above chart compares the focus and key performance elements of the I/T
Availability Profession disciplines.
- Broad Executive Client Interface - Functions as the I/T Executive's
focal point for all of IBM's Availability Services and Solutions.
Pro-actively seeks to understand the client's I/T business issues and
their priority, and recommends appropriate solutions. Teams with
client I/T Management as the person whom they trust to always provide
the right solution for them.
- Consulting Business Perspective - Functions as the I/T Executive, and
operations management focal point for Technical expertise and advice.
Focus on ensuring that plans and strategies are in place to address
complex system needs within a client account.
- System Operational Solutions - Provide via contract, additional
revenue to the IBM business unit through the delivery of end to end,
post sales, operational services to the client.
- System Support - Support activities funded by IBM product divisions
and other IBM units to deliver end to end, post sales, operational
support to the client. This includes software defect support and other
entitled support.
- Broad Perform Business Perspective - Understands client's major
systems, information flow, applications, and relationships with
competition. Understands clients business use of I/T and can
implement operational solutions to support and improve business
posture.
- Broad Operational Client Interface - Single focal point to clients
that provides total systems (HW, SW, Network, Operations) problem
resolution and services solutions. This includes their non-IBM I/T and
overall system direction. Can offer consulting services on post sales
I/T strategy and implementation.
4.4.3 Characteristics of the Profession
- Client contact/exposure
- Professional growth and challenge
- I/TAP-AM builds client relationships based on expert skills in I/T
availability management
- I/TAP-CSM is the single expert interface to clients for
Availability Services satisfaction and revenue growth based on
understanding of the client's business needs
- I/TAP-SSS is the expert interface to clients for Availability
Services Software Support Requirements
- I/TAP-SSR is the expert interface to clients for Availability
Services Hardware and Software Maintenance Requirements.
- You will be a key contributor to the clients value equation which
builds loyalty and satisfaction
- Upward career growth can be realized with opportunity consistent with
senior management positions
- Technical challenge and the opportunity for personal innovation
4.4.4 Potential Candidates
Technical Sources
- I/T Availability Professionals are expected to be sourced from a broad
array of backgrounds with experience in large systems hardware,
software, networks and client environments.
Experience/Ability
- Based on required skills, the closest matches will be found within the
I/T Specialist, SE, CE, PSR, community and other Availability Services
professionals that have current systems technical expertise.
- Candidates should be competent, qualified professionals who can lead
others, communicate effectively, and can build a value-add
relationship with clients.
- Strong account management and project management is essential.
Organizational Sources
- Candidates can be sourced from a wide range of organizations which
provide the background and experiences necessary for this profession.
Figure Figure 18-6 shows possible candidates for the I/T Availability
Profession and possible career movement from an I/T Availability position.
More information on movement from other professions is available in I/T
Availability Career Possibilities.
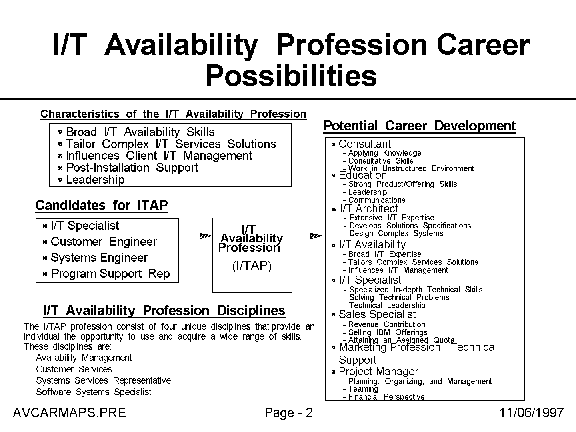
Figure 18-6. I/T Availability Profession Career Possibilities
4.4.5 Career Growth
The migration from traditional career paths to the I/T Availability
Profession opens new growth opportunities for the service and support work
force. Previously, service and support personnel progressed through their
technical career path with somewhat limited opportunity. The typical
growth opportunities were to move into management. These opportunities
were often linked to physical moves, breaks in client continuity and a
change in profession. The I/T Availability Profession provides growth
consistent with management positions for those individuals who prefer
technical challenges in the client environment.
The migration from the traditional career paths into positions in the
I/TAP disciplines will require development of skills and experiences in
preparation for growth and advancement in the I/T Availability Profession.
Entry into the I/T Availability Profession is dependent upon needs of the
business. Advancement into the Consulting and Senior Consulting positions
requires business need and certification of skill and performance levels.
Migration into the I/TAP disciplines can be from existing IBM positions or
disciplines depending on business need and the skills and motivation of
the individual. Primary candidates for the I/TAP disciplines would be
those who currently perform I/T Specialist, SE, CE, or PSR roles.
The I/T Availability Profession provides opportunities for advancement for
those who choose to make a career as an I/TAP. I/TAP also provides a great
foundation of skills for potential career development in other
professions.
As illustrated in Figure 18-6 in topic 4.4.4, some of the professions
available to I/TAPs are: Consultant, Education, I/T Architect, I/T
Specialist, Sales Specialist and Project Manager. Refer to I/T
Availability Career Possibilities for information on making a change from
I/TAP to the other Worldwide Sales and Services Professions.
4.4.6 Certification Nomination Guide
The Consulting and Senior Consulting positions are IBM Certified
positions. For information on I/TAP certification refer to the Worldwide
I/T Availability Certification Nomination Guide.
4.4.7 Performance Elements
- Service Quality - As IBM's quality of service delivered improves, the
results will be displayed through high client satisfaction, increased
loyalty and improved wins versus losses.
- Operational Services Contract Profitability - A key measure of
performance will be the success of the client's operational services
contracts as measured by:
- Contract Profit
- Contract Revenue
- Recovered Cost and Expense (support activities)
- Personal Utilization/Revenue
- Services/Availability Services Revenue and Profit - A key measure of
performance for the I/TAP-CSM will be the success of the client'
availability services contracts renewal and growth measured by:
- Management of service revenue attainment
- Gross profit objectives.
- I/T Systems Availability - A key measure of performance for the
I/TAP-AM will be the attainment of the client's I/T availability goals
as identified by the client.
- Client Satisfaction - Client satisfaction with software service and
support and with operational services provided as measured by
follow-on contracts and survey data.
- Loyalty - Adding value builds client loyalty to IBM, our products and
our services. This profession will be a key contributor to value and
loyalty. The loyalty indicator is our client's renewal decision for
service(s) contracts.
4.4.8 I/T Availability Profession Skills Profile
_______________________________ ________________________________________
| | Profession Positions, with Associated |
| | Skill Levels |
| |________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| I/T AVAILABILITY SKILLS | | | | Cons | |
| | I/T | Adv | Sr | & Sr | Key |
| | Avail | I/T | I/T | Cons | Skill |
| | | Avail | Avail | I/T | |
| | | | | Avail | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| CLIENT ENVIRONMENT |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Client Relationships | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Client Strategy & Planning | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Client Management | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | |
| Systems/Culture | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| BUSINESS ACUMEN |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Market Management | 0 | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Financial Skills | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Consulting Methods | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Value-Add Selling | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| INDUSTRY |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Understand Industry | 0 | 2 | 2 | 3 | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| IBM ENVIRONMENT |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| IBM Organization | 0 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| IBM Vision/Mission/Strategy | 0 | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| IBM Management System | 0 | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| PROJECT MANAGEMENT |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Initiate Projects | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Plan Projects | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Project Track/Report/Deliver | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Manage Project Risk | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| PRODUCTS/TECHNOLOGY/SERVICES |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
| Platforms | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Applications | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Architectures | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Methodologies | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| I/T Related Services | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| PERSONAL |
|_______________________________ ________ _______ _______ _______ _______|
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Leadership | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Communication | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Negotiation | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
| Problem Solving/Decision | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Making | | | | | |
|_______________________________|________|_______|_______|_______|_______|
4.4.9 Professional Development
Growing skills requires a combination of experience, education, training,
coaching and mentoring. These elements are called Skill Development
Activities. Education and training can be separated into several forms
ranging from self study, distance learning, internships, classroom, and
seminars. The integration of these delivery methods can be an efficient
and cost effective way to build your skills. Refer to the Education
Roadmap page of the IEC Course Catalog at
http://w3.lahulpe.ibm.com/roadmaps/index.html for an overview of the
Worldwide Professions and links to the Common Skills Categories and
Professions Roadmaps. Also, refer to the I/T Availability Profession
Skills Development Guide.
4.4.10 I/TAP Profession Position Descriptions
The following position descriptions describe the basic work of each of the
positions within the Professions. Formal descriptions which may contain
legally mandated language necessary for classifying employees in a
geography should be obtained through the approved on-line job library, if
available in the geography, or by contacting the appropriate H.R.
personnel within the geography.
Subtopics:
4.4.10.1 Position Title: I/T Availability Professional
Position Concept:
The I/T Availability Professional is an individual contributor,
representing IBM to clients on all matters concerning the efficient
management of their Information Technology Systems and operations in order
to meet their requirement for access to their business information.
As a member of a team, the I/T Availability Professional is accountable
for client satisfaction with the selection, management and delivery of
Hardware and Software Maintenance, Operations Support Services, and
Business Recovery Services. As a member of a team, the I/TAP, can suggest
plans and strategies to address system needs within the clients I/T
environment.
As a member of a team, the I/T Availability Professional assumes
responsibility for ensuring the effective use of the customers I/T
Resources. The I/TAP is capable of creativity and judgment in their
approach to I/T Services delivery, client environment, client operations,
system configuration and systems management processes and procedures. The
primary responsibility of the I/T Availability Professional is to ensure
that the client achieves benefit from their I/T operations.
This position is capable of analytical ability and creativity in the
development and implementation of plans and solutions to client
requirements and problems. The I/T Availability Professional will use
defined tools, processes, priorities and resources necessary to manage,
analyze design and implement client I/T solutions. This position requires
knowledge of a technology, platform or architecture. The I/T Availability
Professional, participates in projects or programs involving routine
technical or operational activities.
The I/TAP is the entry level to the profession for some disciplines and
presumes skills of a college graduate or equivalent.
Skills
- Possesses an understanding of IBM systems management, operational
services, product technical support functions, service delivery and
offerings associated with these services at department level.
- Generally requires a BA or BS degree or equivalent.
- Draws upon concepts of implementing or supporting I/T services
solutions to collaborate with others to carry out assigned duties.
- Negotiates when required with team members, customer I/T management
other I/T service vendors.
- Recognizes problems which affect implementing or supporting I/T
services solutions.
- Analyses problems using existing tools and methods and support
services.
- Analyzes systems management or systems operational I/T services
solutions and recommends alternatives.
- Challenges the validity of given service delivery agreements and
operational processes in order to enhance and improve benefit to the
client and IBM
Contribution/Leadership
- Works on professional level projects dealing with implementing or
supporting I/T services solutions.
- Work is often reviewed by management and peers for developmental
purposes.
- Understands I/T service delivery issues and trends. Understands role
of the I/T Availability Professional
- May Influence client and team related to systems management,
operational services, technical support and service delivery
solutions.
- May coordinate activities of less experiences I/T Availability
Professionals.
Impact on Business/Job Scope
- Accountable for individual I/T service delivery and services
activities and impact on team results.
- May contribute to business results and measurements.
- May contribute to customer satisfaction with delivered services.
- May supports activities that contribute to I/T services revenue and
business unit objectives for profit, costs and expenses.
4.4.10.2 Position Title: Advisory I/T Availability Professional
Position Concept:
The Advisory I/T Availability Professional is either the individual
contributor, or small team leader which represents IBM to clients on all
matters concerning the efficient management of their Information
Technology Systems and operations in order to meet their requirement for
the continuous access to their business information.
The Advisory I/T Availability Professional is accountable for client
satisfaction with the selection, management and delivery of Hardware and
Software Maintenance, Operations Support Services, and Business Recovery
services. At Advisory I/TAP, the I/T Availability Professional can suggest
and compare plans and strategies to address system needs within the
clients I/T environment.
As leader of a small team, or working independently the Advisory I/T
Availability Professional, assumes Responsibility for the ensuring the
effective use of the customers I/T Resources. The Advisory I/TAP
Professional applies creativity and judgment in their approach to I/T
Services delivery, client environment, client operations, system
configuration and systems management processes and procedures. The primary
responsibility of the I/T Availability Professional is to ensure that the
client achieves benefit from their I/T operations.
This position is capable of analytical ability and creativity in the
development and implementation of plans and solutions to client
requirements and problems. The Advisory I/TAP will use defined tools,
processes, priorities and resources necessary to manage, analyze design
and implement client I/T solutions. The Advisory position requires
significant systems knowledge in a technology, platform or architecture.
The Advisory I/TAP is accountable for projects or programs involving
routine technical or operational activities.
In addition to the attributes of the I/TAP position, typical attributes of
this position include the following:
Skills
- Possesses an understanding of IBM systems management, operational
services, product technical support functions ,service delivery and
offerings associated with these services at department or project
level. Understands the organization and policies concerning the
application of this knowledge in providing service and services
solutions to our clients.
- Works independently in representing clients in all matters related to
I/T services delivery.
- Articulates and compares alternatives to identify the most appropriate
systems management, I/T operations, HW and SW maintenance and recovery
solutions for their clients.
- Negotiates with engagement partners and team members (vendors,
subcontractors, clients, IBMers from other functional areas) to define
the approach and goals to delivery of specific I/T solutions.
- Recognizes potential I/T service and services delivery issues for
their clients that affect the area of systems management, operational
management and technical support which affect project objectives and
recommends appropriate solutions.
- Applies creativity and judgement in implementing or supporting systems
management and systems operational I/T services solutions.
- Independently generates systems management or systems operational I/T
services solutions based on knowledge and analysis of services
offering alternatives.
- Challenges the validity of given service delivery agreements and
operational processes in order to enhance and improve benefit or to
generate complementary benefits or solutions to the client and IBM.
Contribution/Leadership
- Participates on special systems management and operational projects
requiring I/T services and solutions expertise.
- Generally controls the selection of tools, methods, resources
required, the measurements and success criteria to provide contracted
or entitled I/T services and service delivery solutions.
- Understands their department's I/T service delivery issues and trends.
- Provides advice to client and team related to systems management,
operational services, technical support and I/T service solutions.
- Leads small teams which may be involved in identifying the
requirements for, implementing, or supporting I/T services solutions.
- Manages routine technical activities or projects.
Impact on Business/Job Scope
- Accountable for individual, team, or department I/T service delivery
and services activities and impact on results.
- Regularly participates in overall department and/or client planning
for services or service delivery solutions.
- Contributes to business controls and measurements.
- Contributes to client satisfaction with all aspects of delivered
services.
- Supports activities that contribute to I/T services revenue and
business unit objectives for profit, costs and expenses.
- May have budgetary responsibility.
4.4.10.3 Position Title: Senior I/T Availability Professional
Position Concept:
The Senior I/T Availability Professional is either the individual
contributor, or management position which represents IBM to clients on all
matters concerning the efficient management of their Information
Technology Systems and operations in order to meet their requirement for
the highest level of continuous access to their business information.
The Senior I/T Availability Professional is accountable for total client
satisfaction with the selection, management and delivery of Hardware and
Software Maintenance, Operations Support Services, and Business Recovery
Services. The Senior I/TAP guides plans and strategies in place to address
complex system needs within the clients I/T environment within business
unit cost and expense guidelines.
As a manager, team leader, or working independently the I/T Availability
Professional guides other professionals and assumes overall IBM
responsibility for ensuring the effective use of the customers I/T
resources. This includes development of strategies on I/T services
delivery, client environment, client operations, system configuration and
systems management processes and procedures. The primary responsibility of
the I/T Availability Professional is to ensure that the client achieves
maximum benefit from their I/T operations.
This position requires analytical ability and creativity in the
development and implementation of plans and solutions to client
requirements and problems. The I/T Availability Professional has
considerable latitude and responsibility to define and decide on tools,
processes priorities and resources necessary to manage, analyze design and
implement client I/T solutions. The Senior I/TAP position requires
significant systems knowledge across multiple technology platforms and
architectures. The senior position is accountable for projects or programs
involving multi-functional, and business unit teams.
In addition to the attributes of the Advisory I/TAP position, typical
attributes of this position include the following:
Skills
- Possesses a full understanding of IBM systems management, operational
services, product technical support functions ,service delivery and
offerings associated with these services at the regional or business
unit functional level. Possesses full understanding of the
organization and policies concerning the application of this knowledge
in providing service and services solutions to our clients.
- Advises others involved in many aspects of I/T services on I/T
services issues and customer relationships in the I/T services area.
- Incorporates input of team members in area of I/T services delivery
implementation.
- Negotiates with engagement partners and team members (vendors,
subcontractors, customers, IBMers from other functional areas) to
ensure quality delivery of I/T services and I/T solutions to their
clients.
- Recognizes potential complex I/T service and services delivery issues
for their clients that affect areas of systems management, or
operational management, or technical support.
- Applies creativity and judgement in developing systems management or
systems operational I/T services solutions.
- Analyzes client I/T operations and implements systems management or
systems operational I/T services solutions. Provides input, where
appropriate, in the development of new elements of I/T services
solutions.
Contribution/Leadership
- Initiates activities in I/T services solutions, new technologies, the
use of business partners, incorporating multi-vendor's solutions and
other special systems management and operational projects.
- Defines the required tools, methods, and other resources required to
meet client I/T solution needs. Decides on measurements, success
criteria to provide contracted or entitled I/T services and service
delivery solutions.
- Understands I/T service delivery issues and trends. Understands
services business strategy to influence product selection and short
and long term planning, and resources.
- Provides technical guidance to lead client and IBM teams and
organizations on complex issues related to systems management,
operational services, technical support and service delivery
solutions.
- Influences client product or service selection, short and long term
planning and resources for I/T service delivery issues, systems
management or product installation and operations issues.
- May discharge the basic management responsibilities common to all IBM
managers.
Impact on Business/Job Scope
- Accountable for I/T service delivery and services activities which
meet client requirements for local account or teams led.
- Regularly participates in overall IBM and/or client planning for
services or service delivery solutions.
- Maintains proper business controls and measurements.
- Fully responsible for customer satisfaction with all aspects of
delivered services by serving as the customer focal-point for all IBM
IT Services.
- Responsible for maintaining or contributing to I/T services revenue
while meeting or exceeding business unit objectives for profit, costs
and expenses.
4.4.10.4 Position Title: Consulting I/T Availability Professional
Position Concept:
The Consulting I/T Availability Professional is either the lead individual
contributor, certified or management position which represents IBM to
clients on all matters concerning the efficient management of their
Information Technology Systems and operations in order to meet their
requirement for the highest level of continuous access to their business
information.
The Consulting I/T Availability Professional is accountable for total
client satisfaction with the selection, management and delivery of
Hardware and Software Maintenance, Operations Support Services, and
Business Recovery Services. The Consulting I/TAP influences plans and
strategies to address complex system needs within the client's I/T
environment which spans regional or country wide operational teams.
As a manager, Key member of a team, team leader, or working independently
the I/T Availability Professional guides other professionals and assumes
overall IBM Responsibility for the ensuring the effective use of the
customers I/T Resources This includes development of strategies on I/T
services delivery, client environment, client operations, system
configuration and systems management processes and procedures. The primary
responsibility of the I/T Availability Professional is to ensure that the
client achieves maximum benefit from their I/T operations.
This position requires a high degree of analytical ability and creativity
in the development and implementation of plans and solutions to client
requirements and problems. The I/T Availability Professional has
considerable latitude and responsibility to define and decide on tools,
processes priorities and resources necessary to manage, analyze design and
implement general business unit directives. The Consulting position
requires expert systems knowledge across multiple technology platforms and
architectures. The I/T Availability Professional is accountable for
project or programs involving multi-functional, country-wide, or regional
teams.
In addition to the attributes of the Senior I/TAP position, typical
attributes of this position include the following:
Skills
- Possesses a full understanding of IBM systems management, operational
services, product technical support functions ,service delivery and
offerings associated with these services at the regional or country
functional level. Possesses full understanding of the organization and
policies concerning the application of this knowledge in providing
service and services solutions to our clients.
- Highly skilled in identifying, coordinating and prioritizing IBM
resources in order to provide the full range services delivery and
support solutions to their customers.
- Serves as a mentor others who are involved in all aspects of I/T
services delivery. Provides guidance to team members in area of I/T
services delivery implementation.
- Leads negotiations with engagement partners and team members (vendors,
subcontractors, customers, IBMers from other functional areas) to
ensure quality delivery of service and I/T solutions for their
customers.
- Is fully capable of anticipating potential I/T service delivery issues
for their customers. Selects, tailors and applies formal or informal
methods to understand future customer, industry and information
technology trends affecting the area of systems management,
operational management and technical support.
- Expert in assessing the impact of implementing services solutions.
Takes the lead in managing the risks associated with the plan for the
solutions to be implemented including the impact on client I/T
operations
- Demonstrates a high degree of skill for analyzing new and complex
systems management and systems operational I/T services issues and
managing their resolution.
- Takes a lead role in managing and coordinating the implementation of
systems management and systems operational I/T services solutions and
provides expert guidance to the implementation team. Provides input,
where appropriate, in the development of new solutions for their
customers.
Contribution/Leadership
- Initiates activities in I/T services solutions, new technologies, the
use of business partners, incorporating multi-vendor's solutions and
other special systems management and operational projects.
- Owns the responsibility to decide on the tools, methods, and other
resources, within their business units objectives. Decides on
measurements, success criteria and resource staffing to provide
contracted or entitled I/T services and service delivery solutions.
- Exhibits strategic vision regarding I/T service delivery issues and
trends and is a leader in applying vision in engagements. Understands
services business strategy to influence product selection and short
and long term planning, and resources.
- Highly skilled in influencing people and organizations, including
client and IBM executive management, on complex issues related to
systems management, operational services, technical support and
service delivery solutions with their client and IBM management.
Requires diplomacy in dealing with difficult customer issues.
- Recognized expert in evaluating I/T organizations to understand
customer I/T service delivery issues, systems management or product
installation and operations issues. Prioritizes and recommends
appropriate solutions.
- May discharge the basic management responsibilities common to all IBM
managers.
- Leads solution delivery teams and gets commitment of needed resources
and effectively applies the expertise of team members including IBM,
client and complementary resources to provide I/T services solutions.
Impact on Business/Job Scope
- Manages I/T service delivery and services activities for local and
national accounts.
- Responsible for identifying, developing, implementing and supporting
Services solutions.
- Maintains proper business controls and measurements.
- Fully responsible for customer satisfaction with all aspects of
delivered services by serving as the customer focal-point for all IBM
IT Services.
- Responsible for maintaining or contributing to I/T services revenue
while meeting or exceeding business unit or country level objectives
for profit, costs and expenses.
4.4.10.5 Position Title: Senior Consulting I/T Availability Professional
Position Concept:
The Senior Consulting I/T Availability Professional is the lead individual
contributor, certified or management position which represents IBM to
clients on all matters concerning the efficient management of their
Information Technology Systems and operations in order to meet their
requirement for the highest level of continuous access to their business
information.
The Senior Consulting I/TAP Availability Professional is accountable for
total client satisfaction with the selection, management and delivery of
Hardware and Software Maintenance, Operation Support Services, and
Business Recovery services in leading edge or critical client I/T
environments. The Senior Consulting I/TAP influences plans and strategies
to address critical system needs within the clients I/T environment which
spans regional or major country or international operational teams and
projects.
As a manager, key member of a team, team leader, or working independently
the I/T Availability Professional guides other professionals and assumes
overall IBM Responsibility for ensuring the effective use of the
customer's I/T Resources. This includes development of strategies on I/T
services delivery, client environment, client operations, system
configuration and systems management processes and procedures on highly
visible projects. The primary responsibility of the I/T Availability
Professional is to ensure that the client achieves maximum benefit from
their I/T operations.
This position requires a very high degree of analytical ability and
creativity in the development and implementation of visionary plans and
solutions to complex, leading edge and critical client requirements and
problems. The I/T Availability Professional has considerable latitude and
responsibility to define and decide on tools, processes priorities and
resources necessary to manage, analyze design and implement general
business unit directives. The Senior Consulting position requires expert
systems knowledge across multiple technology platforms and architectures.
The Senior Consulting I/TAP is often responsible for developing new
business opportunity and is recognized as an senior expert by members of a
related function and multi-country organizations. The I/T Availability
Professional is accountable for project or programs involving
multi-functional, country-wide, regional teams and international teams.
In addition to the attributes of the Consulting I/TAP position, typical
attributes of this position include the following:
Skills
- Applies professional mastery to IBM systems management, operational
services, product technical support functions ,service delivery and
offerings associated with these services at the regional, country or
international functional level. Possesses full understanding of the
organization and policies concerning the application of this knowledge
in providing service and services of strategic significance to our
clients, business unit, or country objectives.
- Fosters and engages in teamwork at the highest management and
technical levels including IBM management, customer executives and
vendor management in the area of I/T services delivery implementation.
- Leads negotiations which result in lasting agreements and commitments
with engagement partners and team members (vendors, subcontractors,
customers, IBMers from other functional areas) to ensure quality
delivery of service and I/T solutions for their customers.
- Anticipating creates and designs formal or informal methods to address
visionary or strategic trends in information technology affecting the
area of systems management, operational management and technical
support.
- Takes a lead role in managing and coordinating the implementation of
systems management and systems operational I/T services solutions and
provides expert guidance to the implementation team. Provides input,
where appropriate, in the development of new solutions for their
customers. Guides market selection, business strategies with executive
level review.
Contribution/Leadership
- Exhibits strategic vision regarding global service line business
strategies with I/T service delivery issues and trends and is a leader
in applying vision in engagements.
- Recognized expert by peers, multi-country organizations, client,
vendor and subcontractors in evaluating I/T organizations to
understand customer I/T service delivery issues, systems management or
product installation and operations issues. Prioritizes and recommends
appropriate solutions.
- May manage IBM I/T services groups or departments with people
responsibilities.
- Leads business unit, country or international strategic delivery teams
in marketing, developing, implementing, or supporting service
delivery, systems management and operation support service solutions.
Impact on Business/Job Scope
- Manages I/T service delivery and services activities for local,
national or international accounts.
- Develops and implements strategic technology strategies for clients
with executive review.
- Responsible for contributing to policy making in the areas of I/T
services based on identified trends and market segments for I/T
services and solutions.
- Is responsible for committing multiple resources and achieving
customer satisfaction, cost, expense, revenue and other business
measurements of critical importance.
- Responsible for maintaining IBM as the services vendor of choice
through value add/quality output on highly visible services and future
business development.
4.4.11 I/TAP Discipline Position Descriptions
The I/T Availability Profession consists of four unique disciplines:
- I/TAP - Availability Management
- I/TAP - Customer Services
- I/TAP - Systems Services Representative
- I/TAP - Software Systems Specialist
Each discipline has positions with unique responsibilities. A summary of
each position for all four I/TAP disciplines is described below.
Subtopics:
4.4.11.1 Advisory I/TAP-Availability Manager (AM)
Position Summary and Responsibilities
The I/T Availability Profession-Availability Manager Advisory position
represents IBM to clients on all matters concerning Systems Availability.
The Advisory Availability Manager contributes to client satisfaction with
system availability support. At the Advisory position, the Availability
Manager recognizes complex problems affecting IT availability within the
clients environment.
As a key member of a team, leader of a small team, or working
independently the Availability Manager can articulate and compare
alternative approaches in assuming some responsibility for system
availability planning and operations for their clients. This includes
participating in the development of strategies on I/T Services, client
environment, client operations, system configuration and systems
management processes and procedures. The primary responsibility of the
Availability Manager is to contribute to attaining the clients system
availability goals.
This position requires some degree of analytical ability and creativity in
the development and implementation of plans and solutions to client
requirements and problems. The Availability Manager at the Advisory
position generally controls their own work responsibilities using their
own methods and can work on special projects. The Advisory position
requires systems management knowledge across multiple platforms and
architectures. The Availability Manager is accountable for individual,
team or local department program results.
This position is the entry position for the I/TAP-AM.
For detailed skill requirements for this position, please refer to the
Advisory I/TAP-Availability Manager skills template in the SKILLS tool.
4.4.11.2 Senior I/TAP-Availability Manager (AM)
Position Summary and Responsibilities
The I/T Availability Profession-Availability Manager at the Senior
position represents IBM to clients on all matters concerning Systems
Availability. The Senior Availability Manager is accountable for total
client satisfaction with system availability support. At the Senior
position, the Availability Manager ensures that plans and strategies are
in place to address complex system needs within the clients I/T
environment.
As a manager, key member of a team, team leader, or working independently
the Availability Manager advises other professionals and effectively uses
group dynamics in assuming overall IBM Responsibility for system
availability planning and operations for their clients. This includes
participating in the development of strategies on I/T Services, client
environment, client operations, system configuration and systems
management processes and procedures. The primary responsibility of the
Availability Manager is to ensure that the clients overall system
availability goals are met.
This position requires a high degree of analytical ability and creativity
in the development and implementation of plans and solutions to client
requirements and problems. The Senior Availability Manager defines and
decides objectives within a business concept and may have responsibility
for tools and assigned resources required to conduct special projects. The
Senior position requires expert systems management knowledge across
multiple platforms and architectures. The Availability Manager is
accountable for local business unit programs involving multi-functional,
teams.
For detailed skill requirements for this position, please refer to the
Senior I/TAP-Availability Manager skills template in the SKILLS tool.
4.4.11.3 Consulting I/TAP-Availability Manager (AM)
Position Summary and Responsibilities
The I/T Availability Profession-Availability Manager at the Consulting
position represents IBM to clients on all matters concerning Systems
Availability. The Consulting Availability Manager is accountable for
total client satisfaction with system availability support. At the
Consulting position, the Availability Manager ensures that plans and
strategies are in place to address complex system needs within the clients
I/T environment.
As a manager, key member of a team, team leader, or working independently
the Availability Manager guides other professionals and assumes overall
IBM Responsibility for system availability planning and operations for
their clients. This includes development of strategies on I/T Services,
client environment, client operations, system configuration and systems
management processes and procedures. The primary responsibility of the
Availability Manager is to ensure that the clients overall system
availability goals are met.
This position requires a high degree of analytical ability and creativity
in the development and implementation of plans and solutions to client
requirements and problems. The Consulting Availability Manager has
considerable latitude and responsibility to define and decide on tools,
processes priorities and resources necessary to manage, analyze design and
implement general business unit directives. The Consulting position
requires expert systems management knowledge across multiple platforms and
architectures. The Availability Manager is accountable for project or
programs involving multi-functional, country-wide, or regional teams.
For detailed skill requirements for this position, please refer to the
Consulting I/TAP-Availability Manager skills template in the SKILLS tool.
4.4.11.4 Senior Consulting I/TAP-Availability Manager (AM)
Position Summary and Responsibilities
The I/T Availability Profession-Availability Manager at the Senior
Consulting position represents IBM to clients on all matters concerning
Systems Availability. They have mastered the skill of managing IT
availability for their clients and have mastered the business unit or
country operations, strategies and objectives in leading-edge critical
situations. They anticipate, create, and define innovative and visionary
concepts and can reach lasting agreements during complex negotiations.
With a vision of overall IT services strategies, the Senior I/TAP-AM
manages IT services departments, business units, country or global teams.
They are responsible for quality output and value-add for highly visible
IT availability management services solutions and contribute to policy
making for IT services.
The I/TAP-AM at the Senior Consulting position is responsible for
committing multiple resource and achieving customer satisfaction, cost,
expense, revenue and other IT availability management services business
objectives for a business unit, country or global programs and projects.
For detailed skill requirements for this position, please refer to the
Senior Consulting I/TAP-Availability Manager skills template in the SKILLS
tool.
4.4.11.5 Advisory I/TAP-Customer Services Manager (CSM)
Position Summary and Responsibilities
The I/TAP-Customer Services Manager at the Advisory position is
responsible for contributing to IBM services revenue. As a member of the
client relationship team and with a focus on IT services, they establish
and sustain credible relationships with client IT executives which result
in opportunities to place IT services solutions in their accounts.
With a professional knowledge of their client's IT environment, they
independently can recognize problems and proactively apply creativity and
judgement to assess opportunities for placing IT services solutions.
They can work on special projects and generally control their own work
priorities and methods when identifying client IT services needs. The
Advisory I/TAP-CSM provides IT services advice to others and can lead
small IT services teams when placing IT services solutions with their
clients. They manage routine IT services activities.
They are responsible for generating IT services revenue while maintaining
the business unit's objectives for profit, costs and expenses and are key
contributors to client satisfaction with all functions of IBM's
Availability Services.
This position is the entry position for the I/TAP-CSM.
For detailed skill requirements for this position, please refer to the
Advisory I/TAP-Customer Services Manager skills template in the SKILLS
tool.
4.4.11.6 Senior I/TAP-Customer Services Manager (CSM)
Position Summary and Responsibilities
The I/TAP-Customer Services Manager at the Senior position is responsible
for contributing to IBM services revenue. As a member of the client
relationship team and with a focus on IT services, they establish and
sustain credible relationships with client IT executives which result in
opportunities to place IT services solutions in their accounts.
With a professional knowledge of their client's IT environment and local
business unit processes, they can recognize complex problems and
proactively apply creativity and judgement to assess opportunities for
placing IT services solutions.
They can conduct special projects and define and decide on priorities and
objectives when identifying client needs. The Senior I/TAP-CSM provides
on-going IT services guidance to others and directly influences people
outside IT services when placing IT services solutions with their clients.
They may have department management responsibilities or lead
multi-functional teams who are experts in areas outside of their own.
They are responsible for generating IT services revenue while maintaining
the business unit's objectives for profit, costs and expenses and are
fully responsible for client satisfaction with all functions of IBM's
Availability Services.
For detailed skill requirements for this position, please refer to the
Senior I/TAP-Customer Services Manager skills template in the SKILLS tool.
4.4.11.7 Consulting I/TAP-Customer Services Manager (CSM)
Position Summary and Responsibilities
The I/TAP-Customer Services Manager at the Consulting position is
responsible for contributing to IBM services revenue. As a member of the
client relationship team and with a focus on IT services, they establish
and sustain credible relationships with client IT executives which result
in opportunities to place IT services solutions in their accounts.
With a professional knowledge of their client's IT environment and local
business unit or country operations, they proactively analyze complex/new
IT services situations and assess opportunities, impacts and risks for
placing IT services solutions.
They can conduct special projects with considerable latitude in
responsibilities to define and decide on priorities, processes and
resources within their business unit or country objectives. The Consulting
I/TAP-CSM is recognized as the expert for identifying opportunities for
placing IT services solutions with clients and possess vision regarding IT
service delivery issues and trends. They may have department management
responsibilities or lead multi-functional teams who are experts in areas
outside of their own.
They are responsible for generating IT services revenue while maintaining
the business unit's objectives for profit, costs and expenses and are
fully responsible for client satisfaction with all functions of IBM's
Availability Services.
For detailed skill requirements for this position, please refer to the
Consulting I/TAP-Customer Services Manager skills template in the SKILLS
tool.
4.4.11.8 Senior Consulting I/TAP-Customer Services Manager (CSM)
Position Summary and Responsibilities
The I/TAP-Customer Services Manager at the Senior Consulting position is
responsible for contributing to IBM services revenue. As a member of the
client relationship team and with a focus on IT services, they establish
and sustain credible relationships with client IT executives which result
in opportunities to place IT services solutions in their accounts.
They have mastered the skill of identifying and placing IT services
solutions for their clients and have mastered the business unit or country
operations, strategies and objectives in leading-edge critical situations.
They anticipate, create, and define innovative and visionary concepts and
can reach lasting agreements during complex negotiations.
With a vision of overall IT services strategies, the Senior Consulting
I/TAP-CSM at manages IT services departments, business units, country or
global teams. They are responsible for quality output and value-add for
highly visible IT services solutions and contribute to policy making for
IT services.
The I/TAP-CSM at the Senior Consulting position is responsible for
committing multiple resource and achieving customer satisfaction, cost,
expense, revenue and other IT services business objectives for a business
unit, country or global programs and projects.
For detailed skill requirements for this position, please refer to the
Senior Consulting I/TAP-Customer Services Manager skills template in the
SKILLS tool.
4.4.11.9 Entry I/TAP-Systems Services Representative (SSR)
Position Summary and Responsibilities
The Entry System Services Representative (SSR) is primarily responsible to
assist in post sale maintenance of IBM equipment in customer accounts.
The Entry SSR possesses the knowledge and training necessary to perform as
an electronics technician prior to becoming an SSR. The Entry SSR acts as
a technical interface to customers for hardware support and the delivery
of operational services as required by the customer.
The Entry SSR performs technical service and/or post sale support for
hardware. Assists in services activities including systems assurance,
installation team, account management, basic problem determination,
discontinuance and relocation for IBM and non-IBM systems.
The Entry SSR using established and varied techniques and procedures
performs basic problem determination and problem solving to resolve
customer hardware and software operational situations.
The Entry SSR has a basic understanding of and is able to articulate IBM's
technical support delivery methodology, particularly, as it relates to
base and enhanced support.
For detailed skill requirements for this position, please refer to the
Entry I/TAP-Systems Services Representative skills template in the SKILLS
tool.
4.4.11.10 Base I/TAP-Systems Services Representative (SSR)
Position Summary and Responsibilities
The Base Systems Services Representative (SSR) is primarily responsible
for the post sale maintenance of IBM hardware and software in customer
accounts. The Base SSR is assigned to accounts for system support and
acts as a technical interface to customers for hardware and software
support and the delivery of services as required by the customer.
The Base SSR will spend a majority of their time working on hardware
related issues using problem analysis and problem solving skills for the
identification and resolution of hardware situations in the customer
environment. May assist in the resolution of software and operational
situations. The Base SSR performs hardware and software services
activities including systems assurance, installation planning, account
management, systems problem determination, discontinuances, relocation,
diagnosis, etc., for IBM and non-IBM systems.
In general, the Base SSR assumes responsibility for developing positive e
relationships with customer management and staff to ensure a high level of
overall customer satisfaction in all assigned accounts. Specifically,
ensures a high level of customer satisfaction with technical support and
operational services.
The Base SSR has a significant understanding of and is able to articulate
IBM's technical support delivery methodology, particularly, as it relates
to base and enhanced support. Responsible for the technical value
relationship by providing technical expertise to protect revenue base and
generate new services business. For detailed skill requirements for this
position, please refer to the Base I/TAP-Systems Services Representative
skills template in the SKILLS tool.
4.4.11.11 Account I/TAP-Systems Services Representative (SSR)
Position Summary and Responsibilities
The Account Systems Services Representative (SSR) is primarily responsible
for the post sale maintenance of IBM equipment in customer accounts. The
Account SSR is assigned to provide accounts with total systems support.
Acts as the primary technical interface to customers for hardware and
software technical support as required by the customer.
The Account SSR uses advanced technical expertise to conduct problem
analysis and problem solving to identify and resolve complex system
hardware and software operational situations. Gives technical assistance
and advice to lesser experienced personnel. The Account SSR plans for and
executes hardware and assists in software services activities including
systems assurance, installation planning, account management, systems
problem determination, discontinuances, relocation, diagnosis, etc., for
IBM and non-IBM systems. The Account SSR acts as the local technical
expert for complex hardware situations.
In general, the Account SSR assumes the responsibility for developing
positive relationships with customer management and staff to ensure a high
level of overall customer satisfaction in all assigned accounts.
Specifically, ensures a high level of customer satisfaction with technical
support and operational services.
The Account SSR has a thorough understanding of and is able to articulate
IBM's technical support strategy, particularly, as it relates to base and
enhanced support. Responsible for the technical value relationship by
providing expertise to protect revenue base and identify new services
opportunities.
For detailed skill requirements for this position, please refer to the
Account I/TAP-Systems Services Representative skills template in the
SKILLS tool.
4.4.11.12 I/TAP Systems Services Representative (SSR)
Position Summary and Responsibilities
The Systems Services Representative (SSR) is an individual contributor
assigned to accounts representing IBM to clients on all matters concerning
the efficient management of their Information Technology Systems and
operations in order to meet their requirement for access to their business
information. Is the primary technical interface to customers for the
coordination of hardware and software support and delivery of operational
services as required by the customer.
As a member of a team, the SSR is accountable for client satisfaction with
the selection, management and delivery of hardware and software
maintenance and operations support services. As a member of a team, the
SSR can suggest plans and methodologies to address system needs within the
client's I/T environment. In general, the SSR assumes responsibility for
developing positive relationships with customer management and staff to
ensure a high level of overall customer satisfaction in all assigned
accounts. Specifically, ensures a high level of customer satisfaction
with technical support and operational services.
The SSR utilizes analytical ability and creativity in the development and
implementation of plans and solutions to client requirements and problems.
On occasion, and, as necessary but not as primary part of job, uses
defined tools, processes, priorities and resources necessary to analyze,
design and implement technical support for client I/T solutions. The SSR
requires knowledge of a technology, platform or architecture. The SSR
participates in projects or programs for planning routine technical and/or
operational services activities.
The SSR has an understanding of and articulates IBM's technical support
strategy, particularly, as it relates to base and enhanced support.
Responsible for the value of the technical relationship by providing
expertise to protect the existing revenue base and generate new services
business. Generally requires theoretical or conceptual knowledge
typically gained through education resulting in a Bachelors Degree or the
equivalent in experience.
The nature of the SSR position takes on a professional/administrative
aspect while requiring carry over of some of the skills from previous SSR
positions.
For detailed skill requirements for this position, please refer to the
Professional I/TAP-Systems Services Representative skills template in the
SKILLS tool.
4.4.11.13 Advisory I/TAP Systems Services Representative (SSR)
Position Summary and Responsibilities
The Advisory Systems Services Representative (SSR) is either the
individual contributor or small team leader who represents IBM to clients
on matters concerning the availability of their Information/Technology
systems and operations in order to meet their requirement for continuous
access to their business information. Is the primary technical interface
to customers for the delivery of technical support and operational
services required by the customer.
As leader of a small team or working independently, the Advisory SSR
assumes responsibility for ensuring the effective use of the customer's
I/T resources. The Advisory SSR applies creativity and judgment in his/
her approach to I/T services delivery, client environment, client
operations, system configuration and systems management processes and
procedures. The primary responsibility of the Advisory SSR is to ensure
that the client achieves benefit from their I/T operations.
In general, the Advisory SSR assumes total responsibility for developing
positive relationships with customer management and staff to ensure a high
level of overall customer satisfaction in all assigned accounts.
Specifically, ensure a high level of customer satisfaction with technical
support and operational services.
The Advisory SSR has analytical ability and creativity in the development
and implementation of plans and solutions to client requirements and
problems. The Advisory SSR is required to have significant systems
knowledge in a technology, platform or architecture. The Advisory SSR is
accountable for projects or programs involving technical or operational
activities. The Advisory SSR will, on occasion and as necessary, act as
an advisor on complex system problems guiding the use of resources in the
use of defined tools processes and priorities necessary to analyze,
diagnose and implement solutions for client I/T issues.
The Advisory SSR has a full understanding of and is able to articulate and
educate others about IBM's technical support strategy, particularly as it
relates to base and enhanced support. Responsible for the technical value
relationship by providing expertise to protect revenue base and generate
new services business.
For detailed skill requirements for this position, please refer to the
Advisory I/TAP-Systems Services Representative skills template in the
SKILLS tool.
4.4.11.14 Senior Professional I/TAP Systems Services Representative (SSR)
Position Summary and Responsibilities
The Senior Professional Systems Services Representative (SSR) is assigned
to geographic/platform territory to provide coordination of skills for a
team of systems services representatives. The Senior SSR uses extensive
systems knowledge to assign territories, make backup assignments and
assist or lead in the planning of complex system hardware/software
changes, install/discontinuance, MES or services activities. Represents
IBM to clients on all matters concerning the efficient management of
their Information/Technology Systems and operations in order to meet their
requirement for the highest level of continuous access to their business
information.
The Senior SSR keeps the team abreast of the technical business
measurements and assumes the total responsibility for them by providing
day to day technical work direction and coordination for all SSR members
in their assigned or associated SSR team.
As a team leader or working independently, the Senior SSR guides other
professionals and assumes overall IBM responsibility for ensuring the
effective use of the customer's I/T resources. This includes development
of strategies on I/T services delivery, client environment, client
operations, system configuration and systems management processes and
procedures. The primary responsibility of the Senior SSR is to ensure
that the client achieves maximum benefit from their I/T operations.
This position requires analytical ability and creativity in the
development and implementation of plans and solutions to client
requirements and problems. The Senior SSR has considerable latitude and
responsibility to define and decide on tools, processes, priorities and
resources necessary to manage, analyze design and implement client I/T
technical support solutions. The Senior SSR is required to possess
significant systems knowledge across multiple technology platforms and
architectures. The SSR at Senior is accountable for projects or programs
involving multi-functional and business unit teams.
In general, the Senior SSR assumes total responsibility for developing
positive relationships with customer management and staff to ensure a high
level of overall customer satisfaction in all team accounts.
Specifically, ensures a high level of customer satisfaction with technical
support and operational services.
The Senior SSR has an advanced understanding of and is able to articulate
and educate others about IBM's technical support strategy, particularly,
as it relates to base and enhanced support. Responsible for the technical
value relationship by providing expertise to protect revenue base and
generate new services business.
For detailed skill requirements for this position, please refer to the
Senior I/TAP-Systems Services Representative skills template in the SKILLS
tool.
4.4.11.15 I/TAP-Systems Software Specialist (SSS)
Position Summary and Responsibilities
The I/TAP SSS is primarily responsible for the software support and
associated services in customer accounts. They are required to
participate in IBM's 24 hour continuous support commitment to its
customers. They are usually based in a center, but may be required to
undertake travel and nights away in the delivery of on-site support and
service.
The I/TAP SSS provides accounts with total systems software support in
assigned areas. They will be the primary technical interface to customers
for software support and the delivery of operational services as required
by the customer. The I/TAP SSS is expected to conduct problem analysis
and problem solving with skills which allows for the identification and
resolution of software problems and operational issues.
The I/TAP SSS plans for and executes software services activities
including installation planning, account management, systems problem
determination, diagnosis, etc. for IBM and selected non-IBM systems. In
general the I/TAP SSS assumes total responsibility for developing positive
relationships with customer management and staff to ensure a high level of
overall customer satisfaction in all assigned areas. Specifically, ensure
a high level of customer satisfaction with software support and
operational services.
The I/TAP SSS needs to have a complete understanding of, and to be able to
articulate IBM's technical support strategy, particularly, as it relates
to the various levels of software support. Responsible for the technical
value relationship by providing expertise to protect revenue base and
generate new services business.
This position is the entry position for the I/TAP-SSS.
For detailed skill requirements for this position, please refer to the
I/TAP-Systems Software Specialist skills template in the SKILLS tool.
4.4.11.16 Advisory I/TAP-Systems Software Specialist (SSS)
Position Summary and Responsibilities
The Advisory I/TAP SSS is primarily responsible for the software support
and associated services in customer accounts. They are required to
participate in IBM's 24 hour continuous support commitment to its
customers. They are usually based in a center, but may be required to
undertake travel and nights away in the delivery of on-site support and
service.
The Advisory I/TAP SSS provides accounts with total systems software
support in assigned areas. May function independently with minimal
direction, or may provide work direction to less experienced personnel.
The Advisory I/TAP SSS is expected to have a high level of problem
analysis and problem solving skills which allows for the identification
and resolution of software problems and operational issues.
The Advisory I/TAP SSS plans for and executes software services activities
including installation planning, account management, systems problem
determination, diagnosis, etc. for IBM and selected non-IBM systems. In
general the Advisory I/TAP SSS assumes total responsibility for developing
positive relationships with customer management and staff to ensure a high
level of overall customer satisfaction in all assigned areas.
Specifically, ensures a high level of customer satisfaction with software
support and operational services.
The Advisory I/TAP SSS needs to have a complete understanding of, and be
able to articulate IBM's technical support strategy, particularly as it
relates to the various levels of software support. Responsible for the
technical value relationship by providing expertise to protect revenue
base and generate new services business.
For detailed skill requirements for this position, please refer to the
Advisory I/TAP-Systems Software Specialist skills template in the SKILLS
tool.
4.4.11.17 Senior I/TAP-Systems Software Specialist (SSS)
Position Summary and Responsibilities
The Senior I/TAP SSS is primarily responsible for the software support and
associated services in customer accounts. They are required to
participate in IBM's 24 hour continuous support commitment to its
customers. They are usually based in a center, but may be required to
undertake travel and nights away in the delivery of on-site support and
service.
The Senior I/TAP SSS functions independently with minimal direction. They
provide accounts with total systems software support in assigned areas and
direct and coordinate the skills of a team of less experienced personnel.
The Senior I/TAP SSS is expected to make use of an extensive background in
systems and problem determination to lead in the planning of complex
system software problem resolution, installations, changes, upgrades and
services activities for IBM and selected non-IBM systems.
The Senior I/TAP SSS keeps their team abreast of the technical business
measurements and assumes the total responsibility for them by providing
day-to-day technical work direction and coordination for all members of
their assigned team. In general the Senior I/TAP SSS assumes total
responsibility for developing positive relationships with customer
management and staff to ensure a high level of overall customer
satisfaction in all assigned areas. Specifically, ensures a high level of
customer satisfaction with software support and operational services.
The Senior I/TAP SSS needs to have a complete understanding of, and to be
able to articulate and educate others on, IBM's technical support
strategy, particularly as it relates to the various levels of software
support. Responsible for the technical value relationship by providing
expertise to protect revenue base and generate new services business.
For detailed skill requirements for this position, please refer to the
Senior I/TAP-Systems Software Specialist skills template in the SKILLS
tool.
4.5 Chapter 19. I/T Specialist Profession
Subtopics:
4.5.1 I/T Specialist Profession Overview
The I/T Specialist profession supports solution construction,
implementation, and systems integration in a Technology, Industry or
Business specialty. The I/T Specialist is proficient in a specialty and
is capable of working with requirements, design, implementation and
production projects and engagements. Depending on their organization or
role, the I/T Specialist either performs services for fee or provides
technical support for product sales.
Subtopics:
4.5.1.1 Role of the I/T Specialist
I/T Specialists deliver high quality solutions to clients in response to
varying business requirements. They utilize product, technology, industry
and business skills. The I/T Specialist often uses tools to manage,
analyze, design and implement. The I/T Specialist has an in-depth
understanding of products, offerings and services within their specialty.
Currently, I/T Specialists are deployed in sales, services, industry,
manufacturing and development, and internal I/T organizations. Across
these organizations, two broad categories of I/T Specialists are defined:
- I/T Specialists primarily applying their technical skills in a
customer fee services and implementation environment. Where it is
required to specifically address these professionals we will use the
term "I/T Specialist - Services".
- I/T Specialists primarily applying their technical skills to support
the sales of IBM products. Where it is required to specifically
address these professionals we will use the term "I/T Specialist -
Technical Support."
Although it is necessary to make this distinction, both of these
categories are considered part of the same overall profession due to the
fact that, in the main, they utilize similar technical and professional
skills. However, it is also recognized that they both require specific
skills related to their deployment. The technical support and services
activities apply for all of the I/T specialist disciplines except
Customized Operational Services (COS), which is services only.
The major responsibilities of the I/T Specialist may include:
- Performing tasks to support activities in such areas as:
- Product and services proposal preparation
- Product support and installation
- Application development
- Network Management
- Performance tuning
- Industry Solutions
- Education
- Client/Server distributed systems
- Migrations and conversions
- Customized Operational Services
- Consulting practice support
- Systems Management
- Systems Integration
- Prototyping/Proof of Concept
- Complex Solutions Design
- Benchmarking
- Capacity Planning
- Analyzing client requirements and estimating scopes of effort
- Ensuring high client satisfaction for projects/engagements performed
- Interacting with client staff/executives, subcontractors, vendors
- Developing and presenting creative solutions to clients
- Providing project documentation
- Employing formal methodologies and tools
- Providing technical advice and guidance to project team members,
customers, and sales teams
- Leading effort to validate new technology (e.g., early support
programs)
- Closing/supporting the sale from a technology point of view
- Identifying and generating incremental Services business or IBM
product revenue
4.5.2 Profession Structure
The I/T Specialist Profession consists of 5 positions:
- I/T Specialist
- Advisory I/T Specialist
- Senior I/T Specialist
- Consulting I/T Specialist
- Senior Consulting I/T Specialist
The Consulting and Senior Consulting positions are certified positions.
Figure 19-1 in topic 4.5.3 and Figure 19-2 in topic 4.5.3 summarize the
requirements of each position of the profession and the developmental
requirements for progression within the profession. Detailed position
descriptions can be found in "I/T Specialist Position Descriptions" in
topic 4.5.10.
The six Major I/T Specialist Profession disciplines are:
- Application Development and Maintenance
The I/T Specialist - Application Development/Maintenance (AD/M)
discipline provides application development services or technical
support, typically in a well-defined project or engagement. He or she
supports the business strategies, the definition of business
strategies, processes, architectures and platforms for solutions
development, application maintenance and data management activities.
The I/T Specialist - AD/M possesses in-depth knowledge of IBM and key
OEM development methodologies and tools required for the design and
development of client solutions. Activities include selection,
requirements analysis, testing, integrating and maintaining
application components and models.
- Client/Server
The I/T Specialist - Client/Server discipline addresses the client's
need to integrate applications in a multi-database, multi-operating
system, multi-network, multi-protocol, multi-platform, and
multi-vendor environment. To do this effectively, he or she must be
knowledgeable in the wide variety of applications, databases,
networks, and platforms that are available from IBM, Business Partners
and other vendors. The I/T Specialist - Client Server understands the
Life Cycle impact of integrating complex applications including the
utilization of CASE, appropriate methodologies, and other tools as
required.
- Customized Operational Services
The I/T Specialist - Customized Operational Services (COS) discipline
focuses on the skills required to provide technical, sales and
billable services in support of COS Site services or connectivity
contracts. An individual in the site services specialty provides
technical advice and guidance on all aspects of the physical plant
(infrastructure) and facilities required for proper operation of the
data center and distributed processing physical environments; the
specialist in the connectivity specialty focuses on the infrastructure
and facilities required for the operation of data communications
products and associated peripheral equipment.
- Industry/Cross Industry Solutions
The I/T Specialist - Industry/Cross Industry Solutions discipline
provides services or support for our customers through highly skilled,
accessible and responsive industry or cross industry individuals.
The I/T Specialist - Industry Solutions has a thorough understanding
of the nature and the products of that industry. They would be
knowledgeable in the trends and directions of the industry and the
market, the players, the problems and solutions unique to the specific
industry. The I/T-Specialist - Cross Industry Solutions has in-depth
knowledge and experience in a solution that might apply to more than
one industry; not necessarily specific to any one industry. An
application may be a particular technology or product area (e.g.,
Image, Multimedia).
- Networking
The I/T Specialist - Networking discipline provides a varied set of
networking services or technical support, to meet client requirements,
typically in a well defined project or engagement. He or she may
perform activities ranging from the design and development of network
solutions to the assurance of multi-vendor, multi-protocol complex
network environments. Activities include support for the
installation, configuration, customization, and maintenance of
networking tools, software, service applications, complex
demonstrations, beta tests and ESP's. Individuals must possess a
thorough knowledge of IBM or OEM solutions as well as understand
competitive multi-vendor networking and network management tools,
techniques and offerings.
- Systems
The Systems discipline represents the Systems Products, Systems
Management and Systems Integration and Test specialties.
- Systems Products: The The I/T Specialist - Systems Products
provides services or technical support related to transaction,
database storage, and operating systems, typically in a well
defined project/engagement or technical support of IBM brand and
software offerings. Activities include planning, design, proposal
preparation, pre-sales activities, installation, conversion, or
release migration of complex operating and transaction systems,
complex demo's, benchmarking and ESP's. Additional activities
include systems programming, systems connectivity, interface
coding, systems integration, performance and tuning, capacity
planning, and problem determination. The I/T Specialist -
Technical support provides technical sales support for Large Scale
Systems, Advanced Workstations, AS/400 systems, Storage Systems
and major software systems products.
- Systems Management: The I/T Specialist - Systems Management
provides systems programming, installation, maintenance,
customization and testing services and technical support for the
client's major centralized computer systems, subsystems,
distributed systems or End User products. Activities may include
planning, designing, implementing and leading installation
projects or operating complex centralized and distributed computer
systems. The I/T Specialist - Systems Management possesses a
knowledge of industry and systems management solutions as well as
IBM and key OEM systems management tools, processes and services.
- Systems Integration and Test: The I/T Specialist - Systems
Integration and Test specialty performs services to integrate and
test hardware solution components in a well-defined engagement.
The solution may consist of IBM as well as third party existing,
modified, converted and new development products. Activities may
include developing appropriate plans, procedures, testing
environment and data and performing system level configuration,
testing facilities. He or she possesses a knowledge of
development, integration and testing of complex systems and
networks as well as test planning, test concepts, tools and
problem reporting techniques.
Subtopics:
4.5.2.1 I/T Specialist Specialities
IBM has a full line of technology products and industry solutions and
technology services. Competencies, skills and experience required to
support these businesses vary, with differences among businesses, segments
and geographies. Some industries have defined Industry Solution
specialities; others have not. In addition to the specialties listed
below, disciplines are mappable to service lines and product brands
directly. The six disciplines of I/T Specialist consists of the following
specialties:
____________________________ ___________________________________________
| Discipline | Specialty |
|____________________________|___________________________________________|
| Application | ° AD/M Business Analysis |
| Development/Maintenance | ° AD/M Data Integration |
| | ° AD/M Application Integration |
|____________________________|___________________________________________|
| Client/Server | ° Client/Server |
|____________________________|___________________________________________|
| Customized Operational | ° COS Connectivity Services |
| Services | ° COS Site Services |
| | ° COS LAN Services |
|____________________________|___________________________________________|
| Industry Solutions | ° Industry Solutions |
| | - Communications |
| | - Finance |
| | - Insurance |
| | - Manufacturing |
| | - Retail/Distribution |
| | - Government |
| | ° Cross Industry Solutions |
| | - Image |
| | - Multimedia |
|____________________________|___________________________________________|
| Networking | ° Network Management |
| | ° Network Integration |
| | ° Computer Telephony Integration |
|____________________________|___________________________________________|
| Systems | ° Systems Products |
| | ° Systems Management |
| | ° Systems Integration & Test |
|____________________________|___________________________________________|
In general, these announced specialties are open for use by all businesses
having the same need, but may not be implemented everywhere within IBM. To
find out if these are implemented in your business or geography in
addition to the disciplines, see your management.
4.5.3 Characteristics of the Profession
The I/T Specialist enjoys "end-to-end" work.
- Specialists work from requirements through design through
implementation project phases and engagements.
- They engage in planning and customization of replicative solutions.
- Those who remain in the specialty to senior levels become design
experts in the specialty and consult as well.
- They enjoy technical leadership and implementing applications, systems
and solutions.
- Some are dedicated to product sales and proposal work (requirements
and external design) and become expert at developing estimates and
plans for their specialty.

Figure 19-1. I/T Specialist Profession Roadmap - #1
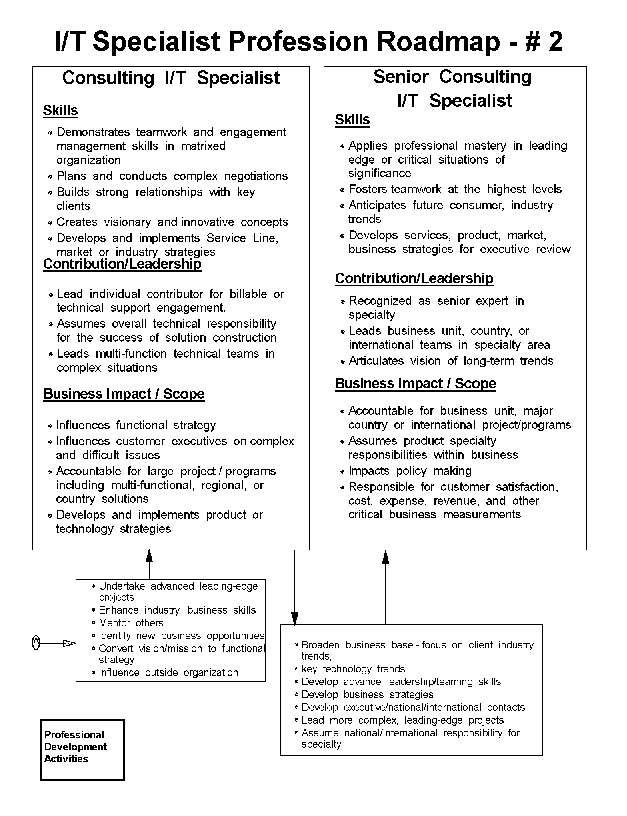
Figure 19-2. I/T Specialist Profession Roadmap - #2
4.5.4 Potential Candidates
Potential candidates range from college hires to experienced I/T
Technicians, Engineers, Analysts, Programmers, Development Managers,
Systems Engineers and Consultants. Some more senior professionals may be
presidents of solution firms or experts in specific industry applications
or solutions.
Figure 19-3 shows possible candidates for the I/T Specialist Profession
and possible career movement from an I/T Specialist position. Most
professionals will stay and grow in the same profession. However, for
those that want to pursue additional career options, many of your current
profession experiences will help you in your new profession. Additional
documentation on the normal possibilities for making a career change from
one of the other Worldwide Professions to the IT Specialist profession is
available in I/T Specialist Career Possibilities.
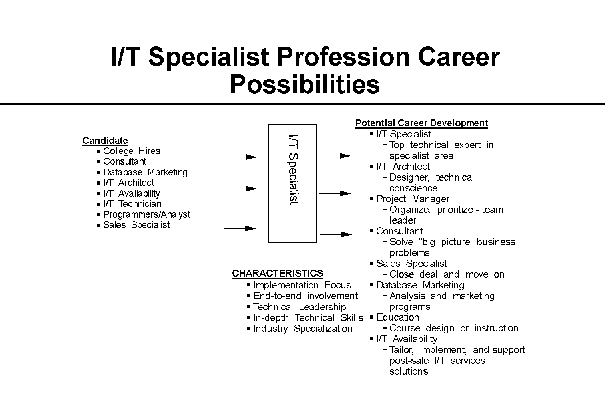
Figure 19-3. I/T Specialist Profession Career Possibilities
4.5.5 Career Growth
I/T Specialists may progress to other careers. Many like the design
component so much that they become I/T Architects who spend most of their
time on design projects. Others enjoy the technology leadership and
become full-time Project Managers. Some enjoy the analysis and
requirements projects and may become Consultants. Still others may enjoy
the technical selling effort and may become product or services sales
specialist. Of course, the I/T Specialist career profession allows a
professional to advance within their specialty both in skill growth and
level based on return to IBM and the business need of the organization.
In the past, the only option for experts were IBM Fellow positions or
senior technical staff member jobs.
Some I/T Specialist disciplines begin at the entry position. Others, like
Industry Solutions Specialist jobs, begin at a higher position in the
development/career specialty and continue to executive levels. If the
specialty starting position occurs higher in the career, this generally
means that the I/T Specialist first developed skills in another area prior
to achieving this competency (e.g., Client/Server).
_______________________ ________________________ _______________________
| Discipline | Starting Position | Maximum Position |
|_______________________|________________________|_______________________|
| AD/M | I/T Specialist | Senior Consulting I/T |
| | | Specialist |
|_______________________|________________________|_______________________|
| Client/Server | Advisory I/T | Senior Consulting I/T |
| | Specialist | Specialist |
|_______________________|________________________|_______________________|
| Customized | I/T Specialist | Senior Consulting I/T |
| Operational Services | | Specialist |
|_______________________|________________________|_______________________|
| Industry Solutions | Advisory I/T | Senior Consulting I/T |
| | Specialist | Specialist |
|_______________________|________________________|_______________________|
| Network | I/T Specialist | Senior Consulting I/T |
| | | Specialist |
|_______________________|________________________|_______________________|
| Systems | I/T Specialist | Senior Consulting I/T |
| | | Specialist |
|_______________________|________________________|_______________________|
Responsibilities at the starting levels generally involve development or
production of deliverables, either software, hardware or documents.
As professionals develop to higher levels of the discipline, they begin to
design and take on project leadership. Eventually, as professionals
become more senior, they will sometimes have sales leadership and business
responsibility as well. These professionals may either be management or
non-management. Some Specialists will manage a team of Specialists. As
in other professions, certified and advanced professionals will be
expected to provide technology or competency leadership and mentoring to
those coming "up" behind them.
Figure 19-1 in topic 4.5.3 shows career progression and skills
developmental activities needed to grow to increasingly responsible
positions within the profession.
4.5.6 Certification Nomination Guide
Once you have developed the necessary advanced skills and expertise, you
may wish to pursue certification within the I/T Specialist profession.
Refer to the Worldwide I/T Specialist Certification Nomination Guide and
Mentoring I/T Professionals for additional information.
4.5.7 Performance Elements
The key performance elements for the I/T Specialist profession are:
- Cost/Profit
- Revenue/Share
- Customer Satisfaction
The depth and breadth of one's skills will be one of the factors which
determine the I/T Specialist's compensation, along with size and
complexity of the project/engagement/contract.
Measurement criteria will include project, solution or engagement profit
for services organizations, or personal revenue for services or cost
management in Internal I/T organizations. Sales, services and industry
groups may include revenue or solution objectives (CAs) and share
objectives. Schedule or milestone objectives are common for services, I/T
and sales organizations for proposal, requirements, design and
implementation projects/engagements. Most include external or internal
customer satisfaction measurements.
4.5.8 I/T Specialist Profession Skills Profile
I/T Specialists deliver high-quality solutions to clients in response to
varied sets of business requirements. They utilize product, technology,
industry and/or services skills to perform a broad array of tasks across a
spectrum of client engagements and projects. They possess an in-depth
understanding of products, offerings and services and their applicability
to specific client needs.
The I/T Specialist Templates are:
- I/T Specialist
- I/T Specialist-Adv
- I/T Specialist-Sr
- I/T Specialist-Cons
- I/T Specialist-Sr Cons
The I/T Specialist profession is further defined by disciplines and
specialties. The templates associated with these specialties are:
- I/T Spec-AD/M Business Analy-xxx
where xxx = (Blank, Adv, Sr, Cons, SrCons)
- I/T Spec-AD/M Data Integn-xxx
- I/T Spec-AD/M Appl Integn-xxx
- I/T Spec-TS-SW Appl Devel
- I/T Spec-Netwk Integn-xxx
- I/T Spec-Netwk Mgmt-xxx
- I/T Spec-Sys Mgmt-xxx
- I/T Spec-Sys Integn & Test-xxx
- I/T Spec-Sys Mgmt Integn-xxx
- I/T Spec-Systems Products-xxx
- I/T Spec-TS-S/390
- I/T Spec-TS-Personal Computer
- I/T Spec-TS-RS/6000
- I/T Spec-TS-AS/400
- I/T Spec-TS-AS/400 Storage
- I/T Spec-TS-RS/6000 Storage
- I/T Spec-TS-S/390 Storage
- I/T Spec-TS-SW Transaction Procg
- I/T Spec-TS-SW Personal Sys Prods
- I/T Spec-TS-SW Wkgp
____________________________ ___________________________________________
| | Profession Positions, with Associated |
| | Skill Levels |
| I/T SPECIALIST PROFESSION |_______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| SKILLS | | Adv. | Sr | Cons | Sr | |
| | I/T | I/T | I/T | I/T | Cons | Key |
| | Spec. | Spec.| Spec.| Spec. | I/T | Skill|
| | | | | | Spec.| |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| CLIENT ENVIRONMENT |
|____________________________ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| Client Relationships | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Relationships With End | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
| Users | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Relationships With Client | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| I/T | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Client Strategy & Planning | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Client Strategic Plans | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Client Tactical Plans & | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Goals | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Client Management Sys / | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | |
| Culture | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| BUSINESS ACUMEN |
|____________________________ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| Market Management | 0 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Financial Skills | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Consulting Methods | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Client Organization & | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Structure | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Manage Consulting | 0 | 0 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Engagement | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Value-Add Selling | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| INDUSTRY |
|____________________________ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| Industry Segments / | 0 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Industries | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| IBM ENVIRONMENT |
|____________________________ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| IBM Organization | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| IBM Formal & Informal | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
| Network | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| IBM Vision / Mission / | 0 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Strategy | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Explain IBM Business | 0 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Strategy | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Explain IBM Trends / | 0 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Directions | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| IBM Management System | 0 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| PROJECT MANAGEMENT |
|____________________________ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| Initiate Projects | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Define Work Products | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Define/Estimate Work Tasks | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Plan Projects | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Project Track / Report / | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Deliver | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Manage Project Risk | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Manage Project Change | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Develop Project Plans | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| PRODUCT/TECHNOLOGIES/SERVICES |
|____________________________ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| Platforms | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Applications | 2 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| I/T Related Services | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Architectures | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Methodologies | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| PERSONAL |
|____________________________ _______ ______ ______ _______ ______ ______|
| Leadership | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Create Client-Driven | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Vision | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Communication - | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
| Presentation | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Foster Teamwork / Enable | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Teams | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Communication | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Interpersonal | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
| Communication | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Communication - Written | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Business - to - Business | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
| Comm | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Negotiation | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Negotiation One-on-One | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Negotiate in Teams | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Prepare For Negotiation | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Prob Solving, | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
| Decision-Making | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Analyze Problems / | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
| Situation | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Risk Awareness / Taking | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
| Quality / Problem | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
| Prevention | | | | | | |
|____________________________|_______|______|______|_______|______|______|
4.5.9 Professional Development
Growing your skills requires a combination of experience, education,
training, coaching and mentoring. These elements are called Skill
Development Activities. Education and training can be separated into
several forms ranging from self study, distance learning, internships,
classroom, and seminars. The integration of these delivery methods can be
an efficient and cost effective way to build your skills. For an overview
of the Worldwide Professions and links to the Common Skills Categories and
Professions Roadmaps, refer to the Education Roadmap page of the IEC
Course Catalog at http://w3.lahulpe.ibm.com/roadmaps/index.html
For each discipline of the I/T Specialist Profession, a high level career
roadmap, experience roadmaps and core knowledge descriptions are available
in the I/T Specialist Career Planning Guide.
4.5.10 I/T Specialist Position Descriptions
The following position descriptions describe the basic work of each of the
positions within the Professions. Formal descriptions which may contain
legally mandated language necessary for classifying employees in a
geography should be obtained through the approved on-line job library, if
available in the geography, or by contacting the appropriate H.R.
personnel within the geography.
Subtopics:
4.5.10.1 Position Title: I/T Specialist
Position Concept:
The I/T Specialist is an individual contributor responsible for providing
I/T services in a billable project/engagement or providing technical
support in a sales organization.
As a member of a team, performs a technical role in support of the
solution construction, implementation, and system integration in a
technology/industry specialty or product sales. The I/T Specialist
assists in delivery of high quality solutions to clients in response to
specific business requirements. Develops technical skills and absorbs
professional knowledge quickly. Performs assigned technical tasks
including study, analysis, programming, product installation, test and
system integration. The I/T Specialist has some specific product-,
technology- or industry-related specialized skills and works with
proposals, requirements, designs, implementations and production
projects/engagements. May use tools to analyze and implement portions of
a customer solution.
The I/T Specialist provides analytical support necessary to develop and
implement solutions for small to medium size projects, or
components/elements of larger projects. On occasion, provides technical
advice to project managers/leaders and gives some technical direction to
team members such as subcontractors or client personnel. May assist in
the identification of new I/T services opportunities. In a marketing
unit, provides the technical knowledge in support of the sale of hardware
and software This can involve participating in the development, packaging
and distribution of a solution, or the justification, requirements or
proof-of-concept in a proposal project. This position requires knowledge
of one major platform, process or architecture.
This is the entry position to the I/T Specialist profession for many
disciplines and presumes skills of a college graduate or equivalent. A
few I/T Specialist disciplines, notably Client/Server and Industry, begin
at higher positions, which generally means developing expertise in another
area prior to entering these disciplines.
Typical attributes of this position may include the following:
Skills
- Understands and applies basic knowledge of information technology and
associated tools of their technical specialty to support attainment of
team and department objectives. Demonstrates required I/T Specialist
proficiencies in technical skills.
- Draws upon concepts of tools, technologies and methodologies to
collaborate with other technical specialists when carrying out
assigned duties.
- Effectively negotiates with technical peers, and occasionally with
customers, to implement technical solutions.
- Recognizes and articulates job related problems to management.
- Analyzes technical problems and creates solutions involving the use of
existing techniques or tools. Performs assigned tasks within schedule
in accordance with established standards and guidance.
- Prepares and recommends technical alternatives involving technology,
methodology, tools, processes and solution components.
- Challenges the validity of given procedures and processes with the
intent to enhance and improve a customer solution.
Contribution/Leadership
- Works on information technology projects with direct customer contact.
- Work is often reviewed by peers and management, for developmental
purposes.
- Understands the standard mission of the I/T Specialist in own area of
specialty.
- May directly influence team members within own project and department
or client team with different ideas and techniques for performing
tasks. Cultivates and maintains a very positive relationship among
team members.
- Position may require coordination of activities of peers and more
experienced team members to implement technical solutions.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Accountable for own results or results of a small work team.
- May support activities that contribute to business results.
Participates in development of proposals, benchmarks, proof of
concepts and selling of hardware, software and services.
- Quality of deliverables impacts customer satisfaction.
4.5.10.2 Position Title: Advisory I/T Specialist
Position Concept:
The Advisory I/T Specialist is an individual contributor responsible for
providing I/T services in a billable project/engagement or providing
technical support in a sales organization.
As a manager of or member of a team, or working independently, performs a
technical role in support of the solution construction, implementation,
and system integration in a technology/industry specialty or product
sales. Delivers high quality solutions to clients in response to varying
business requirements. Performs many assigned technical tasks including
study, analysis, design, programming, product installation, test and
system integration. Has product-, technology-, or industry-related
specialized skills and regularly works with proposals, requirements,
design, implementation and production projects/engagements. Often uses
tools to analyze, design and implement.
The Advisory I/T Specialist provides analytical ability and creativity in
developing and implementing solution deliverables for medium size
projects. Provides technical advice to project managers and team leaders,
as well as giving technical direction to team members including IBM,
subcontractors, or client personnel. Assists in the balancing of
technical work assignments with team members' technical skills to mitigate
risk on the project/engagement/proposal. Provides technical guidance to
newer or less experienced team personnel. Assists and, on occasion, is
responsible for identifying new billable I/T services opportunities and
provides the technical knowledge in the sale of hardware and software
solutions. Assists in selling hardware and software products where
appropriate. This can involve participating and providing specialty
leadership in the development, packaging and distribution of a solution,
or the justification, requirements or proof-of-concept in a proposal
project. This position requires knowledge across several platforms,
processes or architectures.
In addition to the attributes of the I/T Specialist position, typical
attributes of this position may include the following:
Skills
- Understands and applies knowledge of information technology and
associated tools and methodologies of their technical specialty to
support attainment of department/project objectives. Demonstrates
required Advisory I/T Specialist proficiencies in technical skills.
- Is engaged as an independent information technology professional who
advises others on tools, technology, and methodology related to
implementing I/T solutions in their area of technical specialty.
- Compares and articulates alternative approaches to a design, and
implements technical solutions that meet customer needs. Is
knowledgeable of industry products and methodologies, both IBM and OEM
relative to specialty.
- Effectively negotiates with team members (technical peers, project
managers, and customers) to implement technical solutions within the
project/engagement/proposal.
- Recognizes and takes the appropriate actions to resolve problems
related to the technical solution being implemented and completes
technical tasks for the project/engagement/proposal within specialty.
- Applies creativity and judgment in the implementation of I/T solutions
related to project objectives.
- Independently generates technical solutions, based on analytical
skills involving technology, methodology, processes, tools and
solution components.
- Improves the technical procedures and processes within area of
technical specialty to enhance the implementation of a customer
solution.
Contribution/Leadership
- Performs analysis, problem-solving and evaluation activities on
special technical topics related to project/engagement/proposal
objectives.
- Generally controls own work priorities and methods requiring schedule
and risk trade-offs within a department or function to implement a
technical solution. Participates in project activities assigned.
Leads in integrating solutions in specialty.
- Understands departmental mission and vision, and applies this
knowledge to activities on the project/engagement/proposal.
- Provides advice in technical/operational domain of specialization
while working with customers, vendors and subcontractors to implement
I/T solutions.
- May lead small teams in the development and implementation of customer
solutions in area of technical specialty.
- Ensures completion of routine technical/operational activities for a
small project.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Accountable for individual, team or department work products, and for
the impact of the results on functional activities.
- Participates in overall departmental program planning in the areas of
cost, schedule and technical risk.
- Quality of deliverables and verbal communications impacts customer
satisfaction.
- May have budgetary responsibility for small
project/engagement/proposal. Advises clients in the analysis of
business requirements and the selection of technical solutions for
medium sized projects and participates in formulating a technical
approach to integrate hardware, services, system control and
application software into an information processing solutions to meet
medium to large requirements.
4.5.10.3 Position Title: Senior I/T Specialist
Position Concept:
The Senior I/T Specialist is either an individual contributor or manager
responsible for providing I/T services in a billable project/engagement or
providing technical support in a sales organization.
As a manager, team leader, or working independently, advises others and
assumes a technical leadership role in support of the solution
construction, implementation, and system integration in a technology or
industry specialty. Delivers high quality solutions to clients in
response to complex business requirements. Performs many assigned
technical tasks including study, analysis, design, programming, product
installation, test and system integration. Has in-depth product-,
technology-, or industry-related specialized skills and is a strong
technology or industry leader working with proposals, requirements,
design, implementation and production projects/engagements. May design
and develop the tools and methodologies used to manage, analyze, design
and implement technical solutions.
The Senior I/T Specialist provides analytical ability and creativity in
developing and implementing solution deliverables for a medium to large
sized project or major segments of a larger project. Provides technical
advice to project managers and team leaders, and give technical direction
to team members including IBM, subcontractor, or client personnel. Often
balances technical work assignments, team members' technical skills and
project/engagement/proposal risk while providing technical guidance to
newer or less experienced team personnel. Leads in identifying new
revenue producing product and/or I/T services opportunities regionally and
assists in selling hardware and software products where appropriate.
Provides the detailed technical knowledge in the sale of complex hardware
and software solutions. This position requires significant knowledge
across multiple platforms, processes or architectures.
In addition to the attributes of the Advisory I/T Specialist position,
typical attributes of this position may include the following:
Skills
- Applies knowledge of information technology and associated methods and
tools of the I/T Specialist profession to attain
project/function/business unit objectives. Demonstrates the required
proficiency levels for technical skills in area of specialty.
Demonstrates required Senior I/T Specialist proficiencies in technical
skills.
- Advises other I/T professionals (Project Managers, I/T Architects, and
I/T Specialists) on tools, technology, and methodology related to the
development and implementation of I/T solutions. May be asked to
research special topics as part of team responsibilities.
- Works effectively with other team members. Guides and influences team
members, including customer, vendor and subcontractor personnel, and
IBMers from other functional areas, to accomplish the team's technical
and business objectives.
- Negotiates effectively with team members (vendors, subcontractors,
customers and IBMers from other functional areas) to define the team's
role in developing and implementing the technical solution, including
tasks and approaches for producing the solution.
- Recognizes and articulates complex problems related to the I/T
solution being implemented.
- Applies creativity and judgment in implementation of multiple I/T
solutions related to project/engagement/proposal objectives.
- Independently generates technical solutions, based on analytical
skills and business knowledge involving technology, methodology,
processes, tools and solution components.
Contribution/Leadership
- Leads analysis, problem-solving, and evaluation activities on special
technical topics related to project/engagement/proposal objectives.
- Often leads implementation or technical support activities. This
includes leading all or portions of the implementation project,
recommending team members and organizing the team, defining tasks,
tracking and reporting progress, and delivering the customer solution
on time and within budget.
- Understands department/function mission and applies this understanding
to achieve project/engagement/proposal objectives.
- Influences people outside immediate department, through work with
customers, vendors and subcontractors and presentations on
project-related topics to IBM and customer management.
- Provides technical guidance to implementation team members throughout
the project/engagement/proposal life-cycle. May lead implementation
in a small/medium sized project or be responsible for subsystem
implementation in a large project.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Is accountable for quality and timeliness of technical solution that
meets customer needs for teams led or departments managed.
- Regularly participates in overall functional planning. Identifies,
estimates and presents cost, schedule, technical risks for solution
elements, both in marketing and proposal efforts and in implementation
planning.
- Works directly with most levels of customer managers and executives.
Activities affect customer satisfaction. Provides technical
leadership in the development of proposals, and hardware and software
solutions selling.
- Has budgetary responsibility for medium to large project/engagement
proposals. Advises clients in the analysis of business requirements
and the selection of technical solutions for medium to large sized
projects and participates in formulating a technical approach to
integrate hardware, services, system control and application software
into an information processing solution to meet significant, complex
requirements.
4.5.10.4 Position Title: Consulting I/T Specialist
Position Concept:
The Consulting I/T Specialist is either the lead individual contributor or
manager responsible for providing I/T services in a billable
project/engagement or providing the key technical support in a sales
organization.
As a manager, key member of a team, team leader, or working independently,
the Consulting I/T Specialist guides other professionals and assumes
overall technical responsibility for the success of the solution
construction, implementation and system integration in a technology,
industry or business specialty. Delivers new and complex high quality
solutions to clients in response to varying business requirements.
Utilizes in-depth knowledge of leading-edge products and technology in
conjunction with industry and business skills to influence functional
strategy. Influences client personnel and organizations, including
executive management, when issues are complex/difficult and require
considerable diplomacy. Has considerable latitude and responsibility to
define and select tools, processes, priorities and resources necessary to
manage, analyze, design and implement general business unit directives.
The Consulting I/T Specialist position requires expert knowledge across
multiple platforms, processes or architectures. Is accountable for
projects or programs involving multi-functional, country-wide, or regional
teams.
Utilizes high level analytical ability and creativity to analyze
complex/new situations, anticipates potential problems and future trends,
assesses opportunities, impacts and risks while developing and
implementing plans and solution deliverables to customer problems. The
individual focuses skills and experience on large projects. Is recognized
as an expert in his/her specialty and industry. Is responsible for taking
the lead in identifying new revenue producing product and/or I/T services
opportunities nationally. Provides the expert technical knowledge in the
sale of highly complex large hardware and software solutions.
In addition to the attributes of the Senior I/T Specialist position,
typical attributes of this position may include the following:
Skills
- Understands and applies knowledge of services function, business unit,
brand, large country or regional objectives in designing and
implementing I/T solutions for clients. Demonstrates the required
Consulting I/T Specialist proficiency levels for technical skills in
own area of specialty and in related disciplines, and applies those
skills in implementing I/T solutions.
- Understands organizational resources, priorities, needs and policies,
and takes them into account in developing I/T strategies and
solutions.
- Mentors others in the I/T Specialist profession. Provides guidance to
team members (Project Managers, I/T Architects, Sales Specialists, and
other I/T Specialists, among others) in area of new and complex
implementation and/or management tools and techniques. Acts as the
center of competency on all appropriate development tools,
productivity aids, standards, and procedures ensuring they are
effectively utilized on all applicable projects/engagements/proposals.
- Leads negotiations with engagement partners and team members (vendors,
subcontractors, customers, IBMers from other functional areas) to
define project goals and strategies for attaining them.
- Anticipates potential problems. Develops and leads execution of the
technical risk management plan for the solution to be implemented.
- Understands future customer, industry and information technology
trends within specialty and related disciplines. Applies this
understanding to develop/implement robust solutions and to identify
opportunities for future business.
- Analyzes new and complex situations. Selects, tailors and applies
formal methodologies to analyze customer needs and develop
requirements for I/T solutions. Acts as a consultant to the clients
in the analysis of business requirements and the selection of
technical solutions in very large, complex, leading edge projects.
Assesses business and technical impact of solutions.
- Leads the implementation of solution or provides expert guidance to
the implementation team. Identifies development methodology and
technical support tools, and tailors them as required for
projects/engagements/ proposals. Plays the lead role or directs other
technology leaders in formulating a technical approach to integrate
hardware, services, system control and application software into a
information processing solution to meet very large, complex and
leading edge requirements.
Contribution/Leadership
- Conducts special projects. Participates in exploratory activities to
in new market sectors, application solutions, technologies and the use
of business partners.
- Leads selection of methodologies, tools and solution components that
will be employed in developing I/T solutions for clients.
- Exhibits strategic vision of functional or unit mission and applies
vision in engagements/proposals.
- Influences people and organizations, including client and IBM
executive management, on issues related to the development of I/T
solutions or technical sales. Demonstrates skills of a technical
leader/subject matter expert inside and outside organization.
- Leads technical teams in the solution of new and complex problems.
May serve as project manager.
- Leads multi-functional teams. Identifies needs for specialized
expertise outside own area, gets commitment of needed resources, and
effectively applies the expertise of team members to the
development/implementation of I/T solutions and/or proposals.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Is accountable for projects or programs involving multi-functional,
country-wide or regional teams.
- Is responsible for the successful implementation of a solution, or of
a major subsystem of a very large solution, within identified cost,
schedule and functional requirements.
- Leads assessment of cost, schedule and dependencies associated with
solution development and/or implementation as well as technical
proposals.
- Activities directly affect customer satisfaction. Work is often
visible to all levels of customer organization. Works with customers
to ensure understanding of, acceptance of, and satisfaction with the
I/T solution.
- Development and implementation activities produce cost effective I/T
solutions which directly affect functional, business unit, brand, or
country costs and expenses.
4.5.10.5 Position Title: Senior Consulting I/T Specialist
Position Concept:
The Senior Consulting I/T Specialist is either the lead individual
contributor or manager responsible for providing key/pivotal I/T services
in a billable project/engagement or providing key/pivotal technical
support in a sales organization.
As a manager, key team leader, or working independently, technically
directs and advises other professionals and is responsible for the success
of the leading edge or critical solution construction, implementation, and
system integration in a technology, industry or business specialty. Is
responsible for quality output and value-add for highly visible products,
I/T services and future business development. Oversees the delivery of
new and highly complex high quality solutions to clients in response to
unique business requirements. Is expected to have an extensive
understanding of industry trends and emerging technologies. As a
senior-level expert, uses knowledge of leading-edge products and
technology in conjunction with industry and business skills to develop and
implement product, market, business, or technology strategies. Has a
clear vision of IBM's/client's overall strategies and contributes to
policy making. Influences senior client personnel and organizations,
including senior executive management, when issues are unique, complex and
difficult. Is accountable for business unit, major country, or
international projects or programs. This position requires expert
knowledge across multiple platforms, processes or architectures.
Utilizes high level analytical ability and creativity to anticipate,
create and define innovative and visionary concepts in a strategic
environment. The individual focuses skills and experience implementing
plans and solutions for customers for very large, highly complex and
leading edge projects, often developing the new business opportunity. Is
recognized as the senior expert and leader by members of a field, related
functions, and multi-country organizations. Leads business unit, country,
or international teams, conducts special project, or manages functions or
strategic departments. Is responsible for taking the lead in identifying
new revenue-producing product and/or I/T services opportunities
nationally/internationally. Provides the senior-expert technical
knowledge in the sale of highly complex large hardware and software
solutions.
In addition to the attributes of the Consulting I/T Specialist position,
typical attributes of this position may include the following:
Skills
- Applies professional mastery to develop I/T solutions in leading edge
or critical situations, on projects/engagements/proposals of strategic
significance to business unit, country or international objectives.
Demonstrates required Senior Consulting I/T Specialist proficiencies
in technical skills.
- Fosters and engages in teamwork at the highest management and
technical levels of IBM, customer, vendor and subcontractor
organizations.
- Plans and conducts negotiations which result in lasting agreements and
commitments between IBM, customer, vendor and subcontractor
organizations.
- Anticipates future customer, industry and information technology
trends. Applies this understanding to develop a strategic vision
which influences business area, country or international strategic
objectives.
- Develops and implements services, product, market, business or
technology strategies with executive review.
Contribution/Leadership
- Articulates vision of long term IBM, industry and technology
directions which guides business area, product or services strategy.
- Is recognized as the senior expert and leader in a discipline or
specialty by other members of the I/T Specialist profession,
multi-country organizations within IBM, and by customer, vendor and
subcontractor organizations.
- May manage functions or strategic departments.
- Leads business unit, country or international teams.
Impact on Business/Scope
- Is accountable for business unit, major country or international
projects and programs.
- Develops products or technology strategies with executive review.
Implements product or technology strategies with no guidance.
- Applies broad industry, technology, business and professional
knowledge to contribute to policy-making.
- Is responsible for committing multiple resources and achieving
customer satisfaction, cost, expense, revenue and other critical
business measurements.
- Is responsible for quality output/value add for highly visible
products, I/T services and future business development. Analyzes
business requirements and the selection to technical solutions in very
large complex, leading edge projects and formulates technical
solutions to very large, complex and leading edge requirements.
4.6 Chapter 20. Project Management Profession
Subtopics:
4.6.1 Project Management Profession Overview
The Project Management Profession is a well-established and recognized
industry-wide competency. The evolution of this career in the Information
Technology Industry occurred over the last 30 years. In both IBM and
client businesses, the profession supports the management of Information
Technology projects. Project Management is the management of work in the
Information Technology environment. This includes:
- Project Plans
- Schedule
- Resource Plan
- Financial Plan
- Organization Management
Recognized positions within this profession are:
- Project Leader
- Project Manager
- Project Executive.
In Industry terms, these jobs include project administration, marketing or
business case communication and management, methodology, and general
management of resources, subcontractors, finance and other organizations.
Most geographies and many IBM businesses have implemented this profession.
In accord with the business need, these professional jobs are used in
Availability, Consulting, I/T, Marketing and Services.
4.6.2 Profession Structure
The Project Management competency jobs begin with Advisory Project Leader.
The development of the professional expertise begins with leadership of
technology, where Advisory Project Leaders manage project tasks in their
specialty and are responsible for project plans and project administration
on smaller projects or sub-projects of large projects. The Senior Project
Leader is often involved with larger and more complex projects, requiring
more methodology expertise and methodology knowledge within a specialty
area. Project Managers are responsible for project plans and
administration, marketing or business case management, and are expected to
have very high levels of knowledge in one of the following project
areas/associated methods:
- Application Development
- Customized Operational Services (includes construction)
- Managed Operations or Systems Operations
- Solutions and Software Development
- Systems Integration
The most advanced project management professionals can become Project
Executives, with responsibility for managing projects and/or organizations
which increase in size, complexity, technology or business scope, and can
reach geographic/regional or even global breadth.
The Advisory Project Leader is the entry level within the profession and
includes positions for job growth through certification to Project Manager
with further advancement potential to Project Executive levels. All
Advisory Project Leader positions are non-management. The Senior Project
Leader, Project Manager and Project Executive jobs can be either
non-management or management positions.
As in all professions, certified Project Managers and Project Executives
will be expected to mentor those coming up "behind" them for professional
development of the next "generation."
Career progression and growth is based upon business needs and includes
the following options and positions:
- Project Leader (non-certified positions)
- Advisory Project Leader
- Senior Project Leader
- Project Manager/Project Executive (possible Certified positions)
- Project Manager
- Project Executive
Project Leaders, Project Managers and Project Executives are deployed in
IBM I/T organizations, Services and Marketing. They may work directly for
IBM clients on billable contracts or engagements or marketing
projects/proposals, or work in businesses developing, manufacturing or
supporting IBM products.
The Project Manager and Project Executive positions are certified
positions. Figure 20-1 and Figure 20-2 summarize the requirements of each
position of the profession and the developmental requirements for
progression within the profession. Detailed position descriptions can be
found in "Project Management Position Descriptions" in topic 4.6.10.
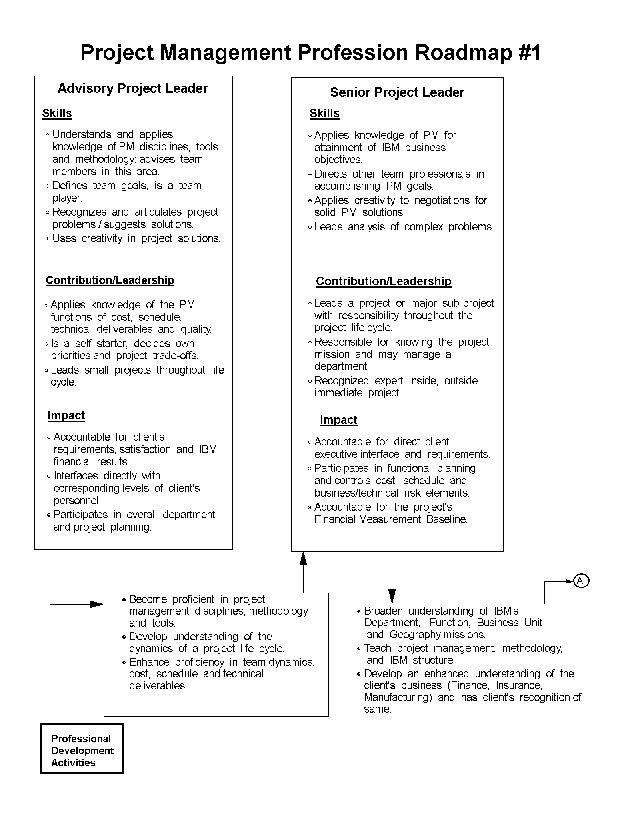
Figure 20-1. Project Management Profession Roadmap - #1
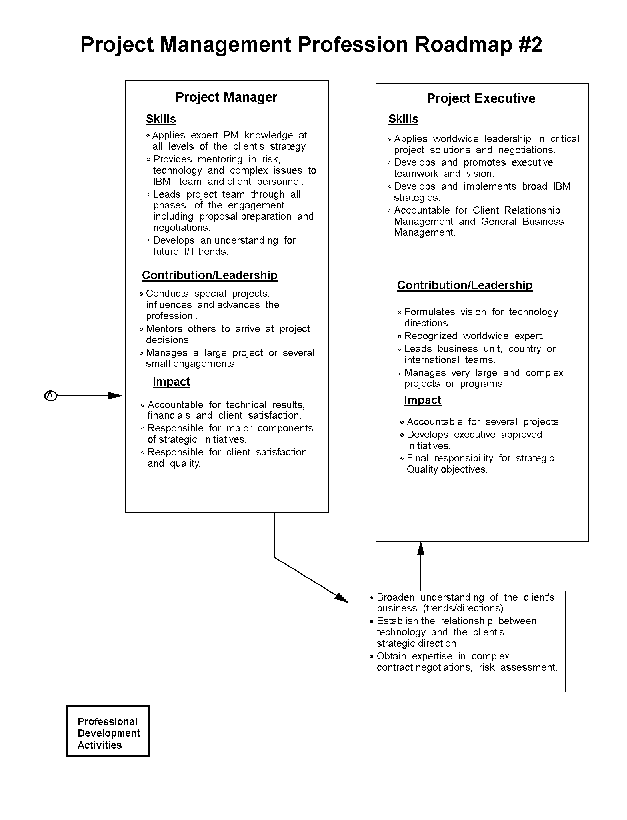
Figure 20-2. Project Management Profession Roadmap - #2
4.6.3 Characteristics of the Project Management Profession
The Project Manager/Project Executives are both business managers and
project directors. They are very knowledgeable in the functions of
project management (Cost, Schedule and Contractual Deliverables), possess
strong financial skills (both IBM and client awareness), are strong
leaders, and are extremely aware of the client's requirements and
strategy. The PM/PEs are extremely experienced and possess significant
skills in developing client solutions. They are known leaders within the
profession and are sought after for their ability to deliver the proposed
solution on time and within budget. They also contribute to the success
and development of new project managers thru the process of mentoring.
These individuals possess strong client relationship skills by being
thoroughly versed in the client's vision, mission and plans, and are able
to deliver the solution to meet the detailed requirements of the end user
and to ensure that the client's long term strategic needs are met as well.
They know when to be both strong and conciliatory with their client and
are accepted as the sole leader of the engagement.
The PM/PEs are experts in business acumen as it pertains to their clients.
Each project is treated as a business opportunity. Each engagement has
its own Financial Measurement Baseline and is managed accordingly. The
PM/PE is keenly aware of the impact each engagement has on the client's
profitability both in terms of present day costs and future profits.
These individuals are knowledgeable about various financial analysis
methods.
The PM/PEs are familiar with the IBM organization and know how to obtain
and bring required resources to the project in a timely and cost effective
manner. They are aware of IBM direction and the trends within the I/T
industry. They are able to craft solutions that meet today's needs and
provide for the client's future requirements.
PM/PEs are highly respected in the profession of project management. They
are able to design and implement a specific project management system for
their projects, including an organization structure, reporting lines, and
reporting information. They are able to guide, direct or perform all
aspects of project management depending upon the project requirements,
personnel assigned, and project status. They possess significant skill
levels in planning, directing, estimating, tracking and reporting on all
tasks associated with a project. For each project, these individuals
review the plan and perform a risk assessment analysis and develop
contingency plans. Within each project change is going to occur. It is
the PM/PE's responsibility to manage and control this change. They must
assess its impact on the project and alert the client of the effect these
changes will have in terms of cost, schedule and deliverables. Besides
managing an IBM staff, the PM/PEs are often called upon to manage the
client staff along with outside subcontractors. These individuals must be
treated the same and yet managed differently.
Finally, the PM/PEs must possess strong interpersonal skills. They must
have strong leadership ability with the capability of motivating the team
and guiding them and the project to a successful implementation. The
PM/PEs should have solid negotiating skills in order to develop contracts
or to convince management to proceed with project changes on a day-to-day
basis. The PM/PEs must be able to communicate both up and down the
organization structure. They must be able to present their ideas to
senior management and obtain executive level support, and then be able to
translate their vision to the team in terms of technical direction.
The PM/PEs are expected to be billable and to be leaders both inside and
outside of IBM.
4.6.4 Potential Candidates
Potential candidates for the Project Manager Profession could be Project
Leaders, Managers or Executives (in positions of leadership with strong
technical expertise).
These candidates can come from the following organizations:
- Service Organizations
- Field Operations
- Consulting
- Industry Sector
- Outside Companies
Figure 20-3 shows possible candidates for the Project Management
Profession.
More information on movement from other professions is available in
Project Management Career Possibilities.
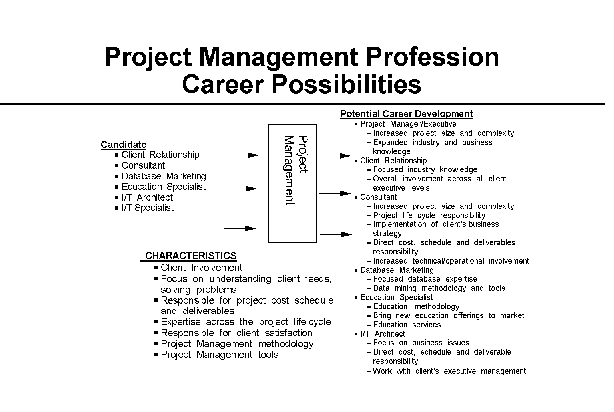
Figure 20-3. Project Management Profession Career Possibilities
4.6.5 Career Growth
Project Leaders usually have a specialty in application, solutions, or
technology and have advanced to project leadership through their expertise
in one of these areas. Specialists and Project Leaders can develop and
progress to become Project Managers. I/T Specialists who have expanded
their competency to full time design and have become I/T Architects often
develop into Project Managers, due to their leadership and repeated
management of design projects. Consultants who lead smaller engagements
may develop into Project Managers. Finally, general managers who have
managed development or technology businesses can become Project
Executives.
In addition, the Project Management Profession can build the skills and
experience to position an employee to pursue career growth in other
professions, as illustrated in Figure 20-3 in topic 4.6.4.
4.6.6 Certification Nomination Guide
The Worldwide Project Manager Certification Nomination Guide contains the
criteria, required documentation, and process for certification in the
profession. Additional information can also be found in Mentoring I/T
Professionals.
4.6.7 Performance Elements
The key performance elements for the Project Manager Profession are:
- Revenue
- Profit or Financial/Cost Management
- Customer Satisfaction
- Follow-on Business/New Business
- Mentoring/Professional Development
- Utilization/Resource Management
4.6.8 Project Management Profession Skills Profile
__________________________ _____________________________________________
| | Profession Positions, with Associated Skill |
| Project Manager | Levels |
| Profession Skills |_________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| | Adv PL | Sr PL | Project| Project| Key |
| | | | Mgr | Exec | Skill |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| CLIENT ENVIRONMENT |
|__________________________ _________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Client Relationships | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Y |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Relationships With | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Client Exec | | | | | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Relationships With End | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Users | | | | | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Relationships With | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Client I/T | | | | | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Client Strategy & | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | Y |
| Planning | | | | | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Client Executive Vision | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Client Critical Success | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Factors | | | | | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Client Management | 2 | 2 | 3 | 5 | Y |
| Sys/Culture | | | | | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| BUSINESS ACUMEN |
|__________________________ _________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Market Management | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | Y |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Financial Skills | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | Y |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Market Driven Quality | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Consulting Methods | 2 | 2 | 3 | 5 | Y |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Value-Add Selling | 2 | 2 | 2 | 5 | Y |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| INDUSTRY |
|__________________________ _________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Industry | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | Y |
| Segments/Industries | | | | | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| IBM ENVIRONMENT |
|__________________________ _________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| IBM Organization | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | Y |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| IBM | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | Y |
| Vision/Mission/Strategy | | | | | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| IBM Management System | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | Y |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Service Providers in I/T | 3 | 4 | 5 | 4 | |
| Industry | | | | | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Explain IBM Key Projects | 3 | 4 | 5 | 4 | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Explain IBM Major | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Alliances | | | | | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| PROJECT MANAGEMENT |
|__________________________ _________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Initiate Projects | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Y |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Define Project | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Objects/Benefits | | | | | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Define Scope/Boundaries | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Develop Project Plans | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Plan Projects | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Y |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Define Work Products | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Define/Estimate Work | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Tasks | | | | | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Develop Project Cost | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Structure | | | | | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Project | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Y |
| Track/Report/Deliver | | | | | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Track and Report Status | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Report on Projects | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Manage Project Risk | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Y |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Assess Proposals & | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Project Risk | | | | | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Manage Project Change | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Contracting for Projects | 3 | 3 | 3 | 5 | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Manage Subcontractors | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Select PM Processes & | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Tools | | | | | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| PRODUCTS/TECHNOLOGY/SERVICES |
|__________________________ _________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Platforms | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | Y |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Applications | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | Y |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Architectures | 2 | 3 | 4 | 3 | Y |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Methodologies | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | Y |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| I/T Related Services | 3 | 3 | 3 | 5 | Y |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| PERSONAL |
|__________________________ _________ ________ ________ ________ ________|
| Leadership | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Y |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Empower and Motivate | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Foster Teamwork/Enable | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Teams | | | | | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Communication | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | Y |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Interpersonal | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
| Communication | | | | | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Business-to-Business | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Comm | | | | | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Facilitate Meetings | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Negotiation | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Y |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Negotiate One-on-One | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Prob Solving, | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | Y |
| Decision-Making | | | | | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Analyze | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
| Problems/Situation | | | | | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Risk Awareness/Taking | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
| Quality/Problem | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
| Prevention | | | | | |
|__________________________|_________|________|________|________|________|
4.6.9 Professional Development
The dynamic skills necessary for the Project Management Profession are
resident in the Skills V2 Tool under the Job Role Template List. The
Project Management Templates are:
____________________________________ ___________________________________
| Job Role Template Name | Job Category Name |
|____________________________________|___________________________________|
| Project Leader-Adv | Project Management |
|____________________________________|___________________________________|
| Project Leader-Sr | Project Management |
|____________________________________|___________________________________|
| Project Manager | Project Management |
|____________________________________|___________________________________|
| Project Executive | Project Management |
|____________________________________|___________________________________|
For an overview of the Worldwide Professions and links to the Common
Skills Categories and Professions Roadmaps, refer to the Education Roadmap
page of the IEC Course Catalog at
http://w3.lahulpe.ibm.com/roadmaps/index.html.
Additional information can also be found in the Project Management Career
Planning Guide.
4.6.10 Project Management Position Descriptions
The following position descriptions describe the basic work of each of the
positions within the Professions. Formal descriptions which may contain
legally mandated language necessary for classifying employees in a
geography should be obtained through the approved on-line job library, if
available in the geography, or by contacting the appropriate H.R.
personnel within the geography.
Subtopics:
4.6.10.1 Position Title: Advisory Project Leader
Position Concept:
The Advisory Project Leader is responsible for leading a team on either a
small project or a definable segment of a larger project. Clients are
either external or internal. The Advisory Project Leader is responsible
for leading a team which establishes and then proceeds to translate
portions of the client's business requirements, such as specific segments,
units or deliverables, into formal agreements establishing specific
solutions, applications or processes ultimately culminating in customer
acceptance of the results. This includes working as a team member with
client, technical or subcontractor personnel to identify business
requirements, and subsequently, working with, and assuming functional
leadership for the initiating, planning, controlling executing and closing
of a specific segment, unit or deliverable within a client's solution. The
Advisory Project Leader should execute a range of process activities
beginning with the request for proposal through development, test and
final delivery. This position requires the Advisory Project Leader to have
solid experience and knowledge across PM methodologies and the disciplines
contained within, with a focus on cost, schedule and contractual
deliverables. At the same time, the Advisory Project Leader must be
enhancing their knowledge and honing skills required to lead an entire
project.
The Advisory Project Leader is at the entry point in the profession and is
presumed to have the skills to successfully lead the activities associated
with a project segment, unit or deliverable. The Advisory Project Leader
will have been exposed to, and participated on projects which have been
run under current PM methodologies.
Skills
- Understands and applies knowledge of project management disciplines
and processes as they relate to the I/T industry and the attainment of
project, department and function objectives. Demonstrates the
required proficiency level for Advisory Project Leader skills.
- Advises other team professionals (Project Managers, I/T Architects,
I/T Specialists and Consultants) on the selection and use of project
management scheduling tools, project management processes and a
project management methodology. May be asked to do specific research
on business and contractual alternatives as a part of the project team
responsibilities.
- Works with other team members to articulate, compare, and implement
solutions and alternative approaches based upon solid project
management principles and disciplines. Team members might include
customer, vendor and subcontractor personnel, as well as IBMers from
other departments and professional areas.
- Negotiates from a project management perspective with team members
(vendors, subcontractor, customer and IBMers from other departments
and professional areas) to define the team's project goals and
approaches for attaining them.
- Recognizes and articulates problems related to the project and to the
project management methodology driven solution being developed.
- Applies creativity and judgement in development of solutions related
to specific project segment, unit or deliverable objectives. Has the
confidence and presence to challenge the validity of given procedures
and processes with a view toward enhancement or improvement.
- Analyzes specific problems and evaluates solutions involving finance,
scheduling, technology, methodology, tools and project components.
Contribution/Leadership
- Understands the objectives related to the project from a cost,
schedule, technical and quality perspective. Individual is a self
starter and empowered. Decides own priorities and is able to make
project trade-offs.
- Understands department/project mission and applies this understanding
in project activities. Provides a positive influence to peers within
the immediate department by displaying exemplary work habits on
specific projects, while clearly and concisely communicating project
results through quality presentations to immediate management.
- Displays proper usage of PM tools and disciplines to implement team
members throughout the project lifecycle. May lead a small project or
assist on a sub-project or major subcontractor effort on a large
project.
Impact On Business/Job Scope
- Accountable for meeting customer's requirements and the results of
project segment, unit or deliverable assigned.
- Participates in overall department and project planning. Identifies,
estimates and presents cost, schedule and business/technical risk for
project segment, unit or deliverable assigned.
- Interfaces directly with corresponding levels of customer's personnel
Activities are related to customer satisfaction.
- The Advisory Project Leader is responsible for the financial baseline
of those activities or tasks assigned and this responsibility impacts
department and project costs and expenses.
4.6.10.2 Position Title: Senior Project Leader
Position Concept:
The Senior Project Leader is responsible for leading a team on either a
project or a major segment of a large project. Clients are either external
or internal. The Senior Project Leader is fully responsible for leading a
team which establishes and then proceeds to translate portions of the
client's business requirements into formal agreements establishing
specific solutions, applications or processes ultimately culminating in
customer acceptance of the results. This includes working as a team member
with client, technical and subcontractor personnel to identify business
requirements and, subsequently, working with, and leading others in the
initiating, planning, controlling, executing and closing of the client's
solution. The Senior Project Leader leads a wide range of process
activities beginning with the request for proposal through development,
test and final delivery. This position requires significant knowledge
across PM methodologies and the disciplines contained within, with
responsibility for cost, schedule and contractual deliverables.
In addition to the attributes of the Advisory Project Leader, typical
attributes of this position may include the following:
Skills
- Understands and applies knowledge of project management disciplines
and processes as they relate to the I/T industry and the attainment of
function/business unit objectives. Demonstrates the requirement
proficiency level for Senior Project Leader skills.
- Advises and directs other team professionals (Project Managers, I/T
Architects, I/T Specialists and Consultants) on the selection and use
of project management scheduling tools, project management processes
and a project management methodology. May be asked to research
complex business and contractual alternatives as apart of team
responsibilities.
- Works effectively with other team members. Guides, leads and selects
team members, including customer, vendor and subcontractor personnel,
as well as IBMers from other functional and professional areas, to
accomplish project management related goals.
- Negotiates effectively with team members (vendors, subcontractor,
customer and IBMers from other functional and professional areas) to
define the team's project goals and establish mutually agreed to
project management solutions.
- Recognizes and articulates complex problems related to the function
and to the project driven solution being developed.
- Applies creativity and judgement in development of multiple solutions
related to project objectives utilizing recognized project management
disciplines.
- Analyzes problems and creates solutions involving finance, scheduling,
technology, methodology, project management tools and solution
components.
Contribution/Leadership
- Conducts projects on special topics related to functional objectives..
- Defines and decides objectives related to the project from a cost,
schedule, technical and quality perspective. May lead and guide the
efforts of others in these areas.
- Understands department/function mission and applies this understanding
in project activities.
- The Senior Project Leader influences people outside their immediate
project. This influence is expressed through working with customers,
vendors and subcontractors. Detailed presentations on project-relate
topics to IBM and customer management also demonstrate a project
management influence.
- Provides project management/business guidance to implementation team
members throughout the project lifecycle. Has the ability to manage
and motivate team members. May lead a small or medium project or be
responsible for major sub-project performance or major subcontractor
performance on a large project. May manage a department.
Impact On Business/Job Scope
- Accountable for meeting customer requirements and the results of
teams/projects, departments managed.
- Regularly participates in overall functional planning. Identifies,
estimates and presents cost, schedule and business/technical risk for
solution element.
- Interfaces directly with customer' s executive management. Activities
are directly related to customer satisfaction.
- The Senior Project Leader is responsible for the financial baseline of
the project assigned and this responsibility impacts function project
costs and expenses.
4.6.10.3 Position Title: Project Manager
Position Concept:
The Project Manager is responsible for leading either a large project or a
definable segment of a very large and complex project. Clients may be
external or internal. The Project Manager is responsible for and leads the
translation of the client's complex business requirements into formal
agreements establishing specific solutions, applications or processes
ultimately culminating in customer acceptance of the results. This
includes working with client personnel and executives to identify business
requirements and, subsequently, working with, and leading others in the
initiating, planning, controlling, executing and closing of the client's
solution. The Project Manager is responsible for a wide range of process
activities beginning with the request for proposal through development,
and final delivery. Starting at the Project Manager test position, expert
level knowledge is required across PM methodologies and the disciplines
contained within, emerging technologies and technical architectures
pertaining to the client served and the vision to influence the client's
actions. There must be overall responsibility for cost, schedule and
contractual deliverables.
In addition to the attributes of the Senior Project Leader position,
typical attributes of this position may include the following:
Skills
- Understands and applies knowledge of project management disciplines
and processes as they relate to IBM and the client's strategic
objectives, functions, business unit and/or country objectives.
Demonstrates the required proficiency level for the skills required of
the Project Manager position.
- Understands IBM's and the client's organizational resources,
priorities, needs and policies.
- Guides other professionals (Project Managers, I/T Architects, I/T
Specialists and Consultants). Mentors others in the Project
Management Profession. Provides guidance to team members in areas of
new or complex implementation and or management techniques.
- Leads negotiations with team members (vendors, subcontractor, customer
and IBMers from other functional and professional areas) to define
team goals and approaches for attaining them. Solid understanding of
minimum, maximum and target positions in customer negotiations and the
strategies employed to reach the target goal.
- Anticipates potential project related problems. Utilizes refined
techniques for identifying, eliminating or containing both technical
and business risk.
- Understands future customer, industry and business/information
technology trends. Applies this understanding in maximizing the
business potential of the existing engagement or in winning new
business. Understands the customer's perspective especially the need
to maximize stockholder value.
- Analyzes new and complex project related problems and creates
innovative solutions involving finance, scheduling, technology,
methodology, tools and solution components.
- Leads the project team in developing and implementing solutions.
Contribution/Leadership
- Conducts special projects. Leads exploratory activities into new
markets, alternative technical solutions and use of business partners
and major subcontractors.
- Leads and guides the efforts of others in understanding and reaching
project decisions. May manage department.
- Exhibits strategic vision of functional or unit mission and applies
vision in engagements.
- Influences people and organizations to include those of the clients
and IBM executives on issues related to project management. Is
respected as a project management subject matter expert both inside
and outside the company.
- Leads project management/business initiatives in new and complex
areas. Acts as the project manager of a large project or perhaps
several smaller engagements. May be directing other project managers.
Recognized expert.
Impact On Business/Job Scope
- Accountable for results of large, complex projects. Cross functional
engagements, international projects and dispersed teams may be
involved.
- Responsible for major components in functional planning. Identifies,
estimates and resolves cost, schedule and business/technical risk for
strategic initiatives.
- Interfaces directly with customer's executive management. Activities
are directly related to customer satisfaction and drive follow-on
business.
- The Project Manager is responsible for the financial baseline of the
project or projects assigned and this responsibility directly impacts
functional and project costs and expenses.
- Responsible for achieving Quality objectives.
4.6.10.4 Position Title: Project Executive
Position Concept:
The Project Executive is responsible for, and leads the translation of the
client's very large, complex or leading-edge business requirements into
formal agreements establishing specific solutions, applications or
processes ultimately culminating in customer acceptance of the results.
All assignments include working with client executives and board members
identify business requirements and, subsequently, working with, and
leading others in the initiating, planning, controlling, executing and
closing of the client's strategic solutions. The Project Executive is
responsible for a wide range of process activities beginning with the
request for proposal through development, test and final delivery. The
Project Executive formulates partnerships among customers, vendors and
subcontractor organizations to address business windows of opportunity for
the IBM Corporation. The Project Executive is expected to have an
extensive knowledge of industry and technology trends and should be
recognized for business acumen by the customer set supported. The Project
Executive must also be an expert in IBM strategy and able to apply that
understanding to articulate a strategic vision which influences or guides
business area and/or international strategic directions. The position also
requires expert knowledge across PM methodologies and the disciplines
contained within, emerging techno- logies and technical architectures
pertaining to the industry served and the vision to influence the
industry's direction. The Project Executive will have overall
responsibility for cost, schedule and contractual deliverables from a
strategic perspective. The Project Executive will also have excellent
skills in client relationship management and general business management.
In addition to the attributes of the Project Manager position, typical
attributes of this position may include the following:
Skills
- Applies project management and professional expertise to define and
lead the development of solutions in leading edge or critical
situations, on projects of strategic importance to business unit,
country or internal objectives. Demonstrates the required proficiency
level for the skills at the Project Manager position.
- Fosters and engages in teamwork at the highest management and
professional levels of IBM, customer, vendor and subcontractor
organizations.
- Plans and conducts negotiations which result in strategic agreements
and commitments between IBM, customer, vendor and subcontractor
organizations.
- Anticipates future customer, industry and business trends. Applies
this understanding to develop a strategic vision which influences
business area, country or international objectives.
- Develops and implements products, market, business or technology
strategies with executive review.
Contribution/Leadership
- Articulates vision of long term IBM, industry, business and technology
directions which guides business area strategy.
- Recognized as an expert and a leader by other members of the PM, I/T
Architect, I/T Specialist and Consultant professions, multi-country
organizations within IBM, and by customer, vendor and subcontractor
organizations.
- May manage functions or strategic departments.
- Leads business unit, country or international teams.
Impact On Business/Job Scope
- Accountable for project, business unit, major country or international
projects and programs.
- The Project Executive fully develops project, product and business
strategies, reviews them with executive management and, upon gaining
concurrence, implements the solutions.
- Contributes to functional policy making.
- Responsible for committing multiple resources and final responsibility
for customer satisfaction, cost, expense, revenue and all other
critical business measurements.
- Final responsibility for achieving quality objectives.
[ IBM intranet home page
| IBM internet home page
| EnterLib
| Internal pubs
| Product pubs
| Reference
| Contact EnterLib
]
















































